Cell and Molecular Biology Exam 1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Types of molecules that make up cells
proteins (amino acids), carbohydrates (sugars), lipids, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA)
Characteristics of all cells
DNA, Inside/outside (cytoplasm/outside), membrane, RNA, proteins
Differences between cells
cellular organelles, shape (within/among), function (within/among)
Cells vary in appearance and function, but they all have the same basic what?
chemistry (central dogma: DNA>RNA>Proteins)
Properties of life
made of cells, sense and respond to stimuli, require energy for metabolism, reproduce, homeostasis (inside and outside), have metabolism
Biological definition for homeostasis
expending energy to maintain internal environment
Who discovered cells and when?
Robert Hooke in 1665
What did Schleiden and Schwann propose?
cells compose all parts of plants and animals (1830s)
Who (and how) was it discovered that cells did not spontaneously generate?
Pasteur in the swan neck flask experiment in 1860s
What did Virchow propose?
cells grow and all cells arise from preexisting cells
What are the 7 parts of modern cell theory?
1. all organisms are made of 1 or more cells; 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in all living things; 3. all cells are produced by division of preexisting cells; 4. cells contain hereditary information (DNA) that is passed from one cell to another; 5. all cells are basically the same in chemical composition and metabolic activities; 6. all basic chemical and physical functions are carried out inside cell; 7. cell activity depends on activities of sub-cellular structure within cell (organelles)
3 domains of life (in order of when they appeared). What did all three arise from?
bacteria, archaea, eukaryotes. A single protocell (almost cell)
Theory of Eukaryotes
in and endosymbiotic event, an archaeal cell ate a bacterial cell and bacteria became a mitochondrion, which is why they have DNA
Characteristics of prokaryotic cell
ribosomes and DNA are in same compartment, so ribosomes convert RNA to proteins very quickly (fast protein synthesis), a membrane, simple cell plan
Main organelles in eukaryotic cells (7)
mitochondria, peroxisome, ER, golgi, nucleus, lysosome, vesicle
Function of ER
Protein and lipid synthesis. It also helps membranes grow or shrink to allow vesicles to move around cell
Function of golgi
package molecules from ER for secretion to another part of cell or excretion
Function of nucleus
store DNA info. double membrane with pores
Function of lysosome
break things down for intracellular digestion
Function of mitochondria
metabolism finishes here. Allows cells to take in O2. Outer and inner membrane. Uses surfaces area to increase metabolism. Has own DNA
Function of peroxisome
neutralizes oxidative toxins in cell and helps with some lipid synthesis
How do prokaryotes accomplish the same metabolism as eukaryotes
they do it across their outer membrane
Cytosol
everything in cell not inside lumen of organelles
Cytoplasm
everything inside a cell
Size range of prokaryotic cells
0.5 micrometers-5 micrometers
Size range of eukaryotic cells
10 micrometers-meters
Four groups of molecules
proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids
Three groups of macromolecules
carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins
What make up macromolecules? How are they linked?
subunits. covalent bonds (share electrons)
How are macromolecules linked? How do they fold?
Linked linearly by covalent bonds, then are folded into 3D shape by other non-covalent bonds
What is the subunit of proteins?
20 amino acids
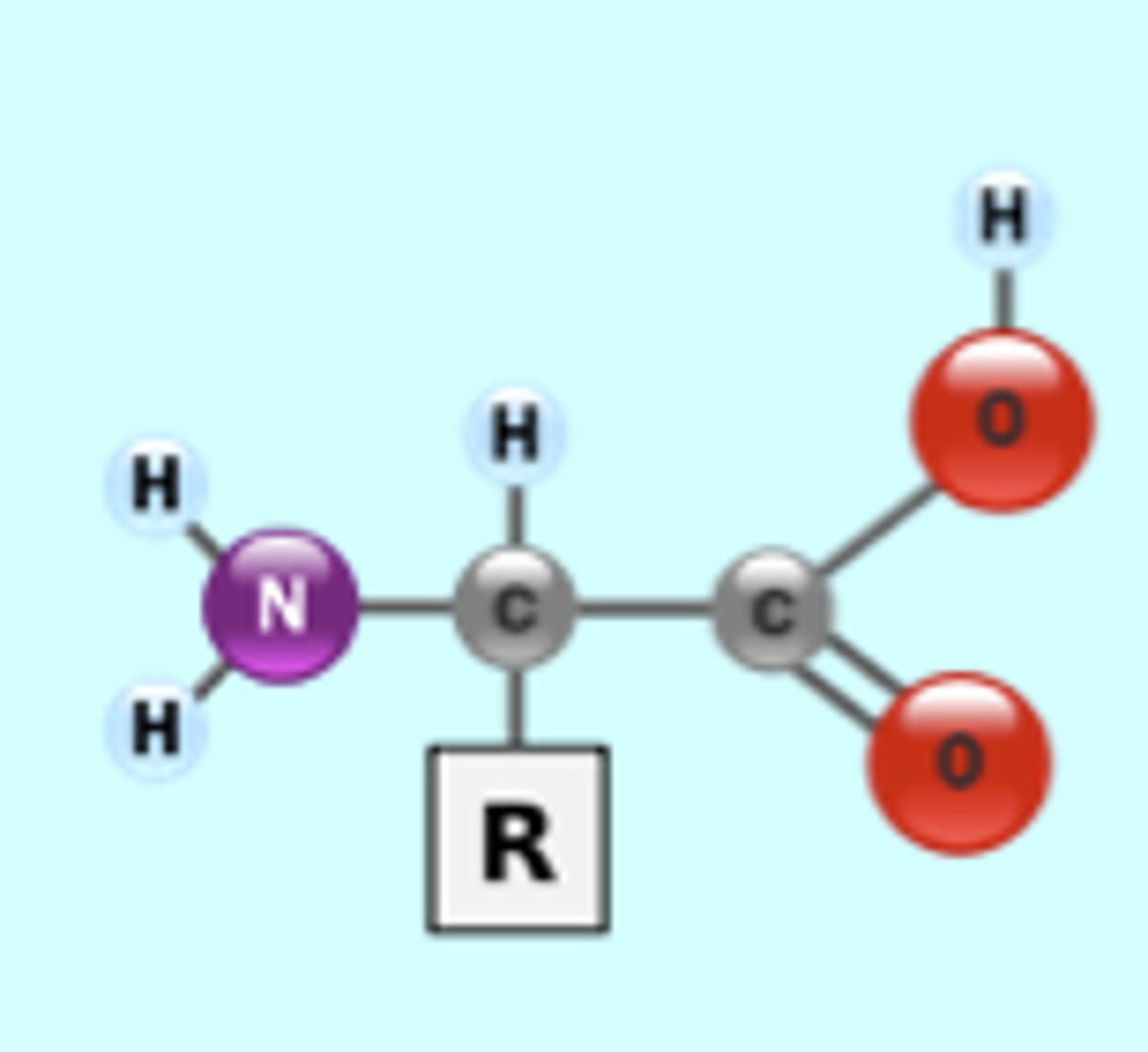
What is the enzyme that allows for covalent bonds?
ribosomes
Are covalent bonds spontaneous or non-spontaneous? Non-covalent bonds?
non-spontaneous. Spontaneous
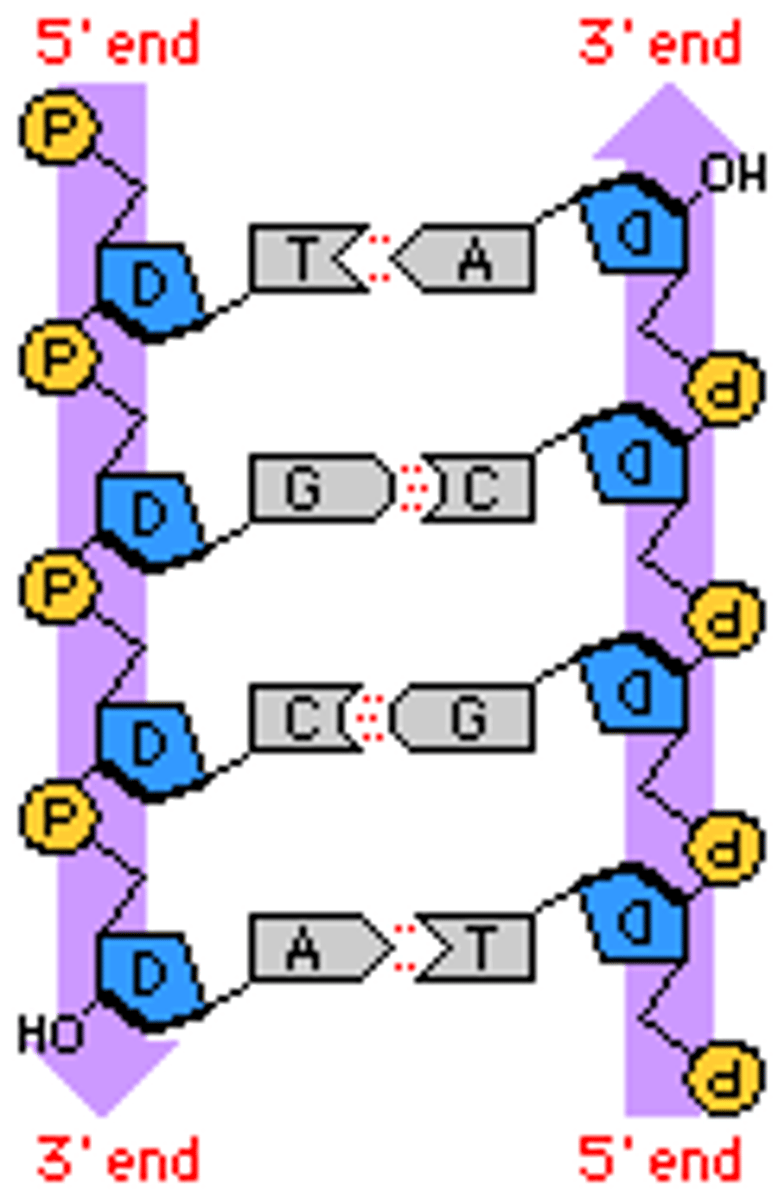
What is the subunit of nucleic acids?
