unit 9: urinary system (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:02 AM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
functions of the urinary system
regulate aspects of homeostasis and eliminate waste products
2
New cards
list two aspects of homeostasis
water balanced and acid-base balance in the blood
3
New cards
waste products
nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs
4
New cards
what are the major structures of the urinary system?
kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, and the renal arteries/veins
5
New cards
produce urine as a result of carrying our the major functions of the urinary system
kidneys
6
New cards
transport urine from kidneys to bladder
ureters
7
New cards
temporary storage reservoir for urine
bladder
8
New cards
excrete urine from bladder out of the body
urethra
9
New cards
deliver blood to the kidneys for processing
renal arteries
10
New cards
carry blood away from the kidneys
renal veins
11
New cards
where do the renal blood vessels enter/exit the kidney?
the hilum
12
New cards
the ureters are ______ with the renal pelvis
continuous
13
New cards
where to the ureters enter the bladder from?
the posterior aspect of the bladder
14
New cards
the ureters run behind what sturcture?
the periotoneum
15
New cards
what aids peristalsis in urinary transport?
gravity
16
New cards
how long is a moderately full bladder?
about 5 inches long
17
New cards
how much urine does a moderately full bladder hold?
about 500 mL
18
New cards
triangular region of the bladder base
trigone
19
New cards
where are the openings of the bladder?
two from the ureters and one to the urethra
20
New cards
what surrounds the neck of the bladder in male anatomy?
the prostate gland
21
New cards
what are the layers of the urinary bladder wall?
detrusor layer and mucosal layer
22
New cards
detrusor muscle
three layers of smooth muscle
23
New cards
what tissue is the mucosa made of?
transitional epithelium
24
New cards
T or F: the bladder can expand significantly without increasing internal pressure
true
25
New cards
T or F: the bladder expanding significantly increases internal pressure
F
26
New cards
what method of movement is used by the urethra
peristalsis
27
New cards
what controls the release of urine?
the internal urethral sphincter and the external urethral sphincter
28
New cards
involuntary smooth muscle
internal urethral sphincter
29
New cards
voluntary skeletal muscle
external urethral sphincter
30
New cards
which is longer, the female urethra or the male urethra?
the male urethra (by about 15 cm)
31
New cards
where is the female urethra located?
next to the wall of the vagina
32
New cards
where is the male urethra located?
through the prostate and penis
33
New cards
how many functions does the female urethra have?
one; carrying urine
34
New cards
how many functions does the male urethra have?
two; carries urine and a passageway for sperm cells
35
New cards
where are the kidneys located?
against the dorsal body wall (between the T12 and L3 vertrbrae)
36
New cards
which kidney is slightly lower and why?
the right kidney is slightly lower because of the position of the kidney
37
New cards
outer region of the kidney
renal cortex
38
New cards
inner region of the kidney
renal medulla
39
New cards
inner collecting tube of the kidneys
renal pelvis
40
New cards
medial indentation where the ureters, renal blood vessels, and nerves enter the kidney
renal hilium
41
New cards
what surrounds each kidney?
the renal capsule and fat
42
New cards
outer layer of the renal capsule that holds the kidney in place and divides the fat that surrounds the kidney into two layers
renal fascia
43
New cards
position of kidney changes and drops in the body cavity because of a loss of perineal fat
nephroptosis
44
New cards
triangular regions of tissue in the medulla
renal pyramids
45
New cards
extensions of cortex-like material inward that separate the pyramids
renal columns
46
New cards
cup-shaped structures that funnel urine towards the renal pelvis
calyces
47
New cards
how much of the body’s total blood volume passes through the kidneys each minute?
