Kinesiology Midterm
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
Range of motion
Arc of motion available at a joint, resulting from the joint structure and surrounding soft tissue
Passive range of motion (PROM)
Arc of motion when moved by an outside force
Active range of motion (AROM)
Arc of motion when movement occurs from muscles acting on the joint
Active assistive range of motion
Arc of motion when moved initially by muscles but completed by an outside force
Protraction, retractions
Scapular (protraction/retraction) is also known as abduction, scapular (protraction/retraction) is also known as adduction
Upward rotation, downward rotation
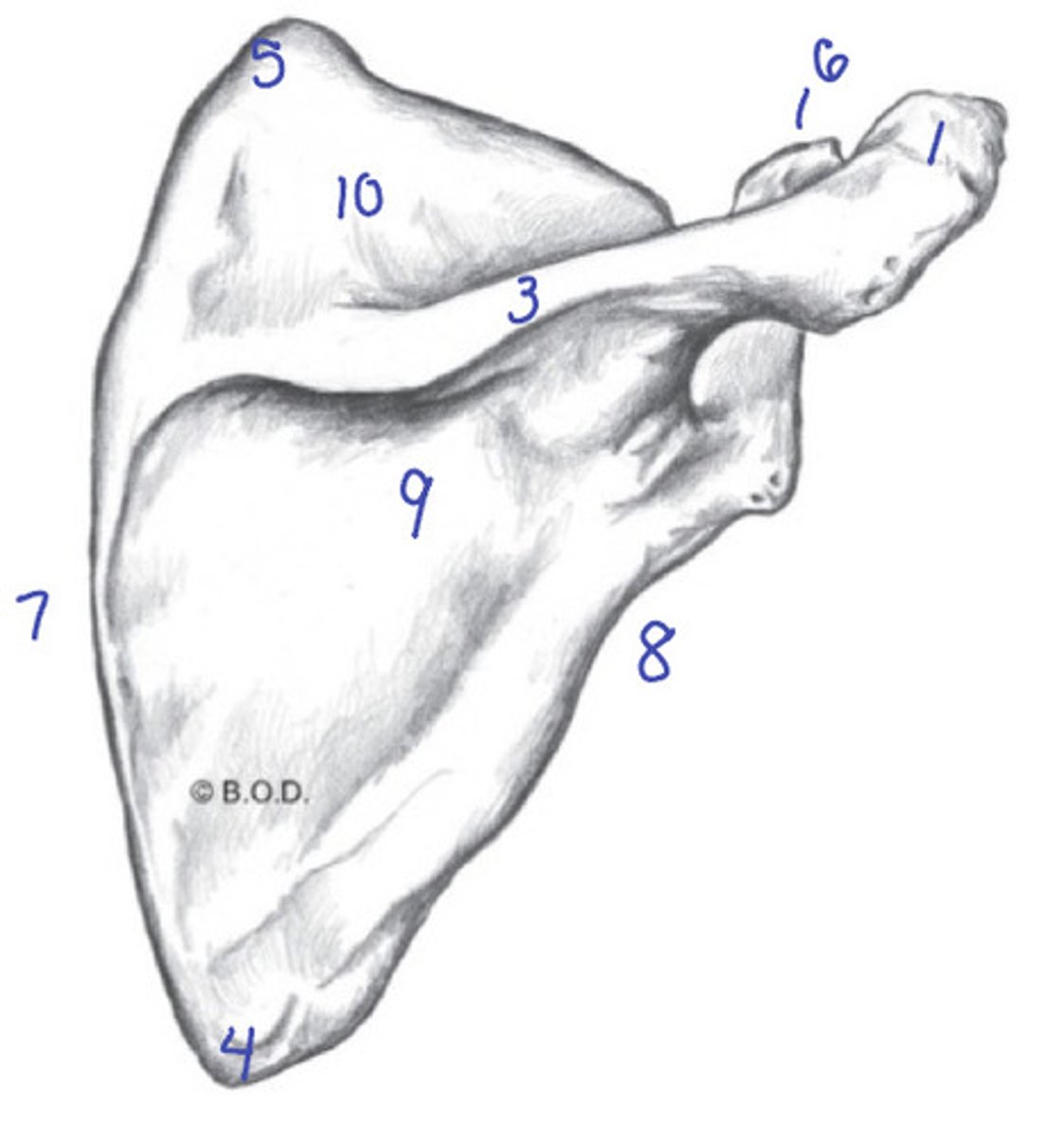
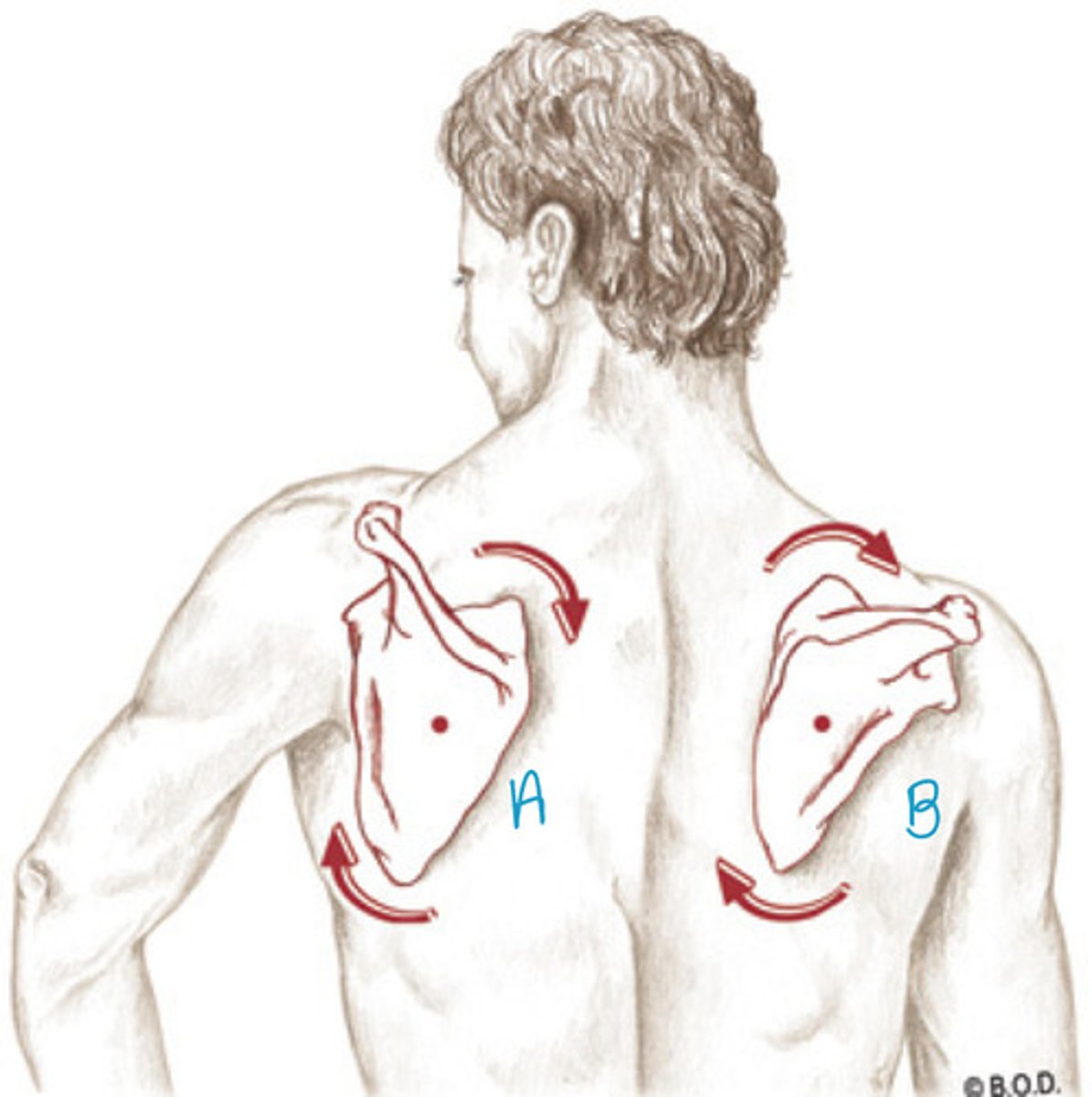
Identify the movements occurring in A and B of the scapula
Initiation
What stage of movement is someone in when they must lean forward (anterior weight shift) in order to stand up, transferring their center of gravity over their feet?