4 nucleotides (A, T/U, C, G)
What are the two kinds of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
How do nucleic acids get their 3D shape?
Two covalently made strands fold with another, and specific lettered nucleotides match with another, creating the double helix shape
What is needed to make a covalent bond?
enzyme
What is another word for macromolecule?
polymer
What are macromolecules made of?
monomers linearly arranged into macromolecules
What do proteins give the cell?
Shape, function, form, and behavior
What forms the cytoskeleton in cells?
proteins (tubulin, actin)
Different kinds of protein functions (only 4 here)
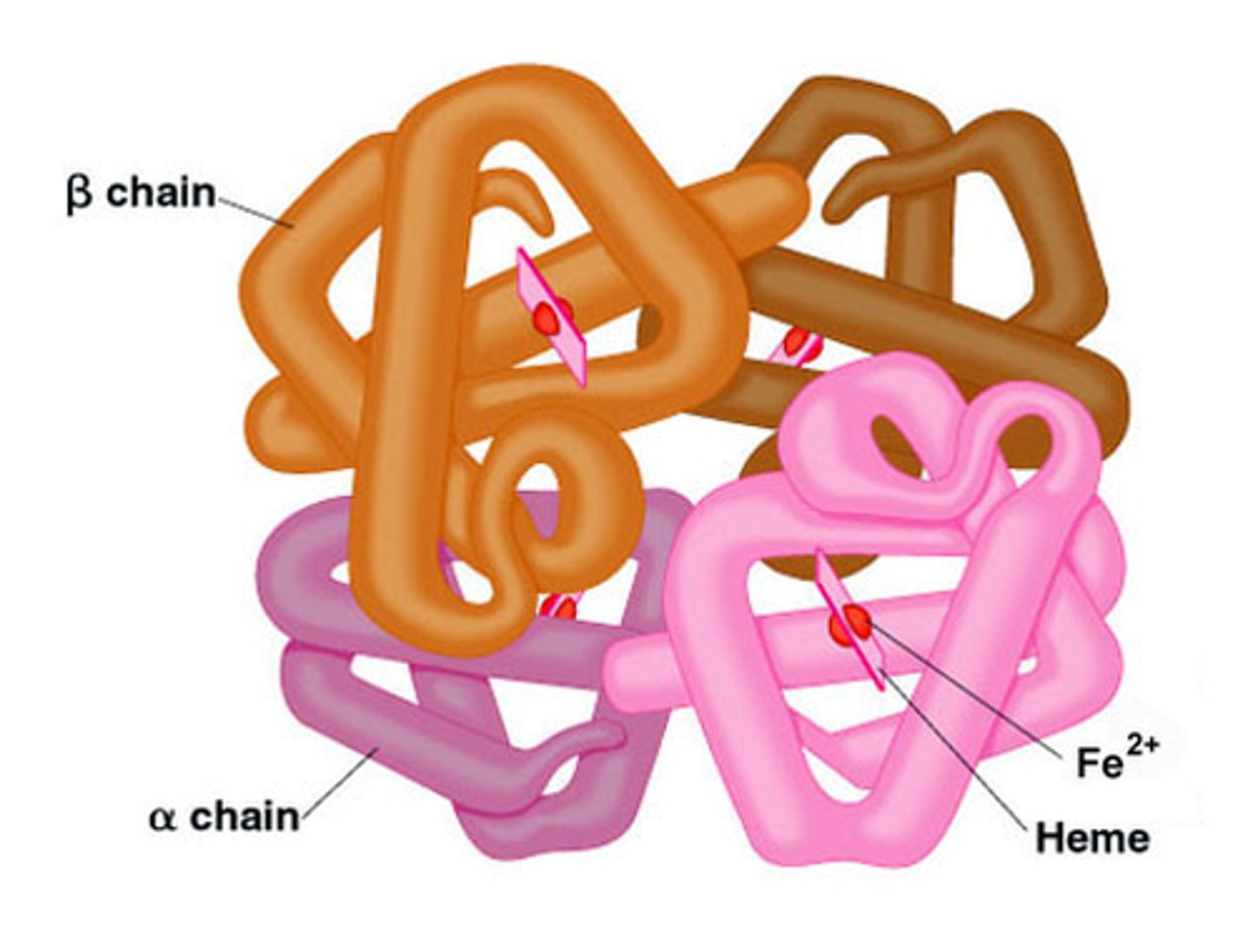
