Unit 5: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
epineurium
surrounds entire nerve with multiple fascicles and blood vessels
perineurium
surrounds a set of nerve fiber bundles
endoneurium
surrounds individual nerve fiber
shingles
viral infection caused by chickenpox's virus
analgesia with ibuprofen vs. aspirin
pain relief through analgesics
Aspirin inhibits prostaglandins and production to reduce pian signals' intensity. Used commonly for headaches
cerebral palsy
damage to developing brain due to meningitis
Parkinson's disease
progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons leads to tremors
reflex
automatic/predictable response to stimulus for homeostasis/protection
somatic reflex
voluntary reflex that controls Skeletal muscles
autonomic reflex
involuntary reflex that controls smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands (I.e., heart rate)
monosynaptic reflex arc
1 synapse with sensory neurons directly synapsing onto the motor neurons
polysynaptic reflex arc
2+ synapses with interneurons (slower)
stretch reflex
a muscle contracts in response to a stimulus (I.e., quads contract when the patella is tapped)
flexor reflex
a limb is withdrawn for protection (I.e., hand on hot stove or foot on sharp) & polysynaptic
reasons to test reflex
to test for abnormalities of the PNS, spinal cord, and nerves → abnormality = spinal cord injury, nerve damage, or neurological disorder
patellar reflex
tests L2-L4 & femoral nerve function, is monosynaptic
1) The knee is tapped.
2) The quads stretch, sending a signal to muscle spindles/stretch receptors.
3) Sensory neuron carries signal to the spinal cord.
4) Sensory neuron directly synapses to motor neuron.
5) Motor neuron sends signal to quads to contract and kick up.
autonomic NS
AAUT (autonomic = automatic, unconscious, targets organs)
has 2 neurons in a chain (pre/post ganglionic), using both ACh and norepinephrine
controls behavior & the endocrine system, maintains homeostasis
** contains both the sympathetic & parasympathetic NS
somatic NS
SAME (somatic = ACh, motor control, exact movement)
1 motor neuron from CNS to muscle with direct synapse from ACh
sympathetic NS (belongs to autonomic NS)
for fight/flight (Stress, Speed up)
efferents exit CNS from spinal cord b/w T1 & L2
pupils: dilate
heart rate: increases
inhibits: secretion of gastrointestinal tract glands
bronchi: dilates for air
triggers: orgasm
inhibits: pee
has antagonistic and cooperative effects with the parasympathetic NS
parasympathetic NS
rest/digest (Poo, Pee, Peace)
efferents exit CNS via CN3, 7, 9, 10, or from sacral spinal cord
pupils: constrict
heart rate: decreases
stimulates: secretion of gastrointestinal tract glands
bronchi: constrict for air
stimulates: erection
stimulates: pee & poo
SLUDD (saliva, lacrimation, urination, digestion, defecation)
conjunctivitis
inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by bacterial/viral infections, allergies, or irritants that cause redness, swelling, & discharge
glaucoma
eye condition that leads to optic nerve damage, common in 60+ year olds with gradual effects of loss on side vision in later stages
cataracts
when crystallin proteins in eye break down & clump together to cloud vision (due to eye injuries, diseases, or genetics) and can progress over time w/ issues of night vision, astigmatism, sensitivity to light/glare,and double vision. It can only be treated through surgery with aging and diabetes as highest risk factor
detached retina
retina separates & causes blurred vision -> blindness. Symptoms are increases in floaters, flashes of light, darkening of FOV, and peripheral vision loss. Occurs due to age, eye injury, myopia (nearsightedness), eye surgeries, etc.
myopia
cornea too curve or eyeball too long, causing light to focus in front of retina & not on
