Forensics exam 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Define Serology
characterizationThe science of body fluid identification and characetization by examining blood, semen, saliva, and urine through the use of presumptive tests and confirmatory tests
What are the first two steps of Serology
Starts with suspects or victims clothing, weapons, and other items that may be evidence
Cuttings and swabs are taken from these pieces of evidence
From what years was forensic serology the most popular forensic lab procedure? What was it replaced with?
Forensic serology was the most important forensic lab procedue from 1950 to the 1980s. It was replaced with DNA techniques and labs. However, with limited funds and the time DNA testing takes, many labs still use basic serology tests.
What are the characteristics and functions of Plasma
Plasma is the straw colored, nonliving portion of the blood. It makes up 55% of an individuals total blood volume, while being 90% water and 10% salts, proteins, amino acids, enzymes, and hormones.
Plasma transports blood cells, products of digestion, and hormones throughout the body.
What portion of blood volume is consists of cells
45%
What are the characteristics of Erythocytes (RBC)
RBC distribute oxygen throughout the body and are used as a classical piece of forensic evidence (serology detection)
What are the characteristics of Leukocytes (WBC)
WBC are the only portion of the blood which carries DNA (only BC to have a nucleus). Due to carryinf DNA, WBC are used for inividial evidence
They are the “cleaning system” for the body, ridding it of pathogens.
What are the characteristics of Thrombocytes (platelets)
They are responsible for blood clotting
What is Serum as related to blood volume
Serum is the liquid that separates from the blood when a clot is formed
What is a Presumptive Test
A presumptive test is a chemical test that uses a change in color to detect the POSSIBLE presence of blood. This is a fast reaction, however it is nonspecific to humans
What presumptive test for blood IS specific to humans
LUMINOL tests
Explain the Kastle Meyer Presumptive test
A possible blood sample is swabbed
A drop of phenolphthalien reagent is added to the cotton swab
A drop of hydrogen peroxide is added to the same swab
If the cotton swab turns pink, the sample is blood. If there is no color change, the sample is not blood
Explain how a Presumptive phenolphthalein test works
The hemoglobin in blood posseses peroxidase-like activity that can oxidize phenophthalien to produce a pink color. Hemoglobin + phenolphthalien + Hydrogen peroxide will produce a bright pink color, indicating a possible blood sample.
However, copper, broccoli, and fruit juice can provide false positives. And this test is nonspecific to humans
What are the three confirmatory tests for human blood
Luminol
Takayama Stain
Ouchterlony test
What is luminol by definition used for
Luminol is a chemical used to detect trace amounts of blood left at crime scenes through a strong blue glow
Explain how luminol tests work
Luminol tests detect Iron in hemoglobin, not blood itself. Hydrogen peroxide and luminol are the principal players in the chemical reaction, but to produce a strong glow a catalyst (Iron) must be present.
Luminol is capable of detecting bloodstains diluted up to 300,000 times and doesn’t affect DNA testing
What is an Ouchterlony test
A confirmatory test that uses antibody reactions to determine if blood is human
Describe the takayama crystal test
A confirmatory test for blood that uses the formation of crystals to indicate the presence of blood
What test can be done to determine if a blood sample is animal or human
A preciptin test
What are the steps to the Preciptin test
Blood sample is injected into a rabbit to form antibodies
The rabbits blood is extracted as an antiserum
The antiserum is placed on the sample blood
The sample will react with human proteins if human blood is present
This test is very sensitive, so only a small amount of blood is needed
What is a key difference between human and animal blood cells
Animals have large nucleic RBC while humans have millions of RBC that do not carry a nucleus
What are the three ways that an individuals blood type may change
Bone marrow transplant
blood transfusion
bacterial infection
What is the Acquired B Phenomenon
As a result of a bacterial infection, the intestines produce an enzyme that alters the A blood group molecule to closely resemble the B molecule. This often affects patients with colon cancer, bowel obstructions, or sepsis
What are the five steps of scene pattern reconstruction
Stain condition
Pattern
Distribution
Location
Directionality
What are the five steps of lab result reconstriction
Genetic marker typing
age determination
source determination
race determination
sex determination
What is the feild of blood spatter evidence
A field of forensic investigation which deals with the physical properties o fblood and the patterns produced under different conditions because of various forces being applied to the blood
Blood follows the laws of physics
What are the four characeristics of blood droplets
1. A blood droplet remains
spherical in space until it
collides with a surface.
