Key Concepts in Vision and Perception
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Sensation
The act of receiving sensory information (internal or external).
Perception
How the brain assigns meaning to this sensory information.
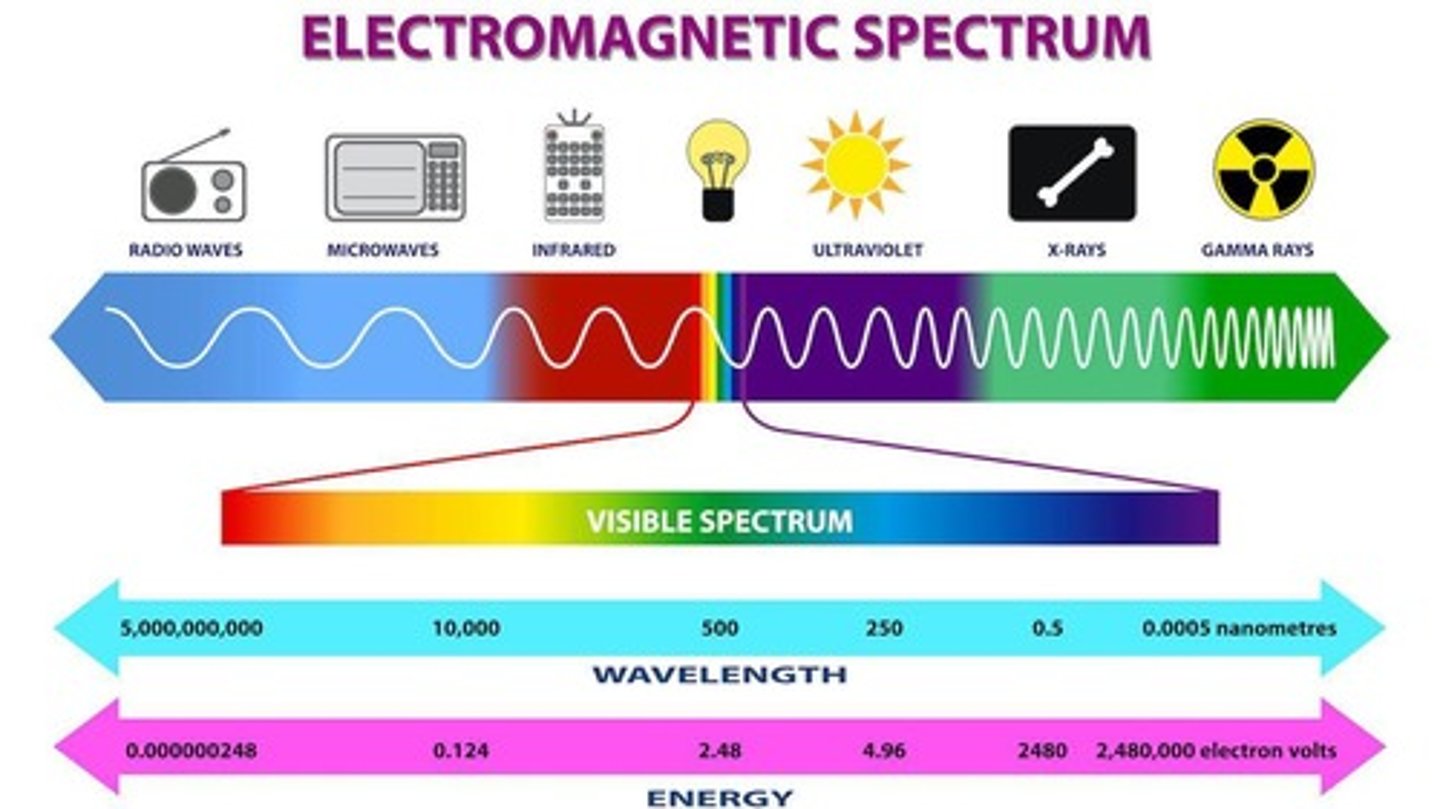
Electromagnetic spectrum
Light is measured in terms of wavelength and amplitude.
Wavelength
Determines colour.