transport protein (hemaglobin), receptor proteins (pick up stimuli and change cell behavior. Ex: rhodopsin), signaling proteins (insulin), enzymes (catalyst)
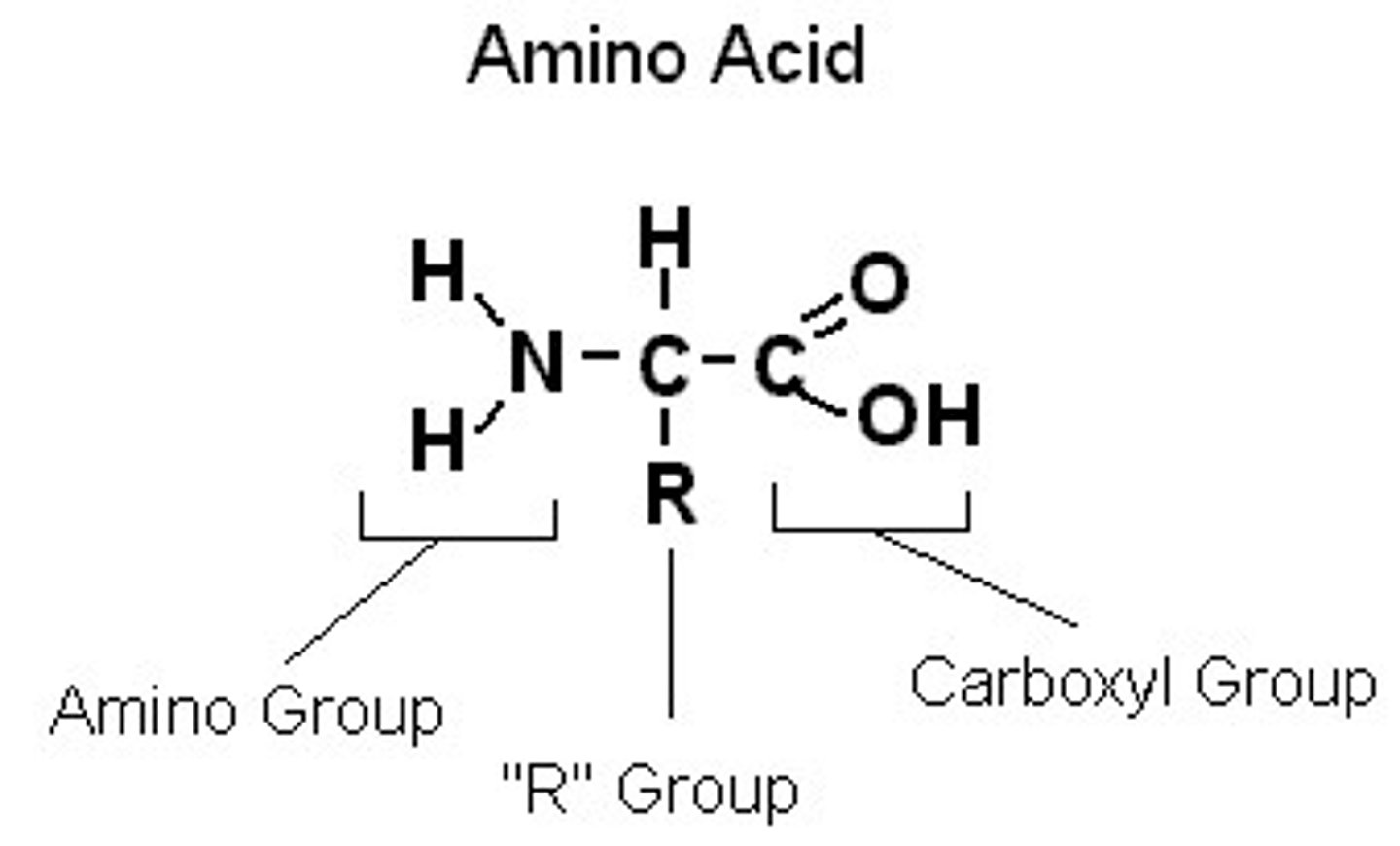
Draw an amino acid and label the ends
Draw protein isomers
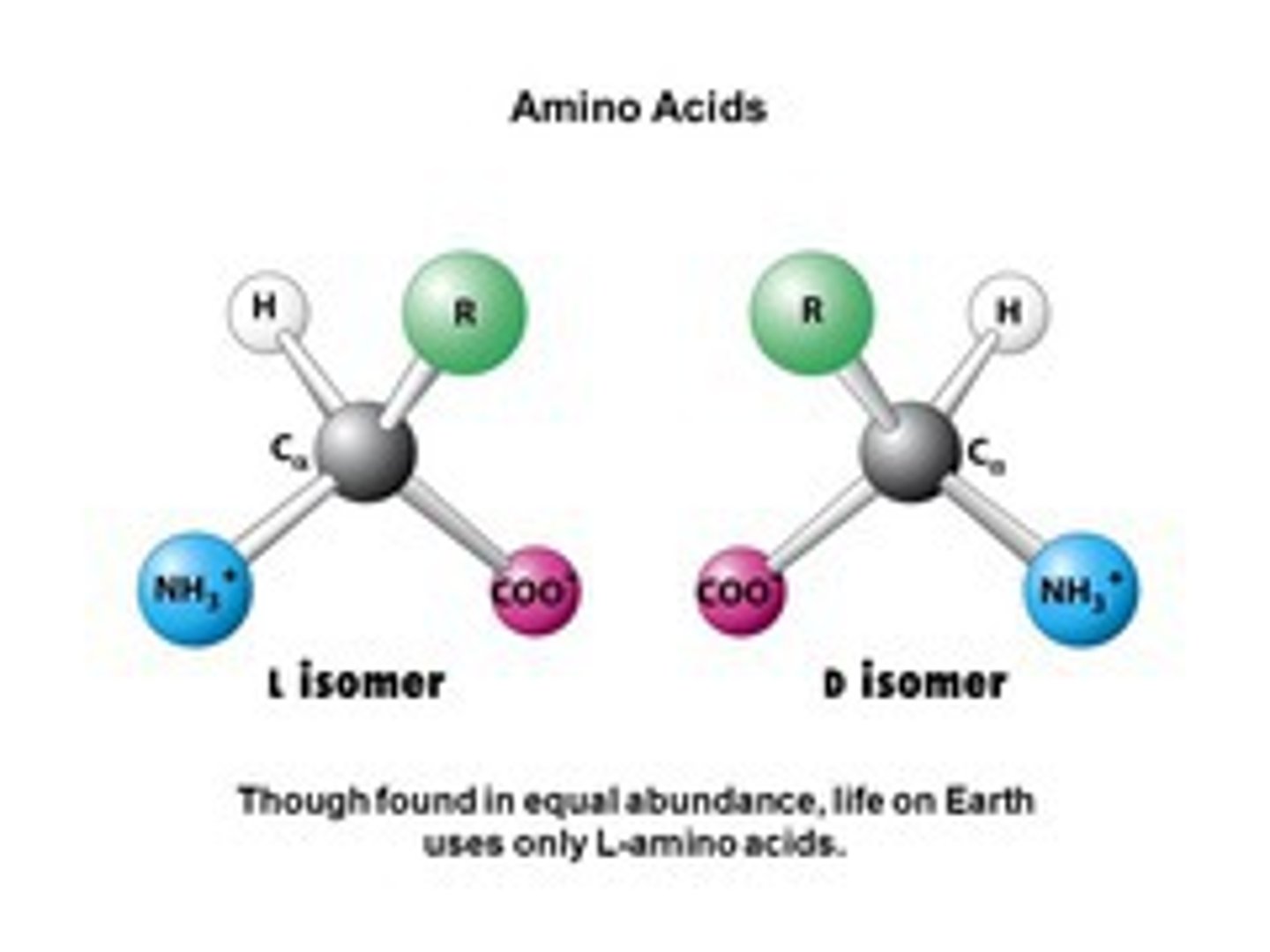
Are proteins L-isomers or D-isomers?
L-isomers
What are covalent bonds in proteins called?
peptide bonds
What is the condensation reaction in a peptide bond?
One OH from carboxyl end of an amino acid and an H from the amino end of an amino acid join to form H2O
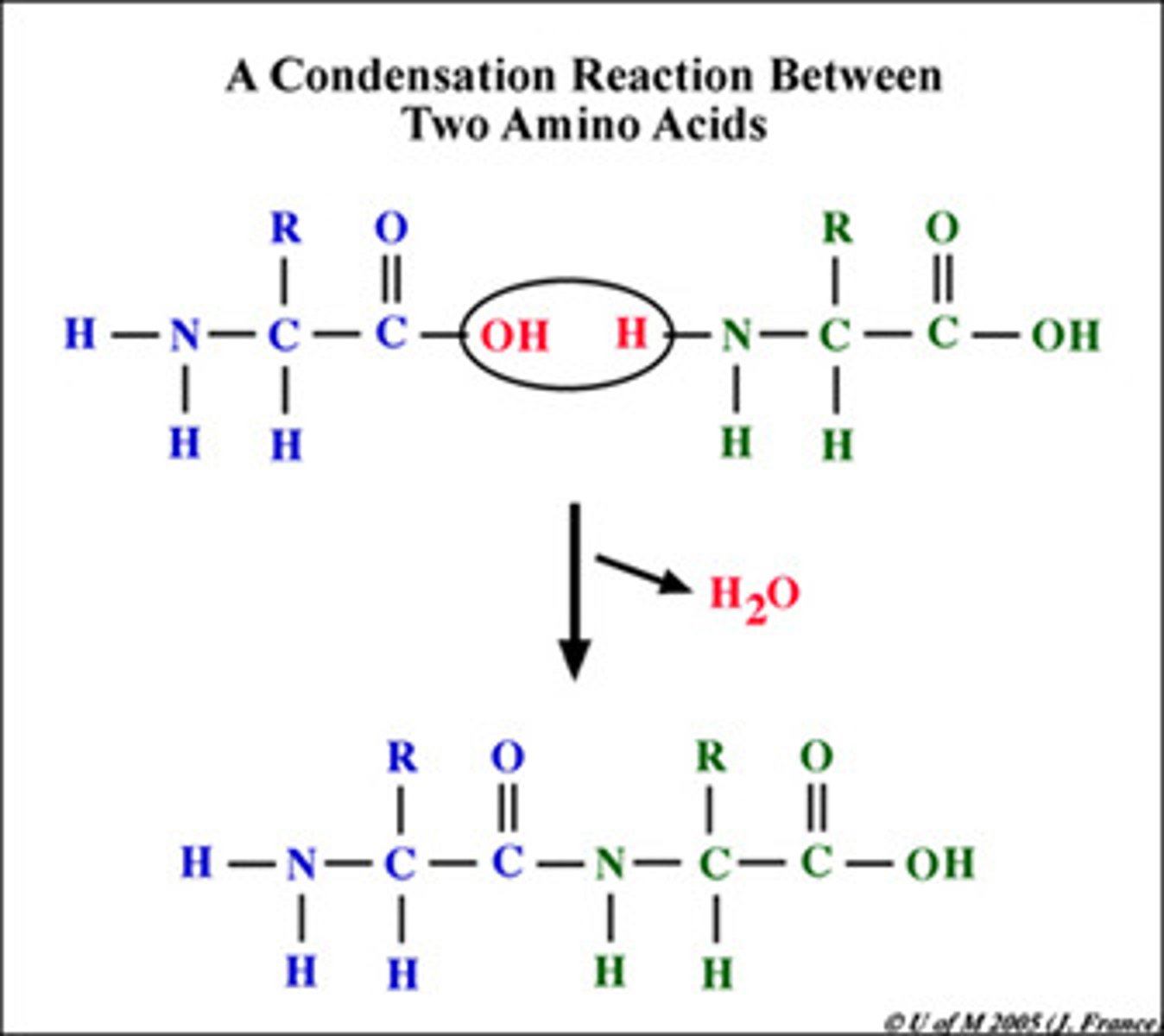
How many side chains are there? Are they molecules? Can they be charged?