Sagittal plane, frontal axis
Flexion and extension occur in the ______________ plane around the ___________ axis.
Frontal plane, sagittal axis
Abduction and adduction occurs in the ___________ plane around the __________ axis
Transverse plane, vertical axis
Rotations occur in the ____________ plane around the _____________ axis
Contractility
______________ (contractility/irritability/extensibility/elasticity) refers to a muscle's ability to develop tension
Irritability
______________ (contractility/irritability/extensibility/elasticity) refers to a muscle's ability to receive and respond to stimuli
Extensibility
______________ (contractility/irritability/extensibility/elasticity) refers to a muscle's ability to stretch
Elasticity
______________ (contractility/irritability/extensibility/elasticity) refers to a muscle's ability to return to its original shape
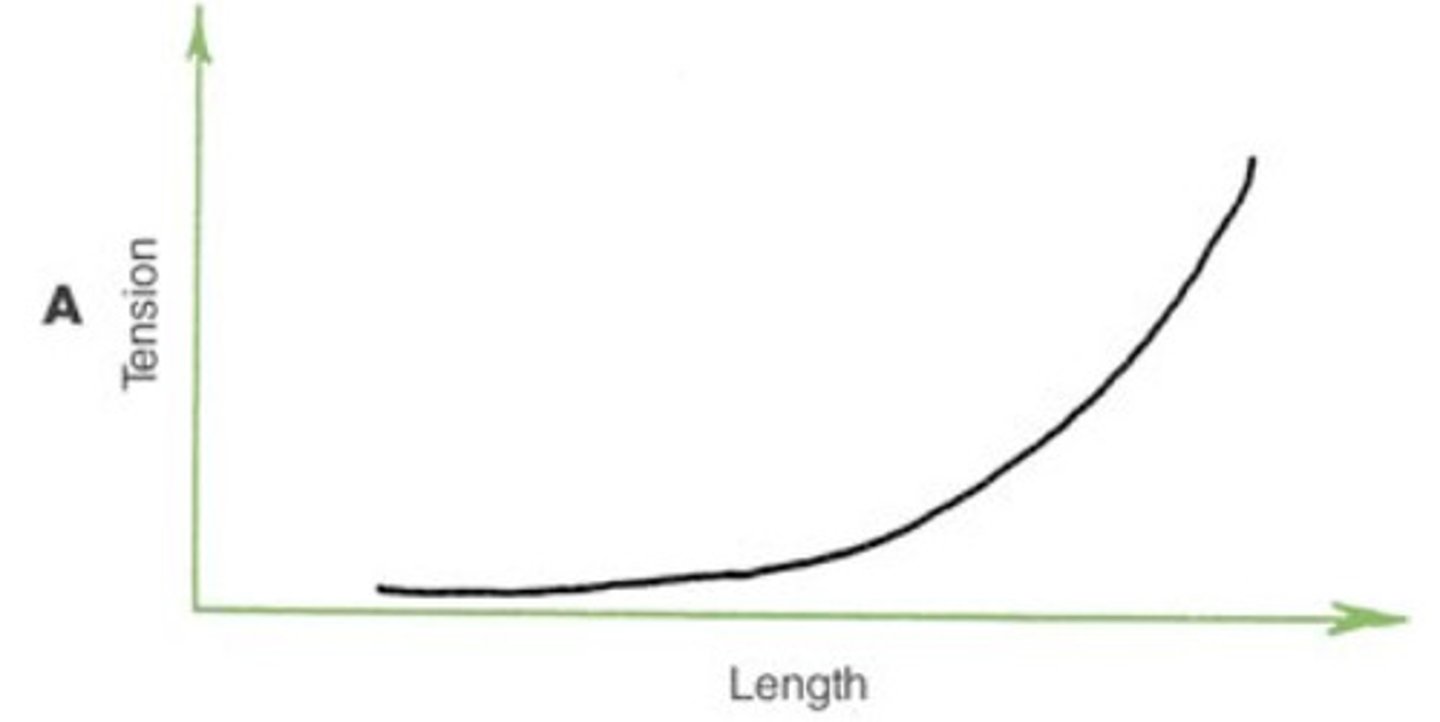
Passive tension
tension applied to load when a muscle is stretched but not stimulated, has more to do with elastic properties
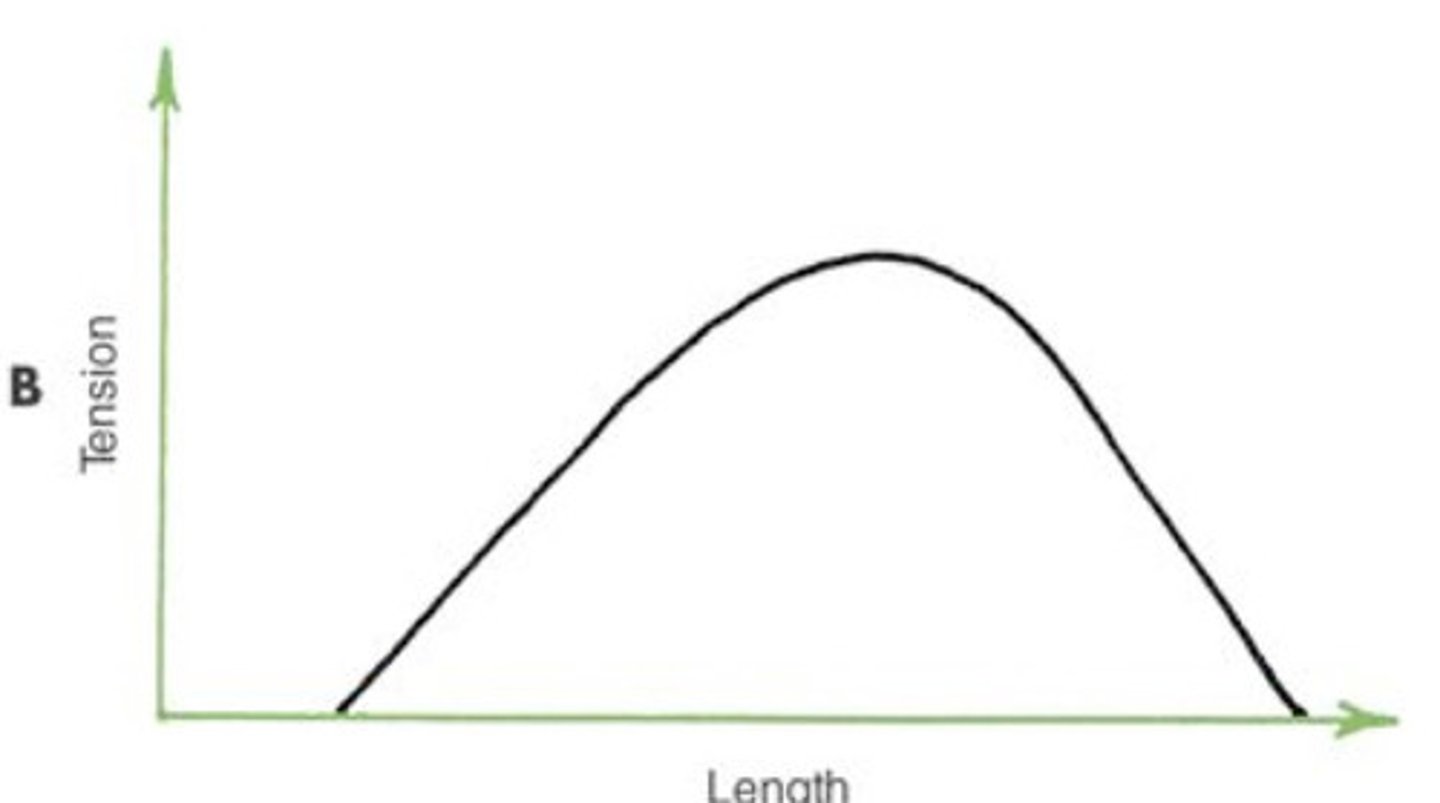
Active tension
Tension due to muscle contraction
Concentric; eccentric
__________ contractions occur when the internal strength of the muscle is greater than the external force, ___________ contractions occur as the muscles lower with control.