diverging lens spreads light out before they enter eye
myopia = minus lens
see close clearly, can’t see far
hyperopia
cornea too flat or eyeball too short, light focuses behind retina
converging lens bends light in to help focus on retina
hyperopia = plus lens
can see far, not close
astigmatism
cornea/lens shaped like football causing uneven focus → blurred edges around lights
cylindrical lens compensates for football shape
color blindness
1+ cones are absent/not working most likely due to genetics w/ red-green color blindness being most common
night blindness
damaged/insufficient rods → bad night vision b/c of Vitamin A deficiency, retinitis pigmentosa, or genetic disorders
corneal transplants’ success
cornea is immune-privileged with no blood/lymphatic vessels, so transplanted cornea can’t be rejected or attacked by immune system despite being foreign
eyelids, eyelashes, and eyebrows’ function
protect eyeballs from foreign objects, perspiration, and sun rays (eyelashes/eyebrows)
eyelids shade/protect & spread lube over eye
pupil size regulation
iris regulates how much light enters by adjusting pupil size
constriction = parasympathetic NS & for bright light
dilation = sympathetic NS & for low light
Vertebrae & nerves
“Come to learn smart concepts”
Cervical (8) - C8 exits above C7
Thoracic (12) - exits below each
Lumbar (5) - exits below each
Sacral (5) - exits through sacral foramen
Coccyxgeal (1) - near coccyx
root
2 branches connecting spinal nerve to cord (not mixed)
dorsal root takes sensory information, ventral root takes motor output
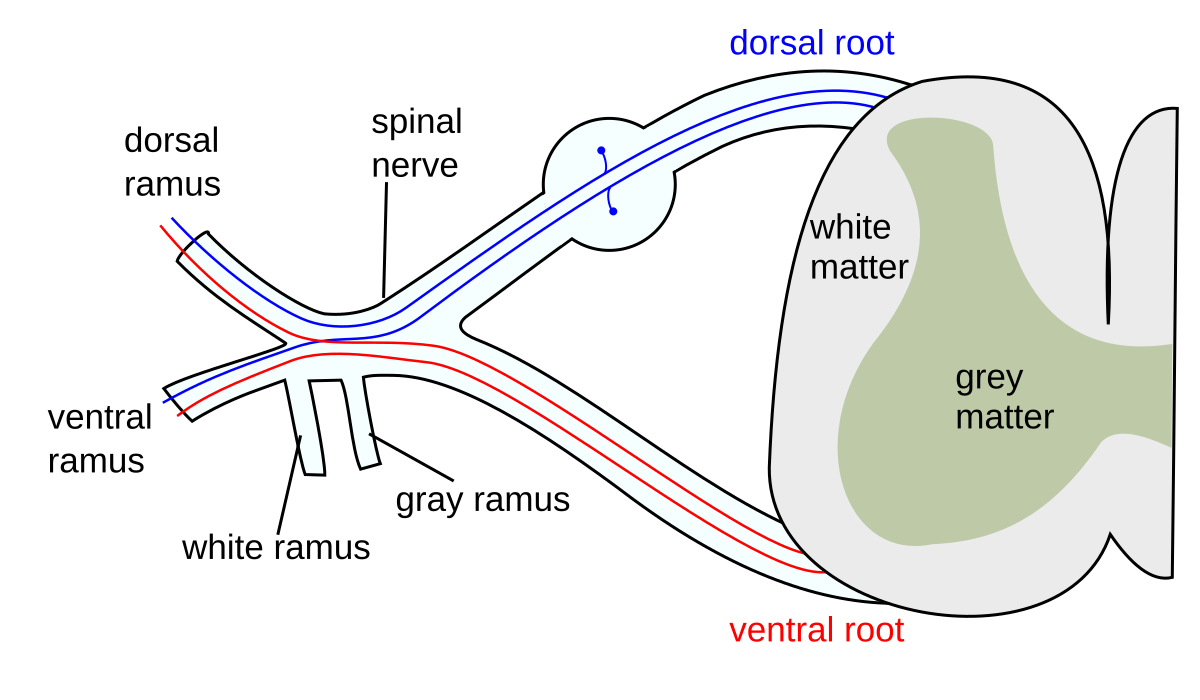
ramus
branches derive individually after roots exit spinal column (dorsal = posterior, ventral = anterior)
connects spinal nerves to autonomic ganglia
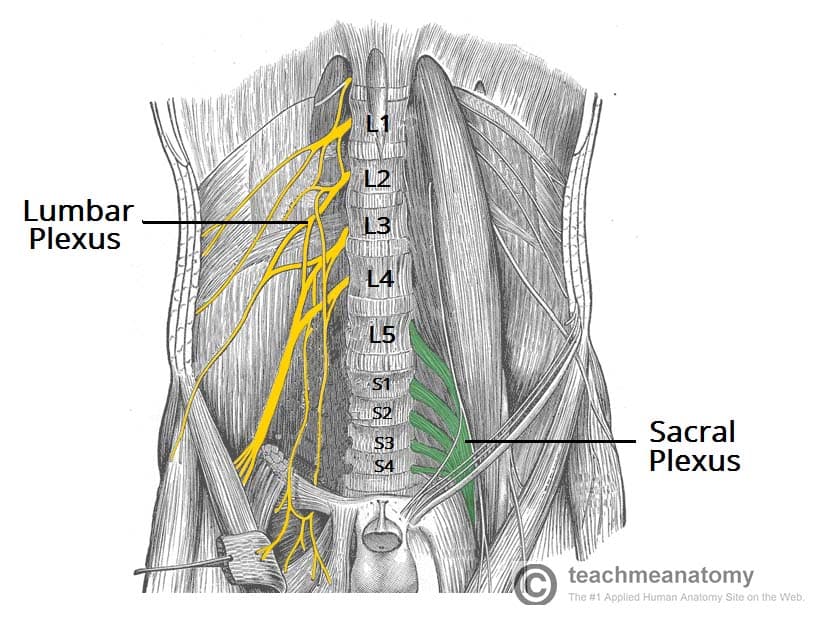
plexus
networks formed by ventral Rami of spinal nerves (cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral plexuses)
sensation
conscious/subconscious detection of changes internally/externally
perception
conscious awareness and interpretation
sensory modality
type of sensation (two types: general & special senses) & brain distinguishes which senses based off where the sensory neurons synapses
sight = occipital lobe
hearing = temporal lobe
touch = postcentral gyrus
general modality
somatic and visceral senses (from touch, pressure, pain, temperature)
special senses
specialized receptors for 5 senses and for equilibrium & spread throughout the head, complex organs, eyes, nose, ear, and tongue
how a sensation turns into a perception
“Silly turtles get cold in Canada”
Sensation: A sensation is detected by the receptors.
Transduction: Receptor converts stimulus into a graded potential.
Generation: Graded potentials are generated. If threshold is reached, an action potential is generated.
Conduction: Action potential travels to the central nervous system.
Integration: Central nervous system integrates and it leads to a perception if it’s a conscious change resulting from the actin potential.
Receptors for sensation
free nerve endings are for pain, touch, temperature, tickle, and itch sensations → AP generated
encapsulated nerve endings are dendrites wrapped in connective tissue for pressure, vibration, and touch → AP Generated
separate cells are specialized to synapse with the sensory neurons (hair, gustatory, and photoreceptors) → triggers neurotransmitters to diffuse with sensory neurons
Other receptors for sensation
exteroreceptors - external changes
interoreceptors - internal changes
proprioceptors - within muscles, joints, and inner ear
mechanoreceptors - mechanical energy
thermoreceptors - thermal energy
nociceptors - detection of pain
photoreceptors - changes in light
chemoreceptors - chemical energy
osmoreceptors - osmotic changes
adaptation