20. Yes. Yes
What are the amino acid categories?
acidic, basic, polar uncharged, non-polar
Characteristics of acidic amino acids?
negative charge, hydrophilic bonds, electrostatic bonds (acid/base)
Characteristics of basic amino acids?
positive charge, hydrophilic bonds, electrostatic bonds (acid/base)
Characteristics of polar uncharged amino acids?
presence of O, H-bonds, hydrophilic bonds
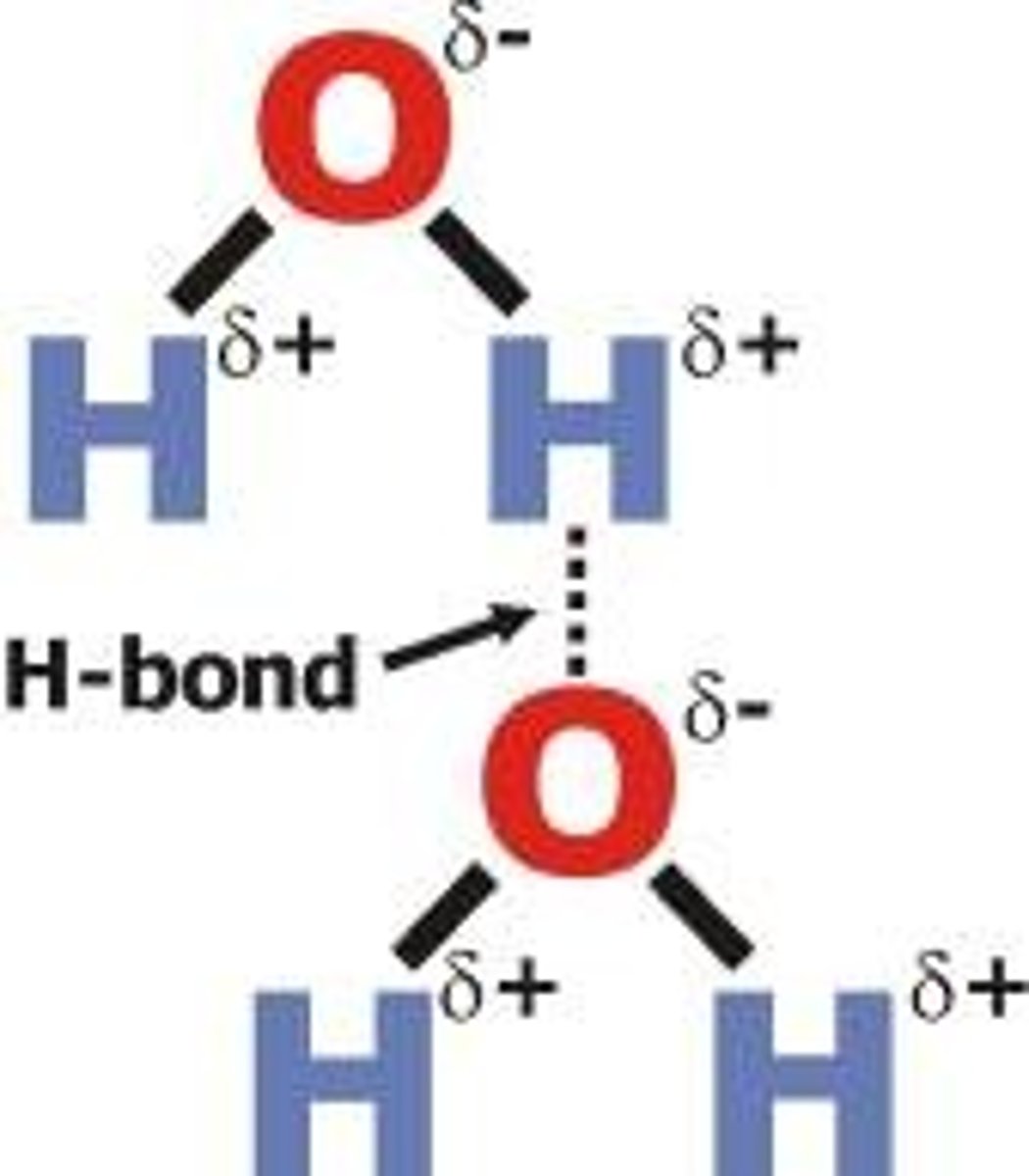
Characteristics of non-polar amino acids?
carbons and hydrogens, Vanderwaal bonds, hydrophobic bonds
What do acidic and basic molecules do with H+?
acidic take H+, basic give away H+
What are van der Waal attractions?
weak non-covalent bonds between atoms close to one another
What might an amino acid do if it were in an aqueous environment?
Fold to expose the hydrophilic ends and create a core of hydrophobic ends
Primary structure (1°)?
amino acid sequence of protein
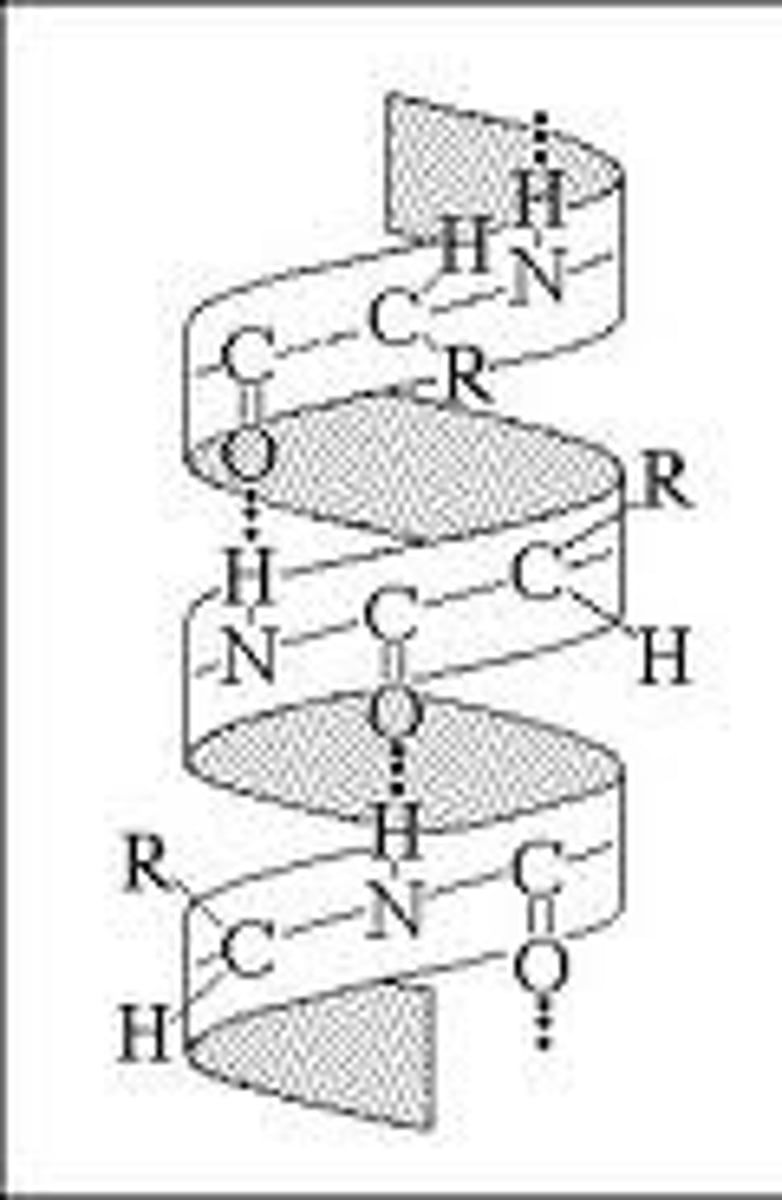
Secondary structure (2°)?
alpha helix or beta sheet or unstructured region. Don't rely on R group to form, and form via H-bonds in backbone atoms to hold.