Isometric contraction
Muscle contracts but there is no movement, muscle stays the same length; occurs when internal and external forces are equal to each other
Law of intertia
The law of ___________ states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion until acted upon by an external force
Law of intertia
Which of newton's laws explains why you need to wear a seatbelt?
Law of acceleration (F=ma)
The law of ___________ explains why an object begins to move and why an object with a higher mass will require increased force to maintain the same speed as an object with lower mass.
Action-reaction
The law of ___________ explains why as a person jumps upward on a trampoline, the trampoline goes down - every action has an equal and opposite reaction
Internal force; external force
____________ _________ comes from within our bodies and provides stability and movement, while ___________ _____________ occurs outside of the body and includes gravity, friction, pressure, and resistance
Tensile force (pulling)
Force applied in perpendicular directions, pulls tissues apart; occurs as a joint moves as the tendon transfers force from muscle tissue to bone
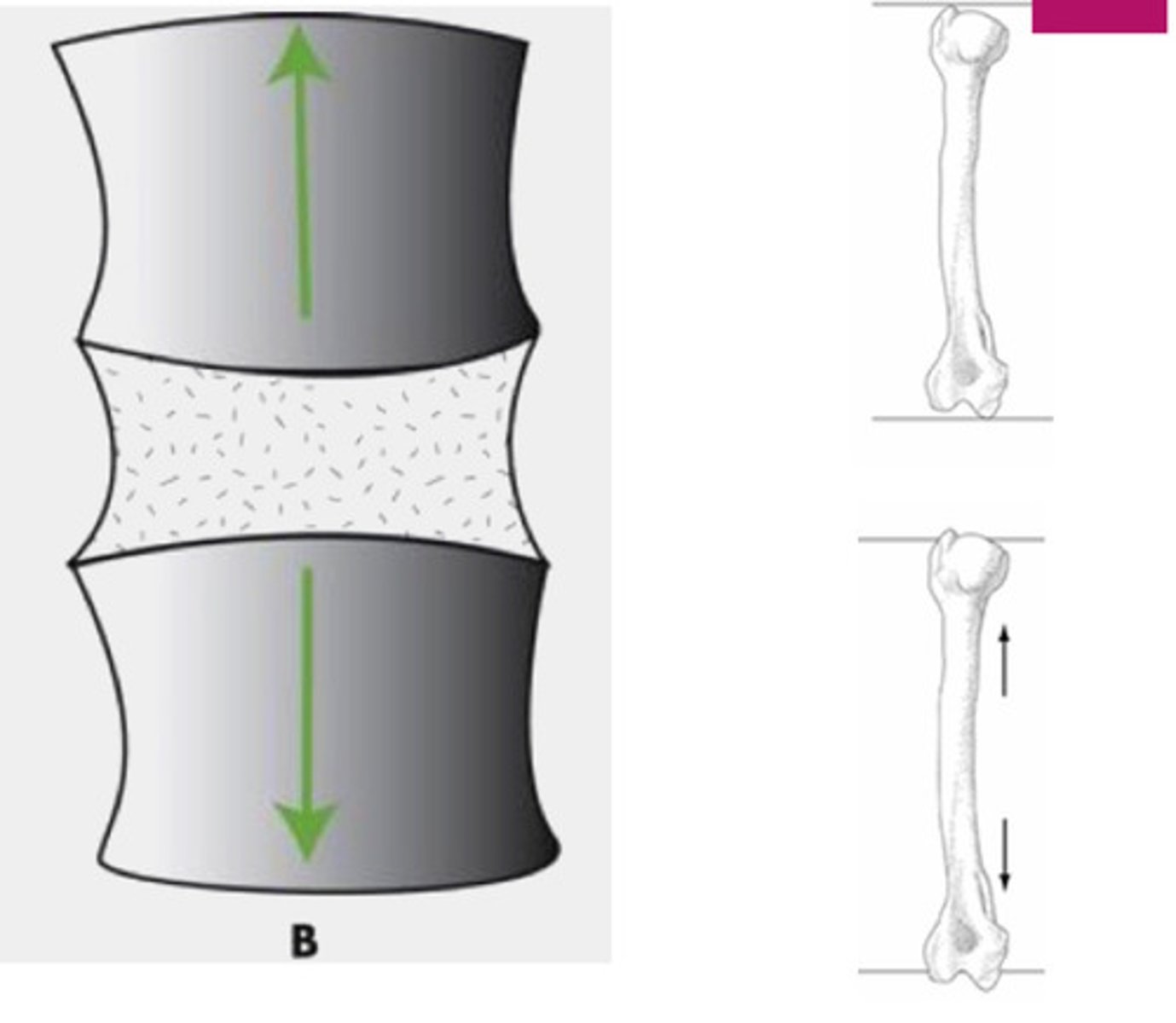
Compression force (pushing)
Force applied in perpendicular directions; can press bones together; weight bearing, gravity, external load
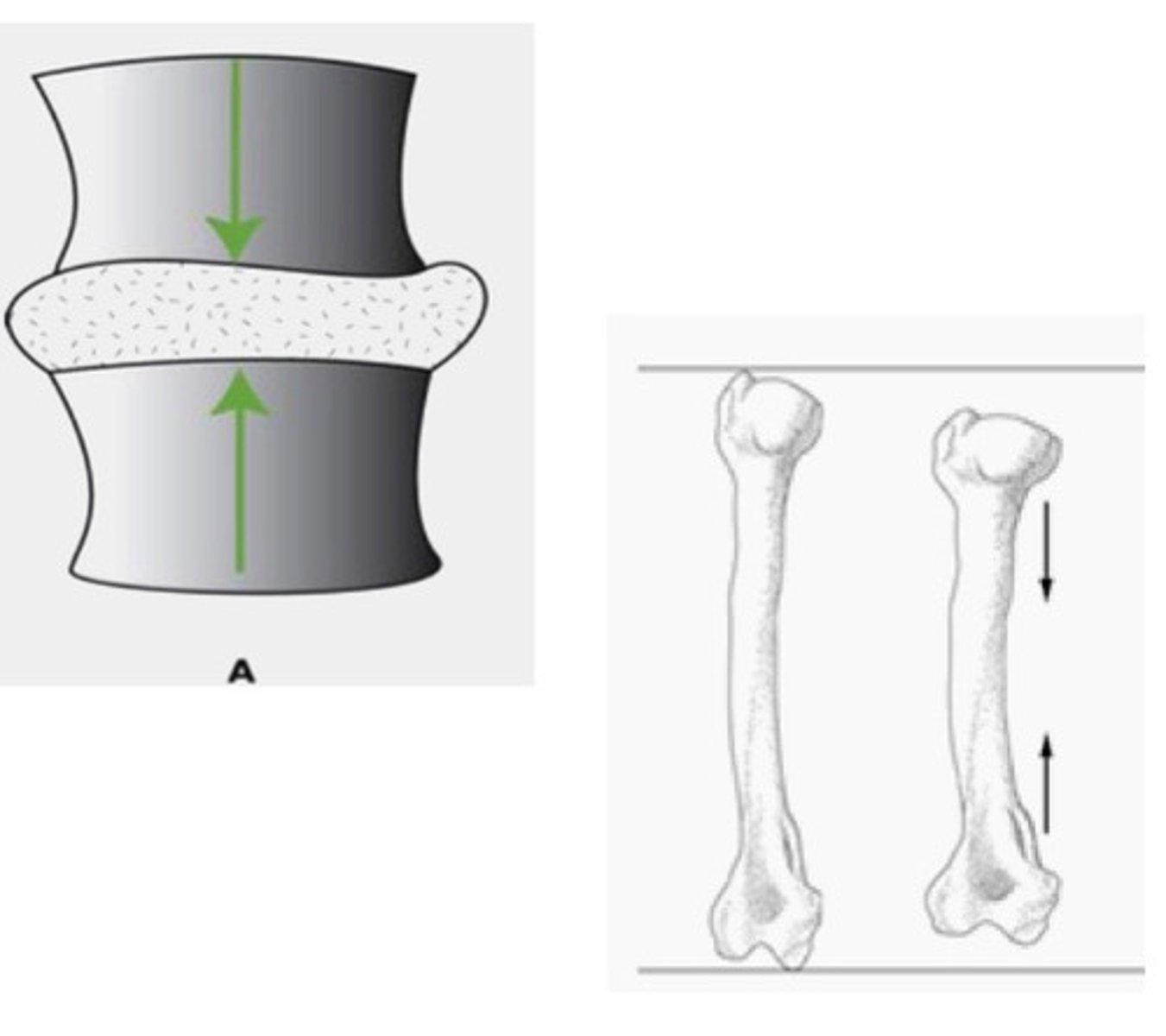
Bending
Force applied in one direction; results in on side being convex and one side being concave
Shear or torsion
____________ and ___________ are forces that occur in two directions
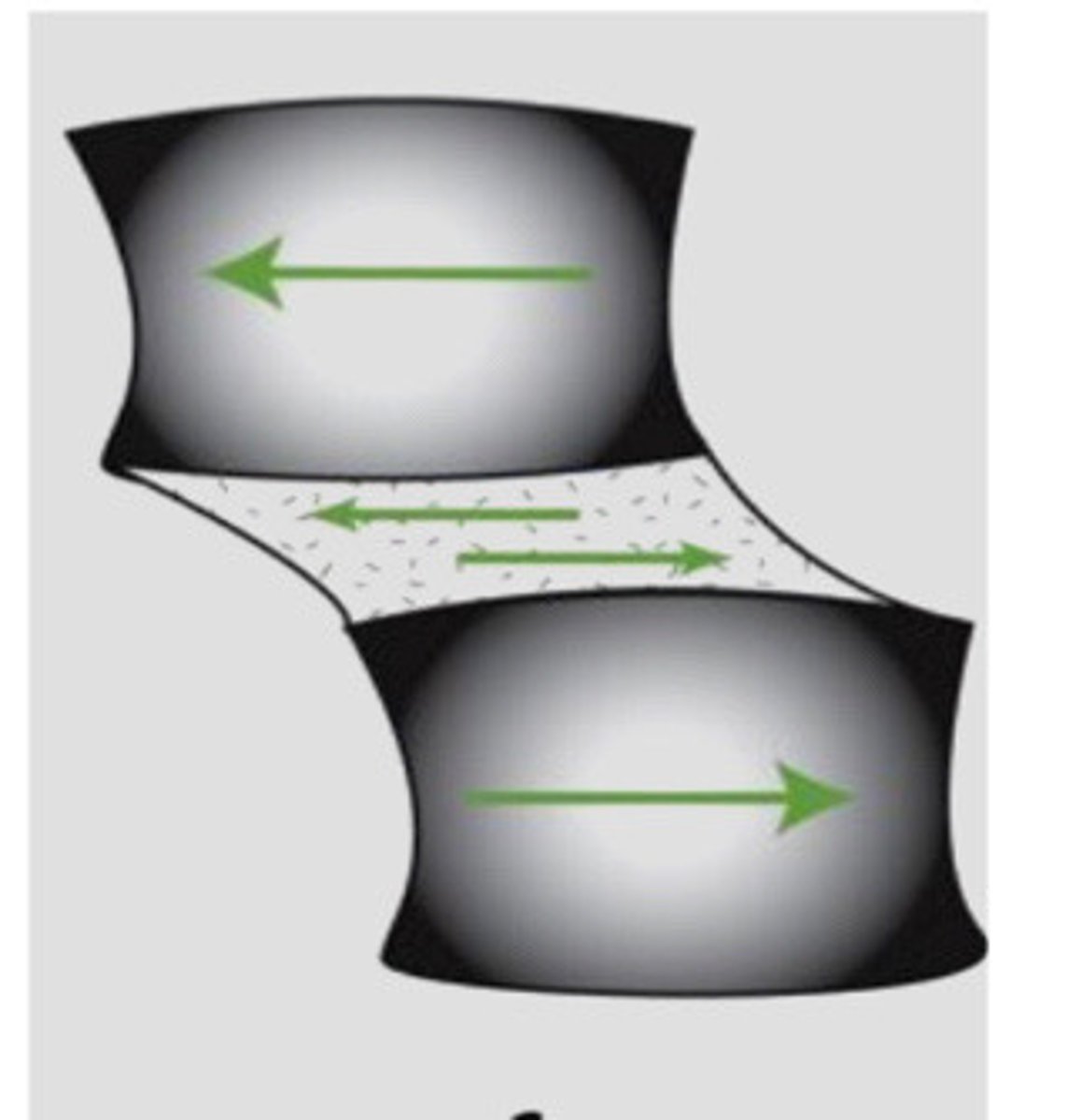
Shear
Deformation results from parallel forces that are internal and in an angular direction
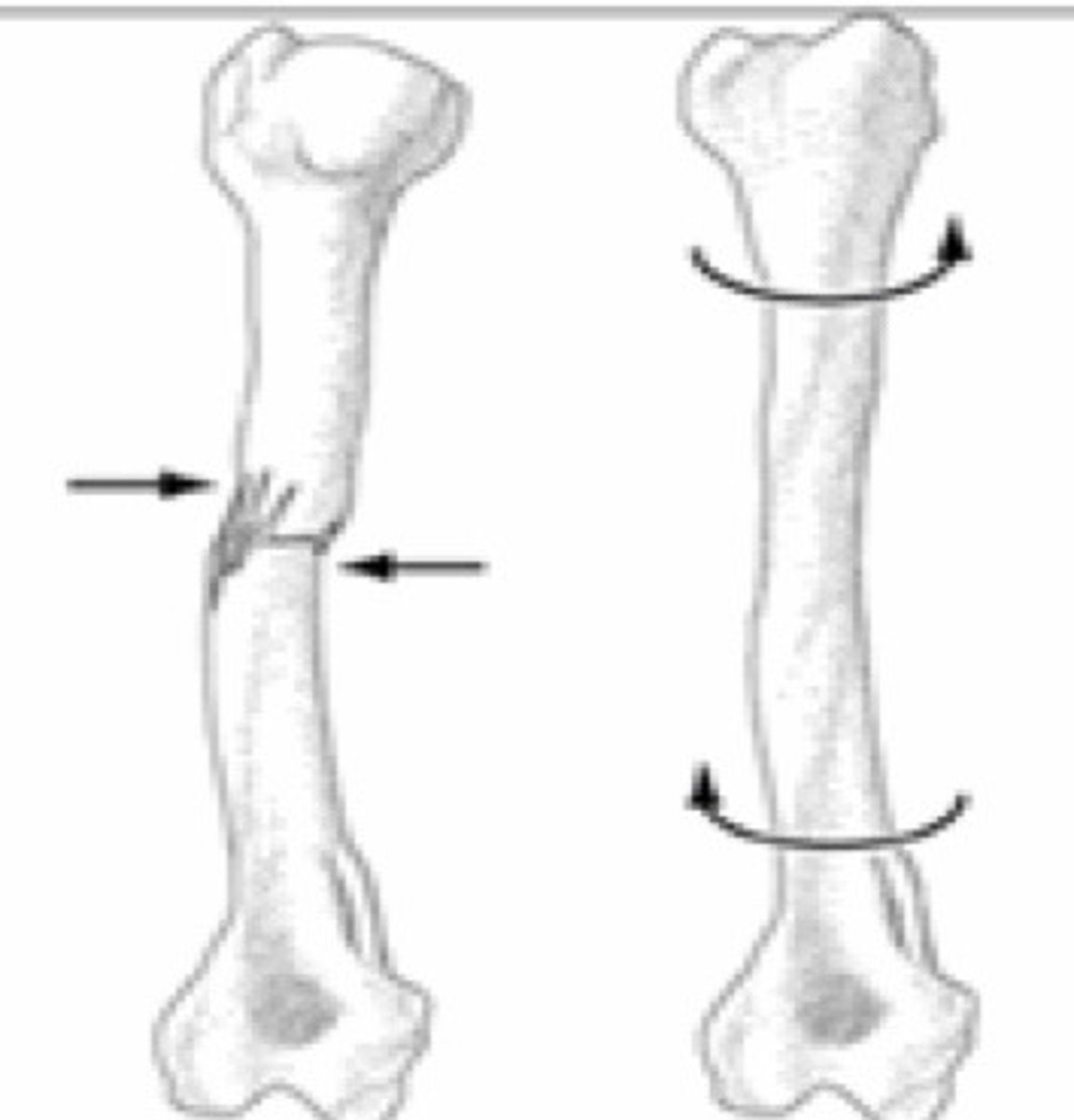
Torsion
act of twisting; stress due to twisting forces exerted on a body
Torque
The ability of any force to cause rotation around an axis (? = Force x Moment Arm)
Easier (greater torque), harder (less torque)
The longer the moment arm, the ________ it is to move the part. The shorter the moment arm, the __________ it is to move the part.
Joint, muscle
In the human body the axis is the fixed point which the motion rotates around, called the ___________ and the effort is the force produced by the ____________
