Bill 110: Lecture 9: The Appendicular Skeleton
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
What bones make up the Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral Girdle; Upper Limb; Pelvic Girdle; Lower Limbs
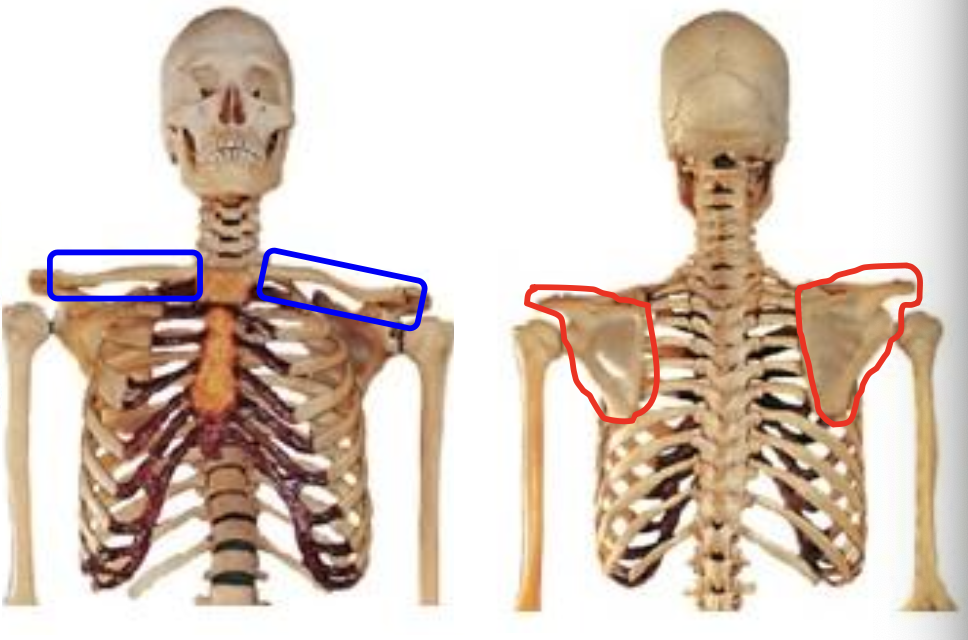
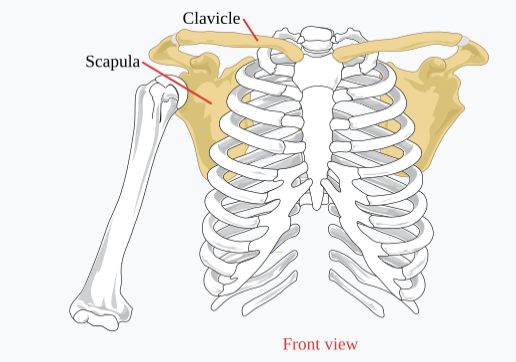
What bones make up the Pectoral Girdle
The clavicle and scapula
What is the function of the pelvic girdle
-positions the shoulder joint
-provides a base of arm movement (major muscles attach here)
-maximizes the range of motion
Clavicles are shaped how?
-s shaped
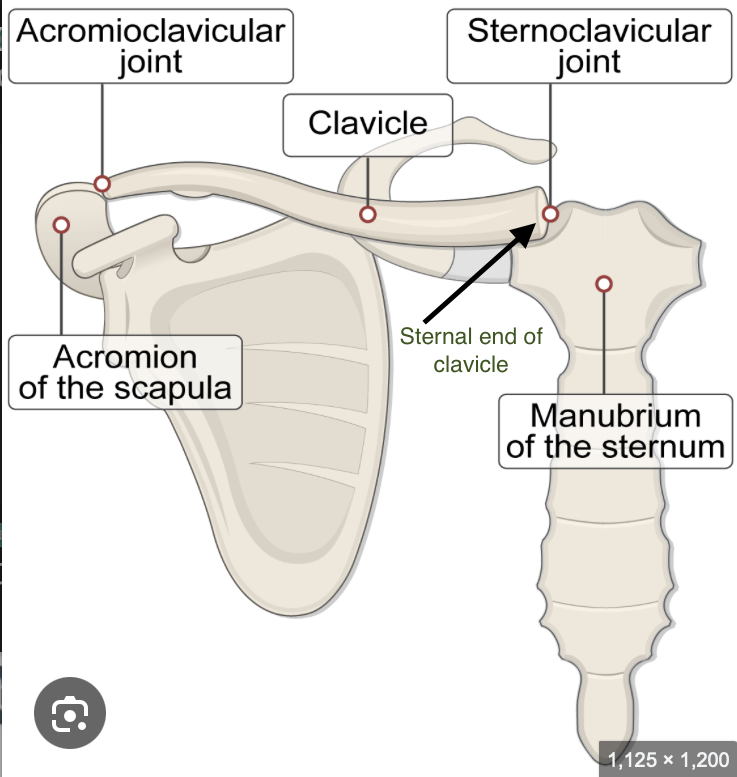
Clavicles are the only direct bony connection between the pectoral girdle and the axial skeleton
The sternal end of the clavicle articulates with the manubrium of the sternum forming the sternoclavicular joint
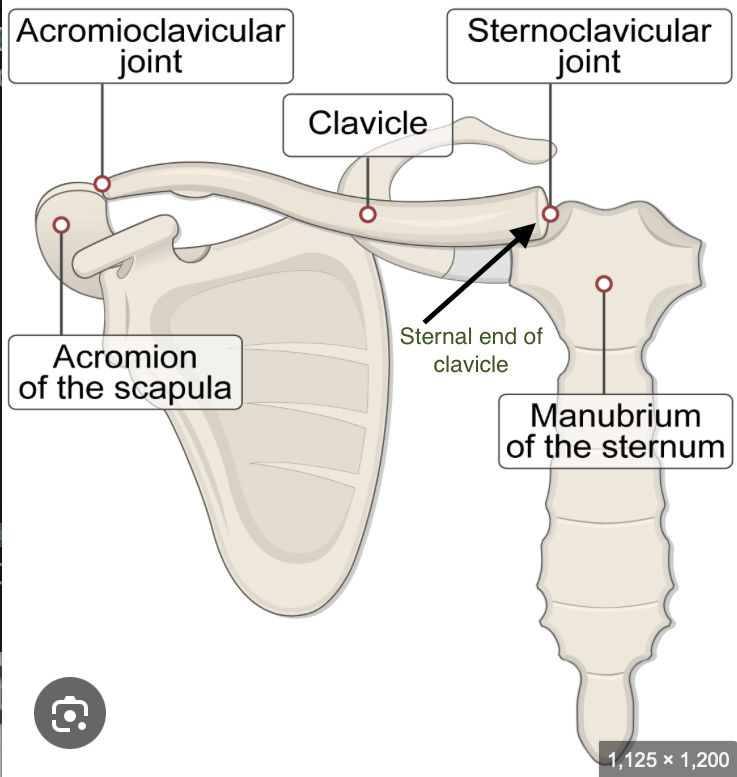

Clavicles have two ends
the Acromial End and the sternal end


The sternal end of the clavicle articulates with the
manubrium of the sternum (forming the sternoclavicular joint)
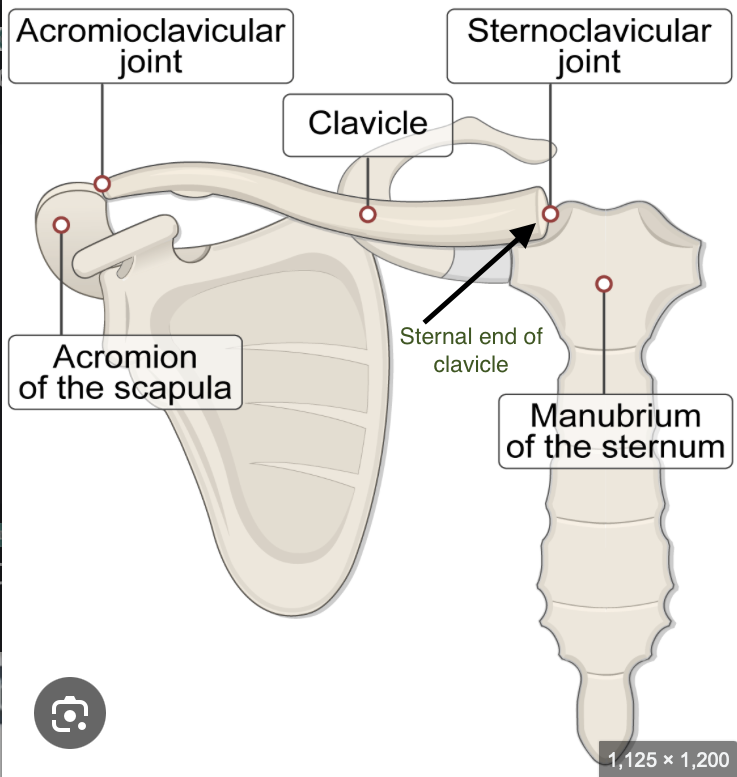
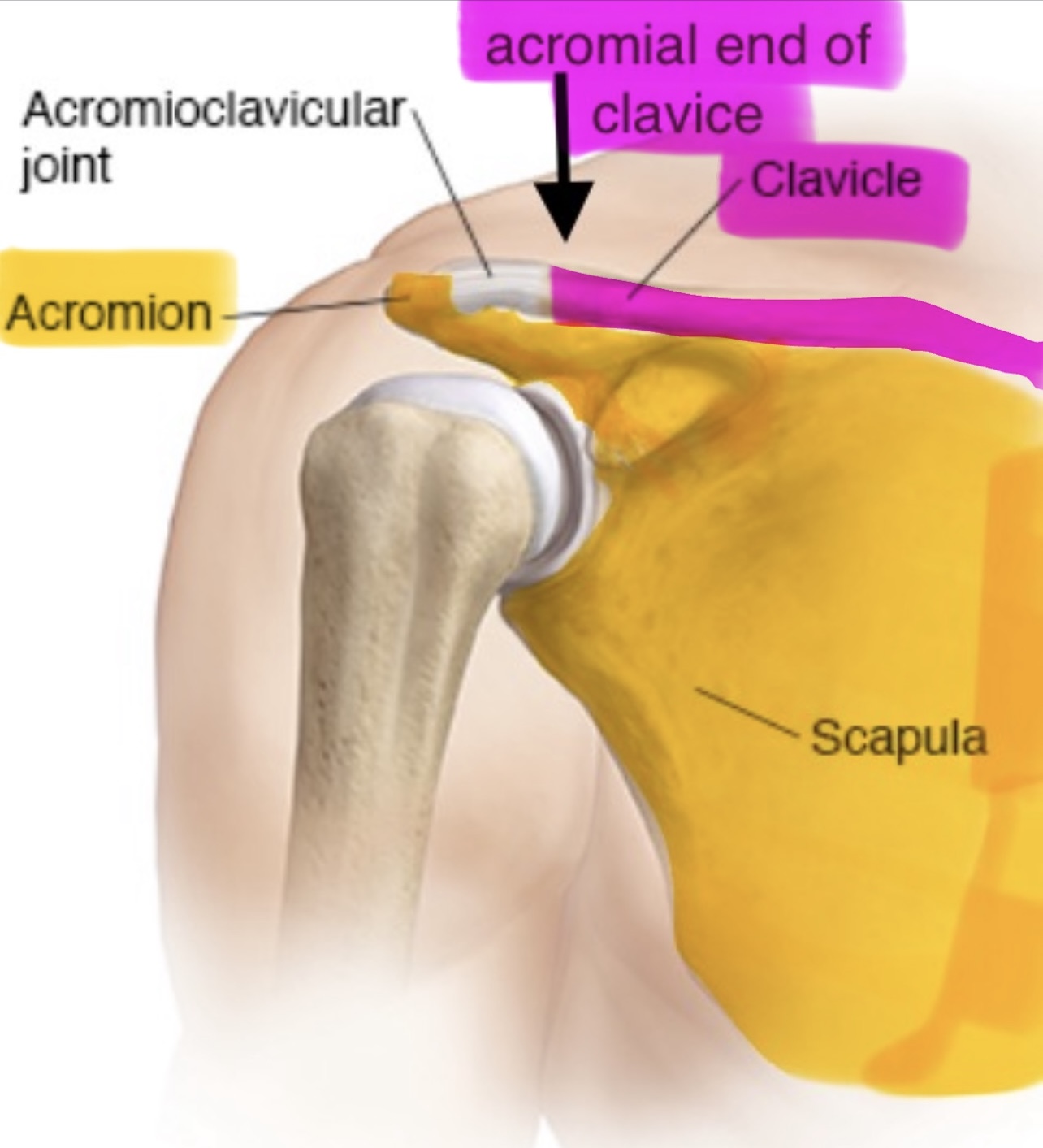
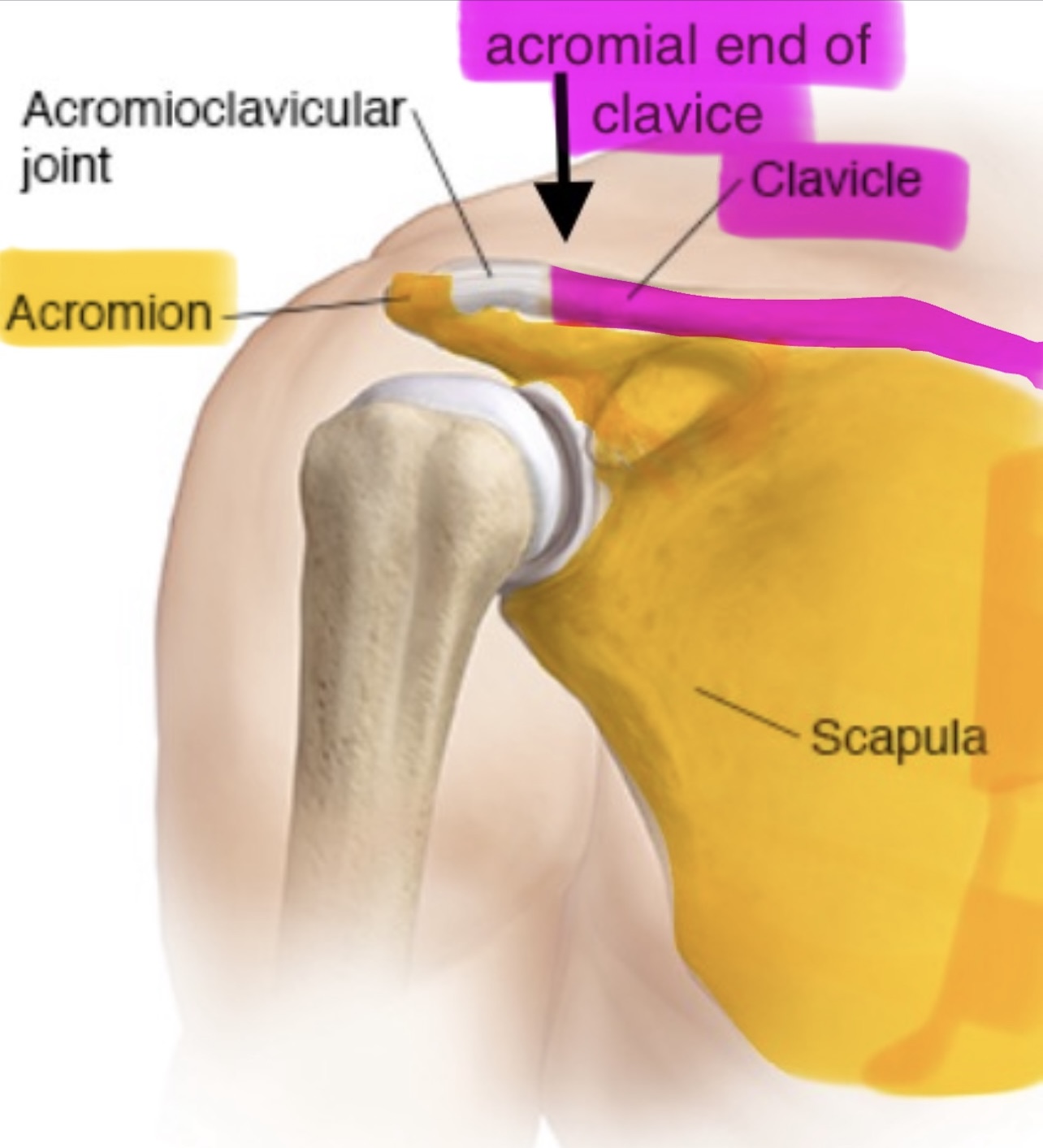
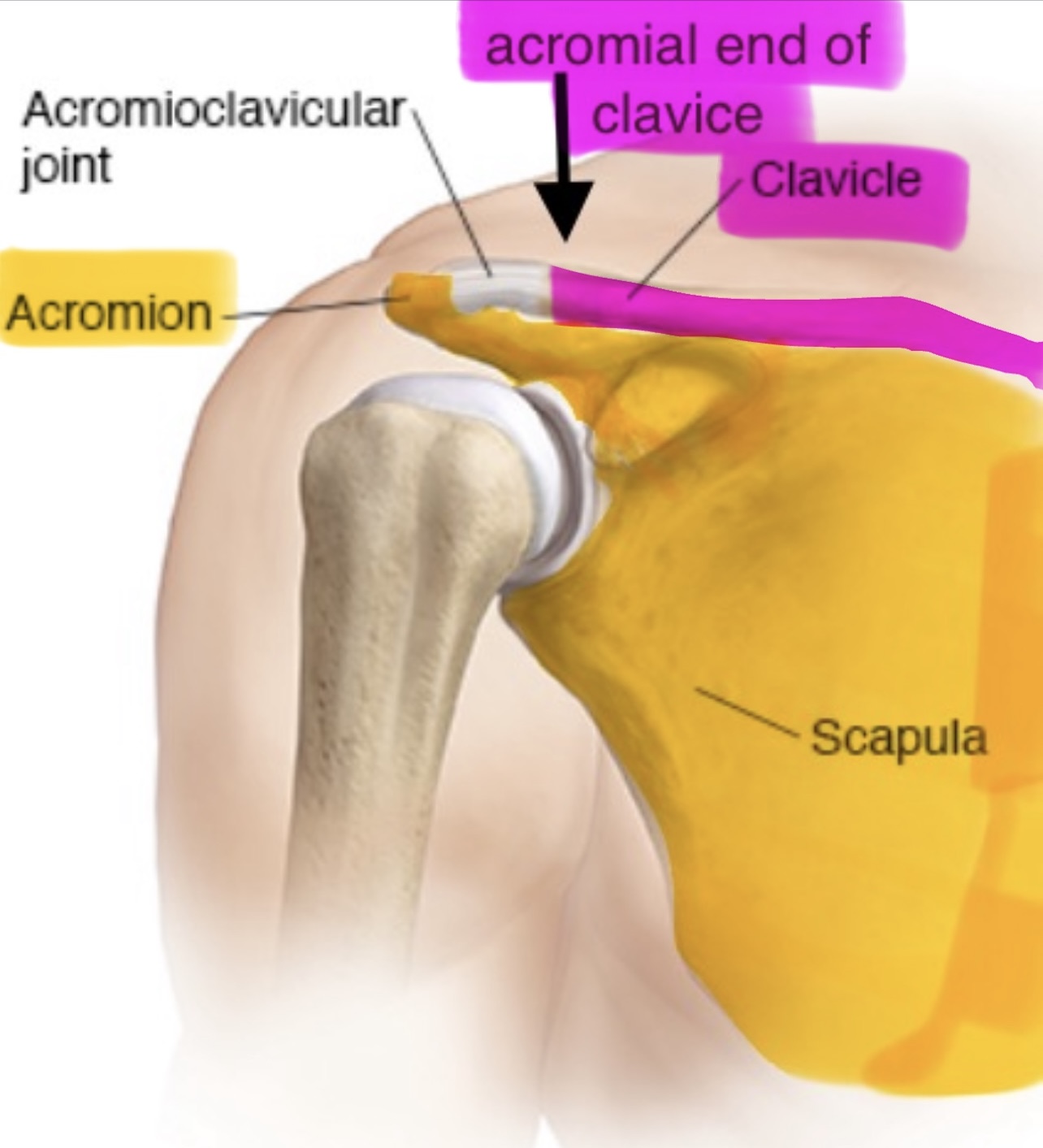
The acromial end of the clavicle articulates with the
acromion or acromial process of the scapula (forming the acromioclavicular joint)

The superior surface of the clavicle is smooth
The inferior surface of the clavicle contains the conoid tubercle (near acromial end) and costal tuberosity (near sternal end)

The conoid tubercle and costal tuberosity are attachment sites for
ligaments
the sternoclavicular joint is the only bone that connects the
arm to the body
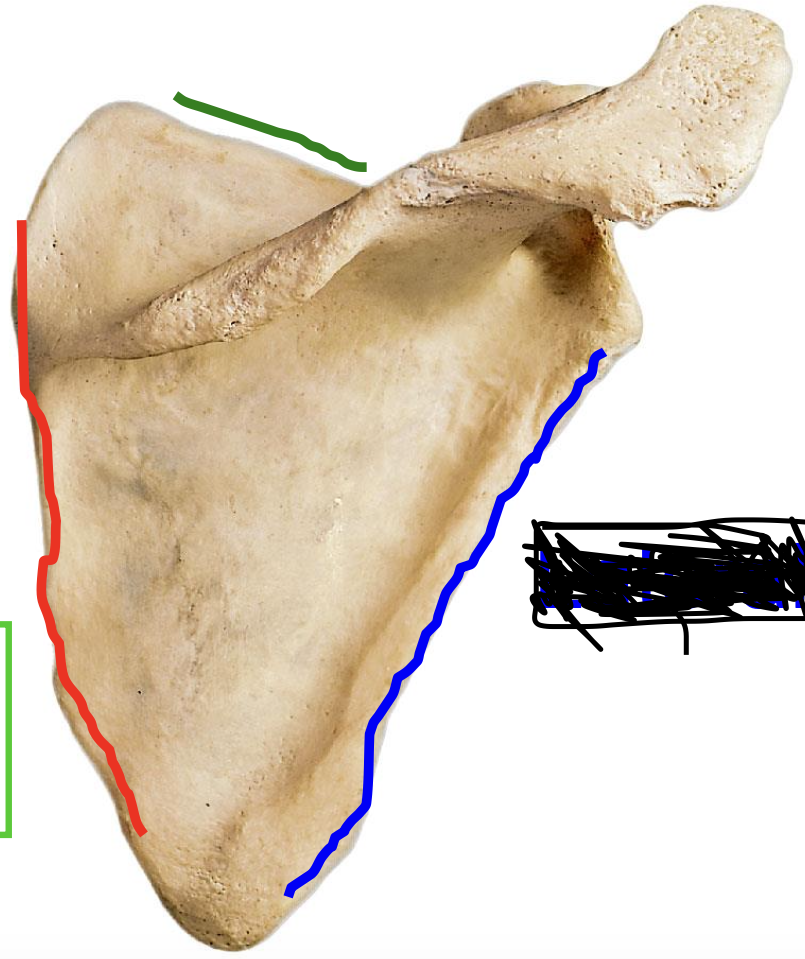