Characteristics of alpha helix (within 2°)
Hydrogen bonds between amino and carboxyl groups of amino acids are four apart in sequence, R groups point out from helix, most are right-handed
Characteristics of beta sheet (within 2°)
multiple beta strands, hydrogen bonds between amino and carboxyl groups of adjacent beta strands, R groups point every other amino acid towards or away from adjacent strand. Can be parallel, anti-parallel
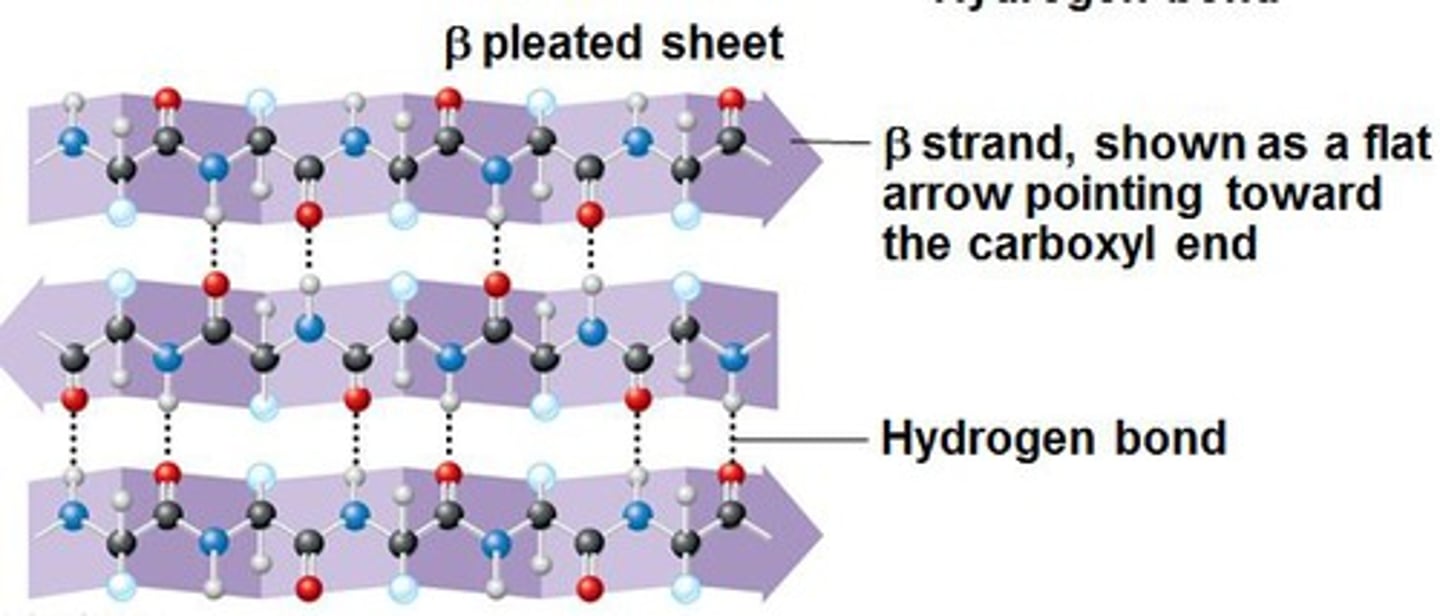
Tertiary structure (3°)?
The three 2° elements (alpha helices, beta sheets, unstructured regions) combine to make a 3D shape
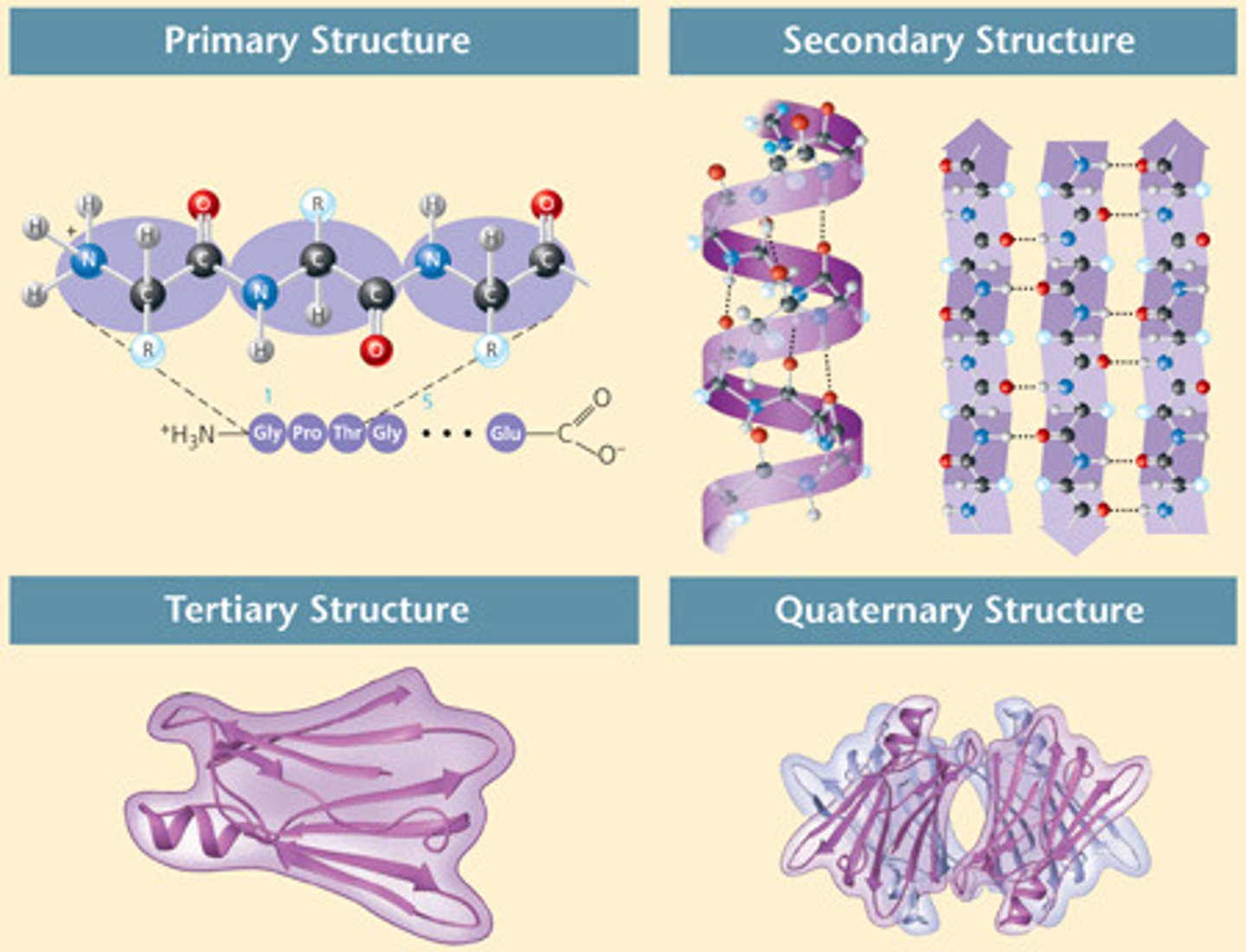
Quaternary structure (4°)?
Organization of several peptides into one protein complex
What is the purpose of chaperone proteins?
sometimes (but not always) spontaneously folding will not be advantageous so chaperones interact with parts of protein to encourage specific folding
What is the one kind of covalent bond that can form between R groups?
disulfide bonds
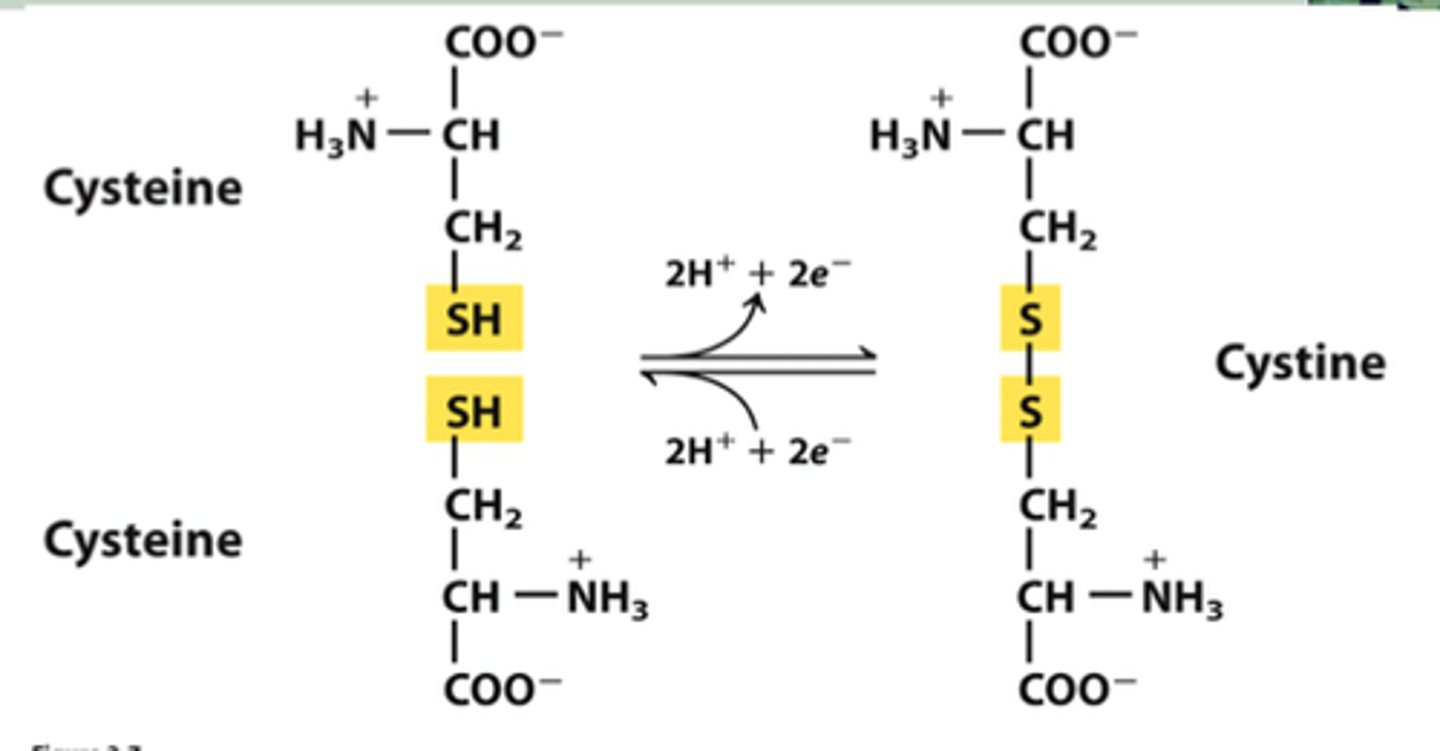
Characteristics of disulfide bonds
formed between sulfur atoms of cysteine side group, redox reaction (LEO says GER), requires oxidizing conditions (in ER and outside cell, but not in cytosol)
LEO says GER
Lose electrons=oxidation, gain electrons=reduction
What is an oxidizing environment?