25%
48
New cards
path of boodflow through the kidneys? (arsia cage pcairi)
aorta, renal artery, segmental, interlobar, arcuate, cortical radiate, afferent arteriole, glomerulus, efferent, peritubular capillaries, cordical radiate vein, arcuate, interlobar, renal, inferior vena cava
49
New cards
structural and functional unit of the kidney responsible for forming urine
nephron
50
New cards
knot of capillaries that force fluid and small solutes our of the blood and into the glomerular capsule under high pressure
glomerulus
51
New cards
beginning of the renal tubule and encloses the glomerulus
glomerular capsule
52
New cards
which layer of the glomerular capsule has foot processes that form part of the filtration membrane? what are those foot processes called?
visceral layer; podocytes
53
New cards
which layer of the glomerular capsule acts as an outer impermeable wall?
parietal layer
54
New cards
low-pressure capillaries that are adapted for absorption instead of filtration
peritubular capillary beds
55
New cards
path of filtrate through the renal tubule (gp cnd)
glomerular capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop, distal convoluted tubule
56
New cards
what is the site of the tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion?
renal tubule
57
New cards
where do the distal convoluted tubules empty into?
the collecting duct
58
New cards
what renal structure receives urine from nephrons and delivers it to the calyces and renal pelvis?
collecting duct
59
New cards
what are the two types of nephrons?
cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons
60
New cards
what type of nephrons are located entirely in the cortex and make up the majority of nephrons?
cortical nephrons
61
New cards
what type of nephron is found at the boundary of the cortex and medulla and plays an important role in concentrating urine?
juxtamedullary nephron
62
New cards
what are the four basic renal processes?
filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion
63
New cards
which renal process moves from the glomerulus to the glomerular capsule?
filtration
64
New cards
which renal process moves from the renal tubule to the peritubular capillaries?
reabsorption
65
New cards
which renal process moves from the peritubular capillaries to the renal tubule?
secretion
66
New cards
which renal process moves from the renal tubules to outside of the body?
excretion
67
New cards
how is urine formed? (gf tr ts)
through glomerular filtration, and tubular reabsorption, then tubular secretion
68
New cards
what substance contains everything that blood plasma does?
filtrate
69
New cards
what substance is what remains after filtrate has lost most of its water, nutrients, and necessary ions?
urine
70
New cards
what substances that aren’t needed does urine contain (name 2)
nitrogenous wastes and drugs
71
New cards
why is urine yellow?
urochrome pigment
72
New cards
what is the normal pH of urine?
6
73
New cards
what is the normal range of specific gravity in urine?
1\.001 to 1.030
74
New cards
what are some substances normally found in urine (name 3)?
sodium, potassium, urea, creatinine, ammonia, bicarbonate ions, etc.
75
New cards
what solutes are NOT normally found in urine (name 3)?
glucose, blood, rbcs, hemoglobin, wbcs, bile, etc.
76
New cards
high blood sugar levels; diabetes mellitus
glycosuria
77
New cards
increased protein levels; hypertension or pregnancy
proteinuria
78
New cards
excessive production of ketones; diabetes mellitus
ketonuria
79
New cards
irritation of urinary tract and blood in urine; kidney stones or UTI
hematuria
80
New cards
excess hemoglobin in urine; hemolytic anemia
hemoglobinuria
81
New cards
excess nitrates in urine; UTIs
nitrituria
82
New cards
excess bilrubin in the urine; liver damage or hepatitis
bilrubinuria
83
New cards
pus in the urine; UTI or gonorrhea. WBCs
pyruria
84
New cards
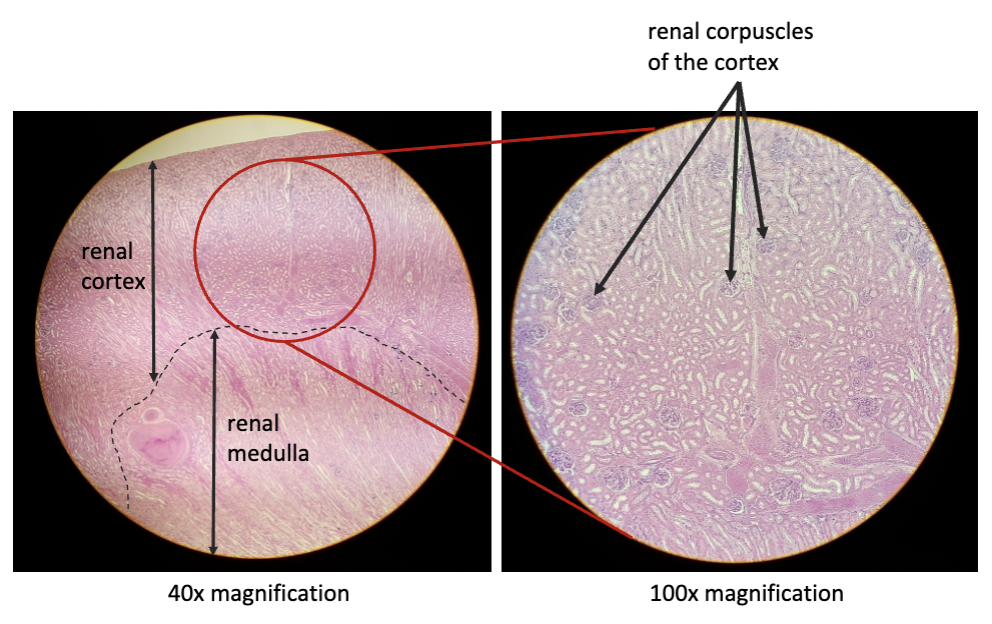
functional kidney
85
New cards
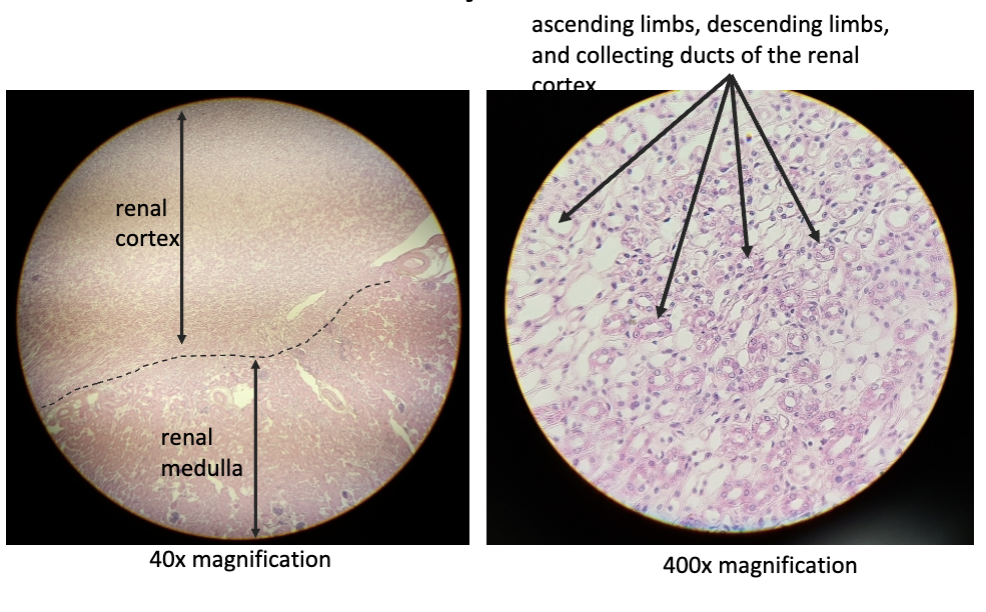
functional kidney (section)
86
New cards
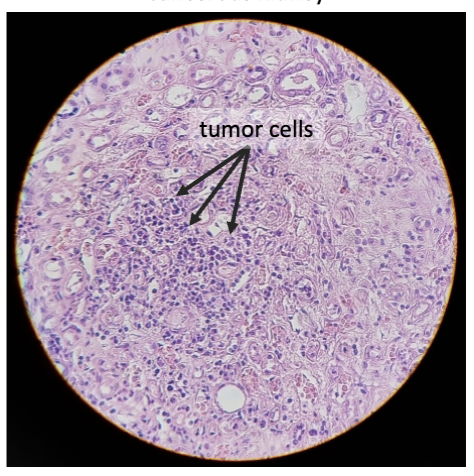
kidney carcinoma
87
New cards
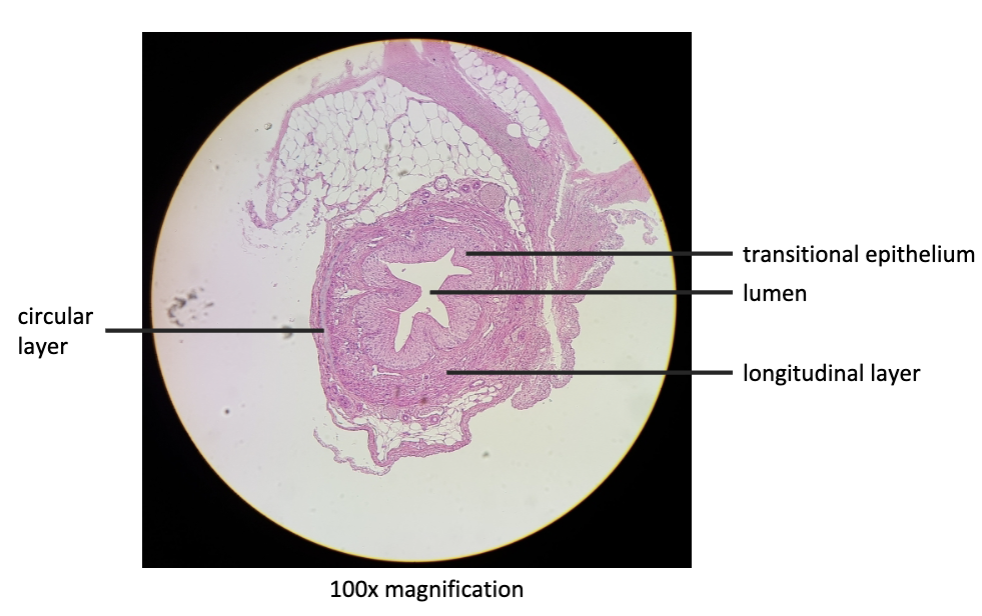
mammalian ureter
88
New cards
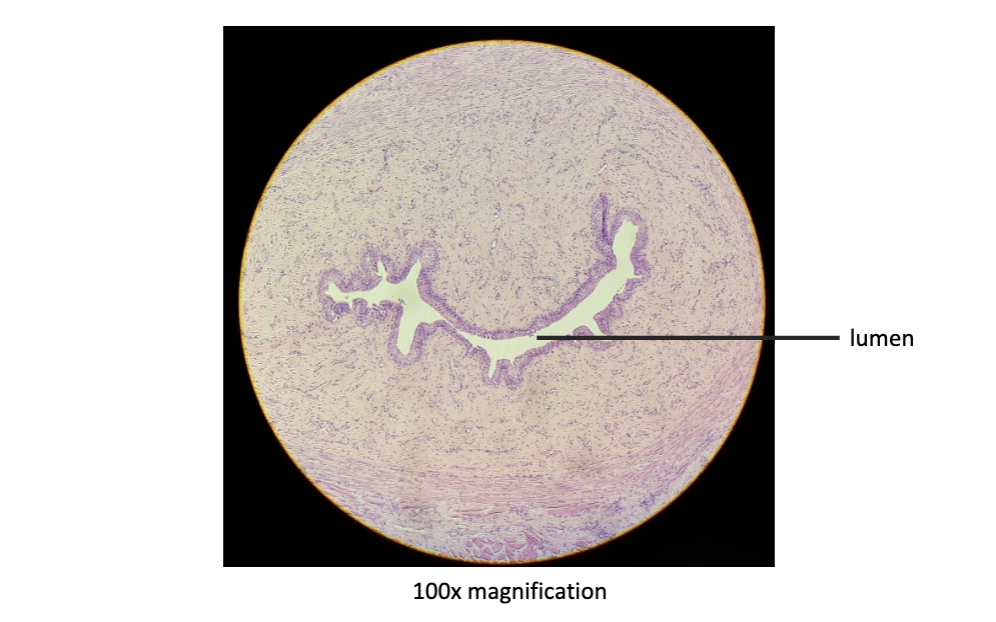
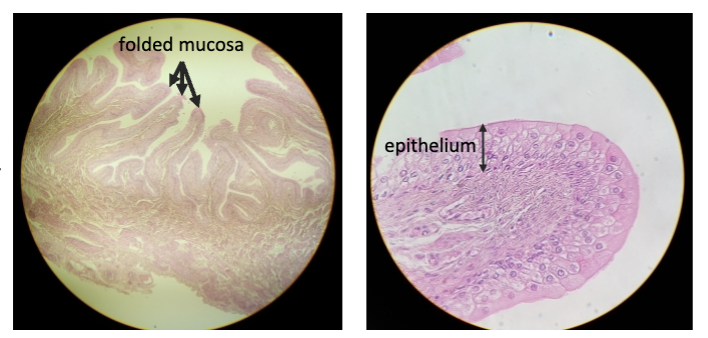
female mammalian urethra
89
New cards
collapsed bladdder
90
New cards
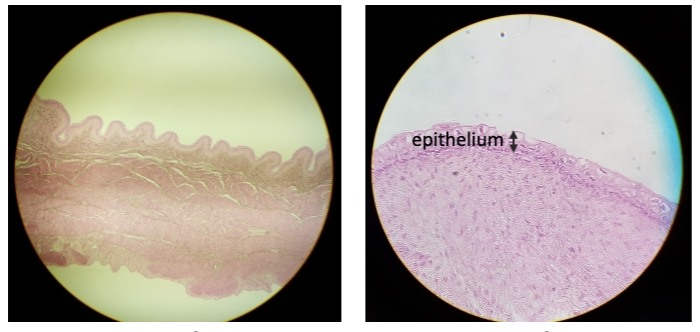
distended bladder
91
New cards
Glomerular Filtration is Selective?
A non-selective process in Urine Formation that separates based purely on size.
92
New cards
Glomerular Filtration
