03 - Innate Immunity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
phases of immune response
immediate innate response: 0-4 hours
antimicrobial peptides → disrupt microbial membranes
complement → opsonize and lyse microbes
resident macrophages → phagocytose pathogens, release cytokines
dendritic cells → sample antigens, prepare adaptive immunity
induced innate response: 4 hours - 4 days
cytokine release → induce vascular permeability, raise temperature
chemokines → recruit neutrophils and monocytes
fever → restrict microbial survival
inflammation → stimulate dendritic cell migration to lymph nodes
adaptive immune response: >4 days
occurs only if innate immune response fails
T cell and B cell activation
barriers of innate immunity
mechanical barriers → tight junctions, mucus, cilia, fluid flow
chemical barriers → low pH, lysozymes, antimicrobial peptides
microbiological barriers → normal microbiota
antibiotics will cause loss of microbiota → C. difficile, Candida
antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)
amphipathic proteins that insert into membranes, forming pores and causing cell death (e.g. defensins)
constitutively expressed or inducible
produced by neutrophils, keratinocytes, paneth cells
can be downregulated by cytokines
IL4 → decreased defensins → eczema → S. aureus
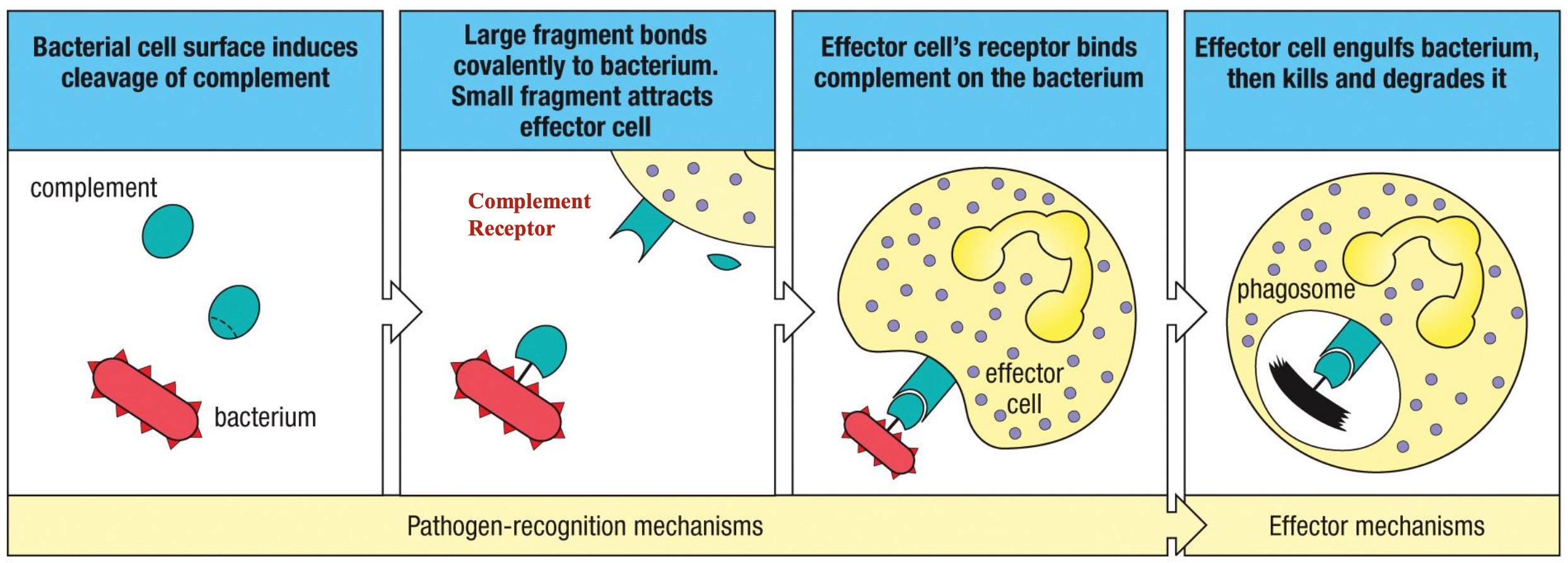
complement
set of proteins found in blood and lymph
opsonization → C3b
inflammation → C3a, C5a
cell lysis → MAC: C5b - C9
complement system pathways
alternative → first-activated
environment at pathogen surface alters C3 conformation to resemble that of activated C3b
lectin pathway → second activated
mannose-binding lectin binds to pathogen surface
activates complement cascade to produce C3b
classical pathway → last activated
C-reactive protein or antibody binds specific antigens on pathogen surface
activates complement cascade to produce C3b
macrophages
mature form of monocytes
found in tissues
long-lived
produce cytokines
initiate inflammation
neutrophils
most abundant WBC
short-lived
attracted by cytokines produced by macrophages
forms pus
kill using reactive oxygen species