One that can accept electrons
Protein domain
Segment of a polypeptide chain that can fold into a compact stable structure and that usually carries out a specific function
Coiled coil (Keratin)
two alpha helices contact each other along their length
How does elastin stretch?
disulfide bonds holding individual elastin proteins together
What is a ligand?
molecules (other proteins, small molecules, ions) that bind to a specific site on a protein
Why are ligands very specific?
When the shapes of ligand and protein matches, it allows for more binding sites
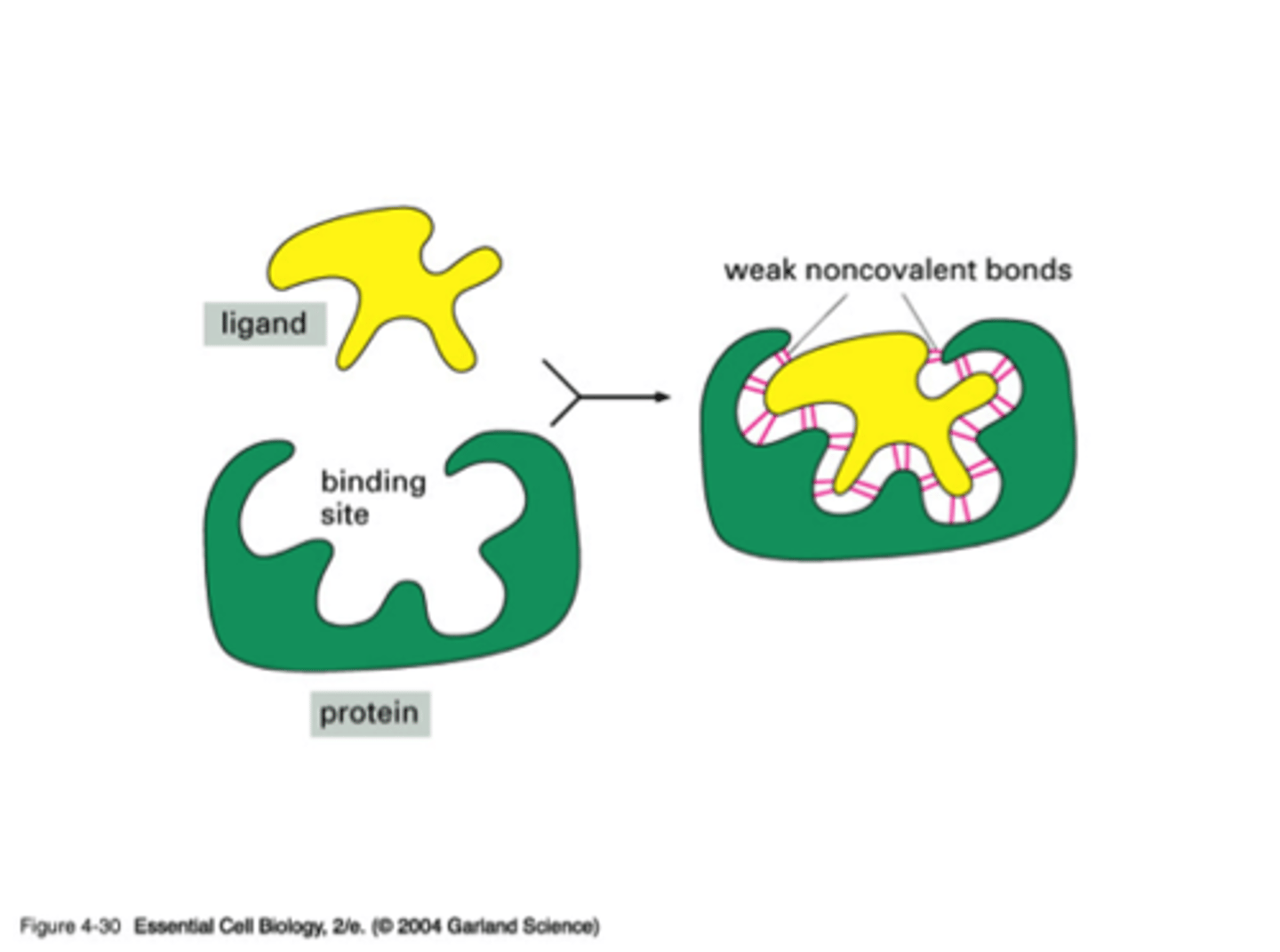
What do ligands connect with? Describe the structure of the R groups when unfolded and folded
R groups of proteins. When the amino acid is unfolded, the R groups don't have to be next to each other, but once folded, R groups are next to one another
What are enzymes?
globular proteins with ligands that catalyze proteins
What is a substrate?
(ligand) molecule on which enzyme acts
What are enzymes capable of (energy and reaction)?
Lowering the activation energy and can catalyze many proteins in many reactions
How are enzymes classified?
Based on the type of reactions they catalyze
What is free energy (G)?
energy available in a system that measures energy of molecule which could in principle used to do useful work at a constant temperature
What are the two ways reactions cause disorder?
1. change in bond energy that releases heat, which disorders the environment around the cell; 2. the reaction can interrupt amount or order by breaking long chains of molecules, or disrupting interactions that prevent bond rotations
What are examples of spontaneous reactions (bonds)?
electromagnetic, Vanderwaal, h-bonds
Characteristics of spontaneous reactions
release energy as heat or create disorder, require energy to get going (activation energy), have a negative change in free energy (G)
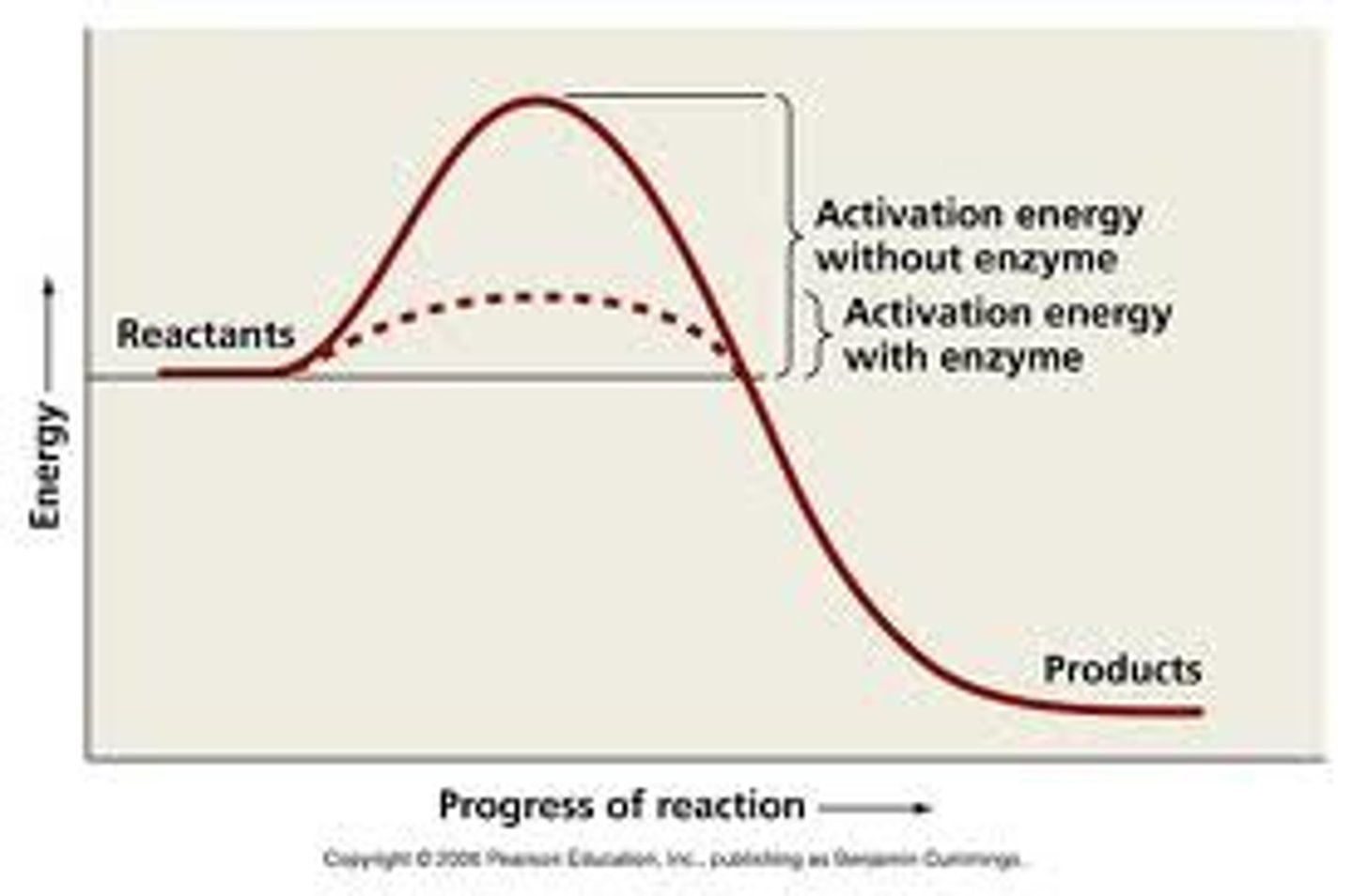
Is a positive change in G a spontaneous or non-spontaneous reaction? Is it favorable or unfavorable?