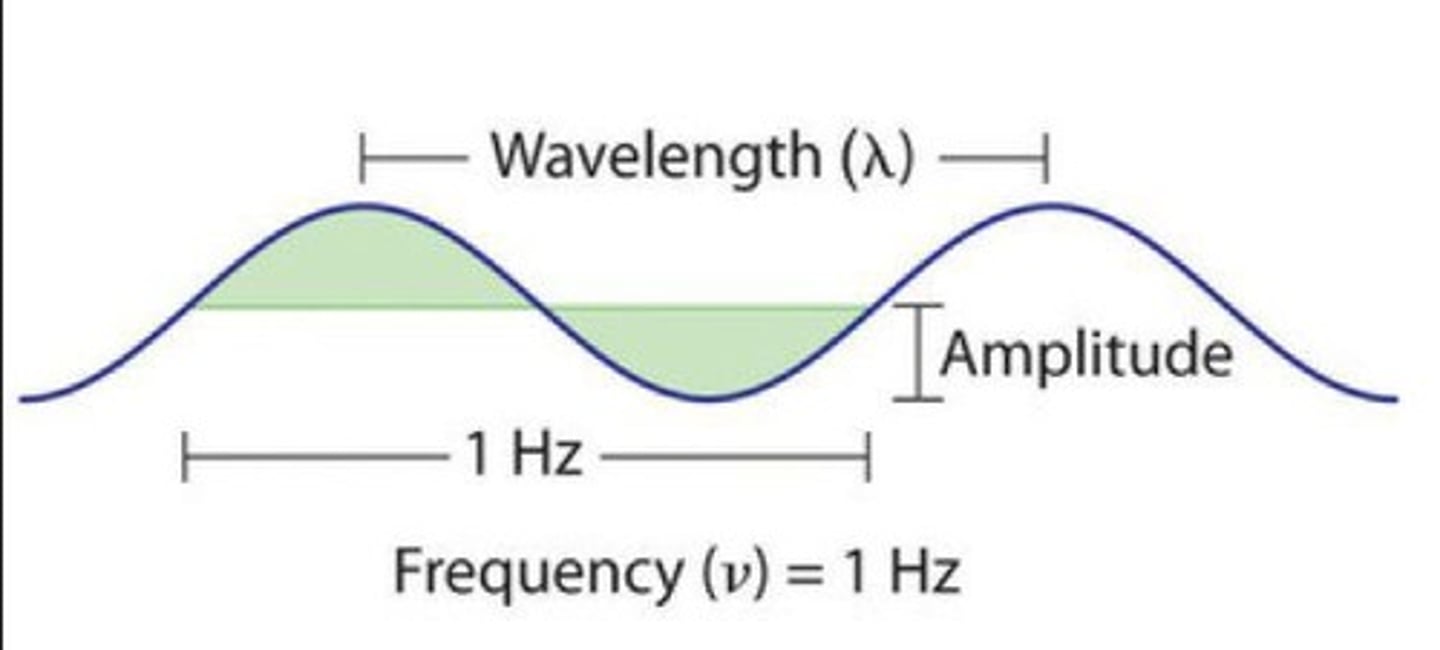
Amplitude
Determines brightness.
Visible light
A tiny portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Cornea
Focuses and places image on retina; transparent (no blood vessels), nourished by anterior and vitreous humour.
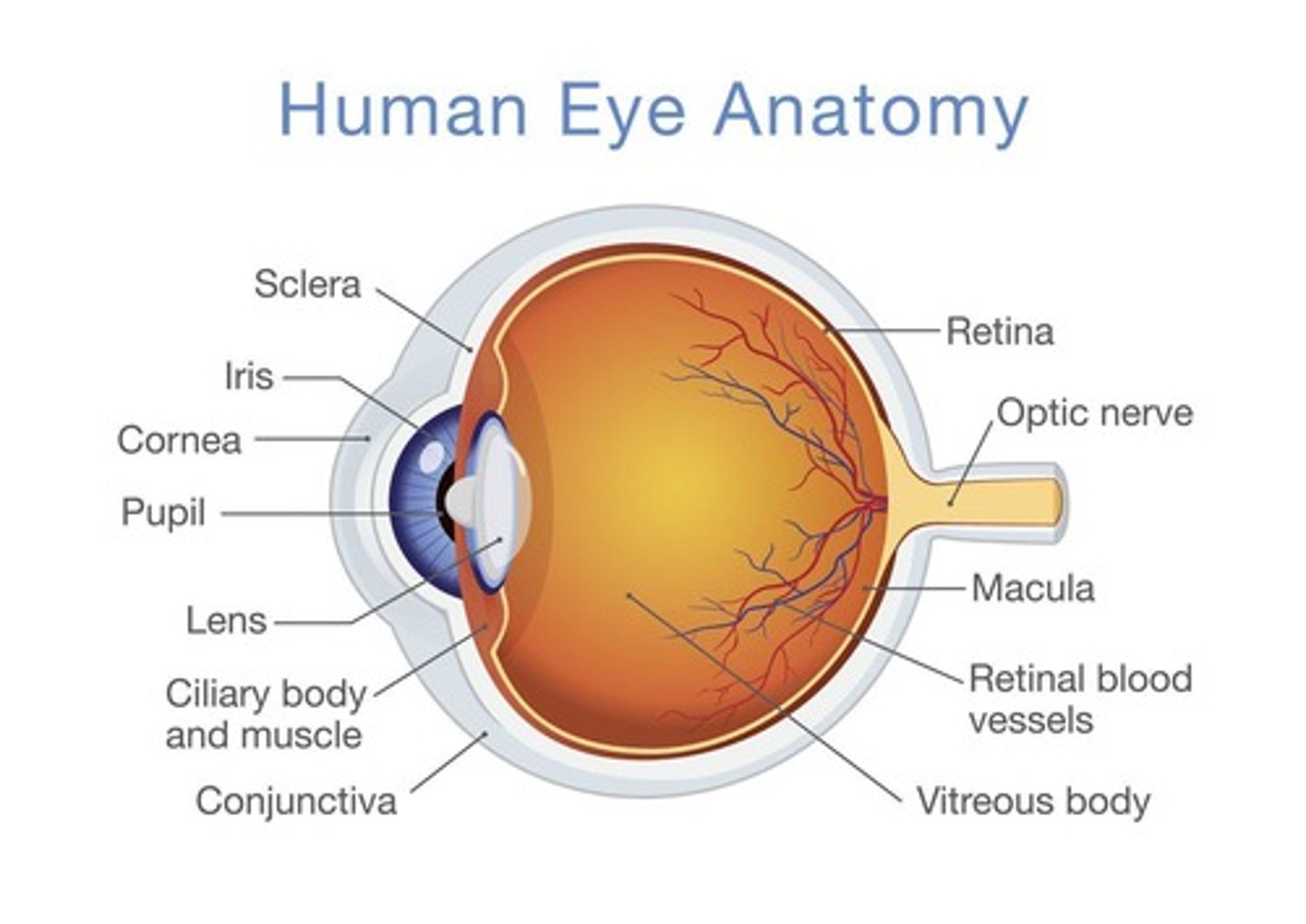