Scapula has three borders (posterior view)
Superior border, medial border, lateral border (posterior view)
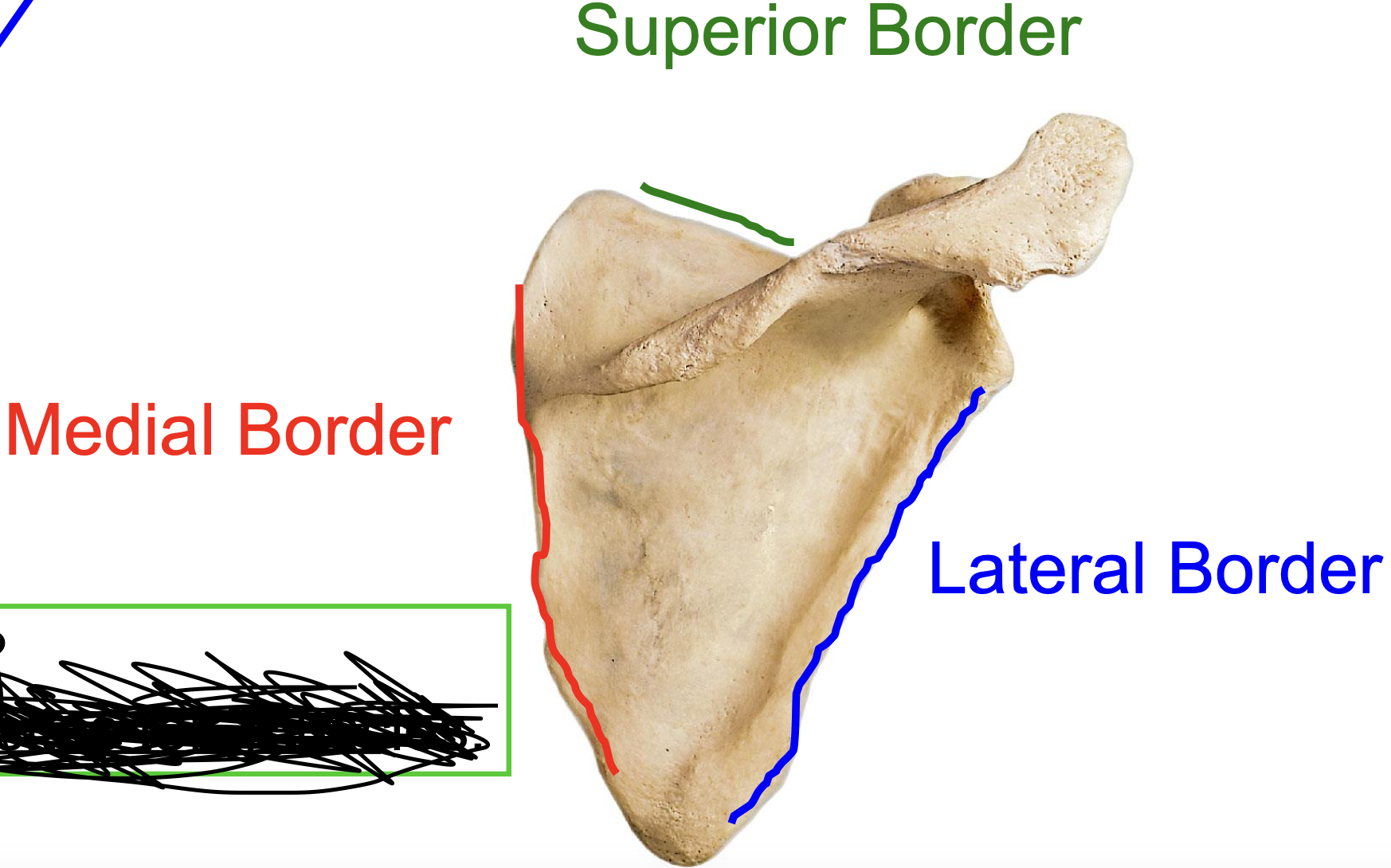
Why are the superial, medial, and lateral borders important?
they are attachment sites for muscles
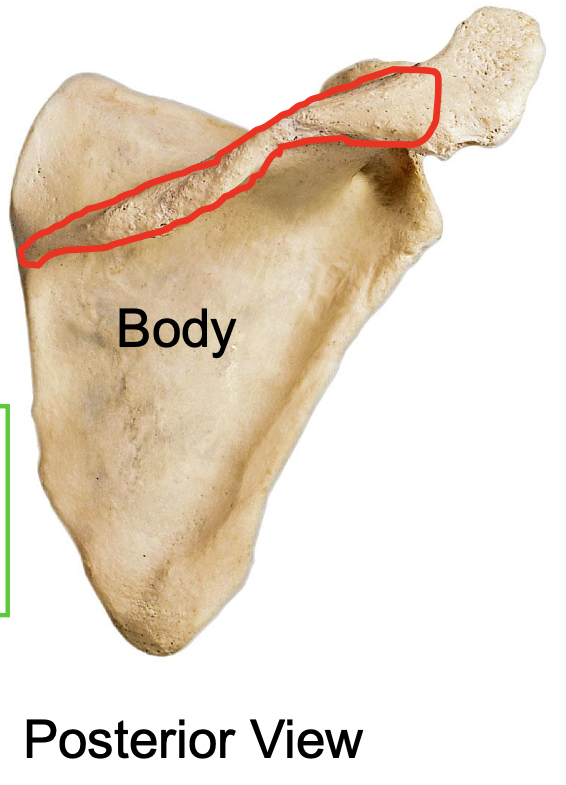
scapular spine of the scapula
a ridge that runs across the posterior side
Why is the scapular spine important
attachment site for muscles (ex: deltoid and trapezius)
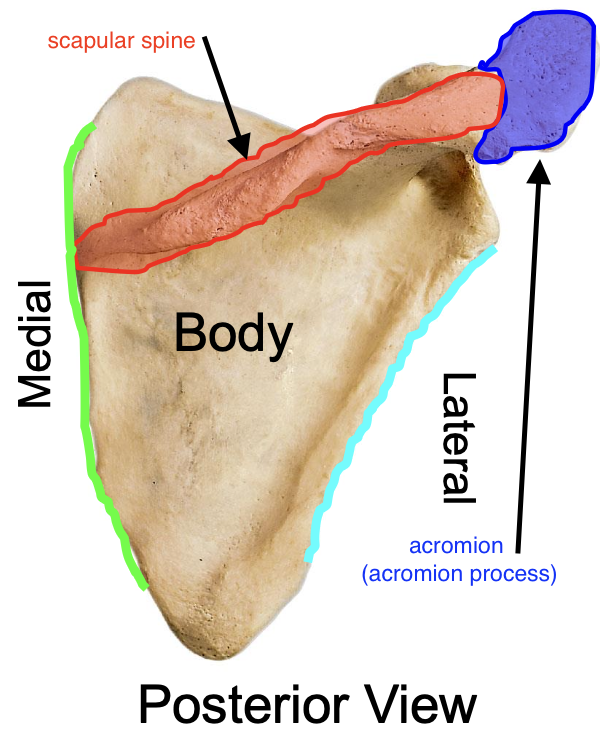
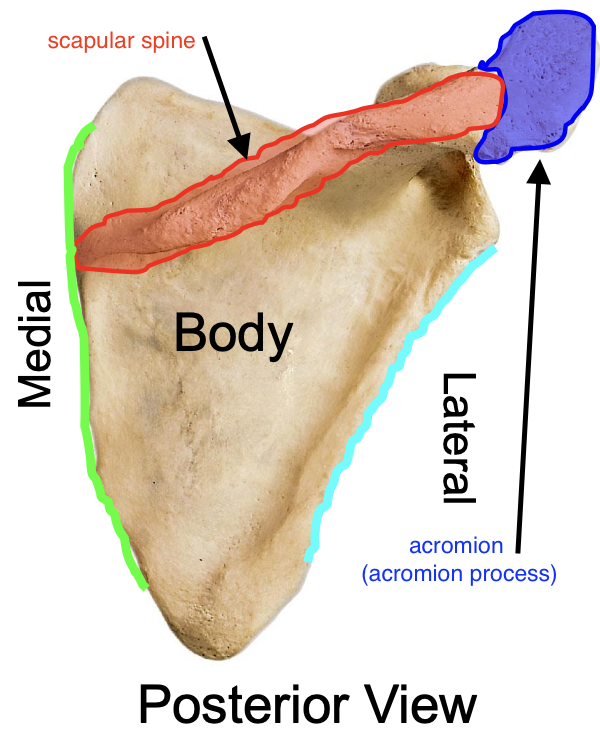
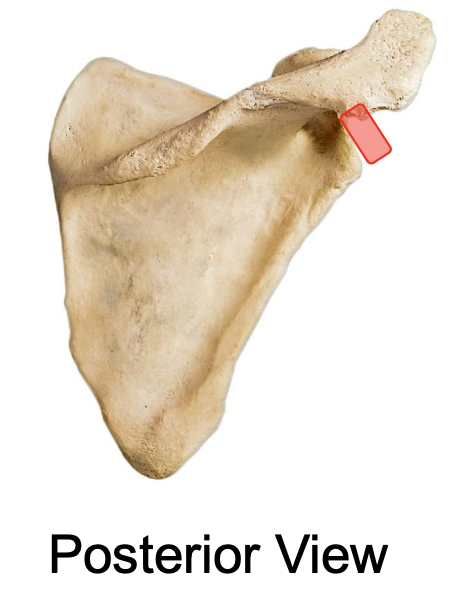
acromion (acromial process) of the scapulae
projects anteriorly at a 90⁰ angle from the lateral end of the scapular spine
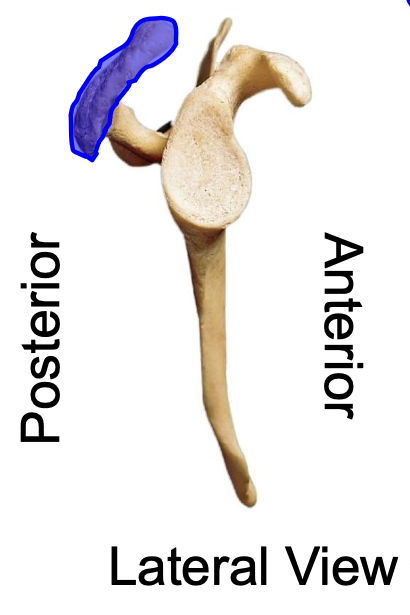
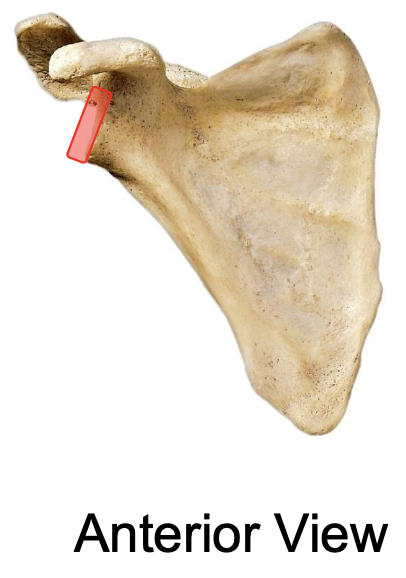
acromion (acromial process) of scapula lateral view
acromion (acromial process) of scapula anterior view
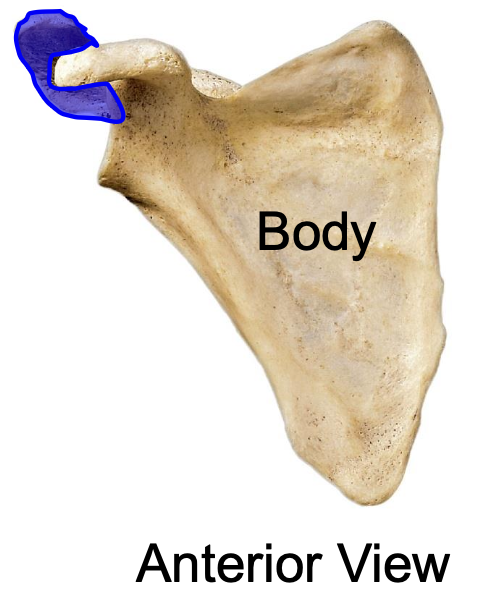
why is the acromion important
the acromion of the scapula articulates with the acromial end of the clavicle, forming the acromioclavicular joint
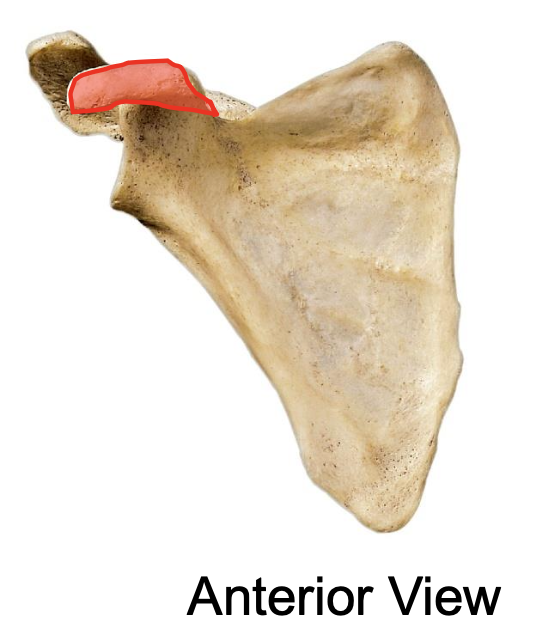
the coracoid process of the scapula
also called “crows beak”
projects anteriorly & laterally (means it can primarilly be seen from the anterior/ lateral view)

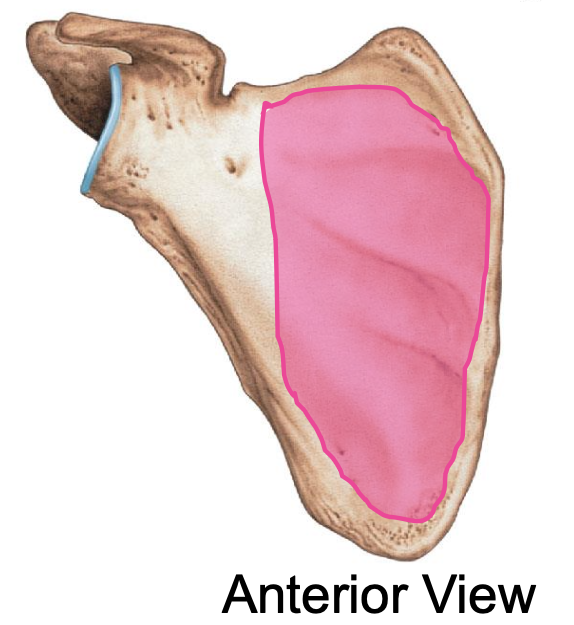
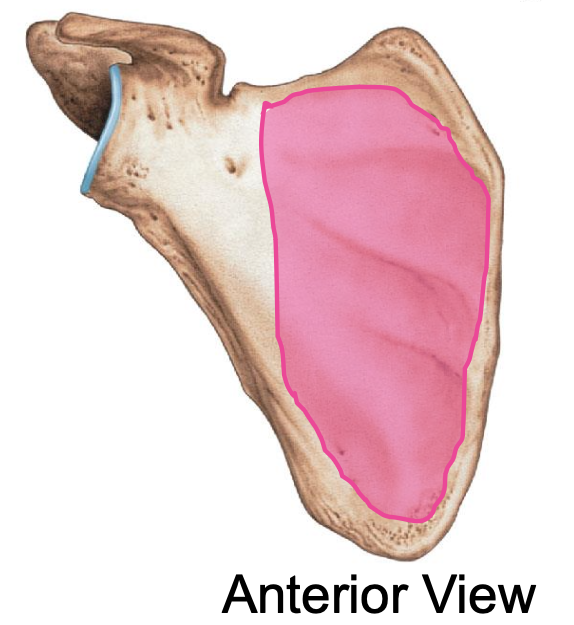
Subscapularis fossa of the scapula
smooth concave surface on the anterior side of scapula
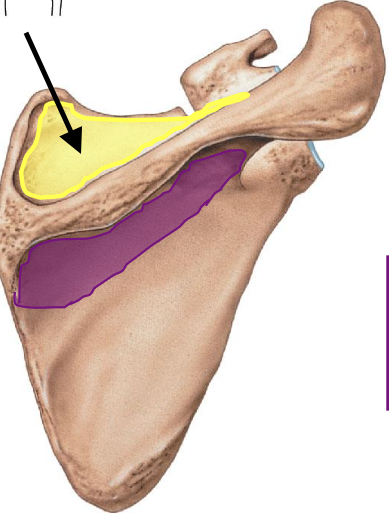
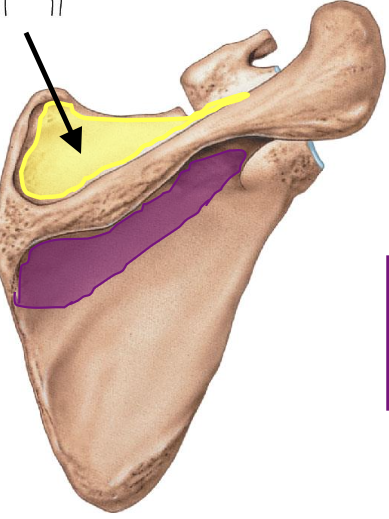
supraspinous fossa from the posterior view of the scapula
a depression superior to scapular spine (posterior view bc scapular spine is on posterior side of scapula)
importance of the supraspinous fossa?
