Chemotherapy Agent
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Precautions wearing for chemo
double flush toilet
double gloving
special linen hamper
Anemia
Reduction in the number of circulating RBCs
Decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit (know the normals)
Treatment:
Iron, folic acid
Erythropoietin stimulating agent
epogen
iron, folic acid, blood transfusions
Transfusion
leucovorin rescue (folinic acid)
extra rest periods- fatigue most common complaint, caregiver assistance
bone marrow transplant
Thrombocytopenia
Reduction in circulating platelets, which increase the risk of bleeding
Client care:
oprelvekin to INCREASE platelets
Bleeding precautions: Avoid IM injections/venipunctures; no Foleys; avoid straining at stool; use electric razor;
Gentle prolonged pressure after puncture
Monitor platelets (if < 50,000 notify HCP), PTT, PT/INR
No NSAIDs
Be alert for signs of bleeding, bruising; assess for petechiae
Neutropenia
Decrease in circulating neutrophils; Incidence and severity of infection are increased
Nadir (lowest blood count after chemo), occurs between days 10 -28 days
Client care:
filgrastim leukopoietic growth factor (ATI 8th ed. p. 206, 9th ed. p. 202)
sargramostim (ATI 8th ed. p. 207, 9th ed. p. 203)
Monitor absolute neutrophil count (ANC) 2500-6000
Mild neutropenia: 1,000 – 1,500 ANC
Moderate neutropenia: 500 – 1,000 ANC
Severe neutropenia: Less than 500 ANC
Neutropenic precautions
Temp Q4h, notify if >100.3 F°
Notify of sore throat, cough, s/s infection
Protective (reverse) isolation
No fresh flowers (minimize raw fruits, veggies)
Dedicated equipment
Avoid crowds and sick people
No vaccines
Monitor ANC
Limit Tylenol- can mask fever
colony stimulating factors
Medication | Therapeutic Effect | Adverse Effect |
Epoetin alfa; erythropoietin (Epogen) | Increase production of RED blood cells | Headache, HTN Increased risk of blood clots |
Oprelvekin (Neumega) thrombopoietic growth fact | Increase the production of PLATELETS | Peripheral edema, cardiac dysrhythmias |
Filgrastim (Neupogen) leukopoietic growth factor | Increase the production of WHITE blood cells | Bone pain, splenomegaly, leukocytosis |
effects of chemo
Chemo causes:
Bone marrow suppression results in
Anemia (SOB, fatigue, pallor)
Thrombocytopenia (risk of bleeding)
Leukopenia/ neutropenia (risk of bleeding)
May also cause:
Hepatotoxicity (Increased liver enzymes, RUQ pain, fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice)
These are DOSE-LIMITING toxicities
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis are not necessarily dose-limiting, unless severe
Treatment of mucositis
Treatment option may include oral solution containing:
lidocaine (2% viscous)-numbing agent
antacid (Mylanta)- soothes
antihistamine (diphenhydramine)
antifungal (Nystatin)
Prednisolone- decrease inflammation
Client considerations:
Use toothettes instead of toothbrush
Avoid hot, spicy foods, roughage, citric acid foods
CI N/V
Consider emetogenic potential of chemo
Acute Emesis: < 24 hours post-chemotherapy
Delayed Emesis: > 24 hours post-chemotherapy
Anticipatory Nausea and Vomiting: Before administration of chemotherapy
Premedication with antiemetics 30-60 minutes prior to chemo admin
Combinations of antiemetics are more effective than single-drug therapy
5-HT3 receptor blocker- ondansetron (Zofran)
dexamethasone (Decadron)
aprepitant (Emend)
treatment of CINV
Client care
Continue medication 48 after treatment
IV fluids if continues
Ginger tea, flat ginger ale
Small frequent bland foods/meals
Monitor fluid & electrolyte status of client
May have accompanying diarrhea
avoid irritating foods
low fiber diet
loperamide (Imodium)
diphenoxylate (Lomotil) -controlled substance (V)
Decreased appetite
At risk for impaired nutrition
Offer high-protein, high-calorie foods
easy-to-swallow foods
custards
milkshakes
mashed potatoes
gelatins
Appetite stimulants:
megestrol (Megace)
dronabinol (Marinol)
Mesna (Mesnex)
to treat hemorrhagic cystitis (irritation of the lining of the bladder from chemo → hematuria)
Mesna to prevent this. Chemoprotectant
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Irritation of the lining of the bladder from chemo metabolites; results in sterile cystitis and hematuria
Client care:
8-10 glasses of water per day
Frequent (q2 hr during day) voiding
Risk lasts for 24 to 48 hours
Mesna (Mesnex)
preventative medication given prophylactically to prevent cystitis
ADR- Diarrhea, headache, nausea, fatigue (mild)
Extravasation?