Choroid
Blood supply to the eye.
Iris
Muscle that contracts in response to light.
Lens
Transparent, focuses light; changes shape via accommodation.
Retina
Sheet of photoreceptors (rods & cones) at back of eye.
Rods
Low light, brightness, low resolution.
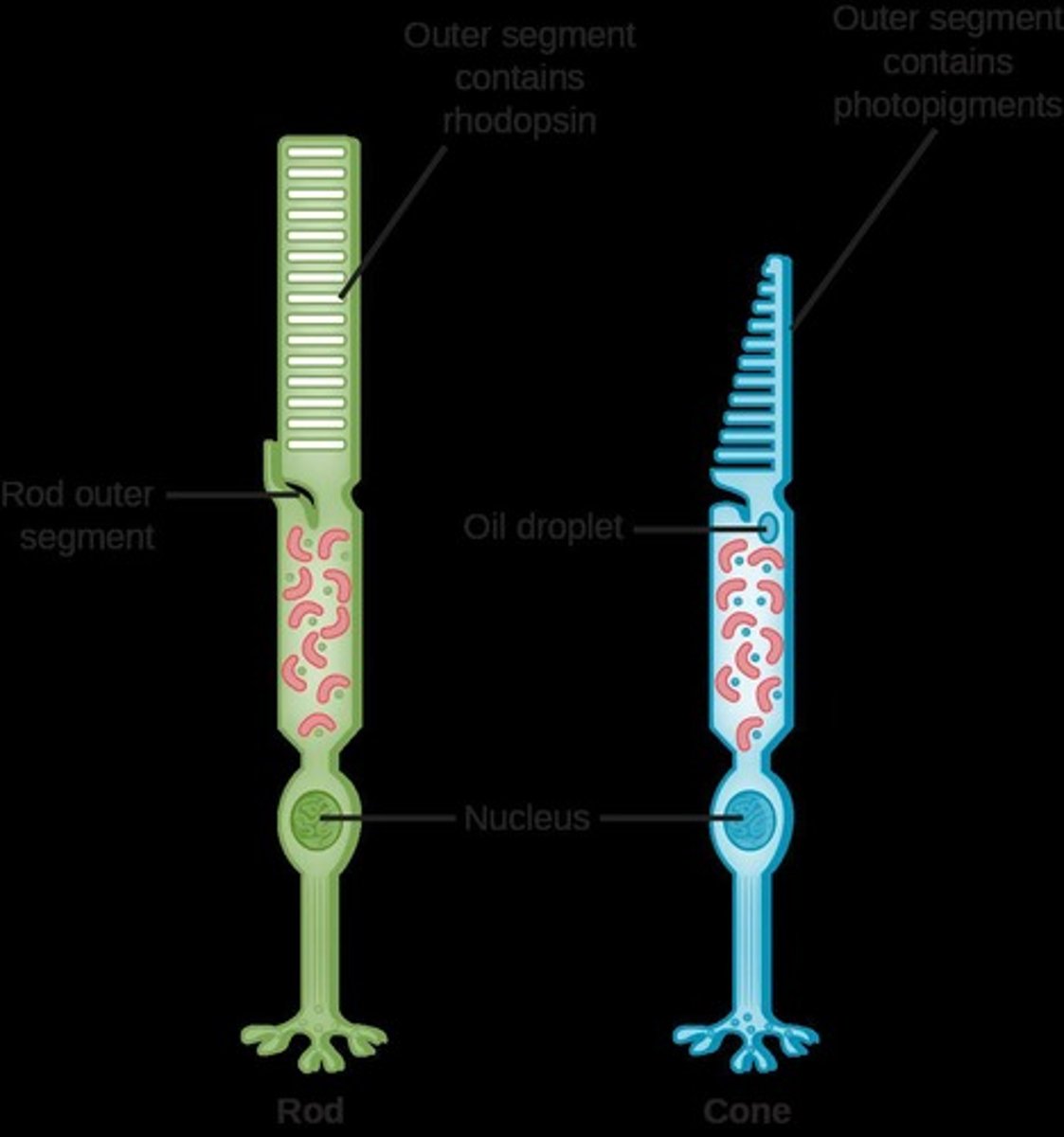