attachments sit for supraspinatus muscle (posterior view)
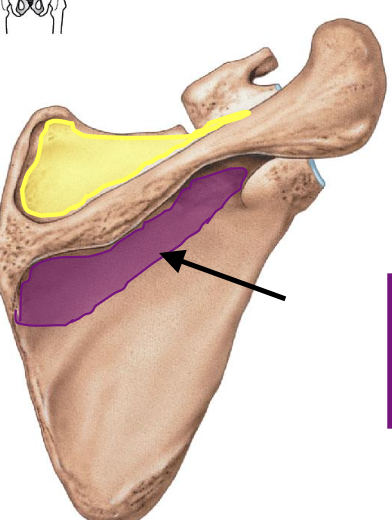
Infraspinous fossa (posterior view)
a depression inferior to scapular spine (posterior view bc scapular spine is on posterior side of scapula)
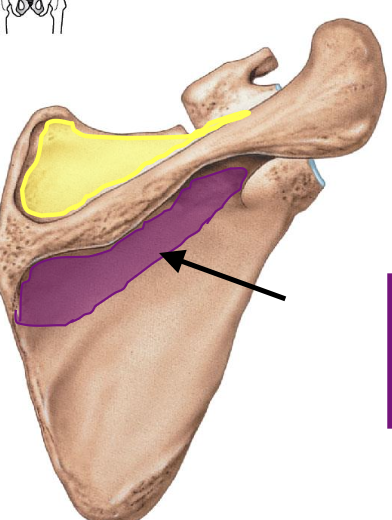
why is the infraspinous fossa important?
attachment site for infraspinatus muscle
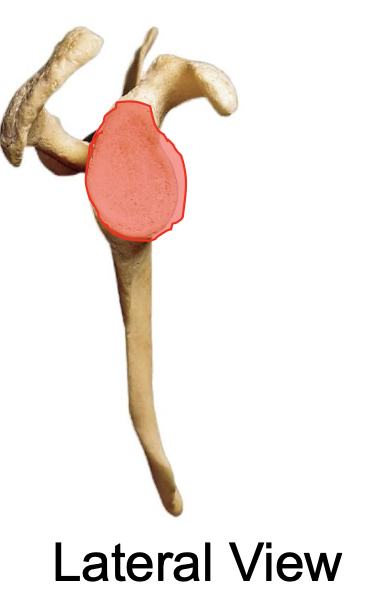
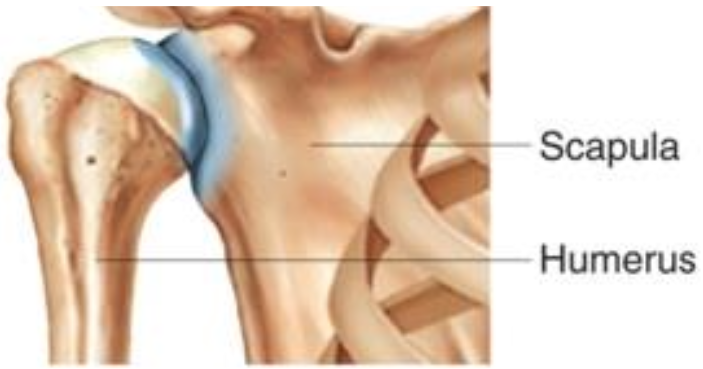
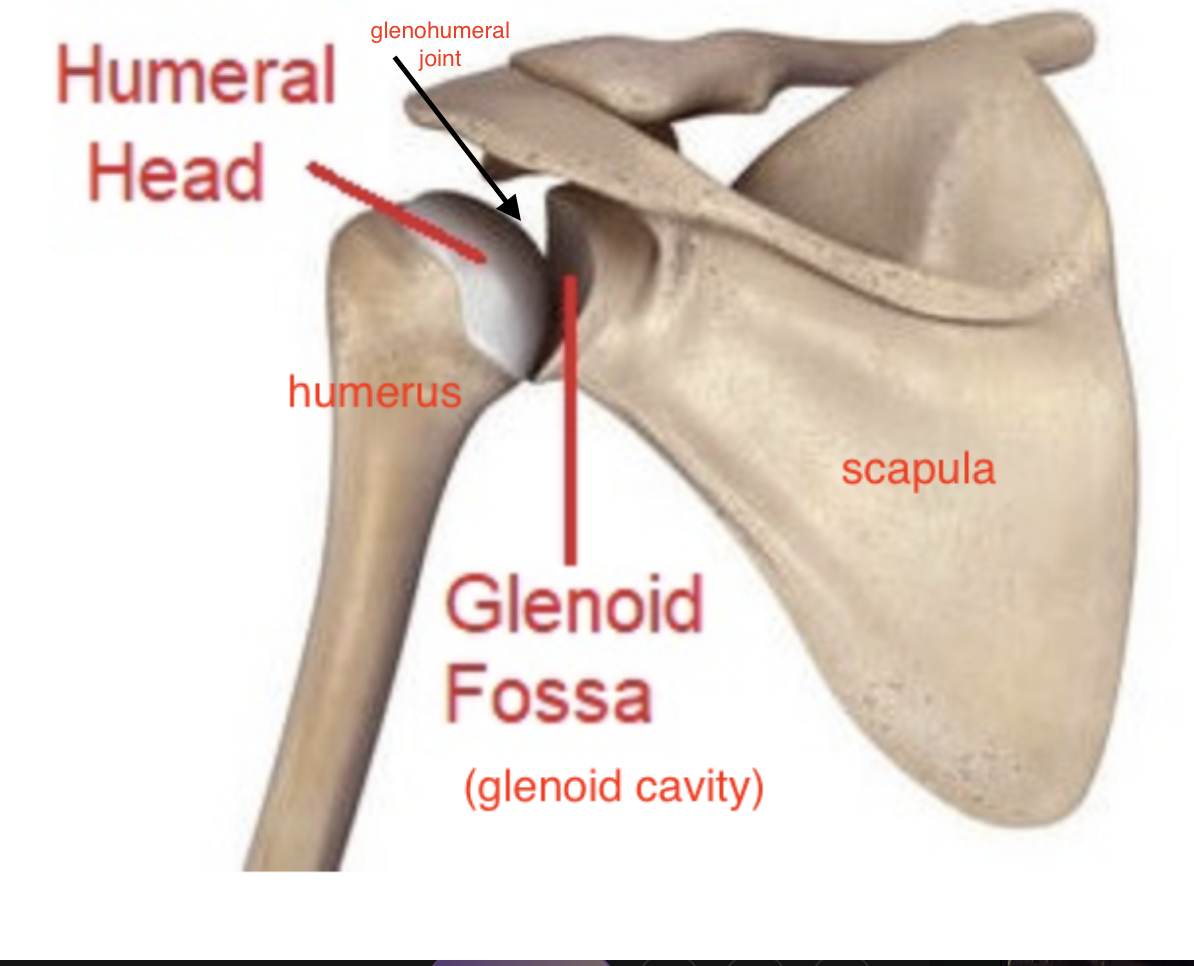
glenoid cavity of the scapula
on lateral side, cup-shaped
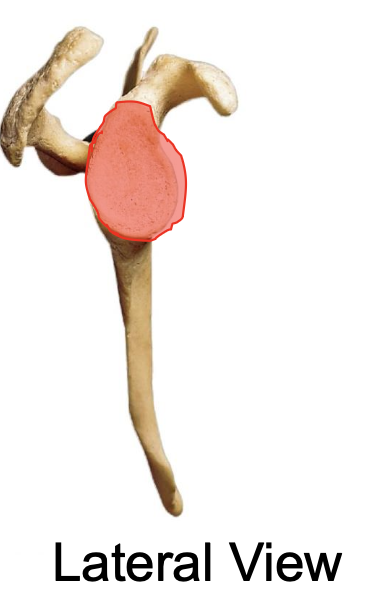
posterior view of glenoid cavity of the scapula
anterior view of glenoid cavity of the scapula
why is the glenoid cavity of the scapula important
where the head of the humerus articulates
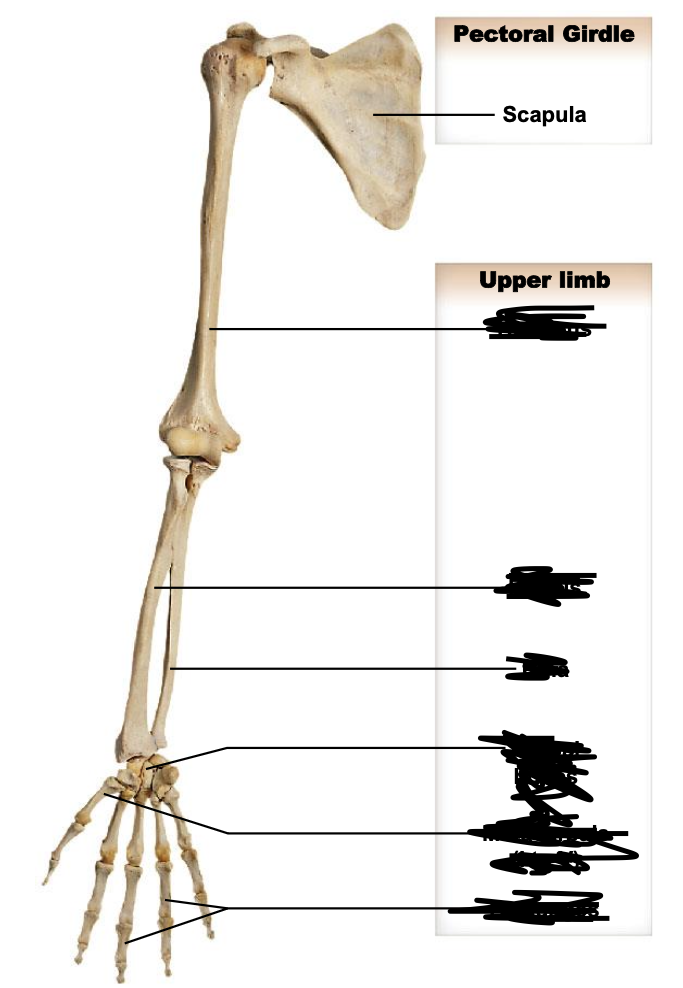
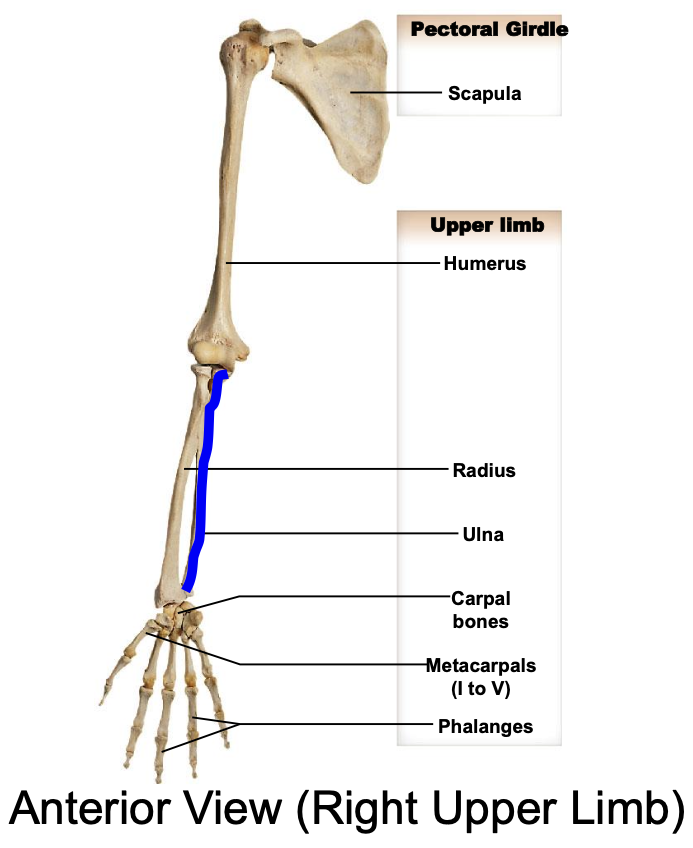
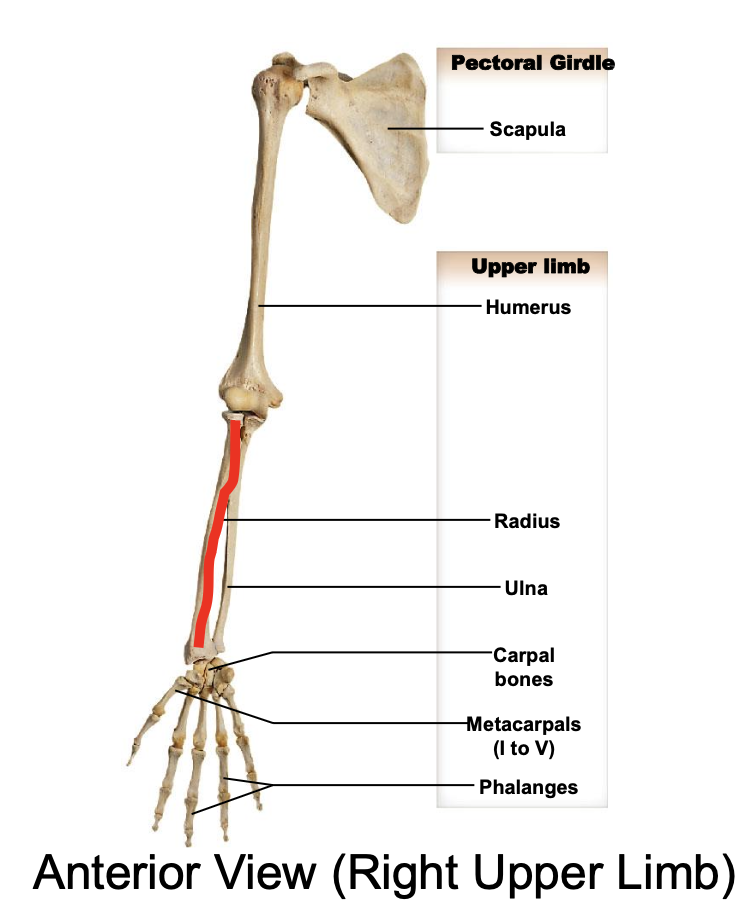
The user limbs of the appendicular skeleton include:
Humerus; radius; ulnal; carpals; metacarpals; phalanges
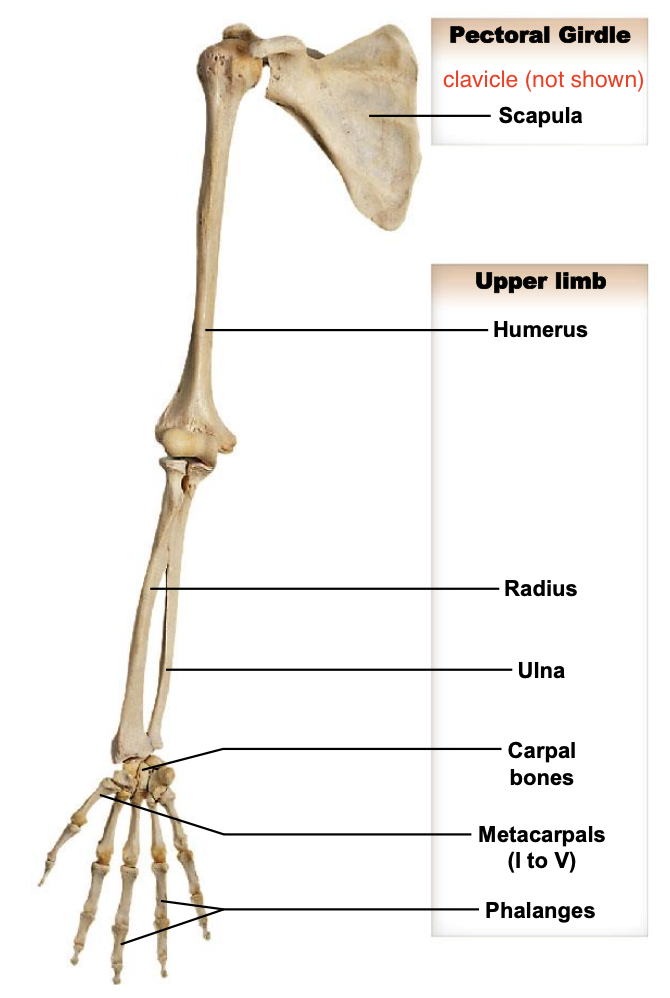
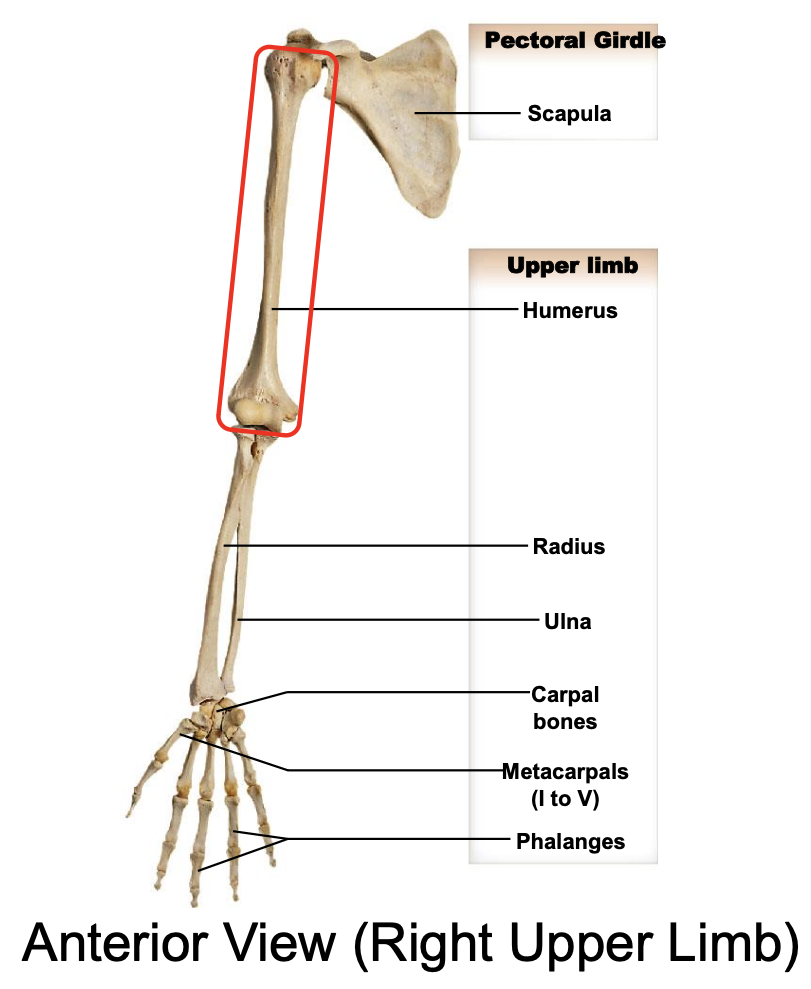
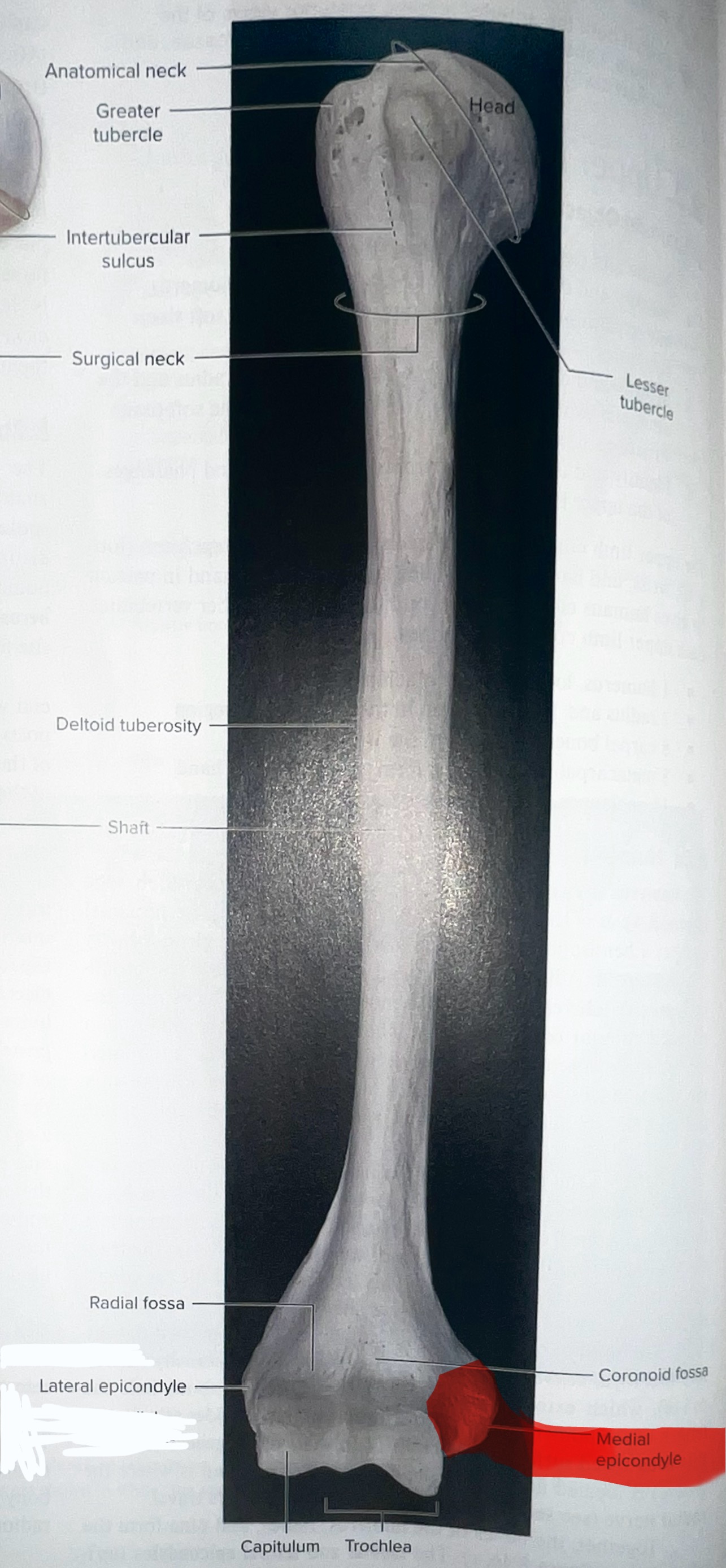