undergoes apoptosis or NETosis (neutrophil extracellular traps)
innate immune receptors
pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
binding facilitates phagocytosis, production of antimicrobial products, cytokine release and inflammation, and expression of co-stimulatory molecules
production of anti-microbial products
binding immune receptors to PAMPs can initiate production of antimicrobial products
acidification → pH of 3.5-4.0 is bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal
respiratory burst → generates reactive oxygen / nitrogen species
antimicrobial peptides → defensins
enzymes → lysozyme, acid hydrolase
pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
danger signals that trigger innate immune response
lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
peptidoglycan
teichoic acid
flagellin
dsRNA
CpG DNA (unmethylated)\
zymosan (fungi)
toll-like receptors
family of transmembrane proteins on macrophages that act as PRRs in innate immunity
sense danger, trigger signal transduction, and induce inflammatory cytokine and interferon release
surface TLRs → sense bacterial products
endosomal TLRs → sense viral nucleic acids
TLR4 → detects LPS from gram-negative bacteria
TLR9 → detects unmethylated CpG DNA
TLR3 → detects dsRNA from viruses
bacterial lipopolysaccharide is recognized by
TLR4, MD2, and CD14 complex
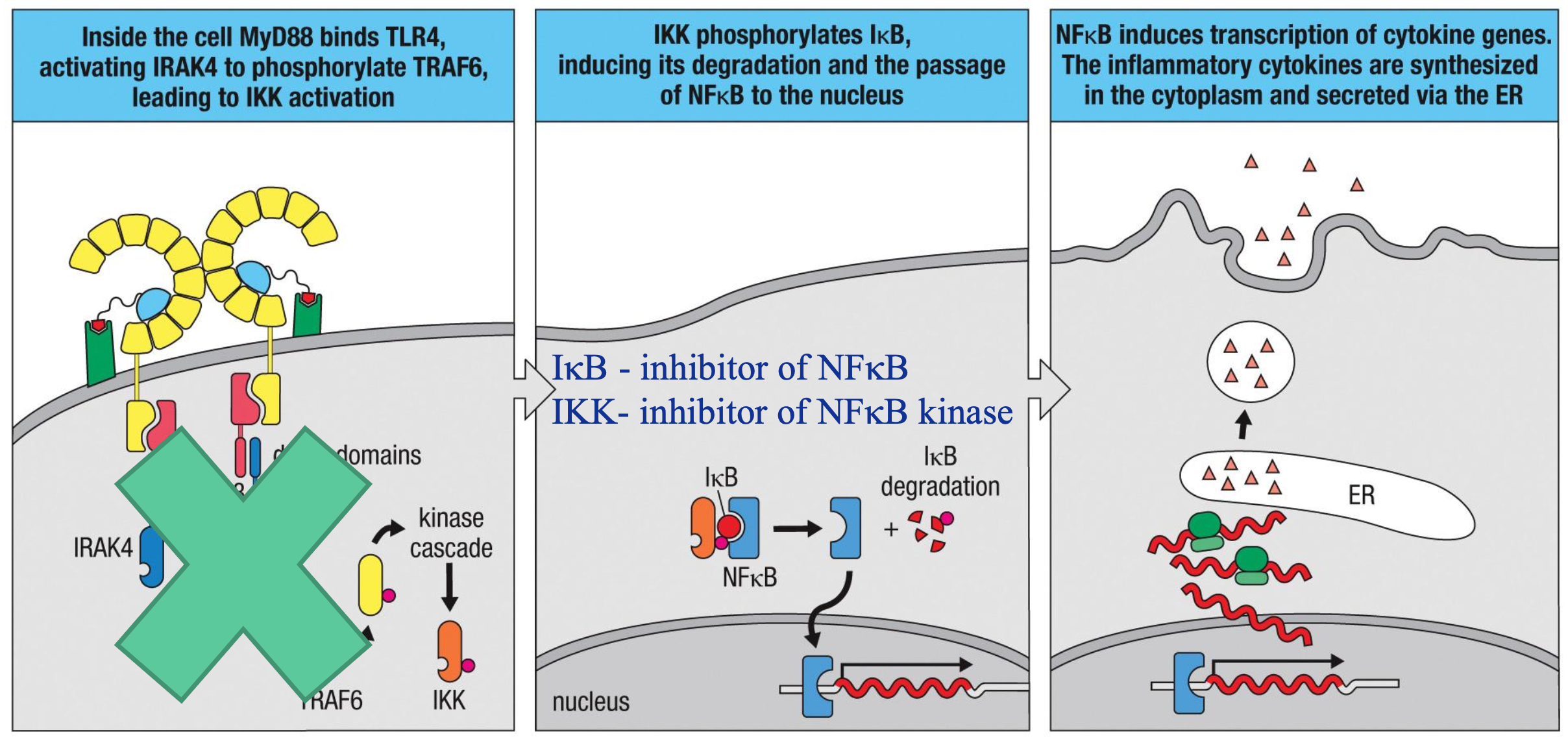
signal transduction for cytokine release
NFκB is the transcription factor that turns on inflammatory genes
TLR engagement → bacterial LPS is recognized by complex of TLR4, MD2 and CD14
IKK activation → inside the cell, MyD88 binds TLR4 to activate IRAK4 for phosphorylating TRAF6; leads to IKK activation
IκB degradation → IKK phosphorylates IκB, inducing its degradation and allowing passage of NFκB into nucleus
IκB → inhibitor of NFκB
IKK → inhibitor of NFκB kinase
NFκB enters nucleus → NFκB induces transcription of cytokine genes for release via ER
steroids upregulate IκB, reducing NFκB and reducing inflammation
intracellular innate receptors
bacteria → NOD-like receptors (NLRs)
detect bacterial cell wall fragments in cytoplasm