Cones
Colour, daylight, high resolution.
Fovea
High-acuity area rich in cones, at 0° visual angle.
Blindspot
15-18° off-centre, no photoreceptors (optic nerve exits).
Ganglion cells
Axons form the optic nerve (127M receptors → 1M axons).
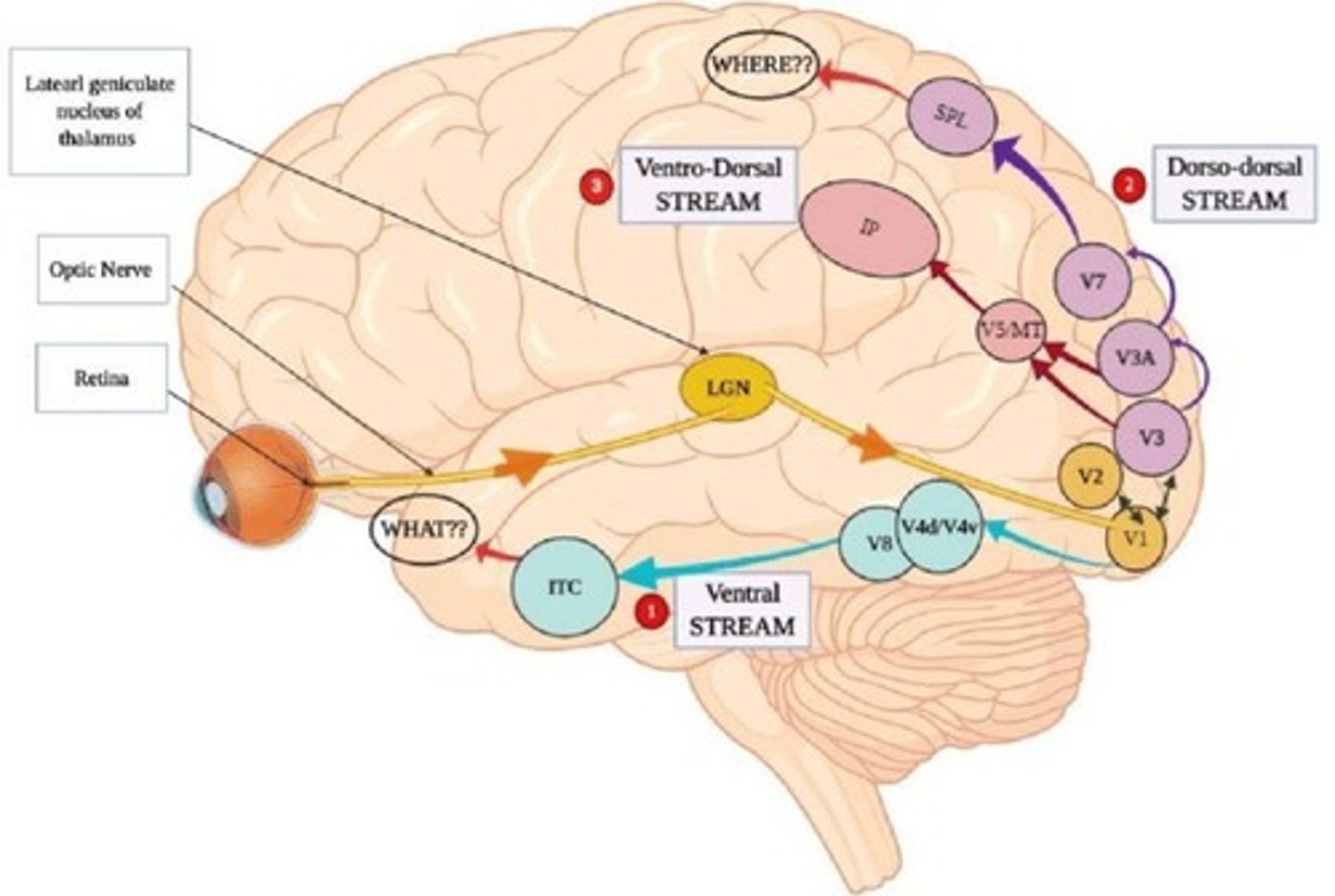