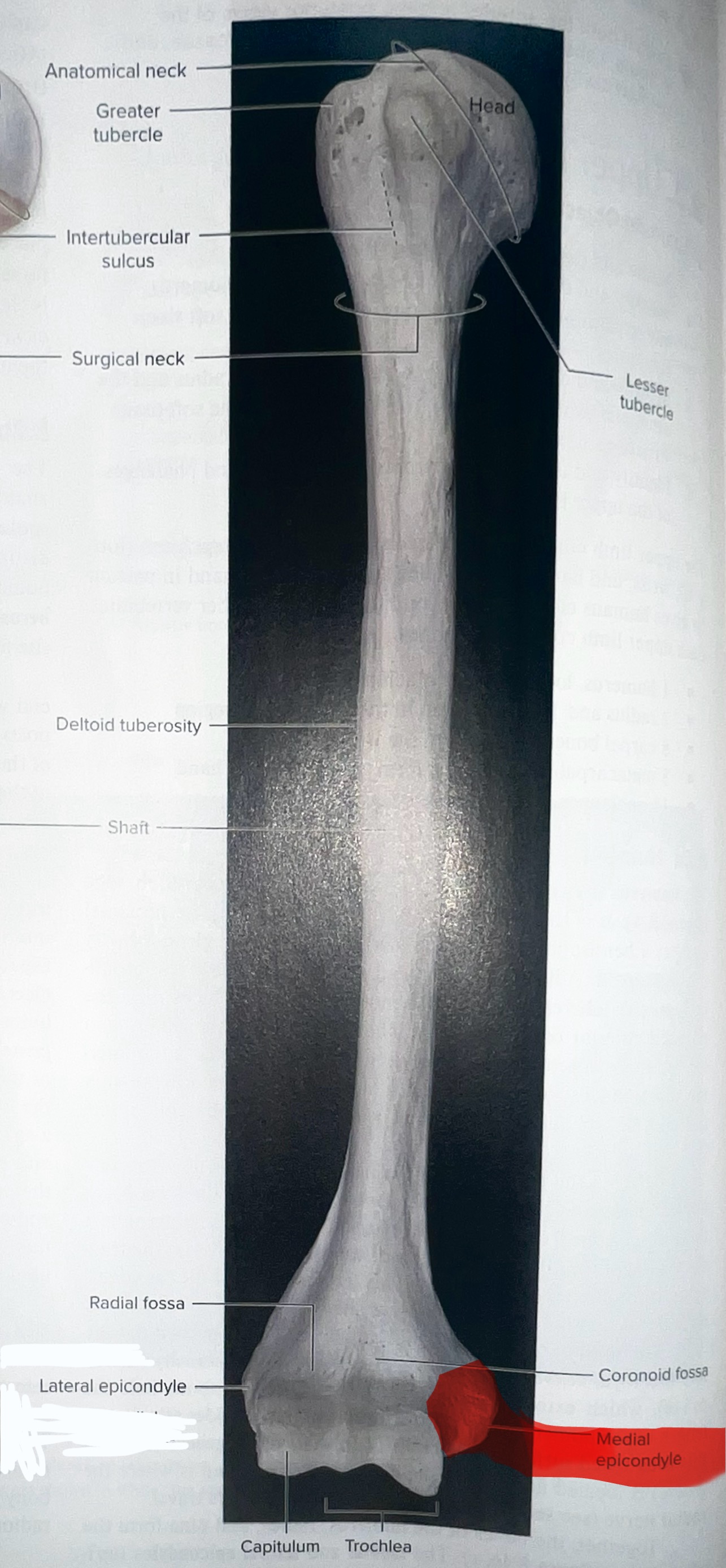
Humerus
head of humerus articulates with the scapula at the glenoid cavity
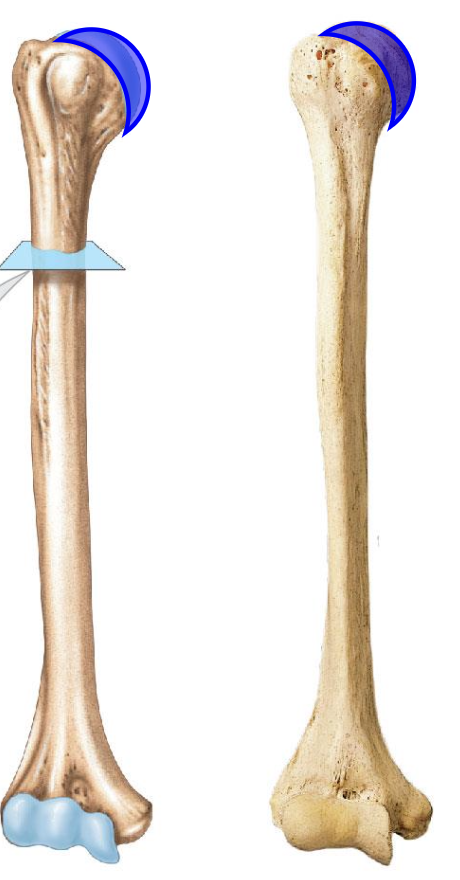
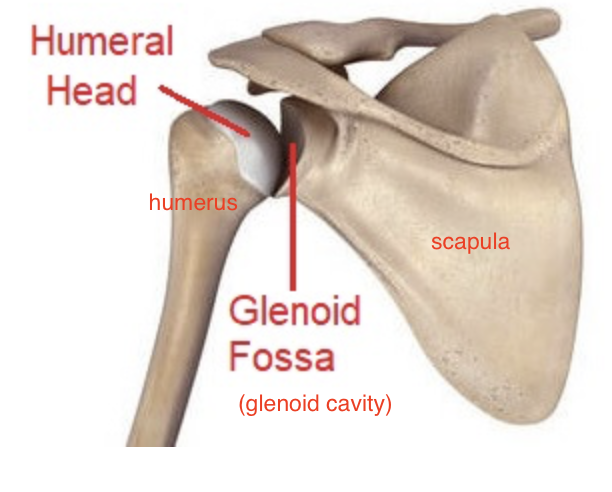

Head of humerus importance
articulates with glenoid cavity of the scapula to form the glenohumeral joint
Head of humerus is smooth and round and located at the
medial portion of the proximal epiphysis of the humerus
Greater tubercle of the humerus
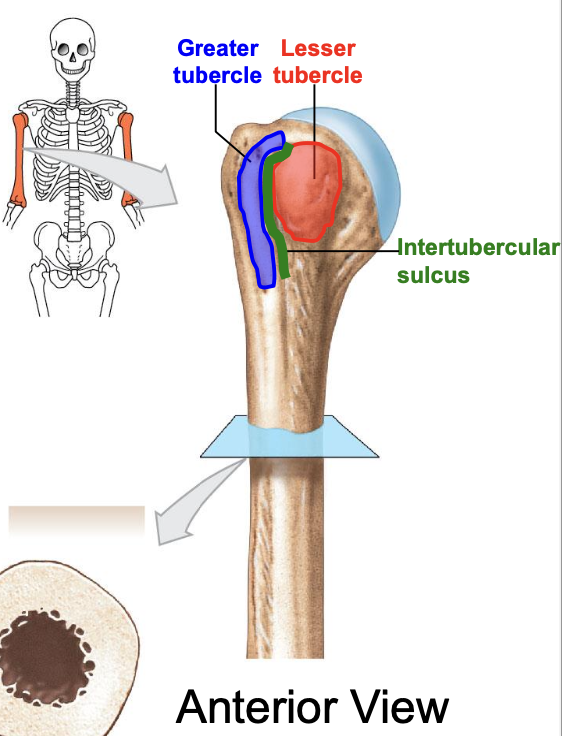
where is the greater tubercle of the humerus
On the lateral edge of the head of the humerus (lateral edge of the epiphyses of the humerus)
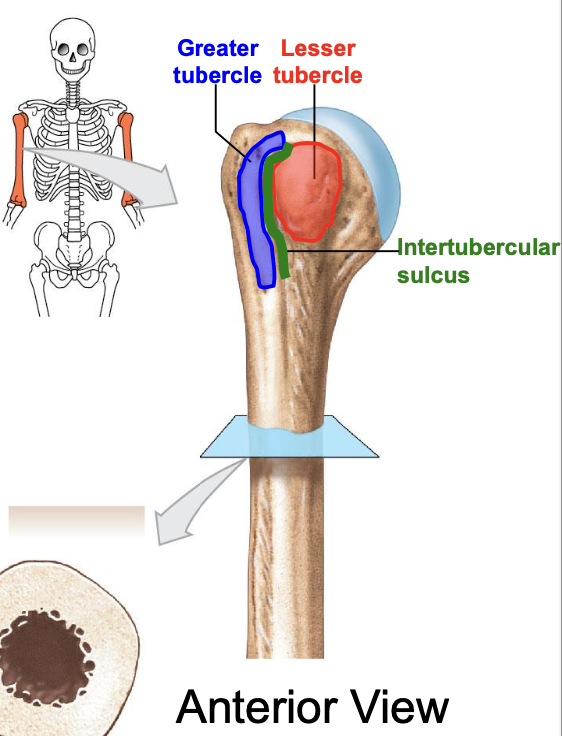
Why is the Greater tubercle of the humerus important?
attachment site for muscles
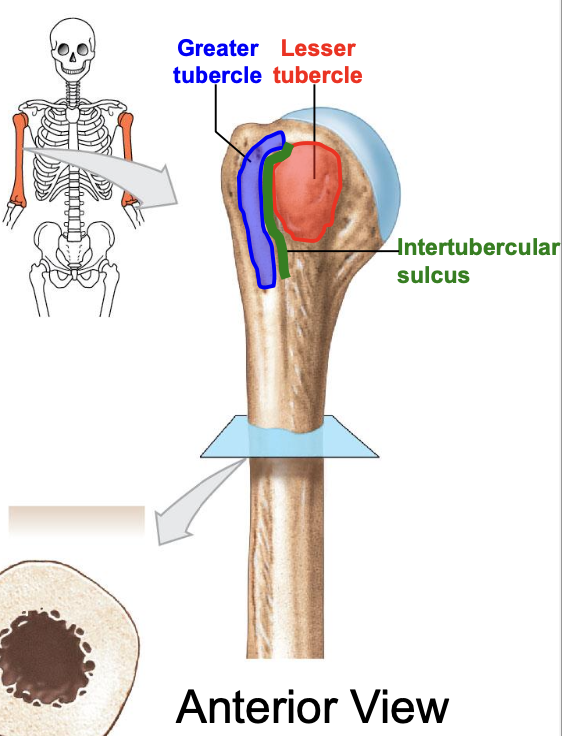
Lesser tubercle of the humerus
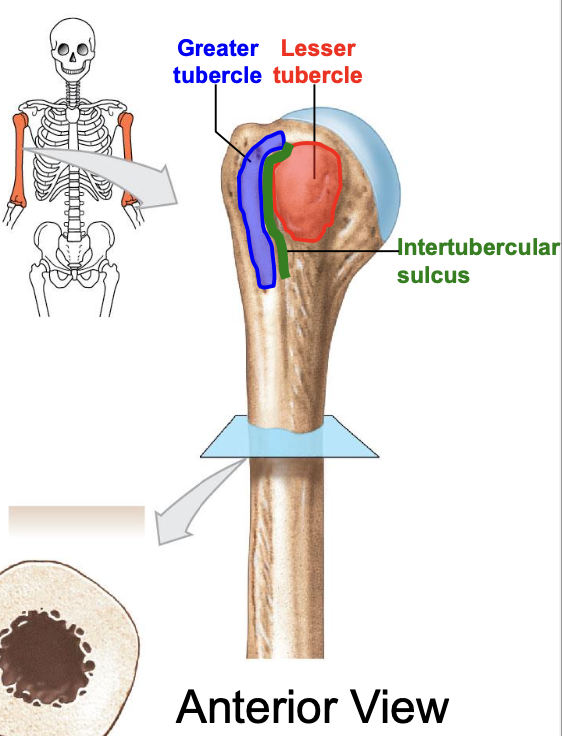
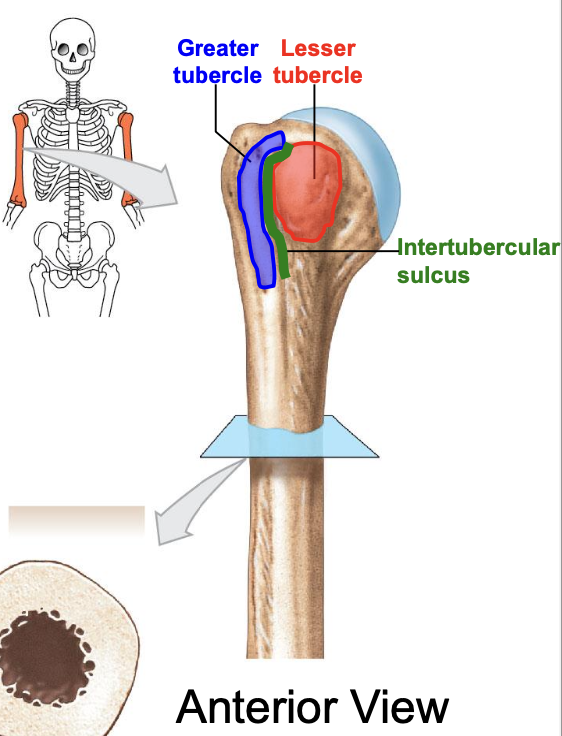
Where is the lesser tubercle of the humerus
on the anterior & medical surface of the epiphyses of the humerus
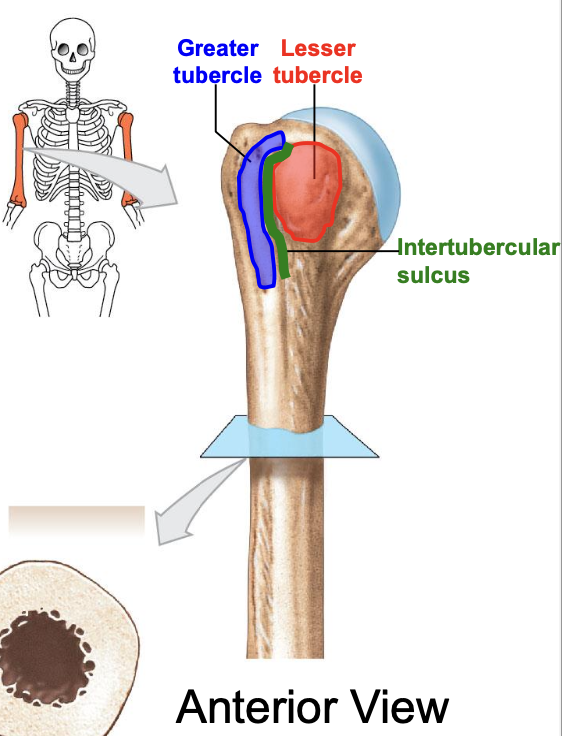
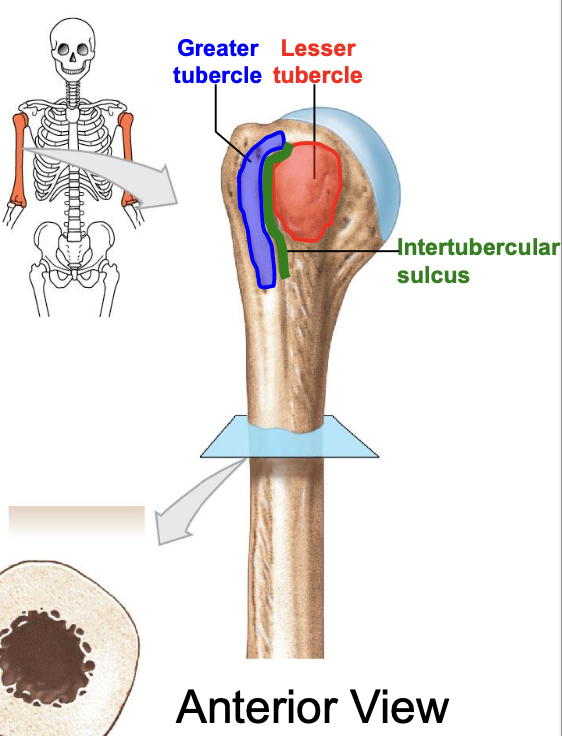
why is the lesser tubercle important?