2. Once a blood droplet impacts
a surface, a bloodstain is
formed.
3. Droplets falling from the
same height, hitting the same
surface at the same angle,
will produce stains with the
same basic shape.
4. How will the shape change
as the height is increased or
decreased?
What is the general volume of blood droplets
0.03 cc to 0.15 cc
What conditions affect the shape of a blood droplet
Size of the droplet
Angle of impact
Velocity at which the droplet left its origin
height
texture of the target surface
What are three questions that can be answered by blood spatter interpretaton
The point (s) or origin of the blood
The type of weapon used
The type and direction of impact that produced the bloodshed
Bloodstain terminology: define the angle of impact
the angle at which blood strikes a target surface
Bloodstain terminology: define bloodtrain transfer
when a bloody object comes into contact with a surface and leaves a patterened blood image on the surface
Bloodstain terminology: Define Backspatter
blood that is directed back toward the source of energy
Bloodstain terminology: define cast-off
blood that is thrown form an object in motion
Bloodstain terminology: define contact stain
bloodstains caused by conact between a wet blood bearing surface and a second surfacet hat may not have blood on it
Bloodstain terminology: define directionality
related to the direction a drop of blood travels in space from its original point of origin
tapered end points in the direction of travel
Bloodstain terminology: define terminal velocity
the greated speed to which a free falling drop of blood can acceletate in the air
What are the four characteristics of High Velocity bood spatter
Greater than 25 feet per second
gives a fine mist apperance
consists of a colelction of small blood droplets
indicated a gunshot, coughing, sneezing, or explosives
What are the three characteristics of medium velocity blood spatter
Velocity of 5-25 ft/s
May inducate blut force trauma
May indicate cutting/stabbing motion
What are the three characeristics of Low Velocity Blood Spatter
Velocity of 5 ft/s or less
Indicates blood dripping from a weapon or wound
Drops are larger than 3mm in diameter
What does a round blood drop indicate
the blood drop fell at a 90 degree angle
what does an elliptical blood drop indicate
the blood was dropped from a less than 90 degree angle
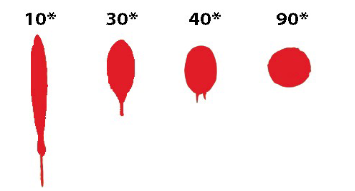
What are the characteristics of these blood droplets in relation to the angle in which they fell
With the elongated tail, at 10* it is easier to determine the direction of travel that the blood droplet took
At about 30* the stain starts to produce a tail, indicating direction of travel
At 40* there is a slight tail
At 90* the droplet is perfectly round
Blood stain patterns: Radical Patterning
Resuts from blood pooling IN an open wound
Blood stain patterns: Pooling
Blood that collects in a puddle
Blood stain patterns: Arterial Spurts
Results from a wound to a major artery
Blood stain patterns: Cast-off (arc)
Blood from a weapon casts off onto ceilings and walls from preperation for another blow
Blood stain patterns: Contact
Bloodied object touches a surface
Blood stain patterns: Trail
Circular drops on a surface from an object
Define the area of intersection and convergence
1. The location of the blood source can be
determined by drawing lines from the
various blood droplets to the point where
they intersect.
2. The area of convergence is the point of
origin—the spot where the “blow” occurred
What are secreters
Secretes are individuals whos blood type antigens are found in high concentration i their body fluids, such as saliva, semen, and gastric juices