Visual pathway
Eye → LGN (subcortex) → V1 (primary visual cortex).
Neural implementation
Energy → transduction → neural signal → processing.
Ventral stream
Object identification (V1 → temporal lobe).
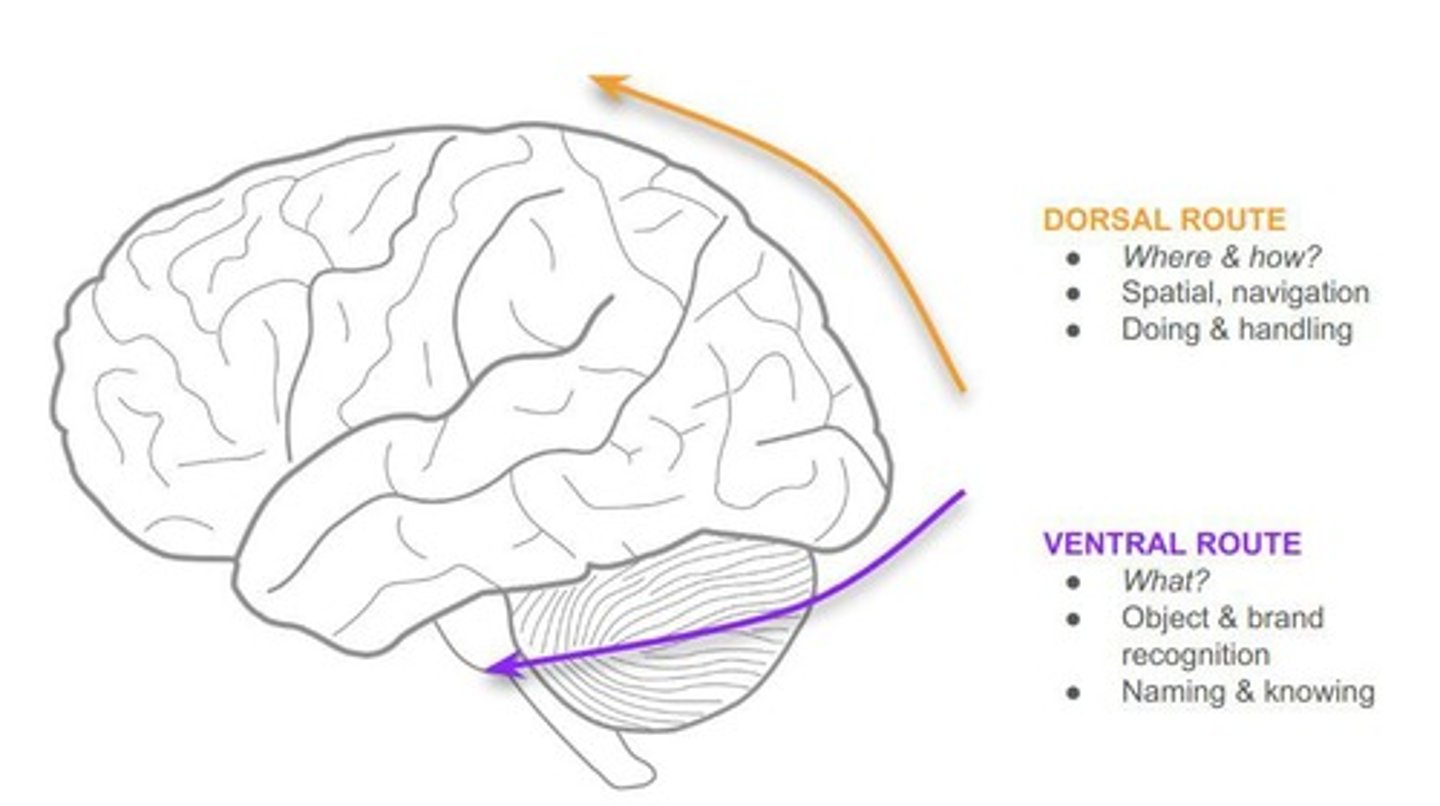
Dorsal stream
Spatial location (V1 → parietal lobe).