the tendon of biceps brachii runs along it
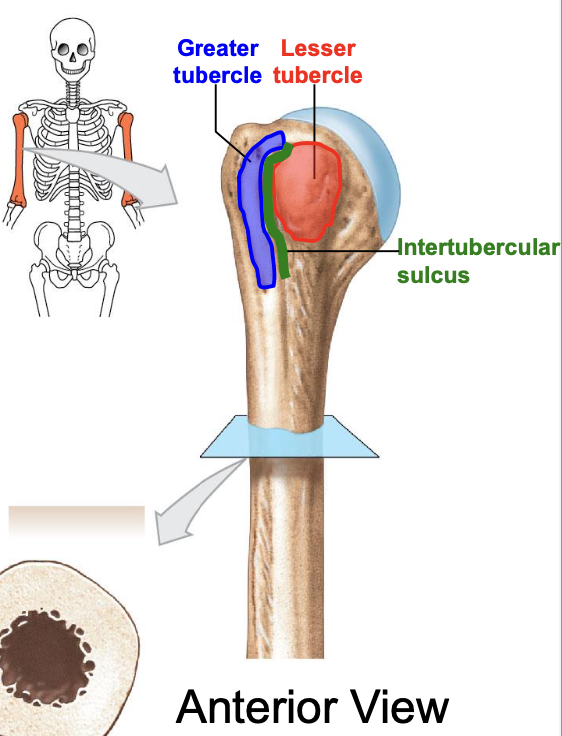
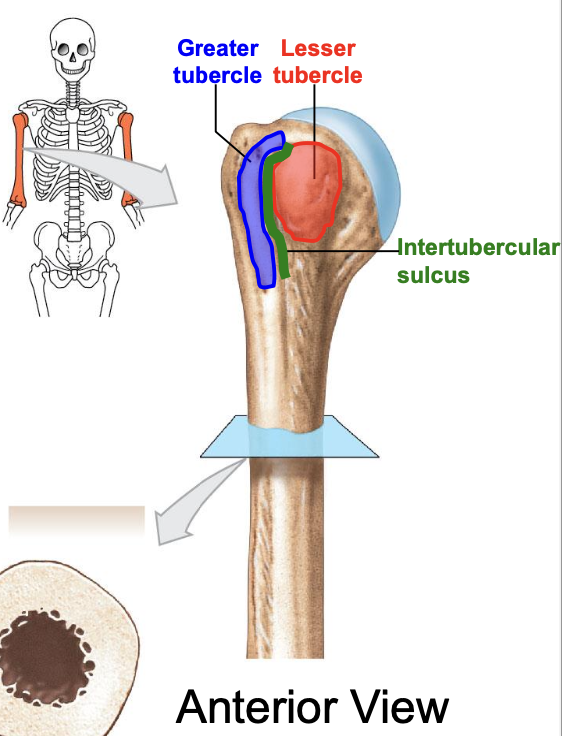
The intertubercular sulcus or groove
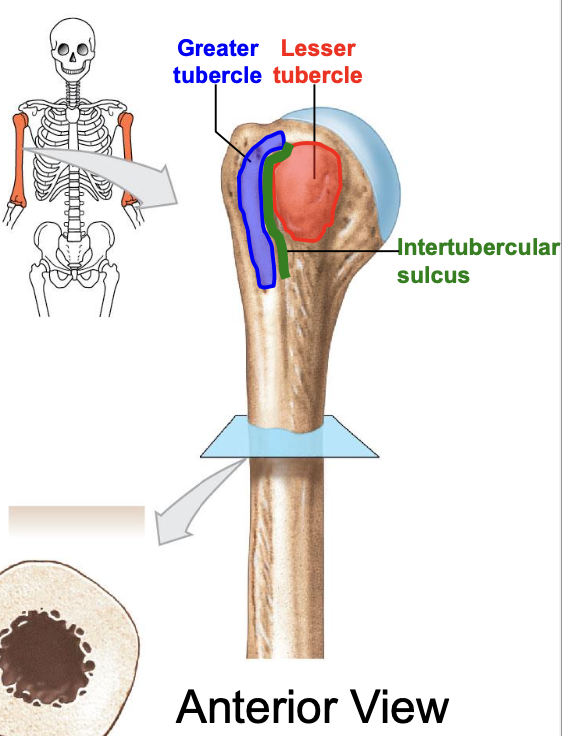
why is the inter tubercular sulcus or groove important
it separates the 2 tubercles
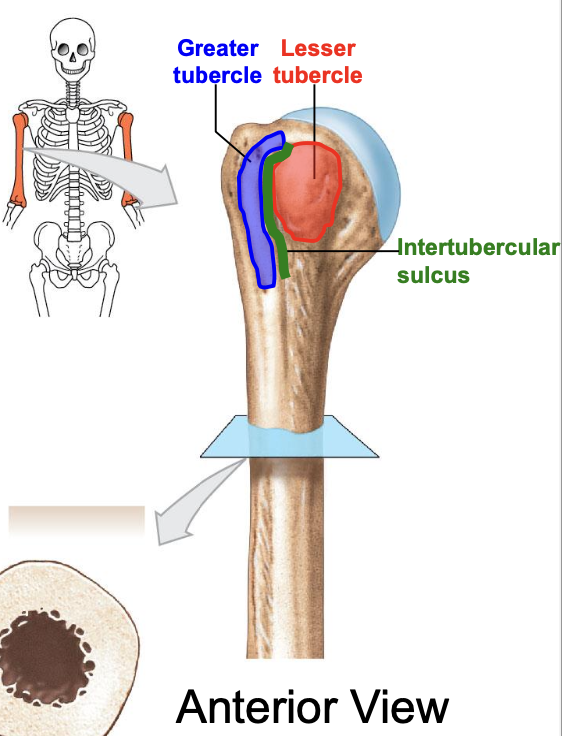

Body or shaft of the humerus is the
long, cylindrical middle part of the humerus
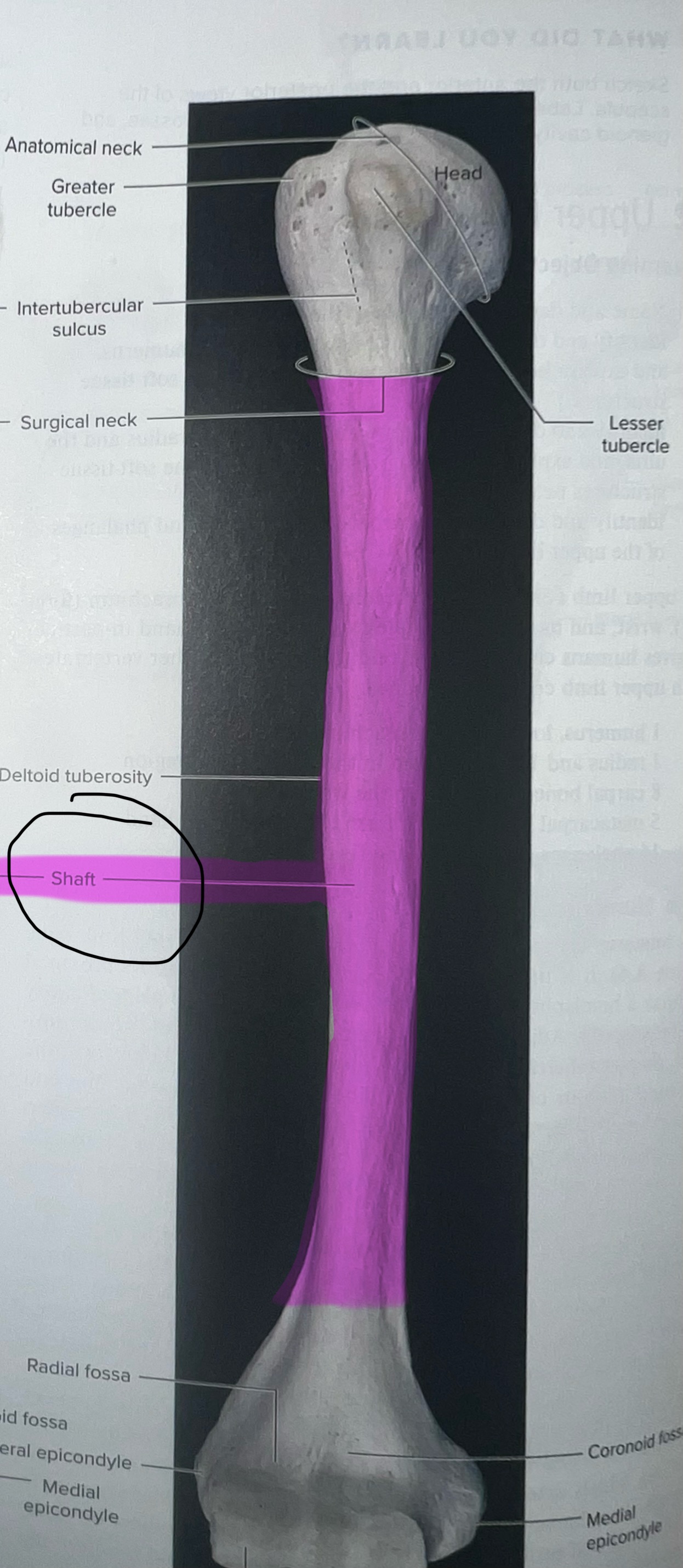

Deltoid tuberosity
an elevation that runs ½ way down the lateral surface of the humerus
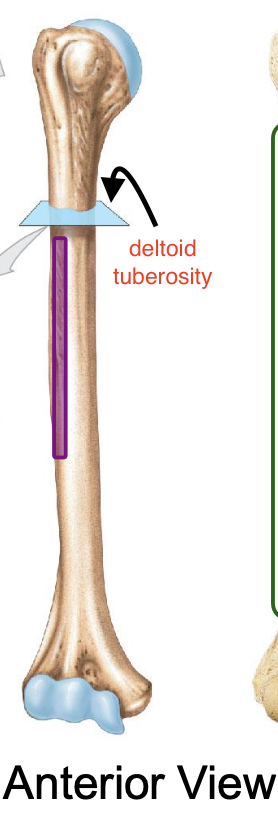
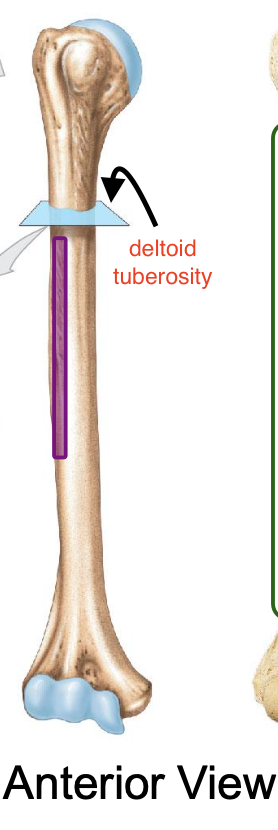
Why is the deltoid tuberosity important
deltoid muscles insert here
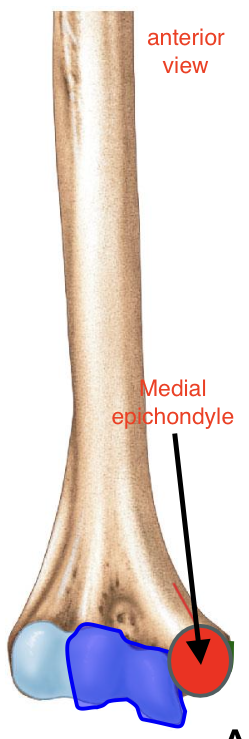
Medial Epicondyle of the Humerus
FUNNY BONE feeling is her
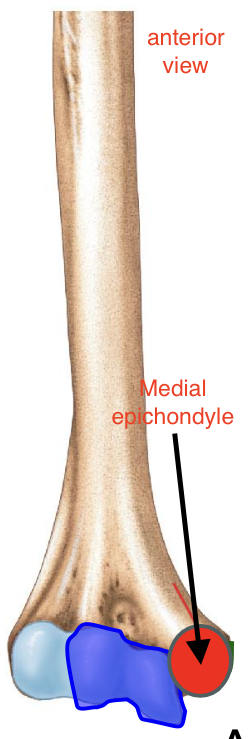
Importance of the medial epicondyle of the humerus?
attachment site for muscles
what nerve crosses the medial epicondyle of the humerus posterior side?
the ulnar nerve
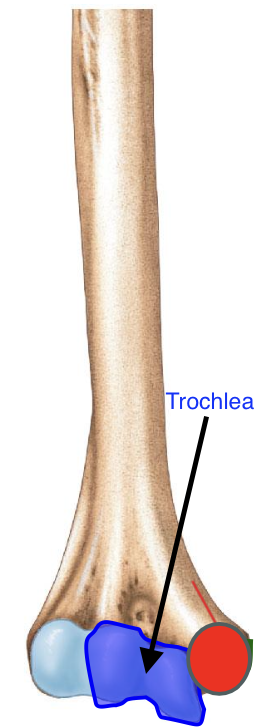
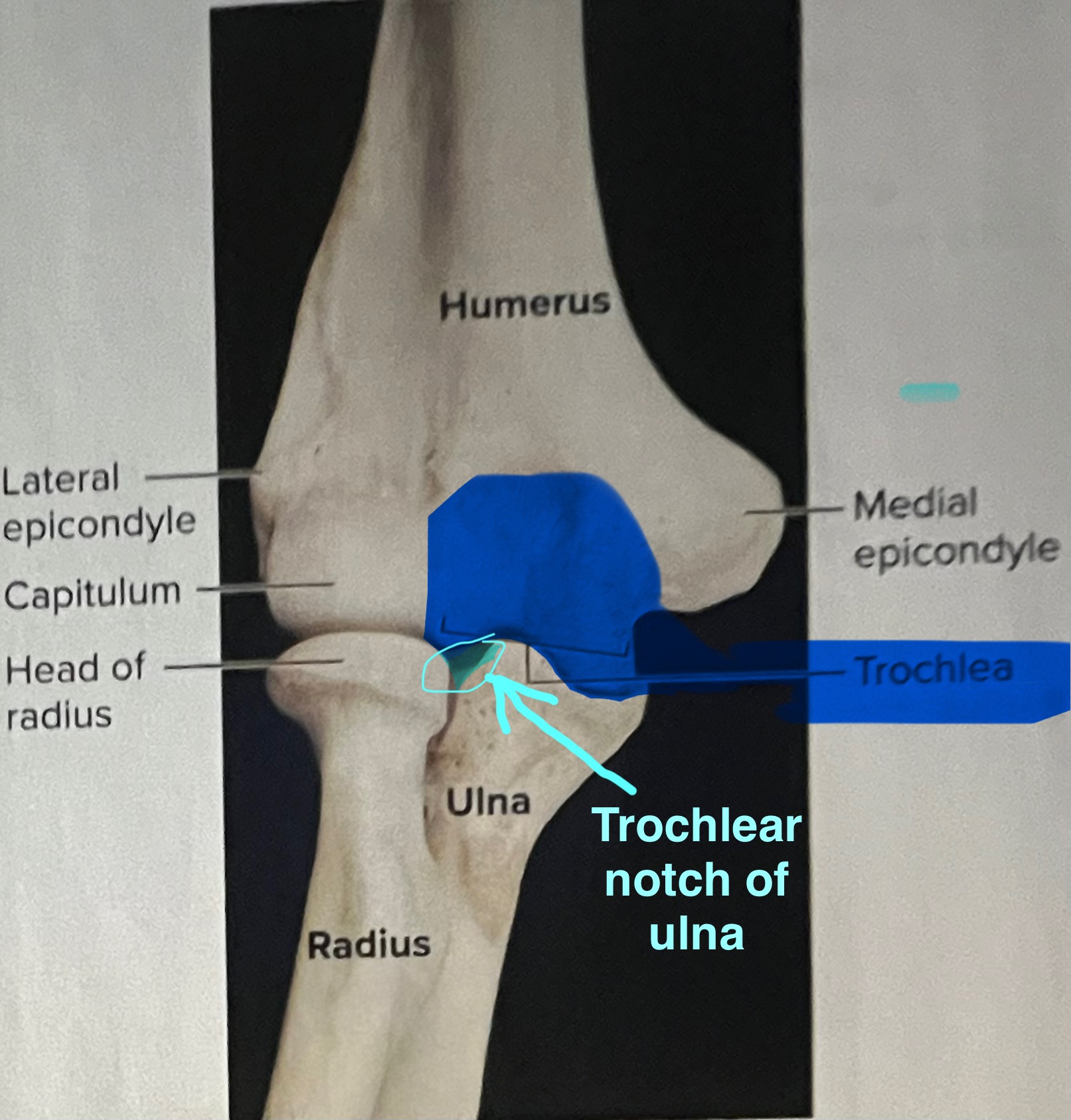
Trochlea of the humerus
the “pulley”
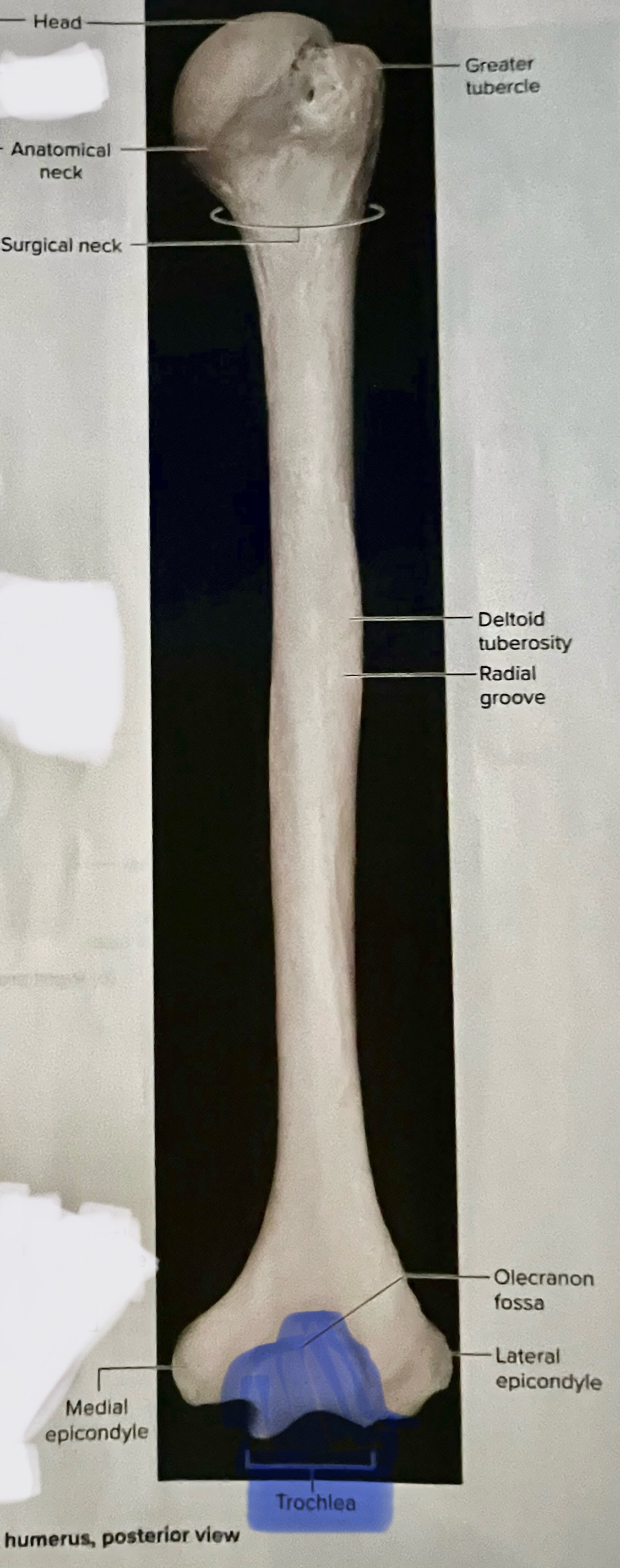
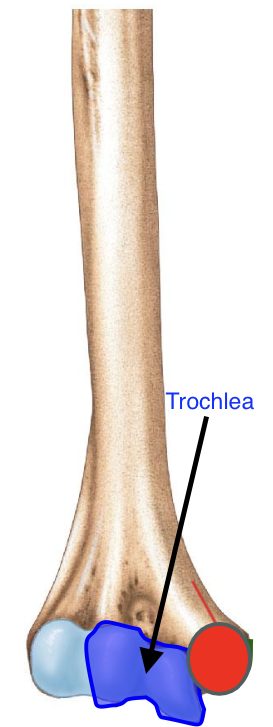
importance of the trochlea of the humerus?