STOP INFUSION OF DRUG
Leave infiltrated access in place
Aspirate any residual drug
Notify the prescriber
Instill antidote thru existing access
Apply sterile occlusive dressing
Warm/cold compresses as appropriate
Elevate affected limb
Other side effects
Photosensitivity
Increased skin sensitivity to UV exposure
Drugs causing: 5-FU, Methotrexate, Taxol, Adriamycin, Vincristine
Sunburn with blisters and erythema; hyperpigmentation
Avoid tanning booths, sunbathing even on cloudy days
Neurotoxicity
Numbness and tingling of fingers and toes most common-peripheral
Sensitivity to cold
Mental status changes may be seen-central
These are usually reversible when Rx stopped
Nephrotoxicity
Initial chemotherapy treatment
Most often hematologic cancers
Vigorous IV Hydration done
Occasionally with bicarbonate
Electrolytes watched closely
Amofostine = drug given to help prevent kidney damage
Sexual side effects
Related to drug, dose, length of treatment, age and sex of patient
Men: impotence, decreased libido, hot flashes, decreased sperm count, gynecomastia
Women: irregular or no menses, vaginal dryness, decreased ova production, painful intercourse, decreased libido, hot flashes
Amofostine
Help prevent kidney damage from chemo agent
chemoprotectant
Methotrexate
Chemoagent
Oral, IV, IM, Intrathecal
ADR: Mucositis, nausea, vomiting, alopecia, bone marrow suppression (esp. neutropenia), photosensitivity, renal toxicity, gastric ulcers
Pregnancy category X (for up to 6 mo after treatment)
Non-vesicant
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)
Indications: colon, rectal, breast, stomach, pancreatic cancer, skin cancers
IV, topical
ADR: mucositis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bone marrow suppression, mild alopecia, photophobia, rash (with topical route)- may last for 2+ weeks after use, radiation recall
Non-vesicant
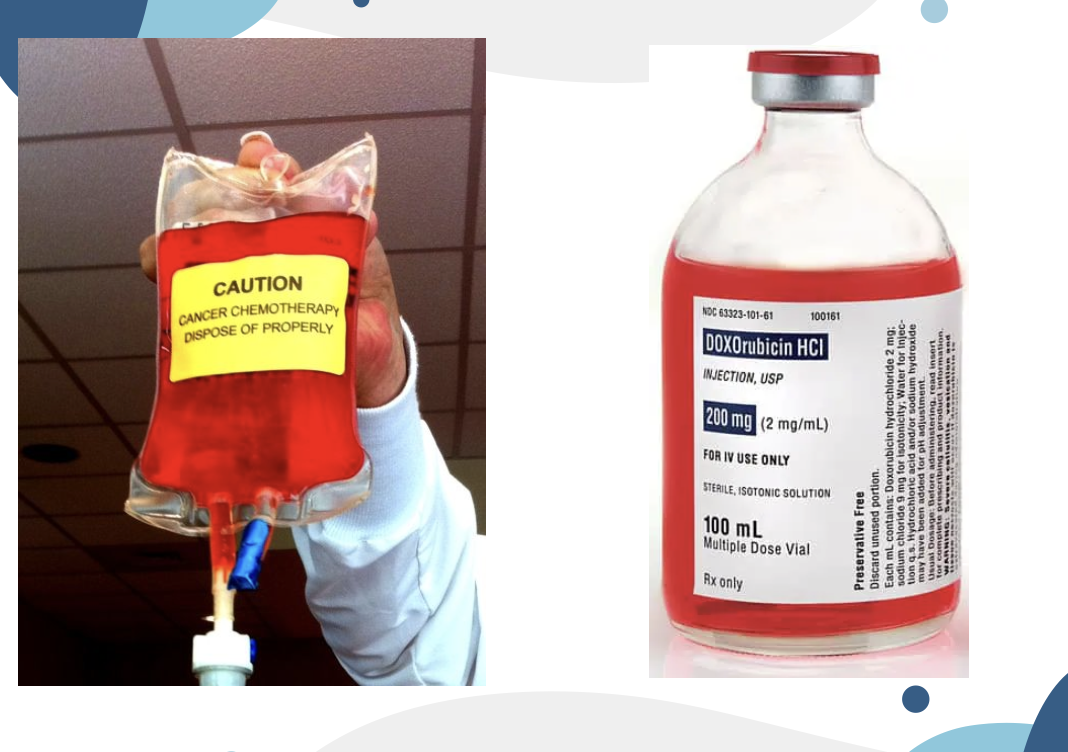
Doxorubicin
Indications: solid tumors (lung, bone, stomach, breast cancers); Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas; sarcomas of soft tissue and bone; carcinoma of ovaries, testes and thyroid
IV infusion “red devil”
ADR: Bone marrow suppression, nausea, vomiting, alopecia, mucositis, cardiotoxicity, radiation recall, photosensitivity, red urine, sweat (not harmful, lasts 1-2 days)
VESICANT
MUGA* / Echocardiogram before dosing
ADR all red stuff
CARDIOTOXIC <3
need baseline cardiac exams
What is radiation recall
Redness in a previously irradiated area (may be months or years prior) after systemic chemotherapy
Pattern corresponds to radiation field
May be painful
Treat symptomatically
antihistamines
analgesics
Vincristine (Oncovin)