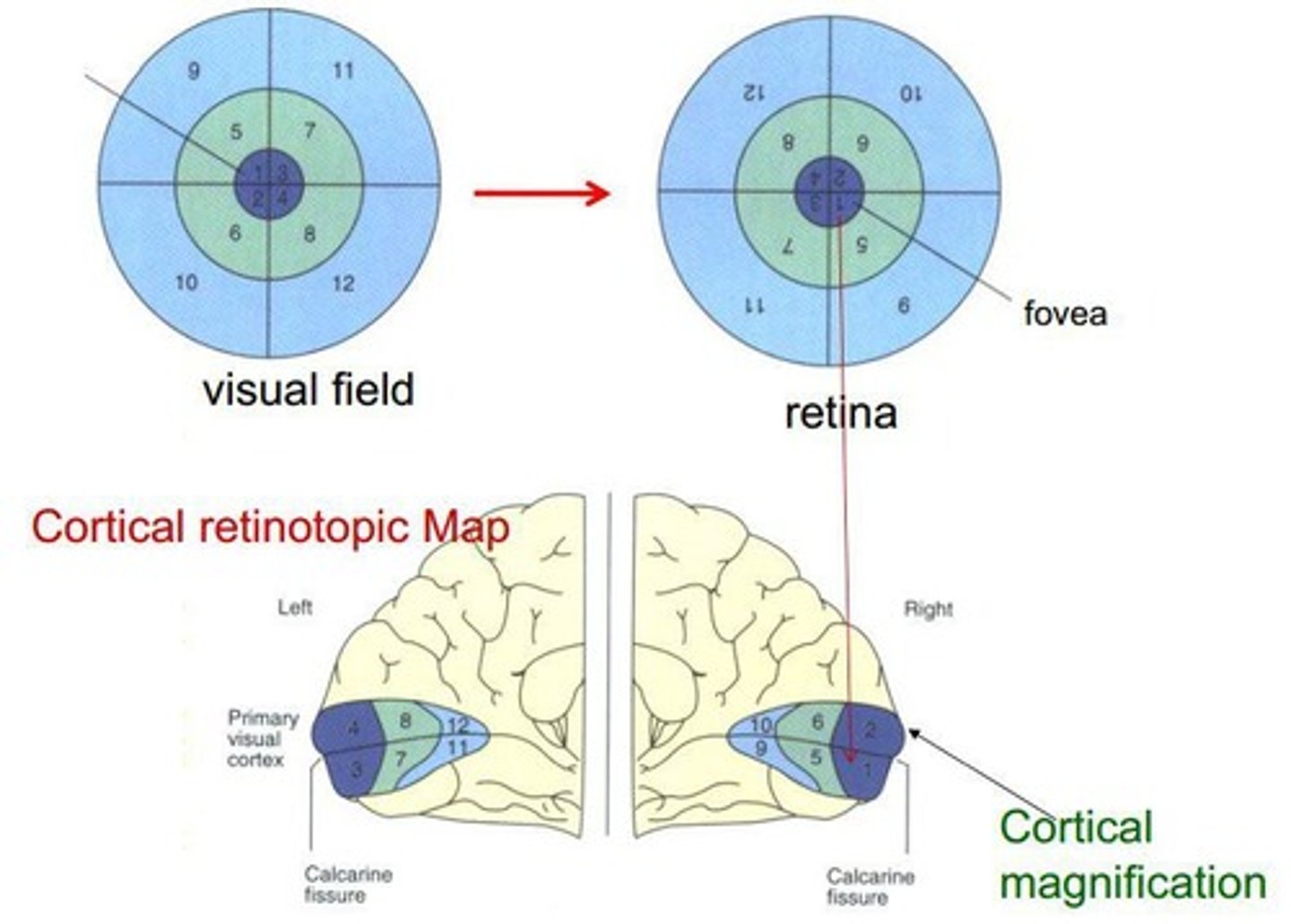
Retinotopic mapping
2D mapping of retina to LGN and V1.