Articulates with the trochlear notch of the ulna, forming the elbow joint
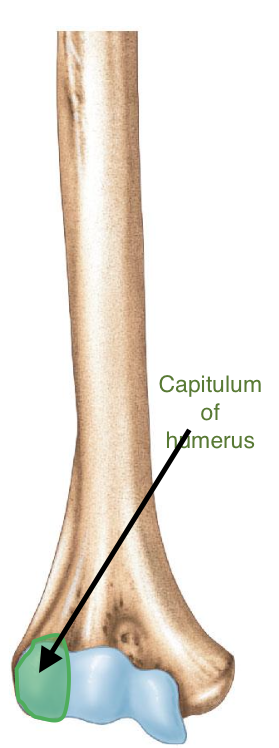
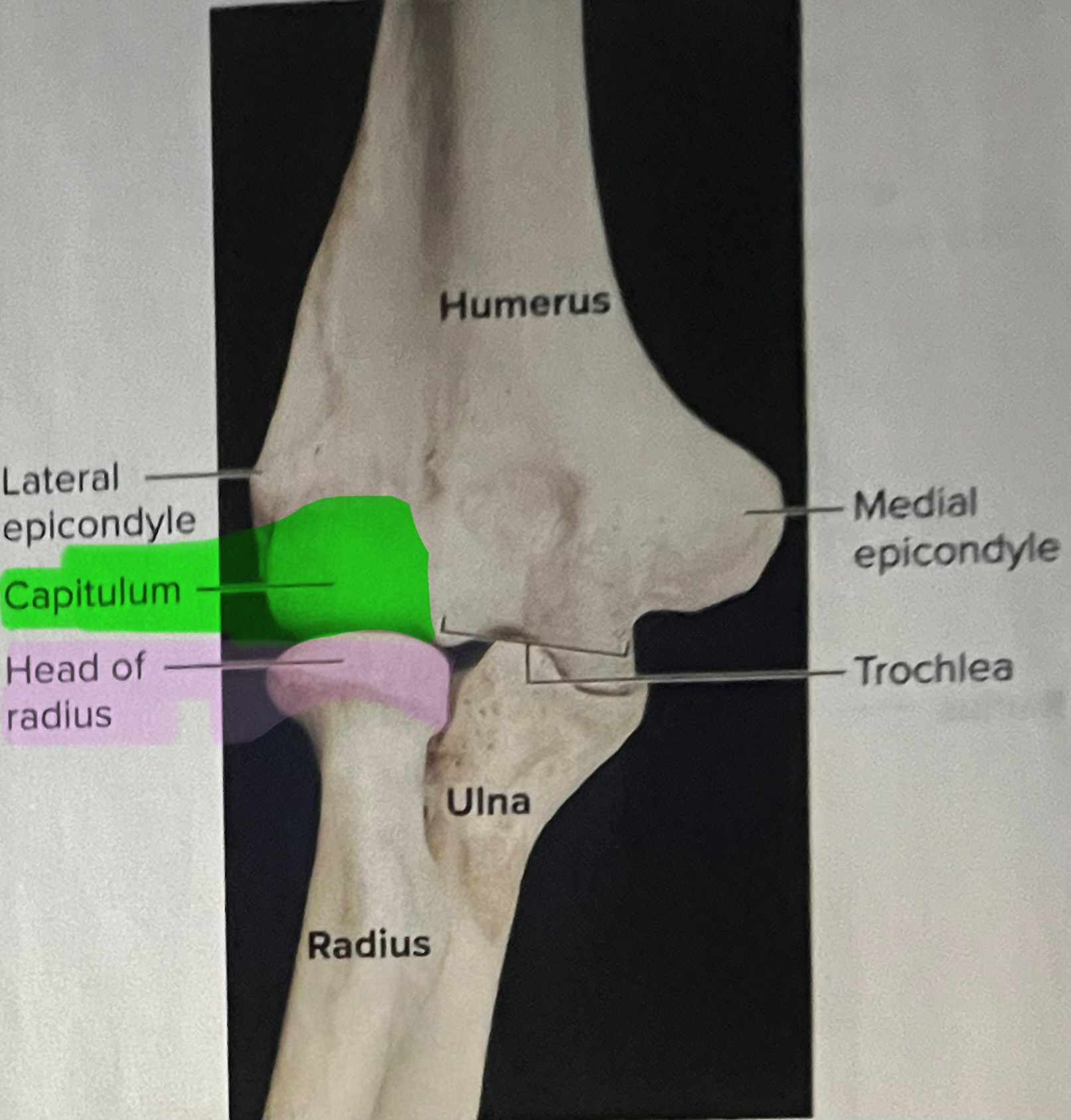
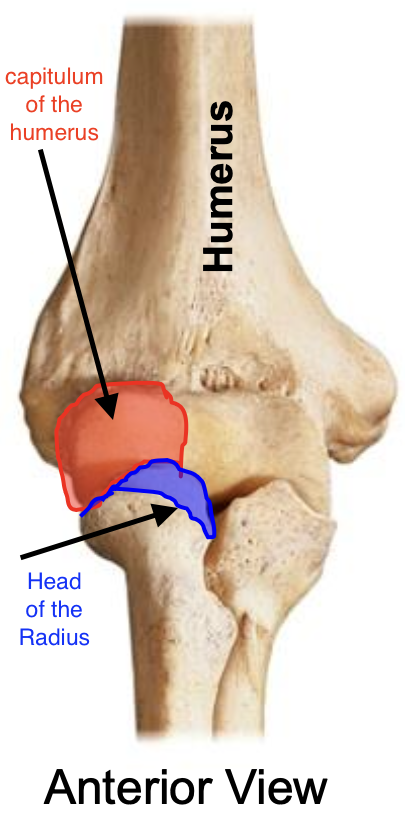
Capitulum of the humerus
“capit” = head
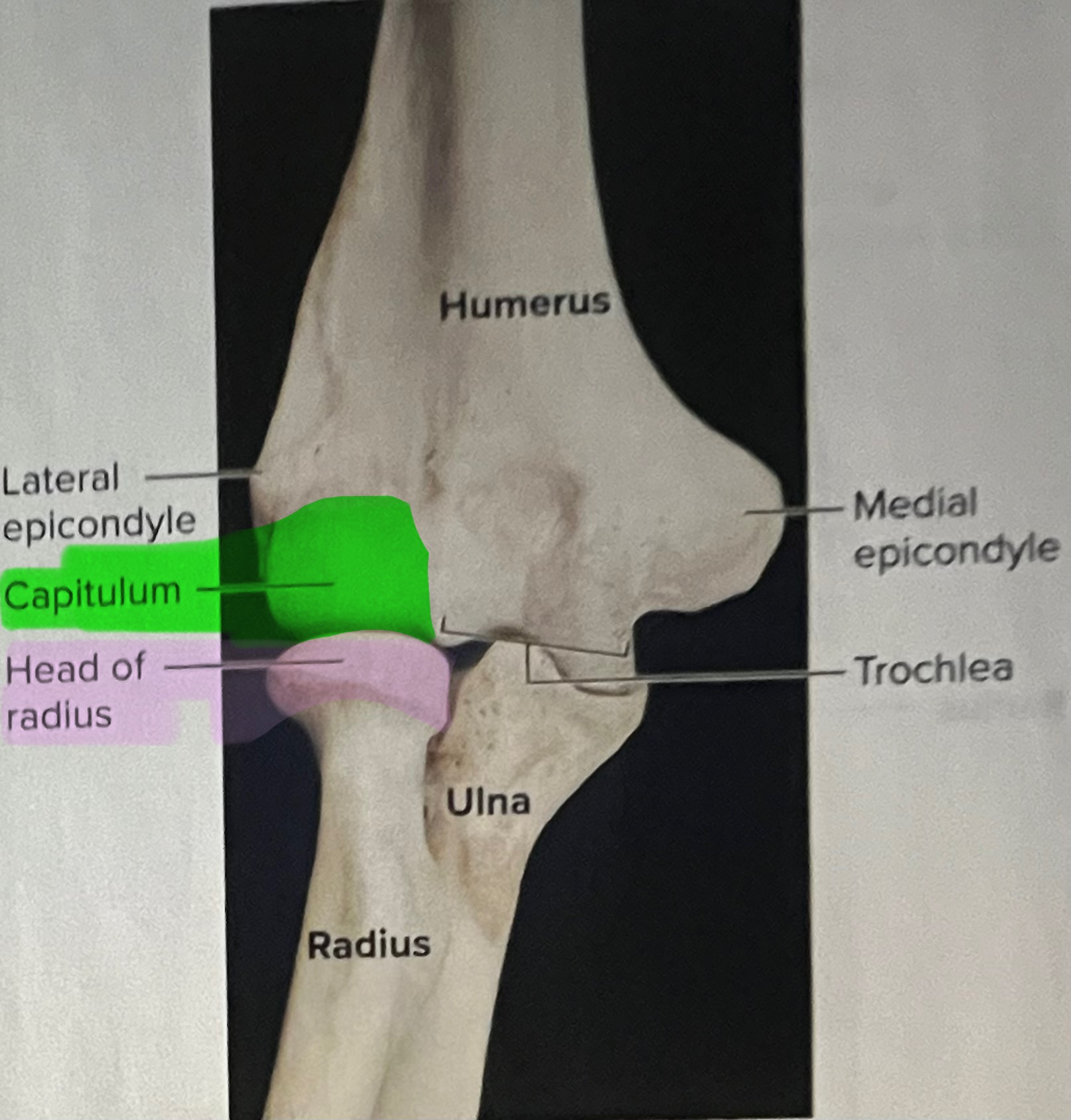
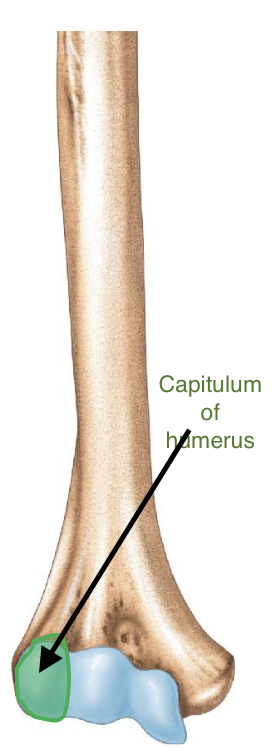
Importance of the capitulum of the humerus
The capitulum of the humerus articulates with the head of the radius, forming the humeroradial joint
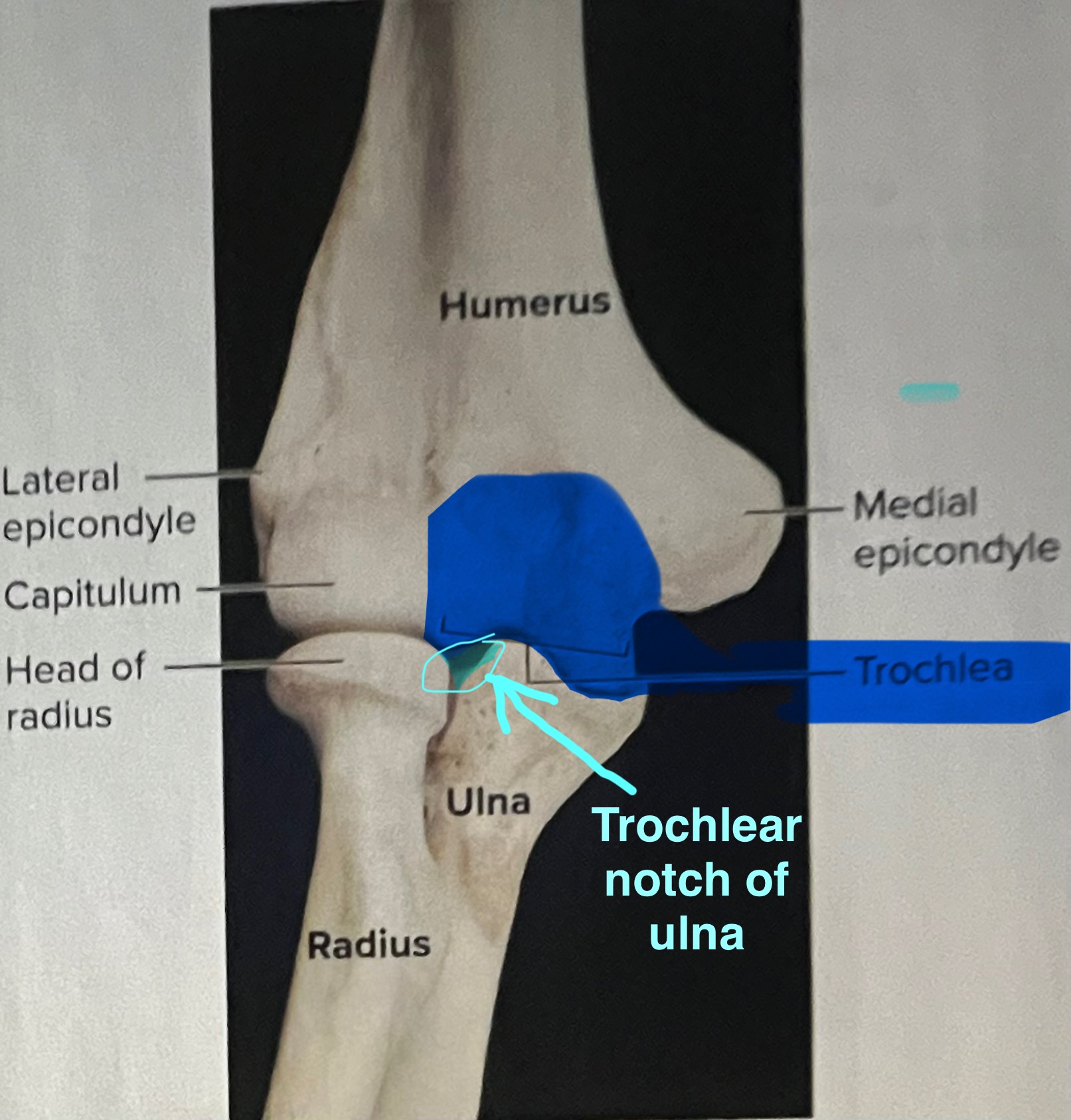
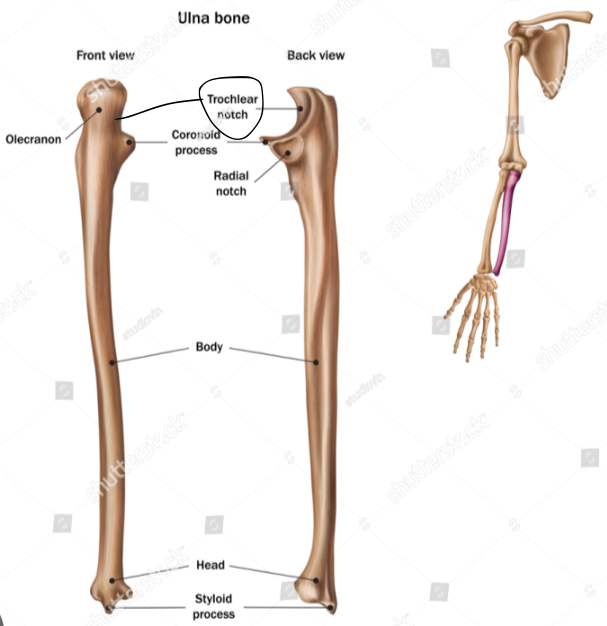
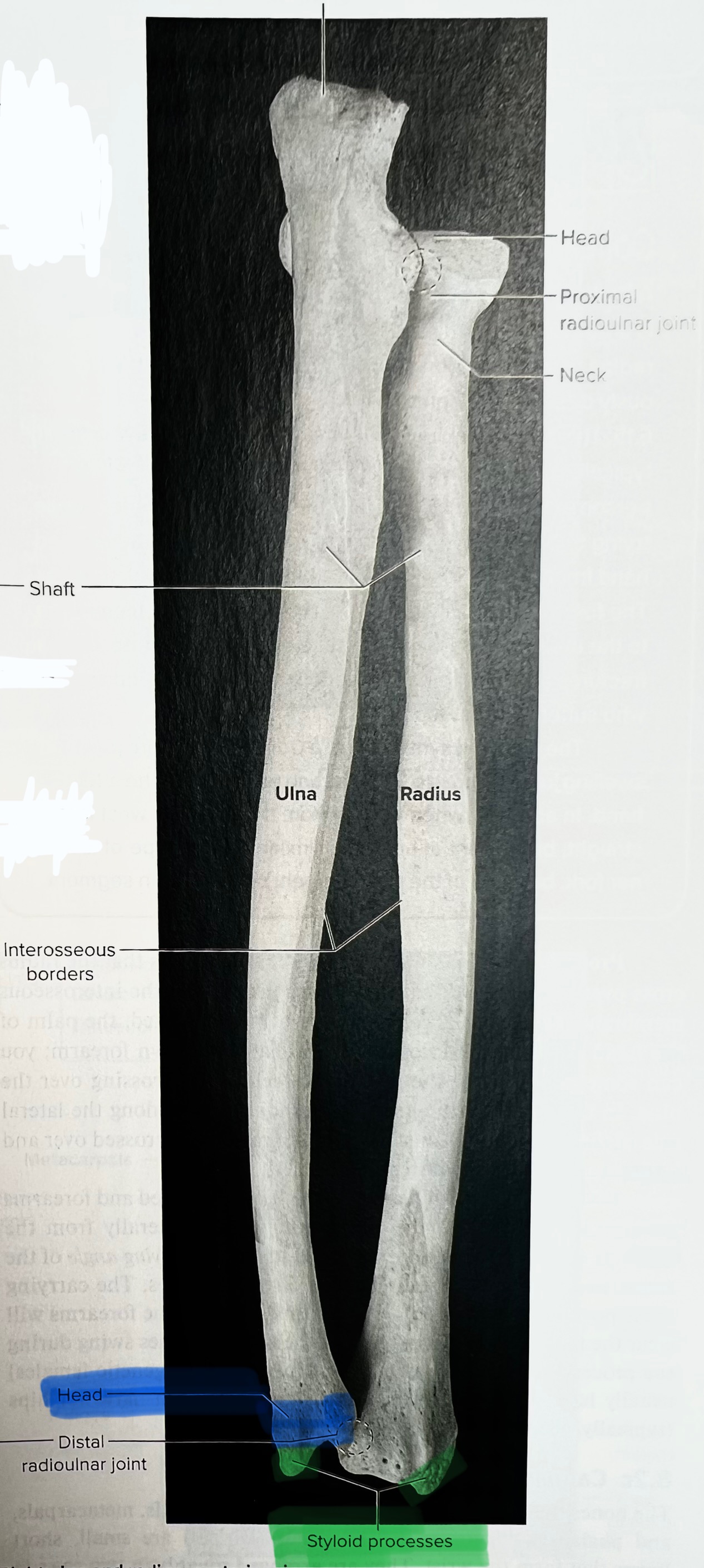
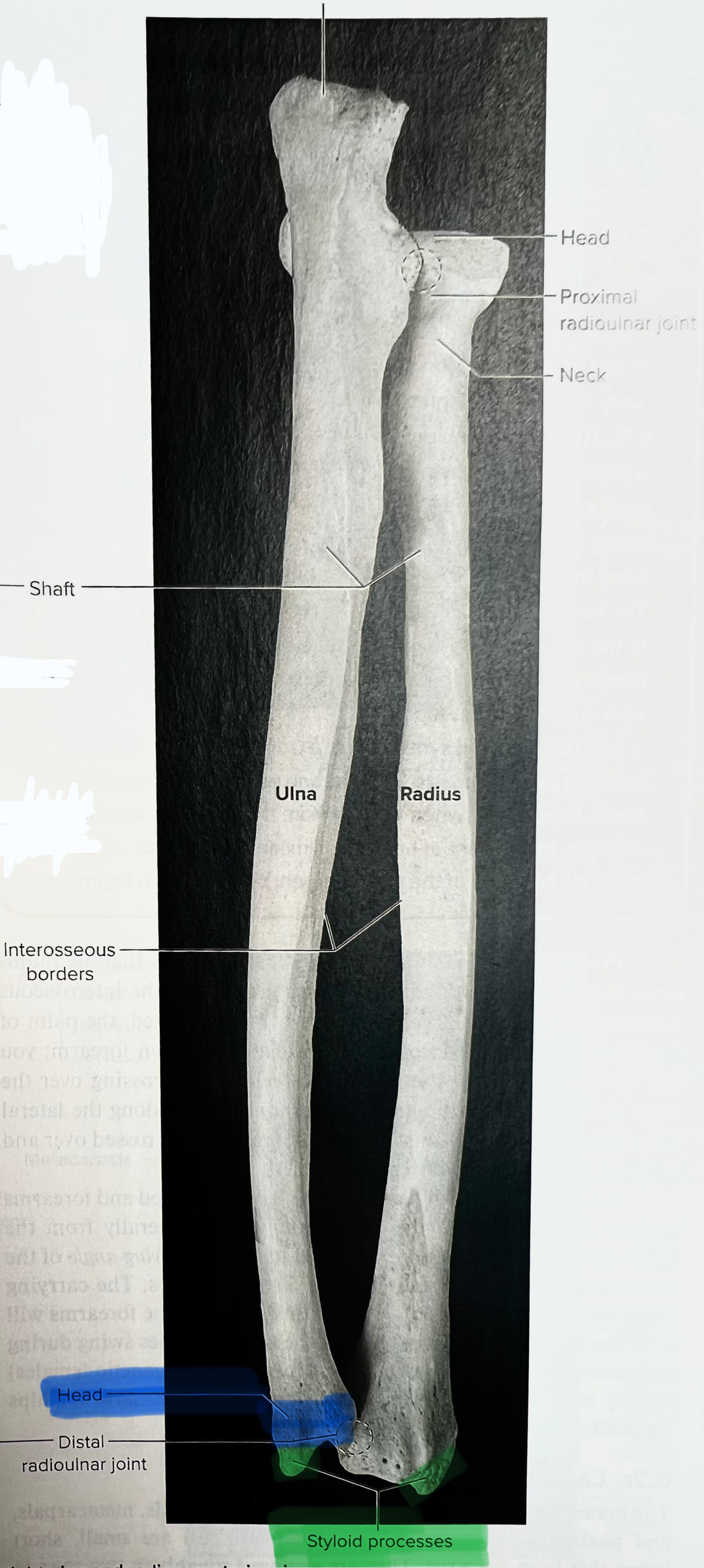
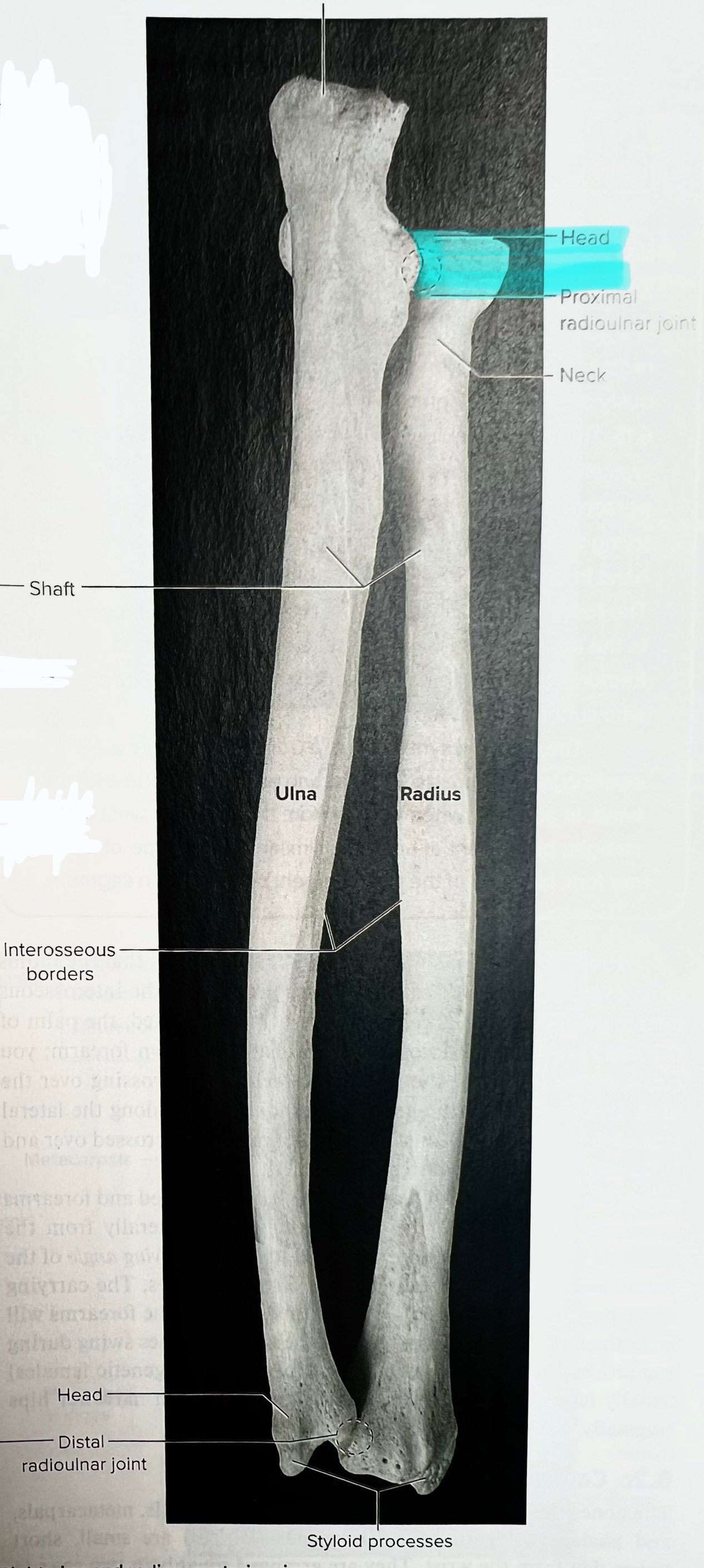
Ulna
The ulna is the medial forearm bone
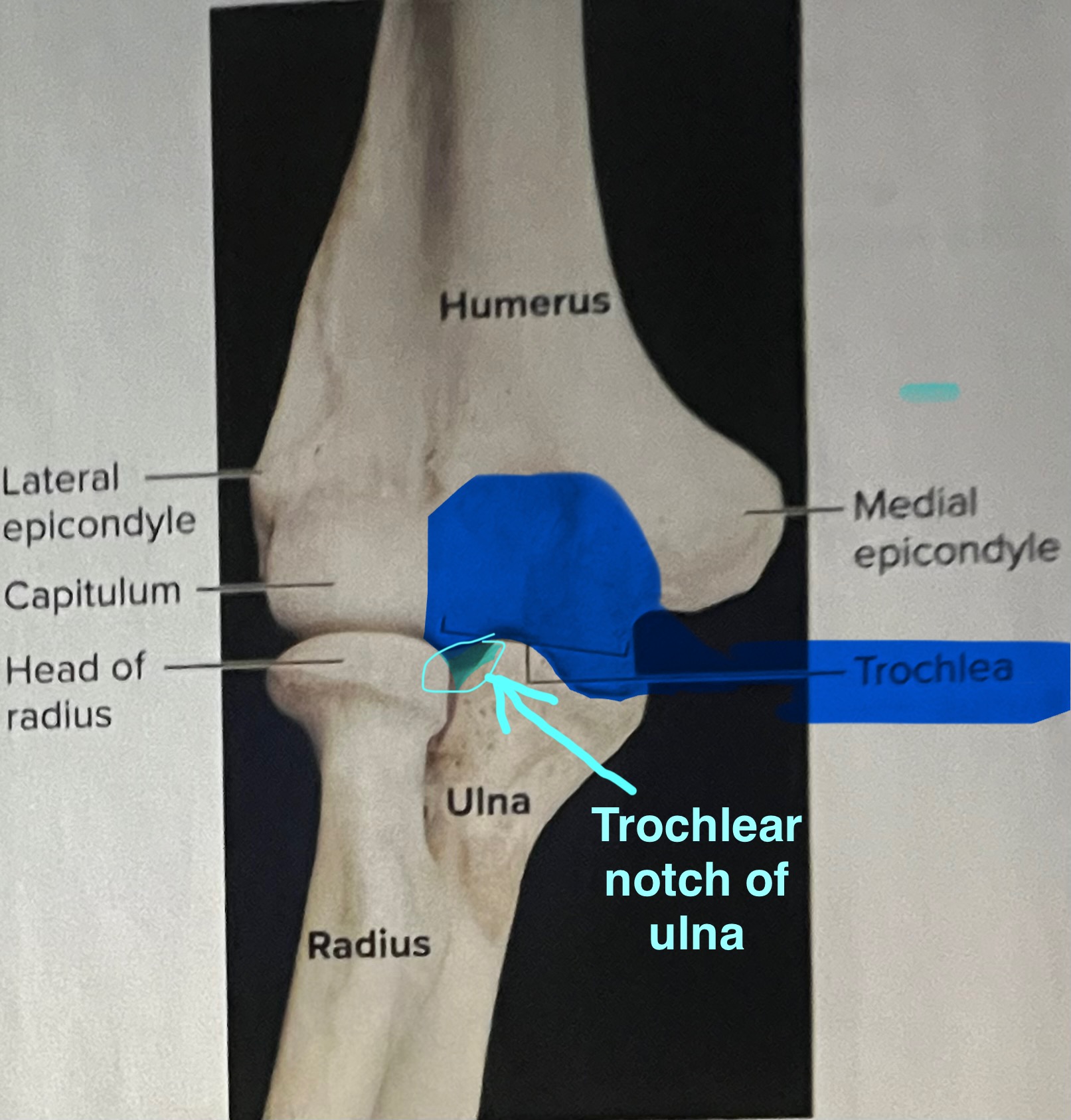
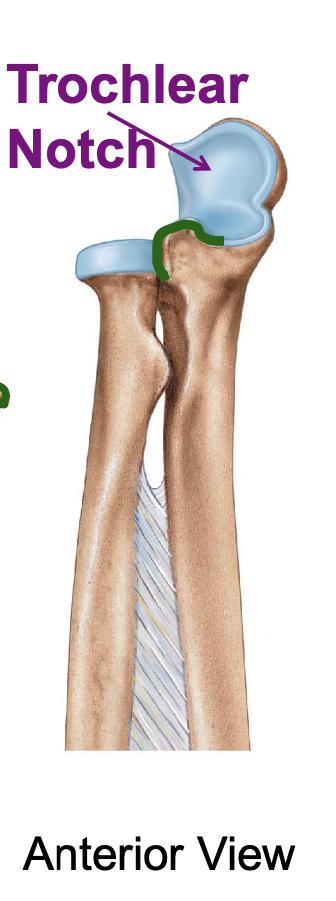
trochlear notch of the ulna
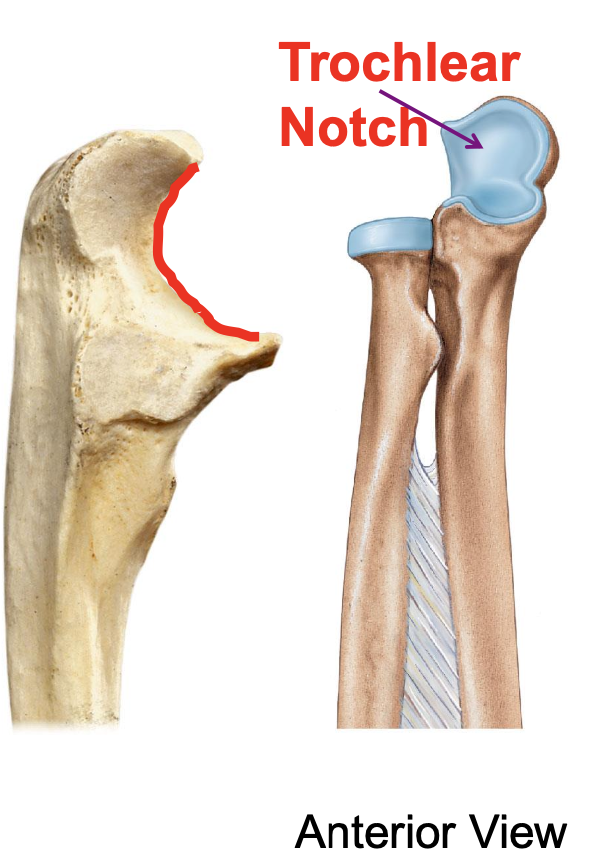
importance of the trochlear notch of the ulna?
