The Neuron: Application of Cell Transport Concepts
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Where are neurons found?
the nervous system
Neuron function
depends on membrane structure and the regulated transport of ions across the plasma membrane
what are neurons?
specialized cells found throughout the nervous system that transmit information through electrical signaling
image of a neuron
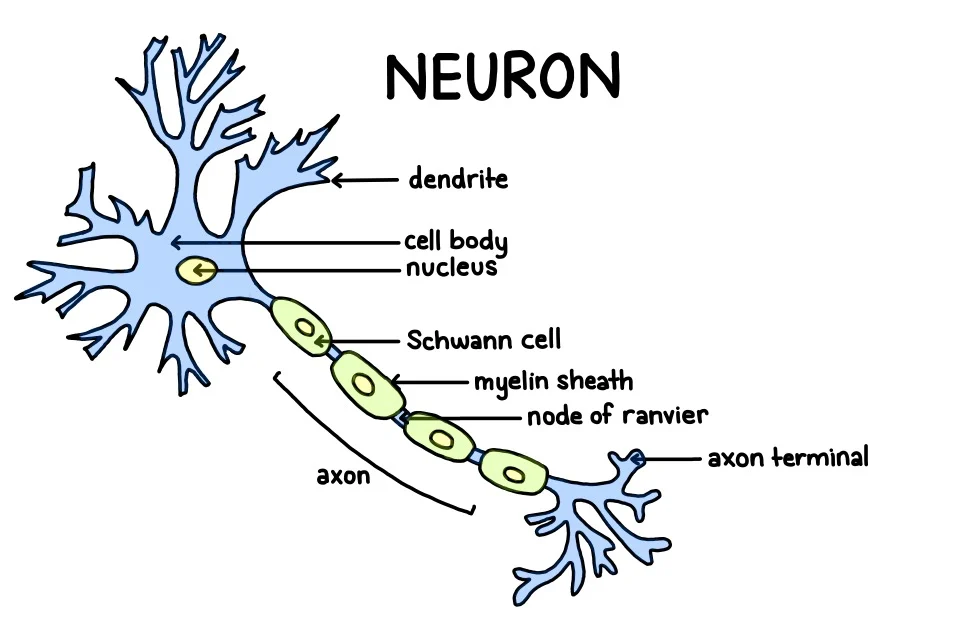
Dendrites
receive incoming signals from other cells
Axon
conducts electrical signals along the axon membrane
Myelin Sheath
-Insulates the axon and increases the speed of signal transmission
-fat is a good insulator
-30 wraps
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath where ions cross the membrane
Axon terminals
transmits signals to other cells
Schwann cell
protects nerves by forming myelin wrapped around them
electrical signals
-long distance communication along the neurons membrane
-generated by regulated ion movement across the neurons plasma membrane
-travels along the neuron
-within
chemical signals
-short distance communication between cells
-acts as synapses
-between
information flow
from a presynaptic cell (a neuron) to a postsynaptic cell (a neuron, muscle, or gland cell)
membrane potential
-every cell has a voltage (difference in electrical charge) across its plasma membrane called membrane potential
-changes in membrane potential act as signals, allowing neurons to transmit and process information
resting potential
-the membrane potential of a neuron not sending signals
-many Na (sodium) ions are located outside the neuron, while many K (potassium) ions are located inside the neuron
-the inside of the neuron is more negatively charged than the outside, creating a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane (because of channels there are more positives leaving)
what type of transport are channels?
passive: facilitated diffusion
what do the concentration gradients represent?
chemical potential energy
sodium potassium pumps
-uses the energy of ATP to maintain these K and Na gradients across the plasma membrane, not the action potential itself
-for every cycle: 3 Na are pumped out, 2 K are pumped in
what type of transport are sodium potassium pumps
active transport protein
Action potential change in ion movement order
1) resting state
2) depolarization
3) rising phase of the action potential
4) falling phase of the action potential
5) undershoot