Moment arm; resistance arm
The ____________ arm is the distance between the force/effort and the axis; the _____________ arm is the distance between the resistance and axis
First class lever
Axis is located between the exerted force/effort and the resistance
Second class lever
Resistance is in the middle; with the axis at one end and force at the other; strong mechanical advantage; large amount of weight can be moved by a smaller force
Third class lever
Exerted force/effort is in the middle with resistance and axis at opposite ends; most common lever in the body; good for speed and distance
False - measure AROM then PROM if needed
When measuring ROM you first measure PROM and then AROM
Firm end feel
___________ end feel occurs when there is tension in the joint but with a slight give such as when trying to touch your toes
Hard end feel
_____________ end feel occurs when bone contacts another bone such as in elbow extension
Capsular end feel
A hard, leatherlike limitation of motion that has slight give; slightly soft
Spasm
An end feel that results in tissue response from harsh movement in the opposite direction
Springy
End-feel: some hard rebound at the end of ROM
Empty
End-feel: occurs when there is no "feel" because the client asks to stop due to pain
3 trials
To measure strength you must perform ____ trials and average them
20 lbs
average grip strength required for most ADLs
Shoulder adducted, wrist neutral, elbow flexed
The shoulder should be __________, the wrist should be __________, and the elbow should be ___________ to measure grip strength with a dynamometer
Tip pinch
Pinch used to pick up and hold small objects with thumb opposed to the end of the index finger forming a circle shape (e.g., picking up a pin)
Lateral pinch
Pinch gauge presented in line with forearm with dial facing up. Client pinches the gauge between pad of thumb and radial side of middle phalanx of index finger such as when holding a key
Palmar pinch
Pinch gauge presented on its side at 45°. Held between pulp of thumb and pulp of index and middle fingers. Client pinches meter between pad of the thumb and pads of index and middle finger; forming an oval shape
ROM testing