the trochlear notch of the ulna articulates with the trochlea of the humerus, forming the elbow joint
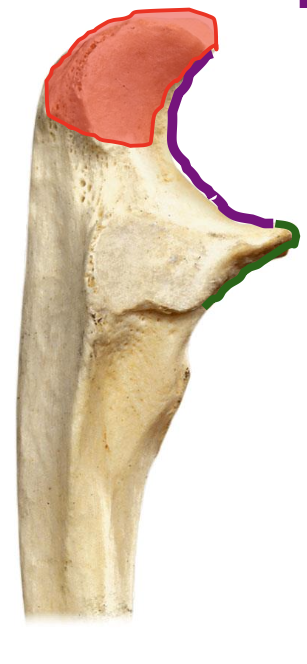
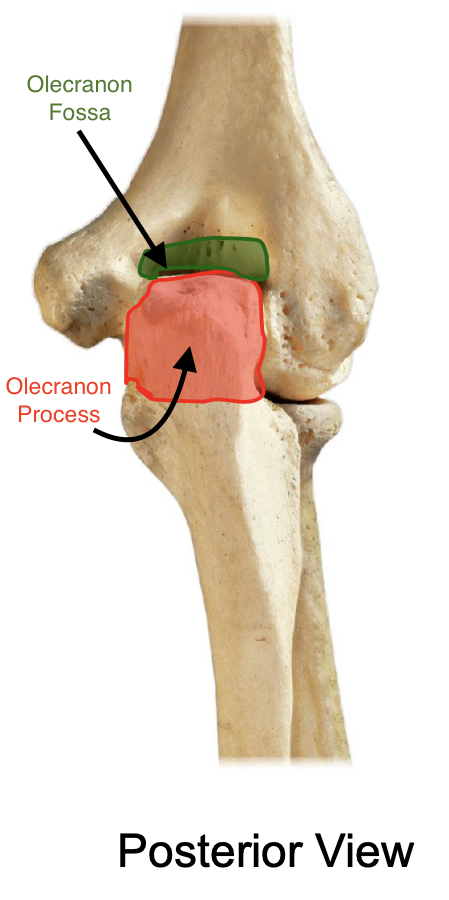
Olecranon process of the ulna
the olecranon process of the ulna makes up the superior or inferior lip of the trochlear other of the ulna?
The superior lip
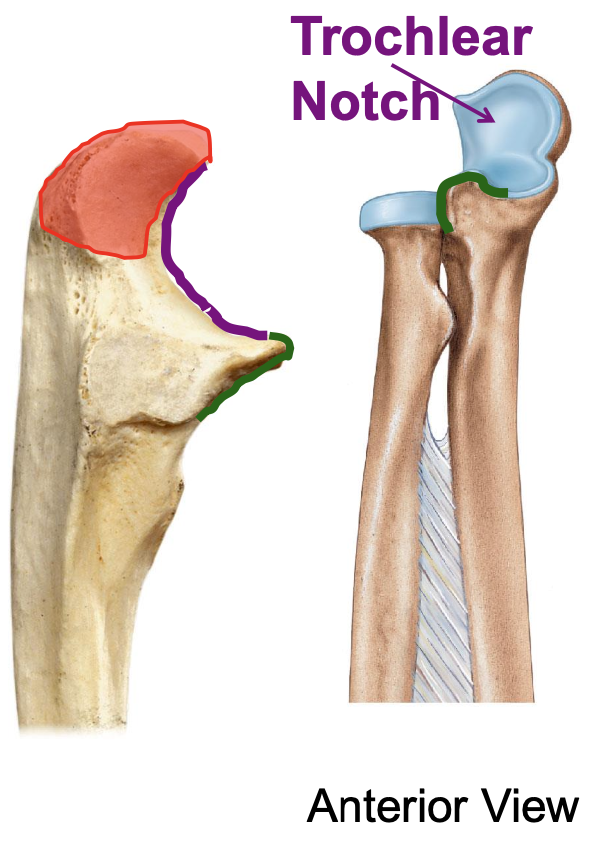
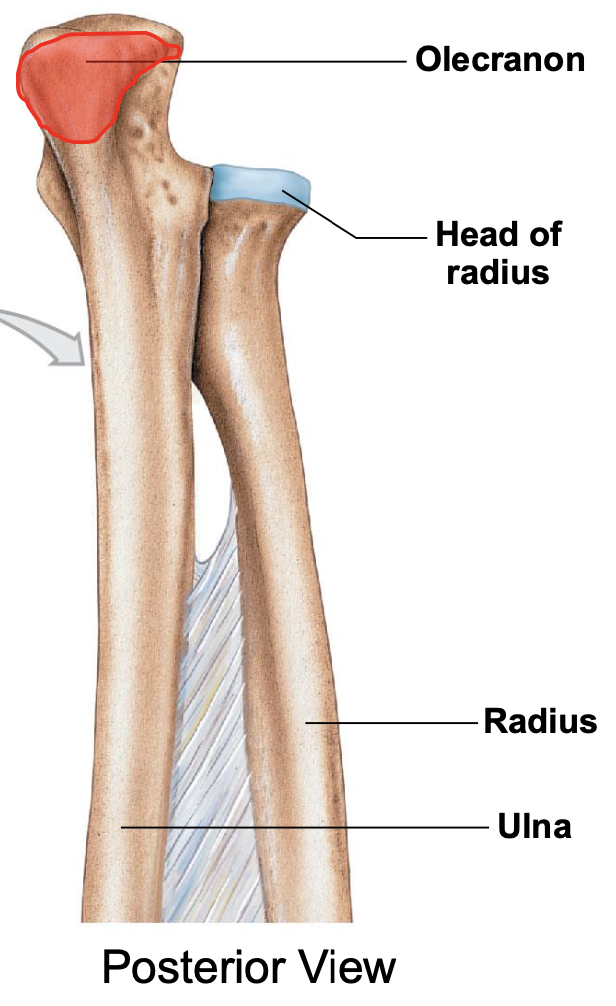
Olecranon process of ulna located on posterior part of elbow (can only be seen from posterior view)
olecranon and trochlear notch of ulna
olecranon process makes the
point of your elbow
radial notch of ulna
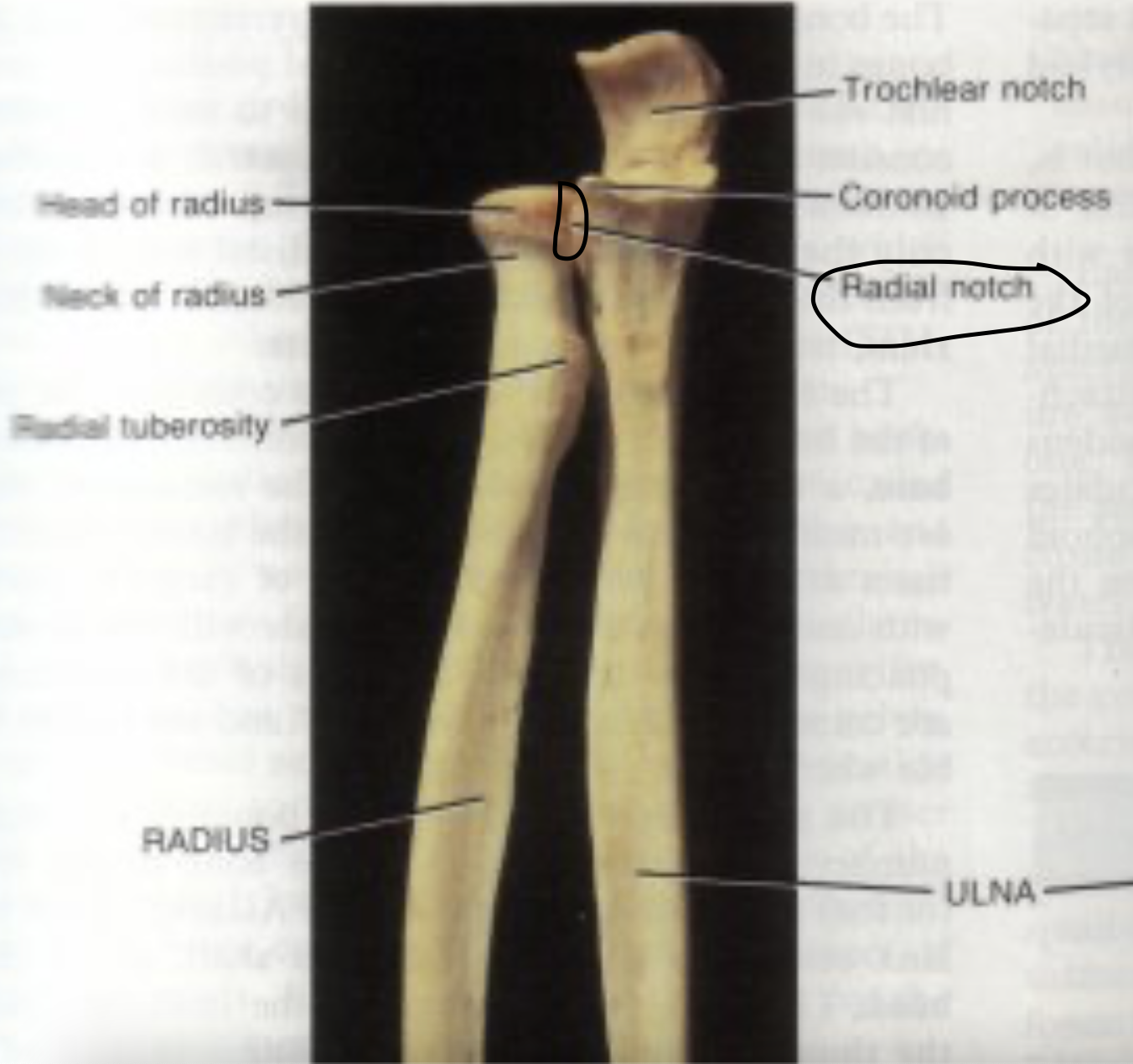
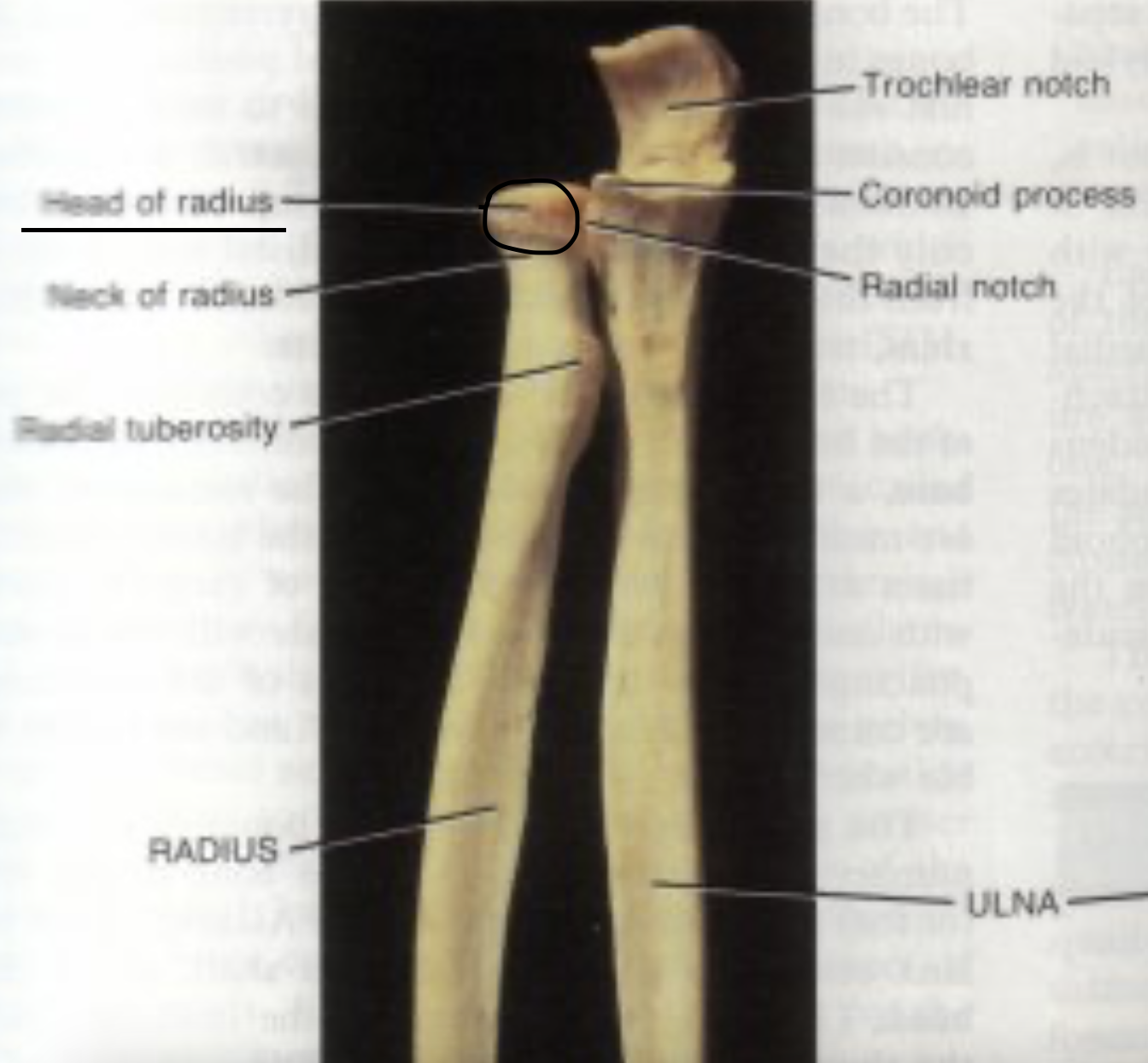
head of the radius
The head of the radius articulates with the radial notice of the ulna at the
proximal end
the olecranon process of the ulna enters into the
olecranon fossa of the humerus when the elbow is extended
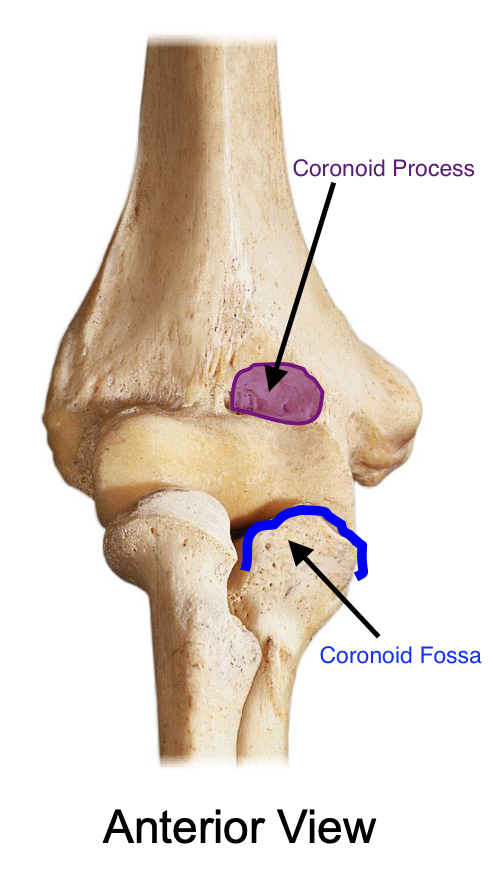