Water and solutes smaller than Proteins or Blood cells are forced through capillary walls into the renal tubule. One second its blood then it goes under high pressure and then its filtrate.
93
New cards
Tubular Reabsorption
Water, Glucose, amino acids, and needed ions are transported out of the filtrate and into the tubular cells to then enter the capillary blood
94
New cards
Tubular Secretion
Hydrogen ions, potassium ions, creatine, and some drugs are removed from peritubular blood and secreted by tubule cells into the filtrate.
95
New cards
Tubular reabsorption happens before Tubular Secretion?
No, they happen at the same time
96
New cards
Reabsorption is equally passive and active?
No, Reabsorption is mostly active and has some passive.
97
New cards
The solutes that travel by secretion (active)
* hydrogen ions
* potassium ions
* drugs
* creatine
* penicilin
* potassium ions
* drugs
* creatine
* penicilin
98
New cards
Solutes Reabsorbed by active transport (out)
* NaCl
* glucose
* amino acids
* bicarbonate (only in the distal tubule)
* glucose
* amino acids
* bicarbonate (only in the distal tubule)
99
New cards
Solutes reabsorbed by passive transport (out)
* Bicarbonate (only in proximal tubule)
* Water
* NaCl (ascending limb)
* Urea (collecting duct)
* Water
* NaCl (ascending limb)
* Urea (collecting duct)
100
New cards
Glomerular Filtration rate
uses inulin to measure the rate at which the glomerulus filters solute from the plasma as inulin can only be filtered and not secreted or reabsorbed. Can detect kidney disease.
125 mL/min.
125 mL/min.