What should be done prior to manual muscle testing
True
T/F? MMT should be done all in one position when possible
Proximally, distally
When performing manual muscle testing remember to stabilize ____________, and apply resistance ________________
3/5 - full AROM without added resistance
Grading to start with for MMT
5/5
MMT: Full AROM, maximal resistance
4/5
MMT: full AROM, moderate resistance
4-/5
MMT: Full AROM, less than moderate resistance
3+/5
MMT: Full AROM, minimal resistance before it breaks
3/5
MMT: Full AROM, unable to take added resistance
3-/5
MMT: less than full AROM, but greater than half AROM against gravity
2+/5
MMT: Full ROM in GE plane and takes minimal resistance
2/5
MMT: full ROM in GE plane with no added resistance
2-/5
MMT: less than full ROM in GE plane
1/5
MMT: Trace - feeling or seeing small amounts of muscle activity without motion
0/5
MMT: no movement or tension
Latismus dorsi and teres major
The _______________ and _____________ muscles are called the handcuff muscles because they are responsible for internal rotation and shoulder extension
T3
Vertebral landmark for the spine of the scapula
T7
The ______ vertebrae lines up with the inferior angle of the scapula
T12
Vertebral landmark for the end of the ribcage
Posterior superior iliac spine
The S2 vertebrae lines up with the ____________ _____________ __________ ____________
Iliac crest
The L4 vertebrae is the bony landmark for the ____________ ___________
Cervical - convex/lordosis
Thoracic - concave/kyphosis
Lumbar - convex/lordosis
Sacral - concave/kyphosis
The cervical spine is (concave/convex)
The thoracic spine is (concave/convex)
Lumbar is (concave/convex)
Sacral is (concave/convex)
*also think about lordosis and kyphosis curves
Transversospinalis
The ______________ group of the cervical spine is responsible for rotation of the cervical spine and are deep muscles
True
T/F? The sternocleidomastoid is involved in all movements of the cervical spine
Trapezius
Responsible for all movements of the cervical spine, huge stabilizer of the neck
Same, opposite, flex
Sternocleidomastoid:
Unilaterally will laterally flex the head and neck to the ____________ side and rotate the head and neck to the _______________ side.
