MGCR 293 Chapter 7: Perfect Competition
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and definitions related to perfect competition and its market dynamics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Market Structure
Refers to the degree of competition in the market for a particular good or service.
Perfect Competition
A market structure where many small firms produce identical products and can freely enter or exit the market.
Price Taker
Firms under perfect competition cannot set prices; they accept the market price as given.
Price Determination
Occurs at the intersection of the market demand and supply curves.
Marginal Revenue (MR)
The additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of a good.
Average Total Cost (ATC)
Total cost divided by the quantity of output produced.
Shutdown Point
The level of output and price below which a firm will cease production in the short run.
Producer Surplus
The difference between a firm's total revenue and its total variable cost.
Long-Run Equilibrium
Occurs when price equals long-run marginal cost and firms earn zero economic profit.
Minimum Efficient Scale
The lowest point at which a firm can produce, minimizing its long-run average costs.
Economic Profit
Total revenue minus total costs (including opportunity costs), can be zero in long-run equilibrium.
Identical Products
Products produced by firms in perfect competition that are indistinguishable from one another.
Free Entry and Exit
The ability of firms to enter or exit the market without significant barriers.
Horizontal Demand Curve
The demand curve faced by perfectly competitive firms is perfectly elastic at the market price.
Short-Run Analysis
Focuses on a firm's decision-making process to maximize profit at given market conditions.
Long-Run Analysis
Examines firm decisions on production levels and market entry or exit, leading to long-run equilibrium.
Elastic demand curve in perfect competition
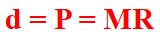
Perfect competition profit maximizing output

Market Structure\n\n
Refers to the degree of competition in the market for a particular good or service.\n\n
Perfect Competition\n\n
A market structure where many small firms produce identical products and can freely enter or exit the market.\n\n
Price Taker\n\n
Firms under perfect competition cannot set prices; they accept the market price as given.\n\n
Price Determination\n\n
Occurs at the intersection of the market demand and supply curves.\n\n
Marginal Revenue (MR)\n\n
The additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of a good.\n\n
Average Total Cost (ATC)\n\n
Total cost divided by the quantity of output produced.\n\n
Shutdown Point\n\n
The level of output and price below which a firm will cease production in the short run.\n\n
Producer Surplus\n\n
The difference between a firm's total revenue and its total variable cost.\n\n
Long-Run Equilibrium\n\n
Occurs when price equals long-run marginal cost and firms earn zero economic profit.\n\n
Minimum Efficient Scale\n\n
The lowest point at which a firm can produce, minimizing its long-run average costs.\n\n
Economic Profit\n\n
Total revenue minus total costs (including opportunity costs), can be zero in long-run equilibrium.\n\n
Identical Products\n\n
Products produced by firms in perfect competition that are indistinguishable from one another.\n\n
Free Entry and Exit\n\n
The ability of firms to enter or exit the market without significant barriers.\n\n
Horizontal Demand Curve\n\n
The demand curve faced by perfectly competitive firms is perfectly elastic at the market price.\n\n
Short-Run Analysis\n\n
Focuses on a firm's decision-making process to maximize profit at given market conditions.\n\n
Long-Run Analysis\n\n
Examines firm decisions on production levels and market entry or exit, leading to long-run equilibrium.\n\n
Perfect competition profit maximizing output\n\n
Occurs where Marginal Revenue (MR) equals Marginal Cost (MC). In perfect competition, this simplifies to when Price (P) equals Marginal Cost (MC), i.e., P = MC.\n\n
Total Profit Formula in Perfect Competition\n\n
\pi = (P - ATC)q\n\n
Competitive firm: Short-run Analysis step 2
Whether to produce at profit-maximizing output or to shut down. The firm will compare the market price (P) with its average total cost (ATC) and its average variable cost (AVC)
A firm’s total profit function
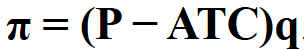
What are the three cases for producing at profit maximiing output or shutdown?
P > ATC: the firm makes positive profit and so it
operates at its profit-maximizing output
AVC < P < ATC: the firm makes a loss (π < 0), but it reduces the loss by operating at q* to cover its total fixed cost in the short run and then shut down in the long run
P < AVC: the firm shuts down immediately.
Long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive firm
A situation where firms earn zero economic profit, and market supply equals market demand, resulting in an optimal allocation of resources.