The coronoid process enters the
coronoid fossa of the humerus when the elbow is flexed
The head of the radius articulates with the
capitulum of the humerus
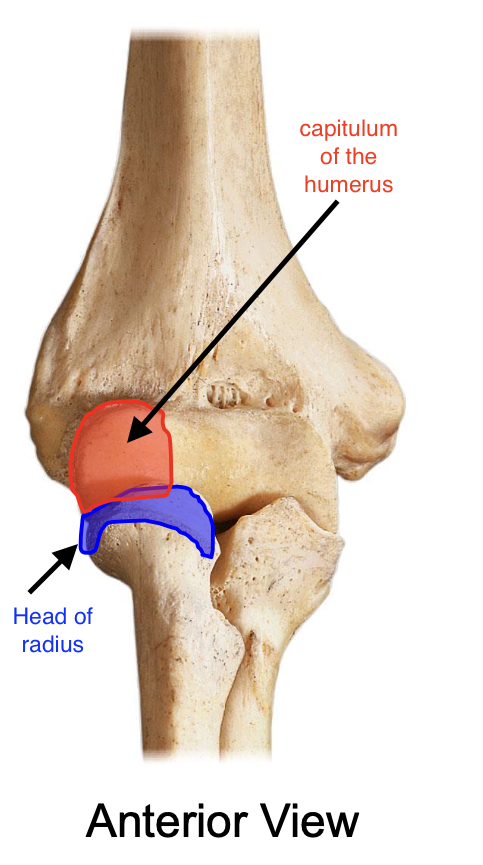
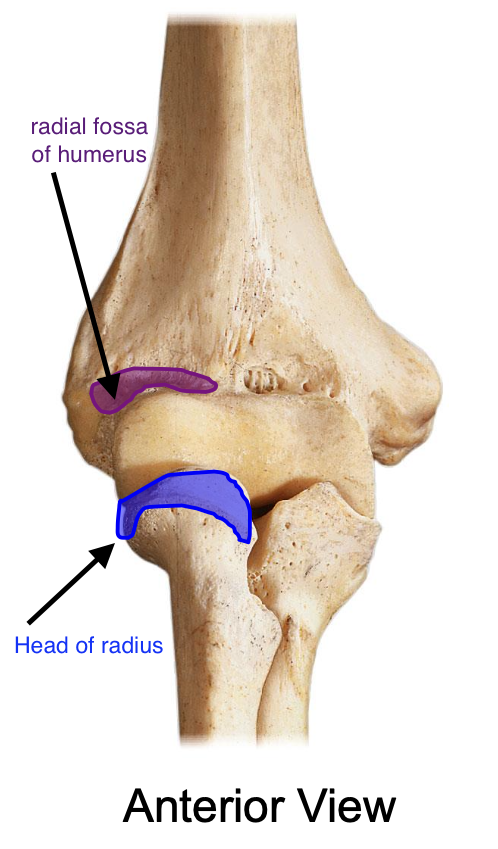
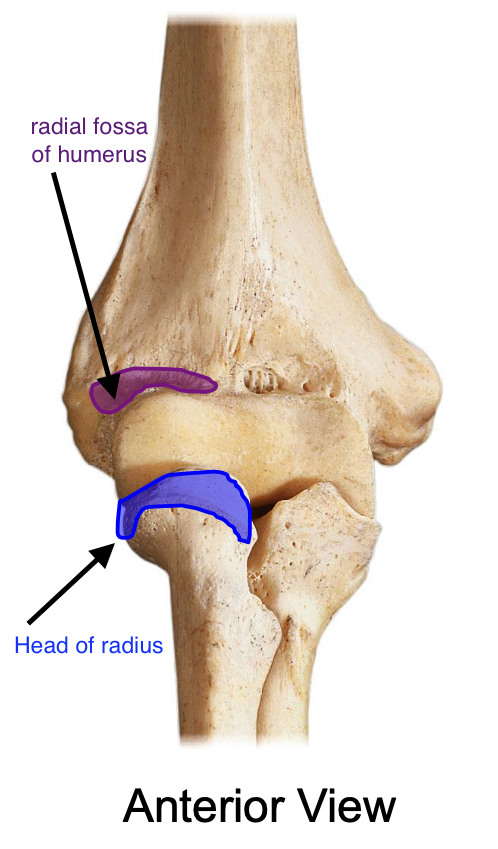
The head of the radius enters into the
radial fossa of the humerus when the elbow is fixed
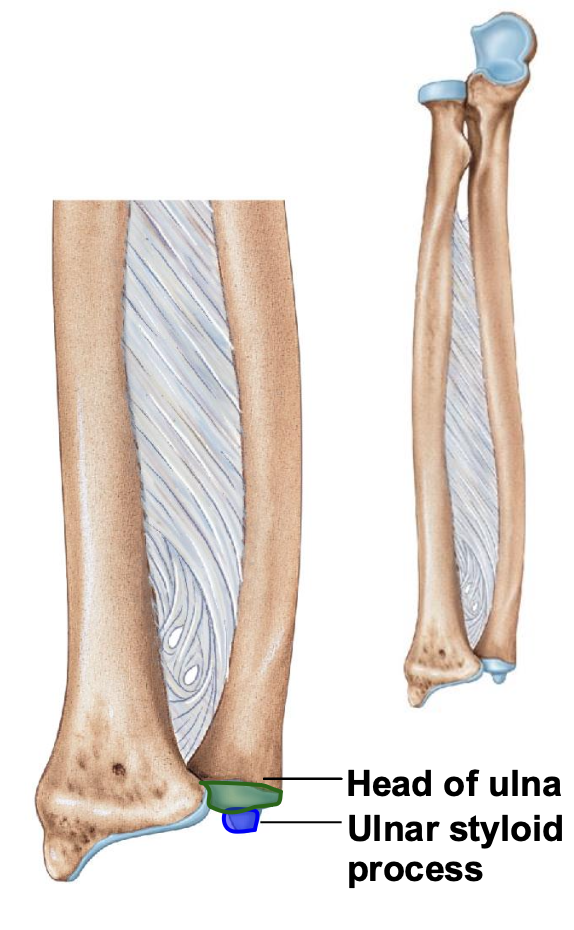
Head of ulna
distal
disc shaped
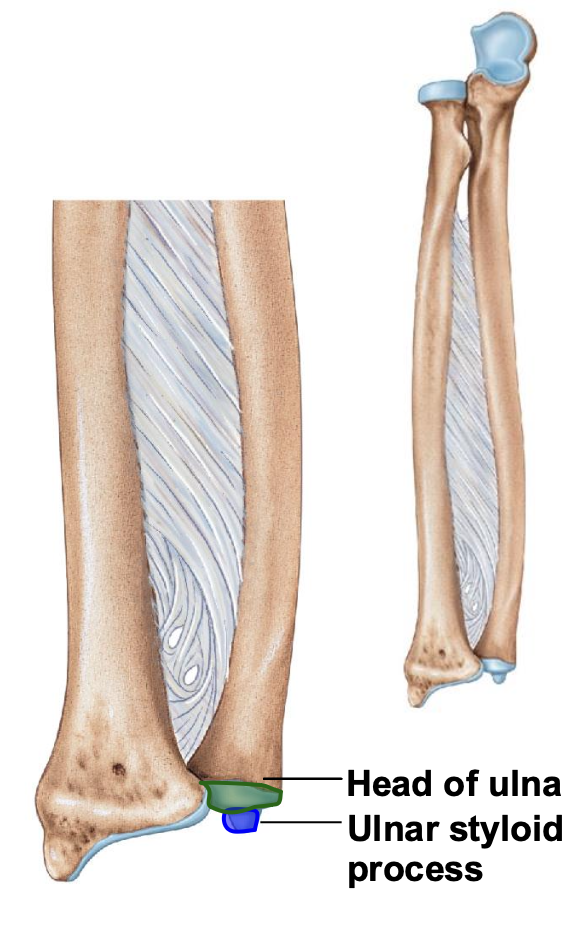
Styloid process of ulna
Medial
Radius
Lateral forearm bone
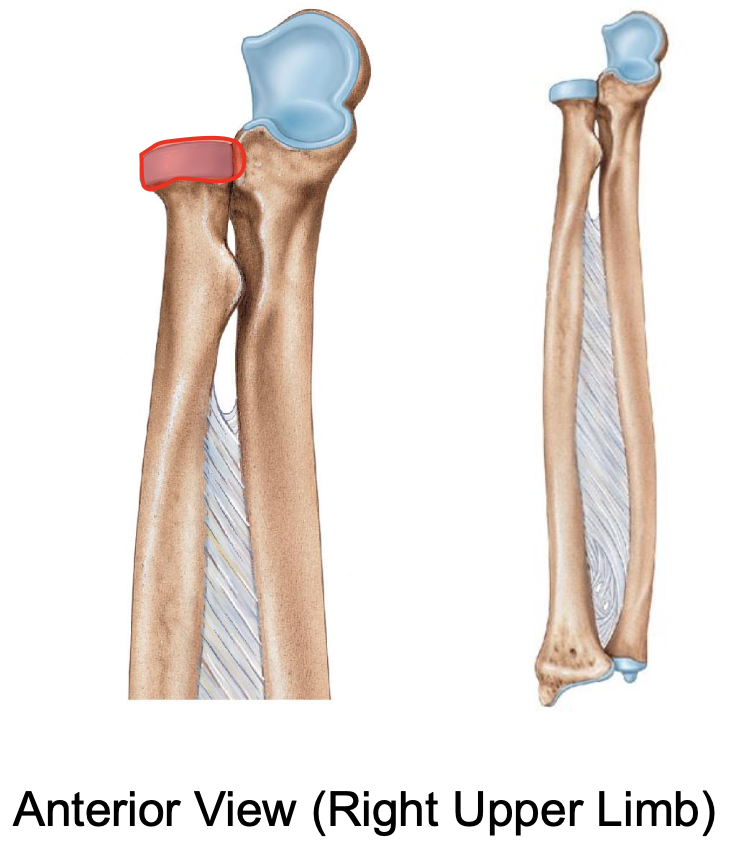
Head of radius
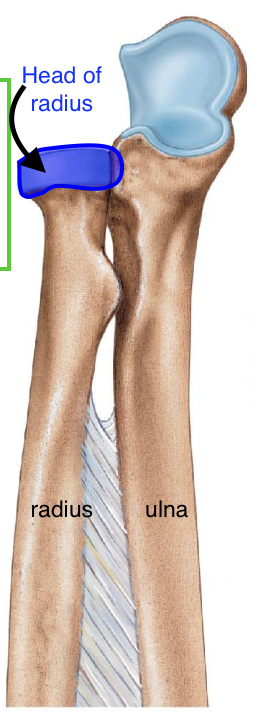
The head of the radius articulates with the
capitulum of the humerus
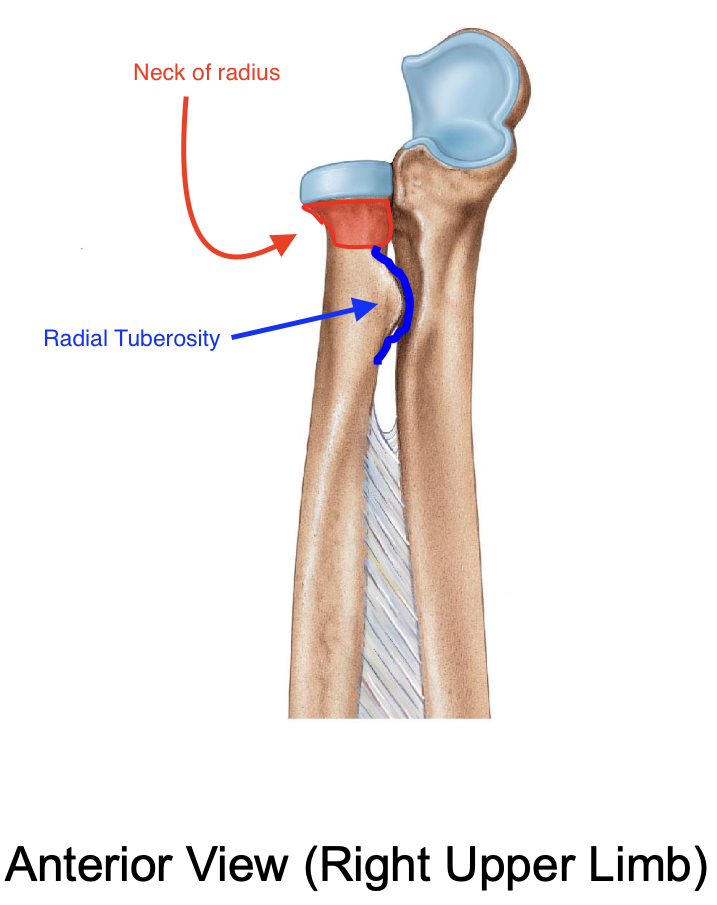
Neck of the radius
The radial tuberosity
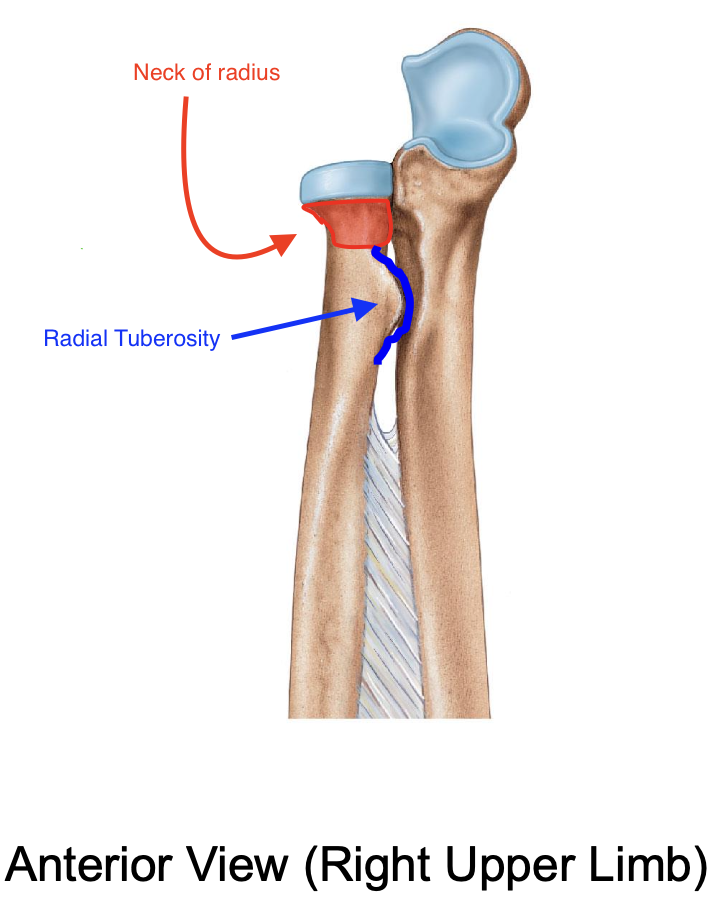
Importance of the radial tuberosity
Attachment site for biceps brachii
ulnar notch