Bilaterally will __________ the neck and assists in elevating the rib cage for inhalation.
False - rotation also occurs at this level
T/F? The movements involved at the thoracic spine level are flexion/extension and lateral flexion
Latissimus dorsi
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the arm; draws the shoulder downward and backward
Protracts/abducts
The Serratus anterior _____________ the scapula
Thoracic
The ___________ spine protects vital organs and is involved in respiratory function
Hamstrings
Muscles that impact the lumbar spine
Lumbar spine
The _________ spine keeps the head in alignment with the pelvis and is involved in body mechanics during lifting
Sagittal
Pelvic tilt occurs in the ___________ plane with the pelvis tilting anteriorly or posteriorly
Frontal
Pelvic obliquities occur in the ___________ plane with one side of the pelvis more superior and the other being more inferior
Rotation
Pelvic ____________ occurs in the transverse plane with one side of the pelvis being more anterior or posterior
In anterior pelvic tilt, there is forward rotation of the pelvis, increased lumbar lordosis, and increased extension of the upper trunk
In anterior pelvic tilt, there is (backward/forward) rotation of the pelvis, increased lumbar (lordosis/kyphosis), and increased (flexion/extension) of the upper trunk
In posterior pelvic tilt, there is backward rotation of the pelvis, a flattening of the lumbar spine, and increased thoracic flexion.
In posterior pelvic tilt, there is (backward/forward) rotation of the pelvis, a flattening of the lumbar spine, and increased thoracic (flexion/extension).
Pelvis
When assessing posture, first assess the ___________, then move up in the body checking for symmetry and alignment
Core
The ___________'s primary job is the support and protect the spine and ensures proximal stability for distal mobility. It can be impacted by muscle strength, pelvis and spine malalignments, cognitive abilities, and cardiovascular health
Stability
Ability to maintain control over the position or movement of your body
Base of support (BOS)
Areas of contact between person, supporting surface, and all of the intervening areas; the larger the distance between the points of contact the better
