BIOL 203 Module 1: Chapter 2
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemical Basis of Life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
How to atoms interact to form bonds and make molecules?
Share or transfer electrons to give atoms full valence shells
Polar covalent Bond
e- not shared equally; partial charge
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
e- equally shared; no charge
Ionic Bond
e- transferred from one atom to another; gives both atoms a full valence shell; full charge
Hydrogen Bond
between water molecules; H+ atom w/ O or N **
Hydrophobic Interactions
NP molecules cluster away from the water molecules —> strength
Van der waals forces
weak electrical attractions due to temporary and minute partial charges
Bonds and interactions in order of strength (highest to lowest)
Polar Covalent, Nonpolar covalent, Ionic, H bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and van der waals forces
NLO - Atoms are made of
Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Properties of Water?
Polar
Hydrogen bonds between water molecules
Water molecules dissociate into an H+ ion and OH- ion
Why is water necessary for life?
Effective Solvent for charged and polar solutes
-Transports nutrients
Water is denser as a liquid than as a solid
-Insulation
High capacity for absorbing energy
-Homeostasis
Cohesive and Adhesive
-Photosynthesis
Multiple water molecules, e-, charged, and bonds
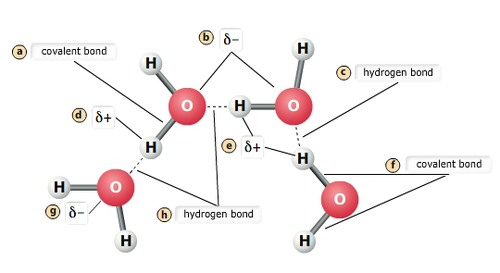
How do charged and polar molecules interact w/ water
Dissolve easily in water due to hydrogen bonding (hydrophilic)
How do nonpolar solutes interact w/ water?
NP doesn’t dissolve (hydrophobic)
Difference in proton concentration when given pH
Acidic: H+ > OH-
Neutral: H+ = OH-
Basic: H+ < OH-
NLO - Acid
Give up P and increases the concentration of the hydronium ion in water
NLO - Base
Acquire P and decrease the concentration of the hydronium ion in water
Functional Groups? Hydrophobic or Hydrophillic?
Amino - depends
Carboxyl - Hydrophilic
Carbonyl - Hydrophilic
Hydroxyl - Hydrophilic
Phosphate - Hydrophilic
Sulfhydryl -Hydrophobic
separately interact to build the large molecule
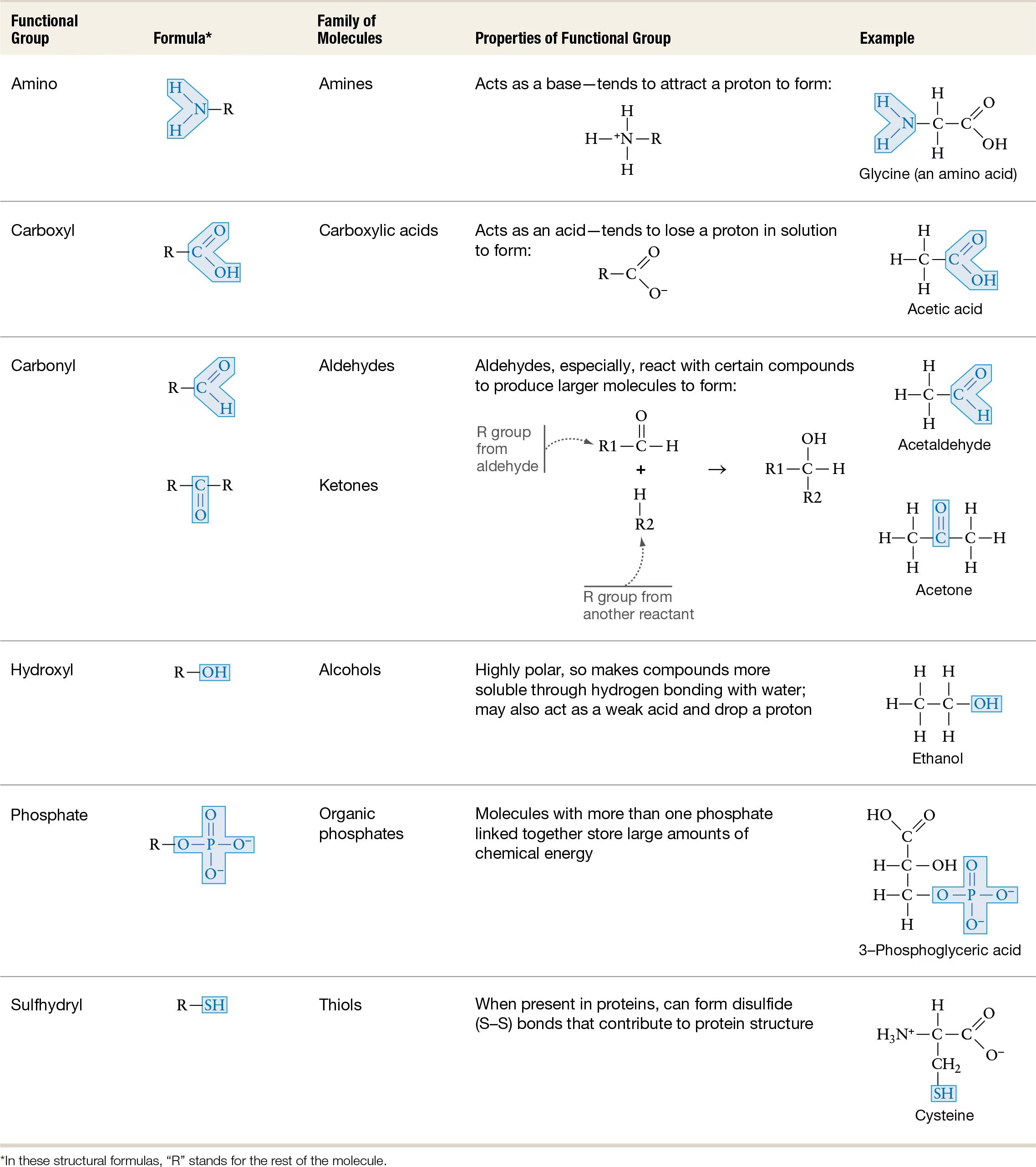
Types of interactions/bonds by functional groups
Amino: hydrogen and ionic bonds
Carboxyl: hydrogen and ionic bonds
Carbonyl: hydrogen bonds
hydroxyl: hydrogen bonds
Phosphate: n/a
Sulfhydrl: di-sulfide bonds
How water is involved w/ the assembly of macromolecules
Condensation/Dehydration Rxn: remove H20 (create)
-water is the product
Hydrolysis: add H20 (destroy)
-water is the reactant
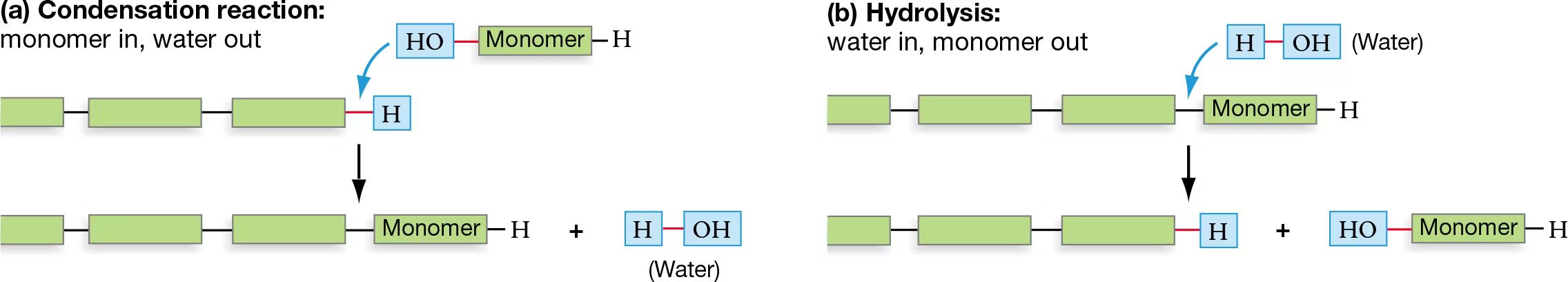
How is water involved w/ the disassembly of macromolecules?
Hydrolysis Rxn: adding H20