Basic Economics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is the original meaning of economics? Which language was it derived from?
“The science of family management (household management)”
Derived from Greek words
How is the term “economics” defined by the Thai professors?
“The study of the use of limited resources to produce goods and services to distribute and treat the needs of human beings in society.”
Explain how the term “economics” has evolved
1). “Household Management”
2). “Economics + Wellbeing”
3). “Merchantilism”
Who came up with the idea of “microeconomics”? Why is he famous?
“Alfred Marshall”
Wrote a book called “theory of the firm” which is the start of microeconomics theory.
Who came up with the idea of “macroeconomics”? Why is he famous?
“John Maynard Keynes”
Wrote a book called “The General theory of employment, interest, and money” which is the original of macroeconomics theory.
What is “microeconomics”?
Studies individual decision-making and small-scale economic units.
how people and businesses make choices when things are limited
Focuses on how households, consumers, and firms make choices.
Examples questions of “microeconomics” (customer, bakery shop, mango prices)
You have limited money. Should you buy bubble tea or save your money?
A bakery must decide: How many cakes to bake, What price to sell them, How to make profit
Why does the price of mangoes go up when it’s not mango season? → Because supply is low and demand is high.
What does microeconomics look at? (Give 3-5 examples)
People
Business
Prices
Market
How resources are used
What is “macroeconomics”?
studies the overall performance and behavior of an entire economy—not individuals, not companies, but the whole country.
Focuses on the whole economy
Example questions of “macroeconomics” (national inflation, government spending)
Why is Thailand’s inflation increasing?
Why is unemployment rising this year?
How does government spending affect the economy?
Why is everything getting more expensive?
Why is the currency getting stronger/weaker?
What does macroeconomics look at? (Give 3-5 examples)
National income (GDP)
Inflation (general rise in prices)
Unemployment rate
Economic growth
Government policies (tax, spending)
Exchange rates
International trade
What is the difference between “GDP” and “GNP”
GDP = activity within the country
GNP = activities that bring money to the country
Who do economics benefits?
Students : understanding economic conditions
Consumers : maximum satisfaction
Manufacturer : efficient use of limited resources
Owner of factors : using factors of production for the benefit of the worth and in maximum net gain
Nation population : understanding the state of economic conditions
Country leaders : improve country’s overall economy
What are the 2 economic units?
Household
Firm
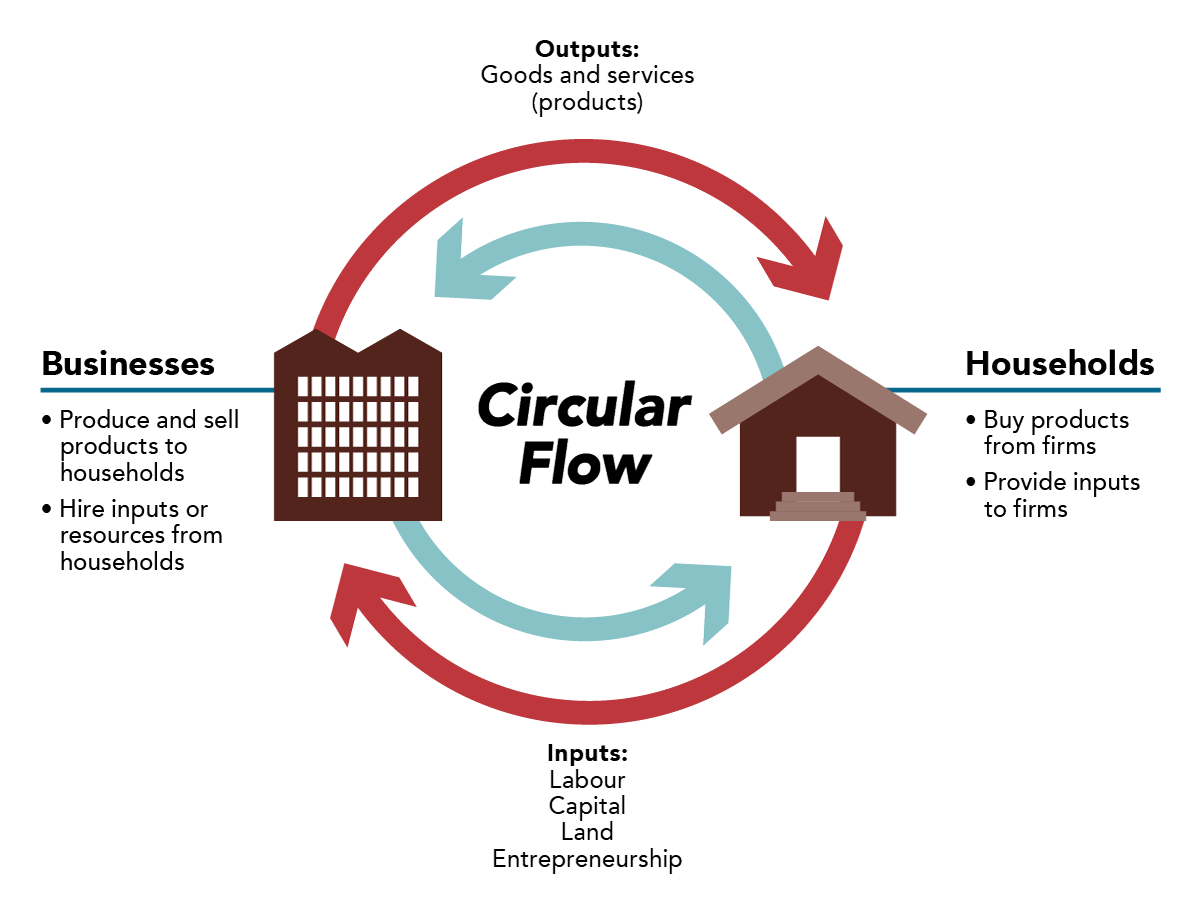
Circular flow of economics
shows how money, goods, and services move around in an economy between households, firms
Households give labor → get income
Firms give goods → get spending
Money flows one way, goods/services flow the opposite way
What are the role of household (consumers) in the flow?
Own factors of production (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship)
Provide labor to firms (working)
Get income (wages, rent, interest, profit)
Use that income to buy goods and services
What are the roles of firms in the flow?
Produce goods and services
Pay households income for their labor or resources
Sell goods and services to households
What are the 2 types of flows?
Physical flow (e.g. labor, goods & services)
Financial flow (e.g. income, money)
Define “economic system”
Resource management by focusing on productivity, expenditure, consumption, production, money, etc.
What are the 2 economic systems?
Market system
Command system
What are the 2 types of market system?
Factor market ; household (labor, capital, land), business
Product market ; goods market (household expenses = business’s income)
What are things that a business has to consider when it comes to production?
What?
How much?
For whom?
How?
How to increase GDP?
When to produce/harvest?
What are the 4 activities involved in economic system?
Production (considering demand)
Consumption
Exchange (how much to produce)
Distribution
What are the 4 classifications of economic system?
Traditional economy
Planned economy (socialism, communism/command system)
Capitalism/ Laizzer-faire capitalism
Mixed economy