non-spontaneous. unfavorable
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
To create order, disorder must be created elsewhere
How do you know if disorder is being created?
G is negative
What are the four ways enzymes lower activation energy?
stabilize transition state, bring two reactants together, alter electron distribution in the substrate, form temporary covalent bonds that change the reaction path
What is an energetically unfavorable reaction?
One whose G is positive

How do enzymes allow cells to perform unfavorable reactions?
by coupling it with a favorable reaction

Will an energetically unfavorable reaction happen spontaneously?
No
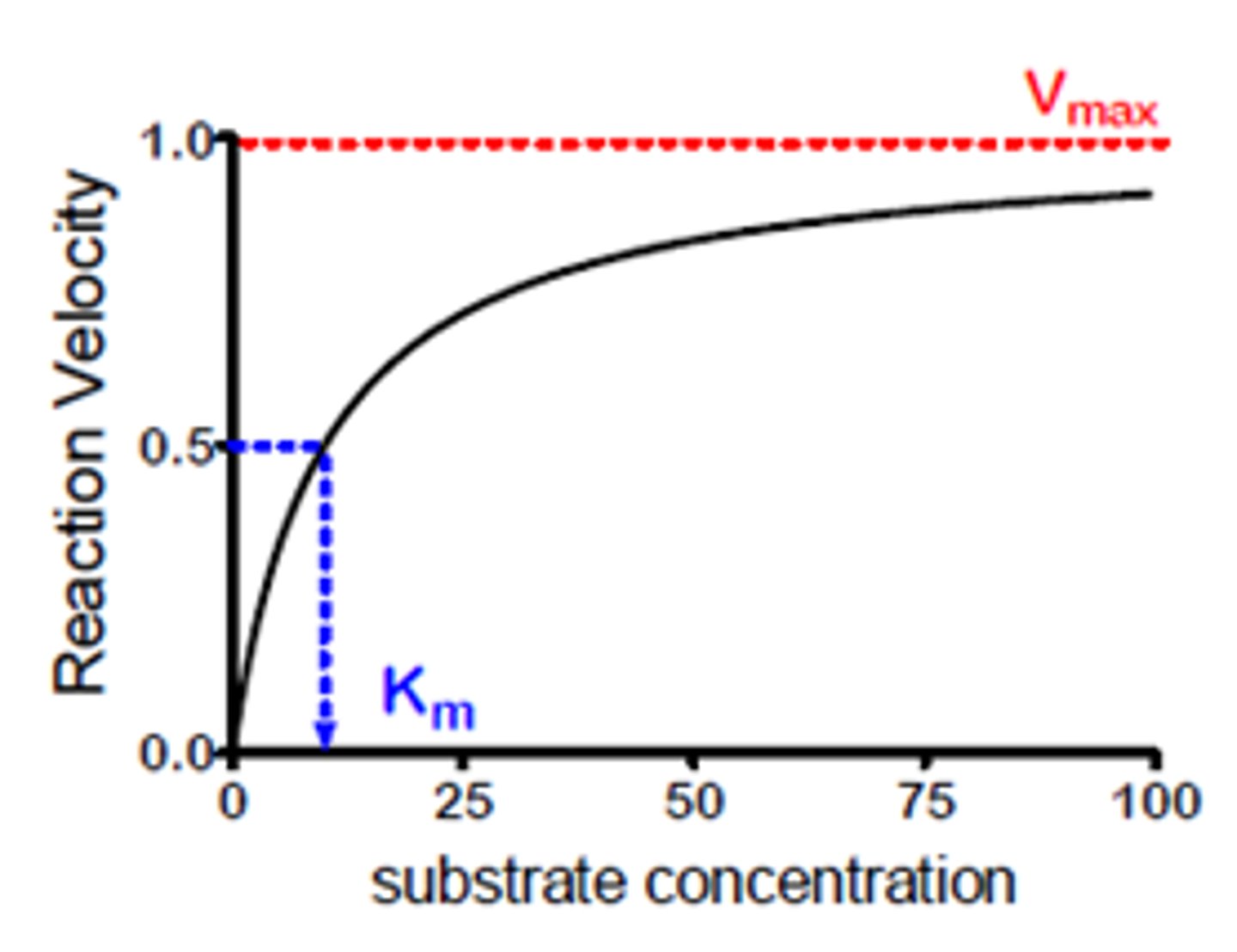
What is a Michaelis constant? Is a low or high Michaelis constant better?
Concentration of substrate at which enzymes works at half its maximum velocity
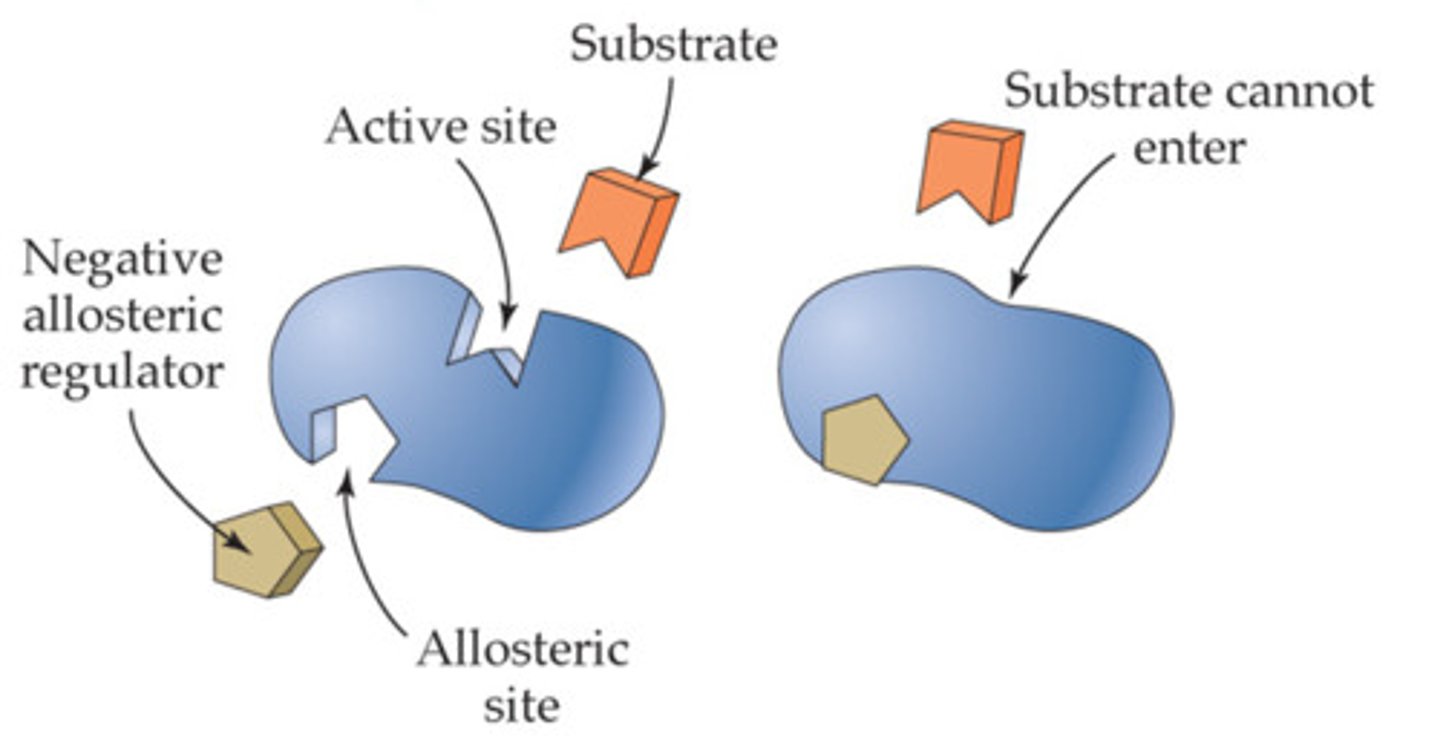
Draw negative allosteric regulation. Label activity of each and on or off
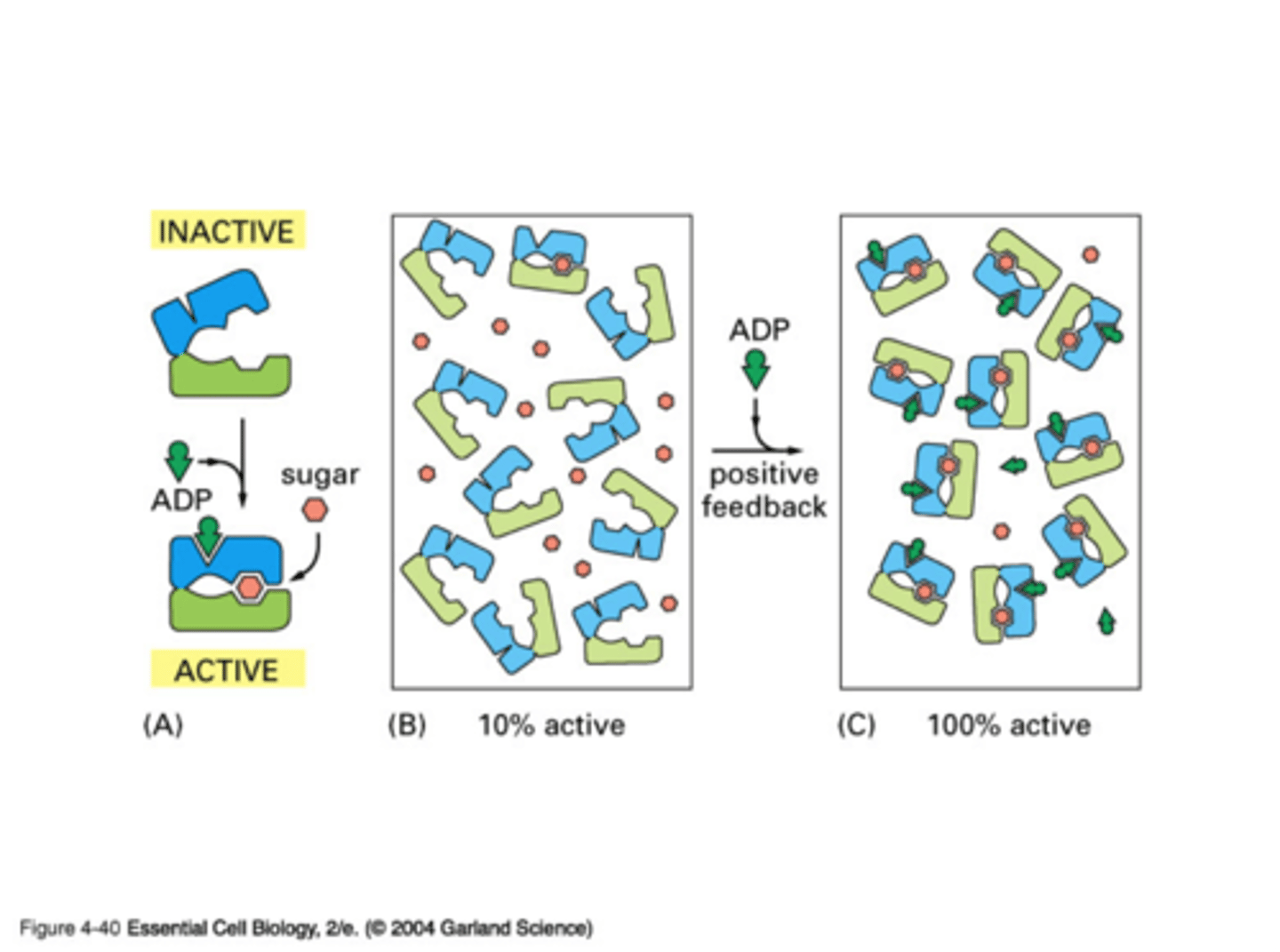
Draw positive allosteric regulation. Label activity of each and on or off
What is feedback inhibition?
Sort of negative allosteric regulation where end product of reaction reduces activity of enzyme early in pathway
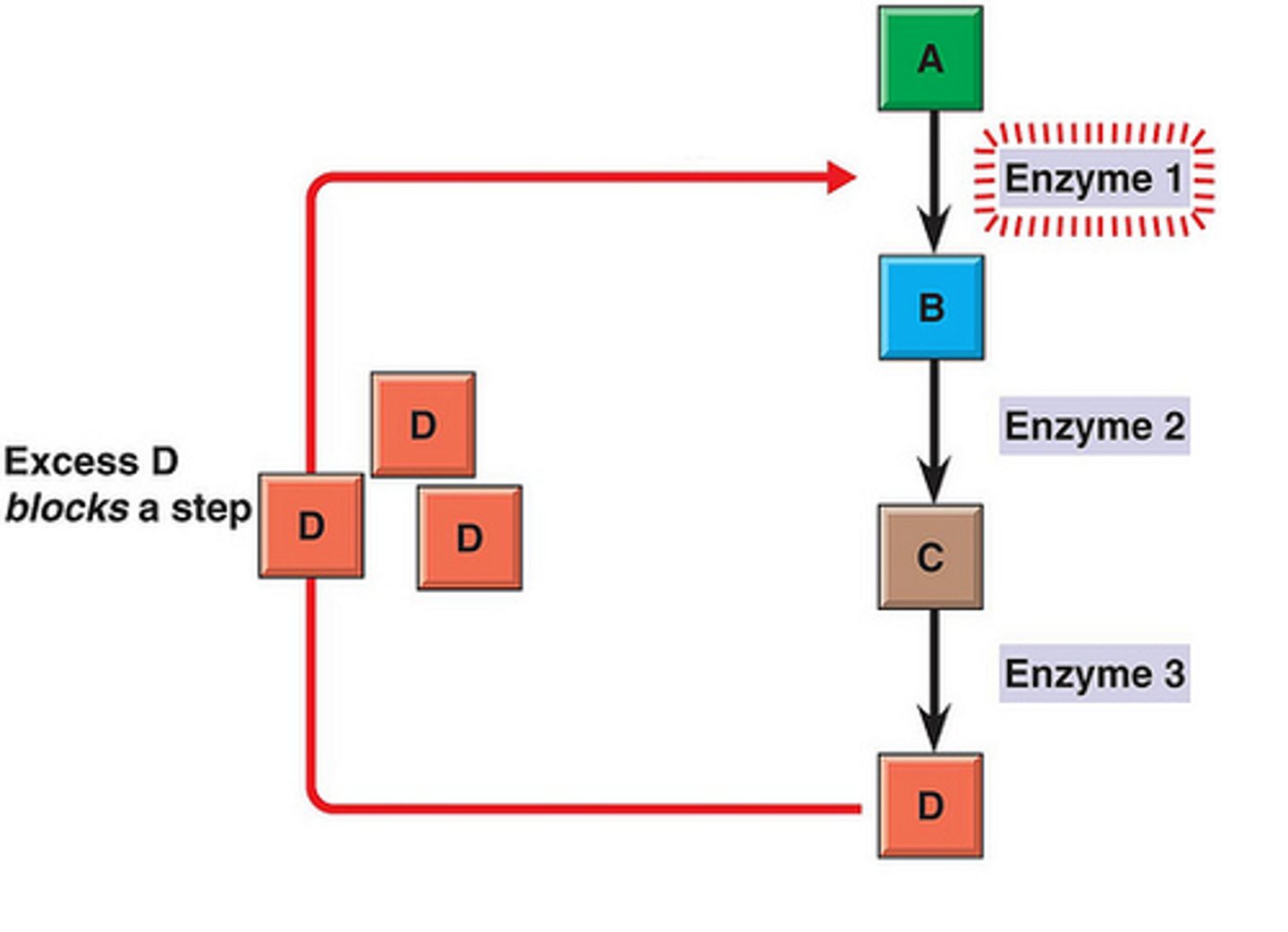
Does G change when reaction is catalyzed?
no