Receptive field
Part of retina a cell responds to.
Centre-surround architecture
Excitation in the centre, inhibition in the surround.
Lateral inhibition
Enhances contrast; neighbours inhibited by 10%.
Monocular blindness
Severed optic nerve in one eye.
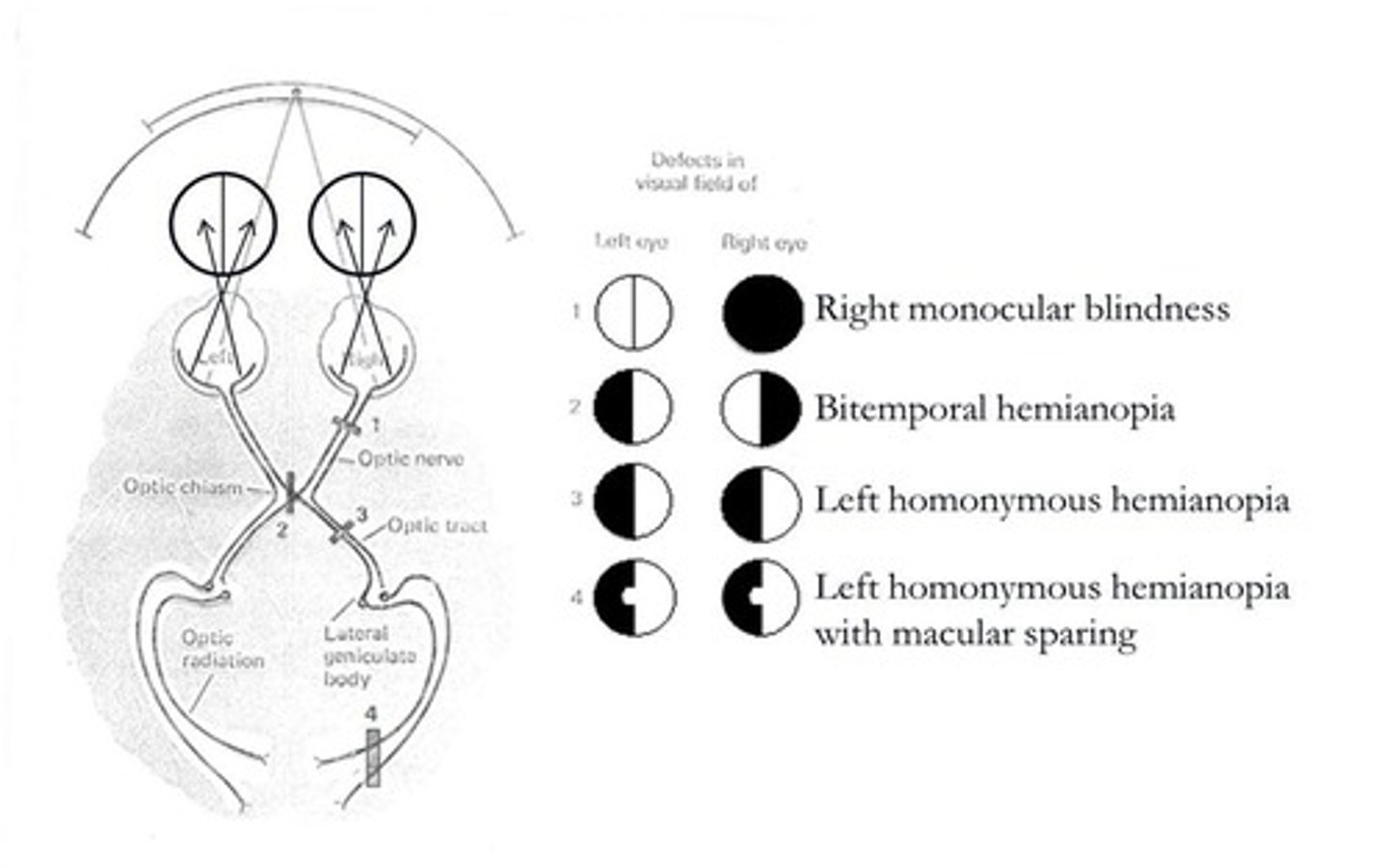
Bitemporal hemianopia
Damage at optic chiasm (nasal retinae affected).