Used in combination with other chemotherapy agents; leukemia, Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, bladder/breast cancers; Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas; Kaposi’s sarcoma
IV infusion
VESICANT
ADR: alopecia, nausea, vomiting, nerve injury (autonomic nerve injury results in constipation, urinary retention; peripheral nerve injury results in peripheral neuropathy- paresthesias, decreased reflexes, loss of sensation), bone marrow suppression (mild)
AUTONOMIC AND PERIPHERAL NERVE INJURY
Paclitaxel (Taxol)
Indications: ovarian, non-small cell lung tumors, Kaposi’s sarcoma, leukemias
IV infusion
VESICANT (usually an irritant, but can be considered vesicant)
ADR: bone marrow suppression, alopecia (severe), arthralgia/ myalgia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, hypersensitivity reactions, mucositis, renal toxicity, radiation recall
severe alopecia
Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
Indications: cancer of the ovaries, breast, blood lymph system, neuroblastoma (mainly in children); retinoblastoma, multiple myeloma, nephrotic syndrome and immunosuppression in rheumatic disorders (ex. SLE, juvenile idiopathic vasculitis)
PO, IV
ADR: hemorrhagic cystitis, alopecia, nausea, vomiting, hemorrhagic colitis, mucositis, neutropenia
Cisplatin
Indications: bladder, testicular, ovarian cancers; off-label cervical, endometrial, prostate cancer; bone marrow transplants
IV infusion
VESICANT
ADR: nause, vomiting (highly emetogenic), nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity (esp. children), bone marrow suppression, alopecia, anaphylaxis
LOTS of VOMITING
Nephrotoxic, ototoxic
Bleomycin
Indications: testicular, lymphoma, squamous cell carcinomas, Hodgkin’s disease
IV infusion
Irritant
ADR: Pulmonary fibrosis and pneumonitis (fatal in 1% of clients), mucositis, stomatitis, acute febrile reaction, mucocutaneous toxicity (rash, erythema, hyperpigmentation, urticaria), alopecia
Pulmonary toxic!
fobrisis, pneumonitis
Hormonal Chemo agents
hormone-blocking tumors (breast cancers, testicular cancers)
Tamoxifen
Indications: breast cancer (treatment and prevention in high-risk women*)
Estrogen receptor blocker; stops growth of breast cancer cells, which are estrogen-dependent cancers
ADR: hot flashes, vaginal discharge, menstrual changes, bone pain (increased calcium), endometrial cancer (<1%), thromboembolic event (DVT, PE, CVA) (<1%), n/v
Stops growth of breast cancer cells
hormonal side effects
Nursing interventions:
Monitor calcium levels
Monitor for abnormal vaginal bleeding, discharge
Administer fluids and antiemetics as needed
Client education: Have yearly gynecological exam (risk of endometrial cancer); report chest pain, shortness of breath, or leg pain/ edema (DVT/ PE); educate client about hot flashes
estrogen EQUALS
clots