Center of gravity (COG)
A point where all your body mass is equalized, as the weight distribution changes, this will migrate in proportion to direction and magnitude of movement
Open chain position
Movement which occurs distally because the proximal segments are stabilized; typically involves isolated joint movement; often seen in non-weight bearing positions
Closed chain position
Movement occurs proximally because distal segments are stabilized; the distal end of the limb is fixed; usually involves multiple joints moving together; often seen in weight bearing positions
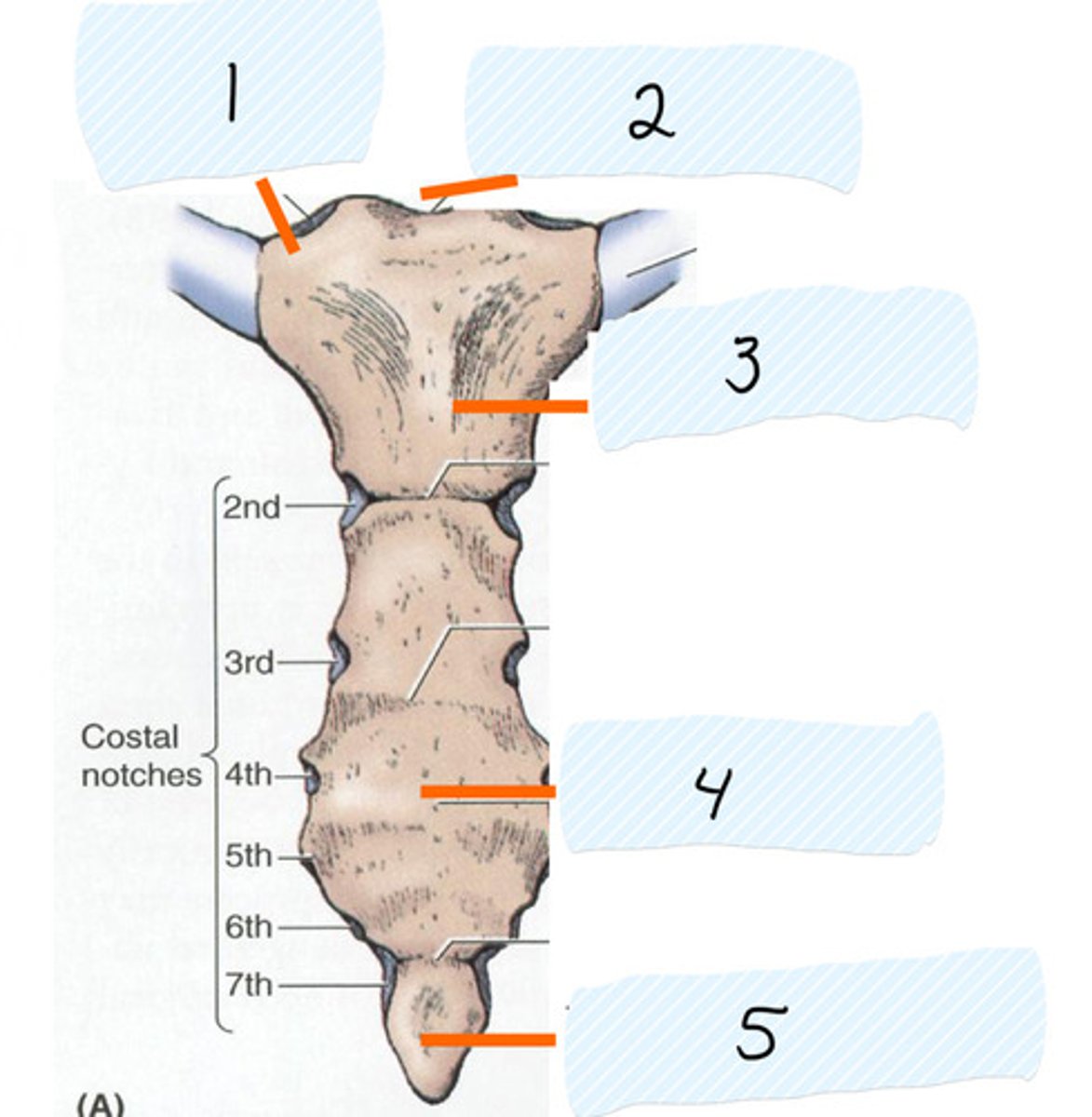
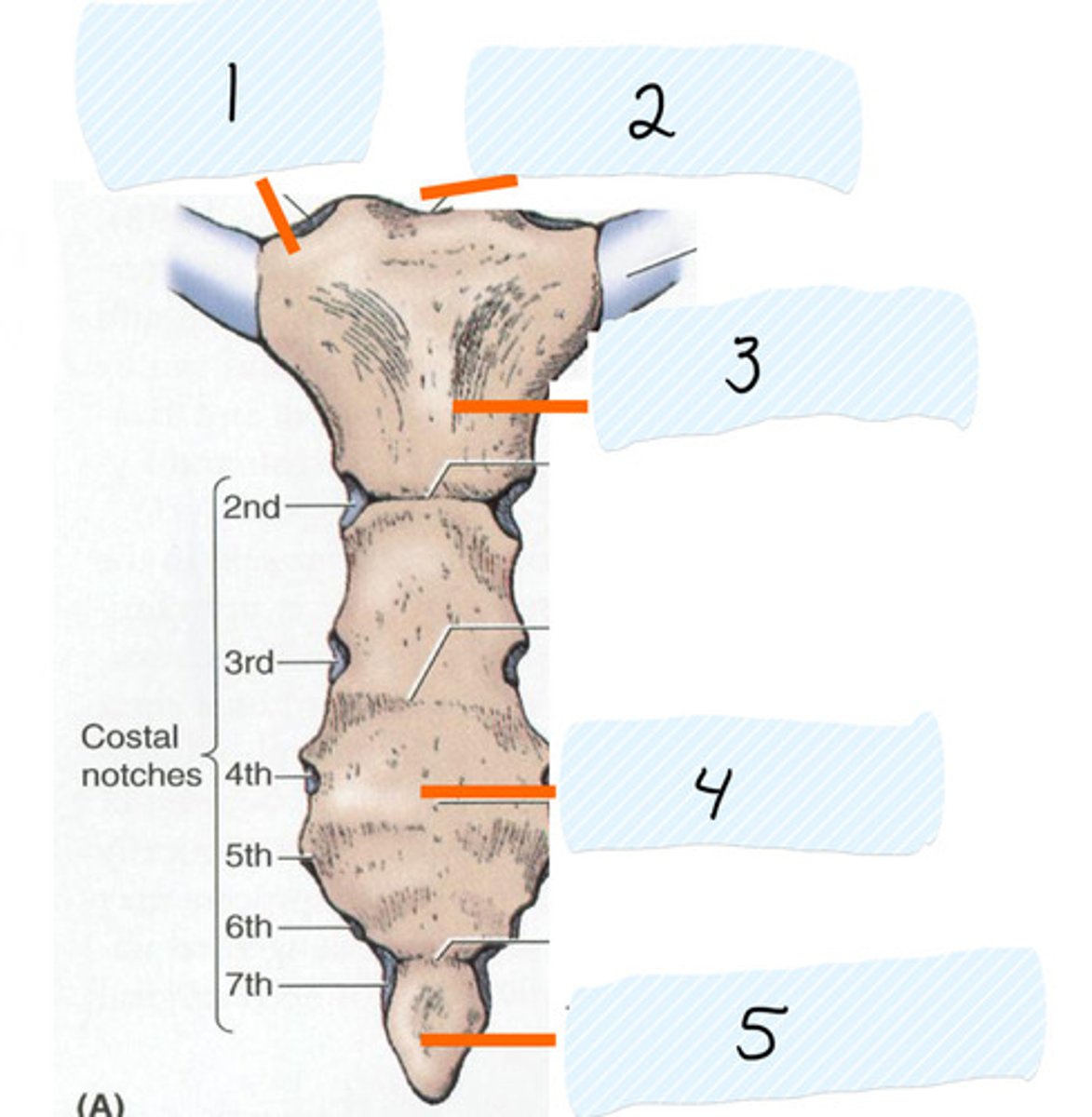
Clavicular notch
Identify 1
Jugular notch
Identify 2
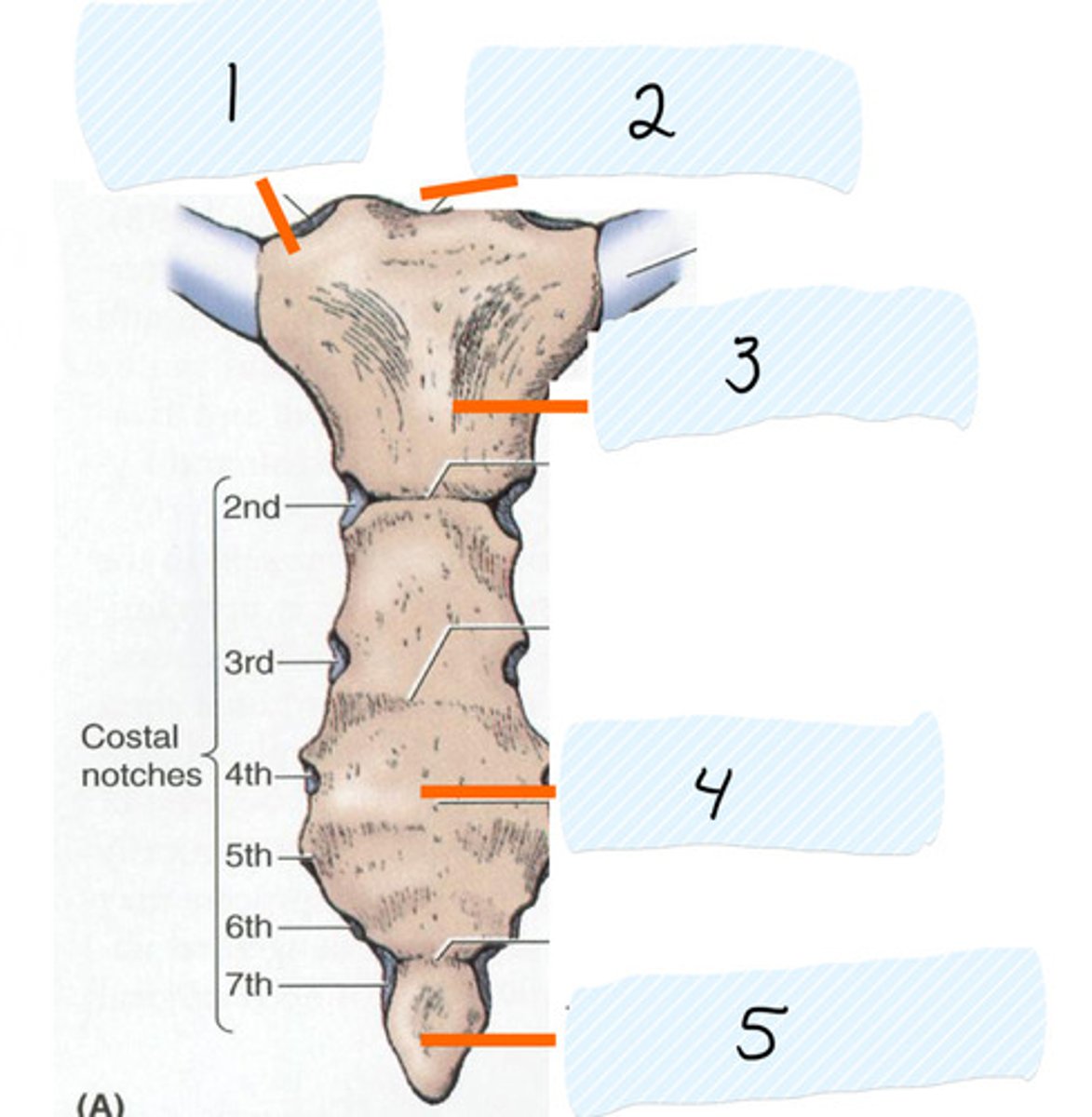
Manubrium
Identify 3
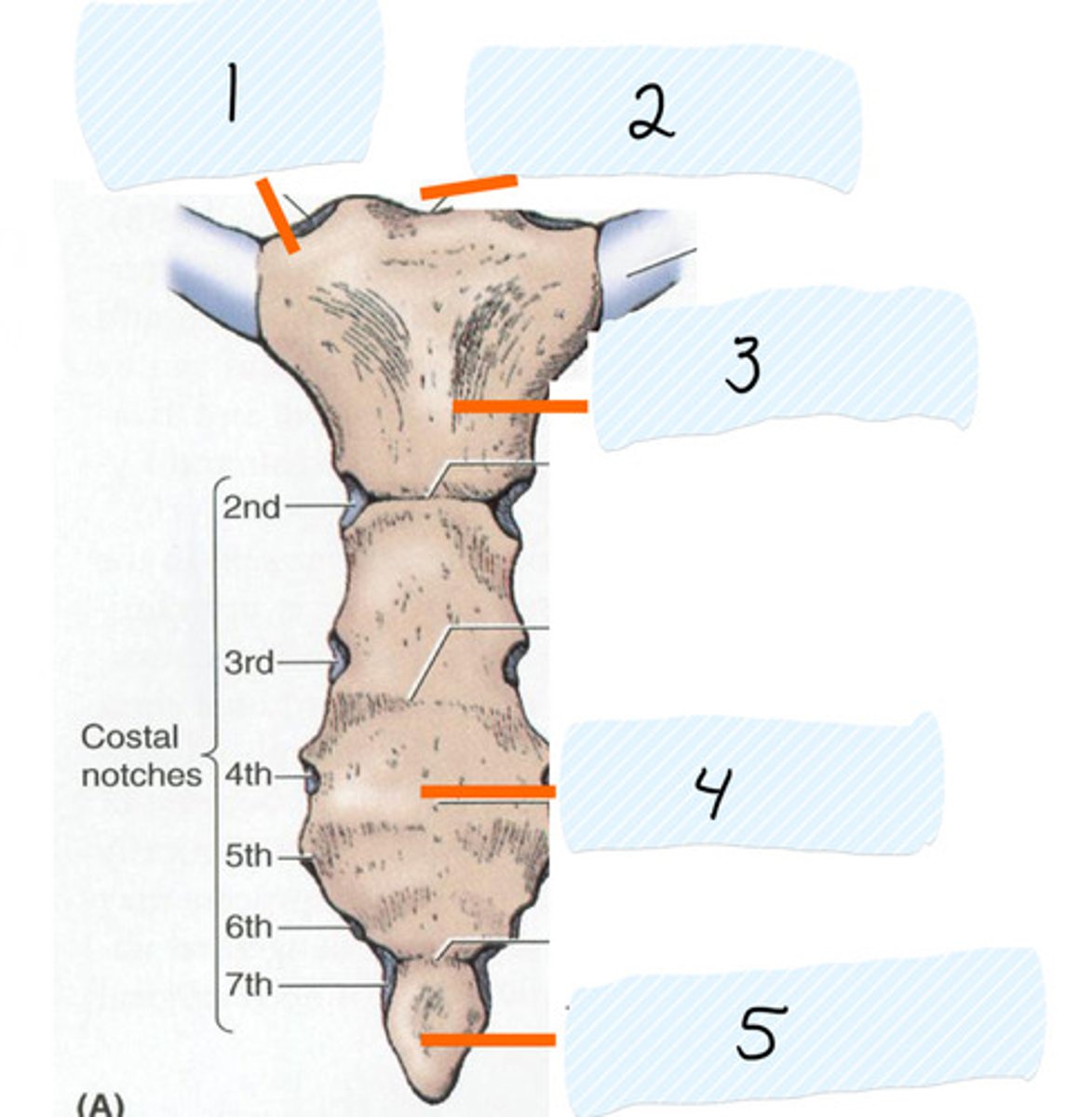
Sternal body
Identify 4
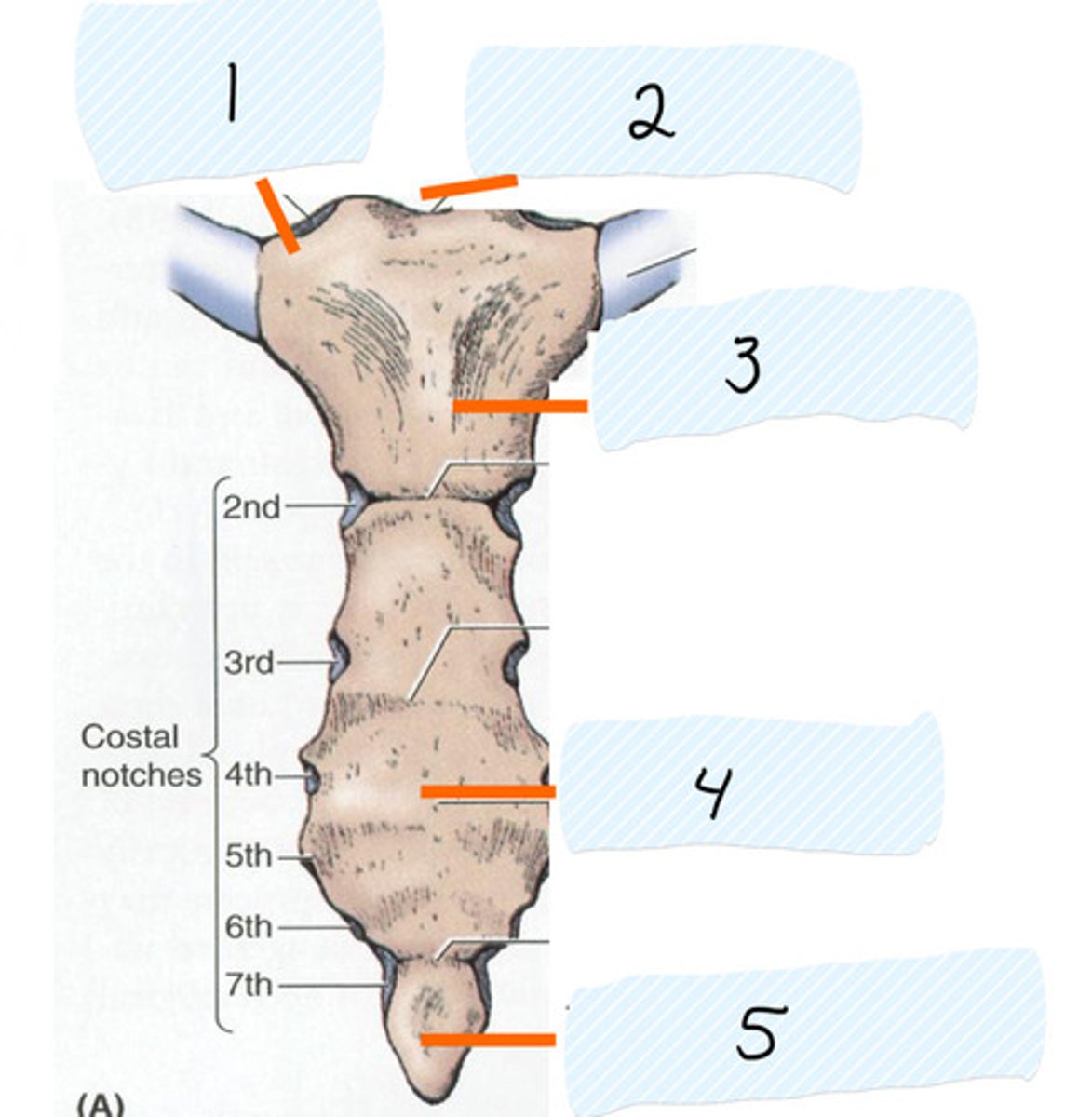
Anterior side
What side of the scapula is the subscapular fossa on? (Anterior/Posterior)
Xiphoid process
Identify 5
Acromion
Identify 1