Left homonymous hemianopia
Right-side lesion post-chiasm.
Macular sparing
V1 lesion spares some central vision.
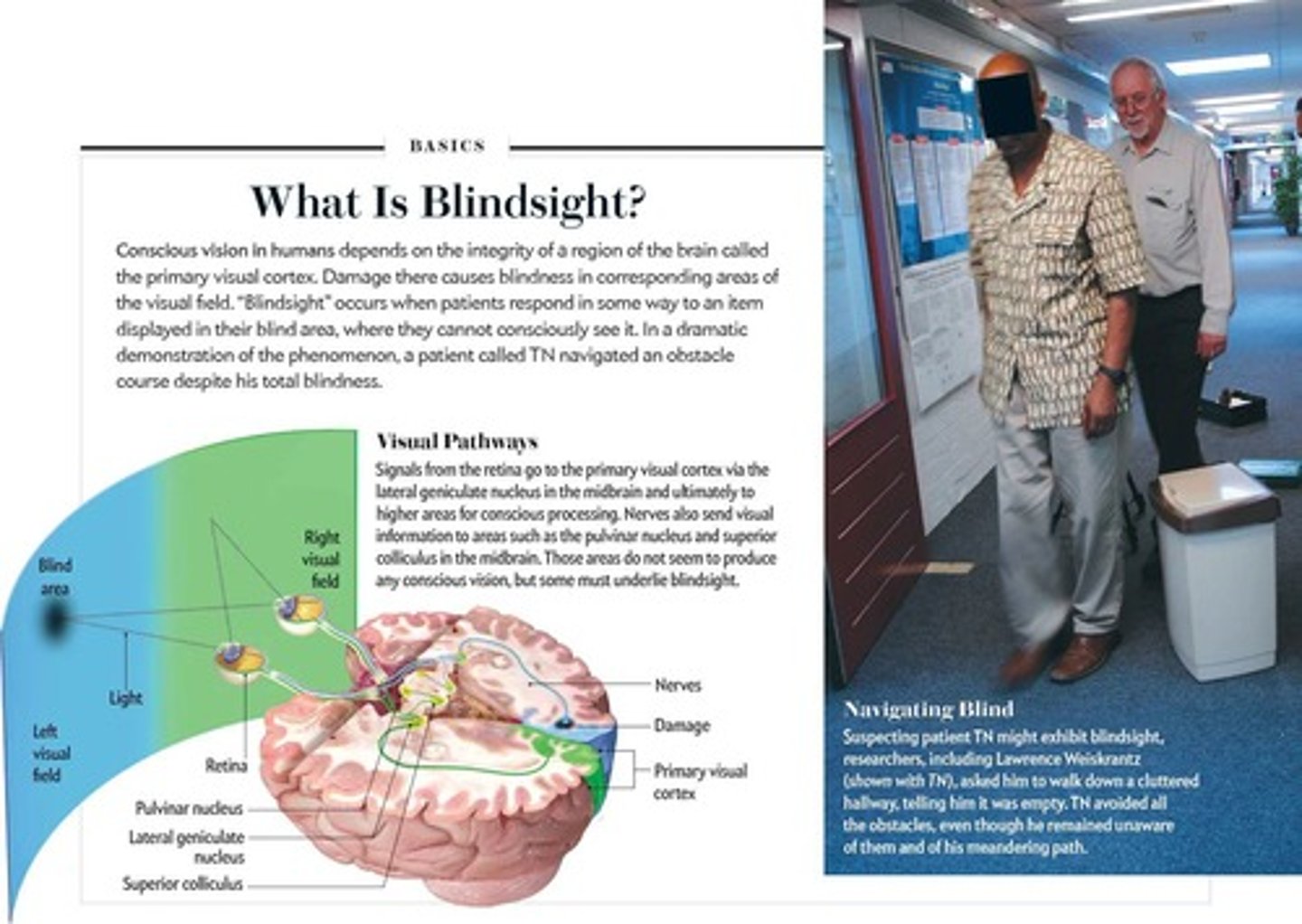
Blindsight
A condition where individuals respond to visual stimuli without conscious visual perception.
How is sensory information implemented neutrally?
1. Sensory organs absorb energy
2. energy is transduce into a neural signal
3.the neural signal is sent throughout the brain where further processing takes place