Respiratory Examination
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
alveoli
tiny thin walled air sac at the end of bronchiole branches where gas exchange occurs
millions of alveoli in each lung
lungs
two lungs each side of the midline in the thoracic cavity
the area between is the mediastinum occupied by the heart, great vessels, trachea and the and left bronchi
pleura
closed sac of serous membrane that covers each lung and separates them from the other organs
consists of two layers
visceral pleura - adhered to lung
parietal pleura - adhered to chest wall and diaphragm
two layers separated by thin film of serous fluid secreted by the membrane to prevent friction when breathing
which sides have which lobes
right side
upper
lower
middle
left side
upper
lower
lung volume for males
6L
lung volume for females
4.2 L
standard respiration rate for adults
12-20/min
features of normal breathing
effortless
silent
unconscious
what does SOCRATES stand for (pain)
Site
Onset
Character
Radiation
Associated factors
Time
Exacerbating
Reliving factors
Severity
common causes of a cough
asthma - wheeze, often nocturnal, worse in mornings
COPD - (smoker) usually produces sputum in mornings
chronic heart failure
interstitial lung disease
drugs
important Q’s to ask about a cough
time of cough - when is it worse?
duration - acute less than 3 weeks, sub-acute 3-8 weeks, chronic more than 8 weeks
relief with inhaler
worse on lying down
wakening
sputum
haemoptysis
what to ask about sputum
colour
amount
taste or smell
solid material
what to ask about haemoptysis
amount, fresh in sputum
coughed up
vomited/ regurgitated
from nasopharynx
serous sputum
appearance
clear, watery, frothy pink
cause
acute, pulmonary oedema
alveolar cell cancer
mucoid sputum
clear and grey - chronic bronchitis/COPD
white and viscid - asthma
purulent sputum
yellow - acute bronchopulmonary infection / asthma
green - longer-standing infection. e.g. pneumonia, bronciectasis, cystic fibrosis, lung abscess
rusty sputum
rusty red - pneumococcal pneumonia
dyspnoea
the sensation that unable to breath properly
orthopnoea
shortness of breath on lying, usually associated with left ventricular failure
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
wakes patient from sleep - usually LVF (in asthma - wheeziness often causes waking in early mornings)
MRC breathlessness scale
degree of breathlessness related to activitites
MRC Grade 1
not troubled by breathlessness except on strenuous exercise
MRC Grade 2
short of breath when hurrying on the level or walking up a slight hill
MRC Grade 3
walks slower than most people on the level, stops after a mile or so, or stops after 15 mins of walking at their own pace
MRC Grade 4
stops for breath after walking about 100yds or after a few minutes on level ground
MRC Grade 5
too breathless to leave the house or breathless when undressing
dysphonia
hoarseness caused by damage to larynx or the nerve to larynx
wheeze
high pitch whistling noise - air passing through narrowed airways
stridor
high pitched, harsh noise caused by obstruction of large airway - always needs investigation (unless viral croup)
IPPE
introduction
permisson
position
exposure
IPPA
inspection
palpation
percussion
auscultation
position for physical assessement
on bed 45 degrees
be on patients right side
what does exposure refer to
remove shirt
leave bra on
need to get at ankles
inspection part 1 of IPPA
discomfort pain
breathlessness
colour - cyanosis - blush discolouration = hypoxia
audible breathing
body mass
confusion
inspection part 2 of IPPA
Hands:
look for finger clubbing - potential COPD, lung cancer, cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, pulmonary fibrosis, mesothelioma, etc
peripheral cyanosis
temp
tobacco staining
radial pulse - check respiratory rate at the same time
asterixis - CO2 retention
tremor
eyes:
conjuctival pallor
inspection part 3 of IPPA
mouth:
central cyanosis under tongue
Neck:
palpate for enlarged lymph nodes (from behind)
submental
Submandibular
Anterior and posterior cervical
Supraclavicular (including scalene nodes)
Pre- and post- auricular
Occipital
Inspect chest wall - anterior and posterior
abnormalities e.g. asymmetry - big breath in and out
breathing pattern and asymmetry of movement
scale nodes
surgical scars - lobectomy
Palpation of IPPA
tracheal deviation
chest expansion
check for symmetry when the patient is breathing
ask the patient to breath deeply, watch your thumbs move apart, this should be equal
feel the rib cage expand and contract
reduced expansion could mean:
unilateral = consolidation, collapse
bilateral = COPD, pulmonary fibrosis
percussion of IPPA
helps establish whether lungs are filled with air, fluid or solid material
start with clavicles
anterior wall - upper lobes
posterior wall - lower lobes
right lateral wall - middle lobe
left lateral wall - lingula
normal percussion sound is resonant, long and loud, low pitched and hollow
a solid area collapse will sound dull and thud-like
pneumothorax will sound hyper-resonant, loud and lower pitched
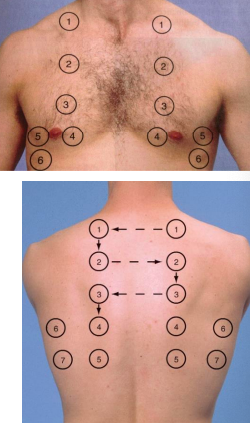
auscultation in IPPA
breathing deeply through open mouth
assess breath sound quailty
assess volume - reduced= collapsed/effusion
vocal resonance
ask patient to say 111 or 99 while listening with stethoscope
over consolidated lung (pneumonia) - clearly audible
over effusion or collapsed lung - muffled
red flags signs for cough - non acute
haemoptysis
breathlessness
fever
chest pain
weightloss
red flag signs for cough - serious acute illness - urgent admission
respiratory rate more than 30 breaths per min
tachycardia greater than 130 beats per min
systolic bp less than 90
diastolic bp less than 60
oxygen saturation less than 92%
peak expiratory flow rate less than 33% of predicted
altered level of consciousness
use of accessory muscles of respiration
suspected lung cancer 40+ - if unexplained
persistent or recurrent chest infection
finger clubbing
supraclavicular lymphadenopathy or persistent cervical lymphadenopathy
chest signs consistent with lung cancer
thrombocytosis
suspected lung cancer 40+ - if 2 or more
cough
fatigue
shortness of breath
chest pain
weight loss
appetite loss