NOD1/2 bind fragments and dimerize
RIPK2 recruited to activate NFκB
viruses → RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs)
detect viral DNA that should not be in cytoplasm
virus infects cell, and its RNA accumulates in cytosol
RIG-1 / MDA5 bind viral RNA to activate adaptor proteins
activates interferons and NFκB
cytokines
substances released by macrophages for inflammatory response at site of infection
TNF-⍺ → induces vessel permeability
IL-1β → induces fever, activate endothelial cells to express adhesion molecules
IL-6 → trigger acute phase by inducing CRP and MBL production
CXCL8 (IL-8) → recruits neutrophils
CCL2 → recruits monocytes
IL-12 → activates NK cells to secrete cytokines
NLRP3 inflammasome
multi-protein complex of innate immunity that senses pathogens and cellular damage, triggering inflammation and producing cytokines
activated by ATP and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
activates caspase-1
converts pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into IL-1β and IL-18
positive feedback loop → cytokine storm
IL-5 induces proinflammatory pathways
acute phase proteins
IL-6 induces hepatocytes to synthesize acute-phase proteins
C-reactive protein (CRP) → opsonizes microbes, activates complement
activates classical pathway
serum indicator of systemic inflammation
mannose-binding lectin (MBL) → binds mannose residues on pathogens, activates complement
interferons ⍺ and β
produced by virus-infected cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells
inhibit viral replication by shutting down protein synthesis
upregulate MHC1 to enhance CD8+ recognition
activate NK cells to kill virus-infected cells
induce antiviral genes in neighboring cells
activate dendritic cells and macrophages
induce chemokines to recruit lymphocytes
NK cells
innate cytotoxic T cells without T cell receptors that kill stressed, infected, and transformed cells
multiple receptors → balance of activating vs inhibitory signals
ligands → glycoproteins in cells undergoing stress
activated by IFN-⍺, IFN-β and IL-12
produces IFN-ɣ to stimulate T cells and macrophages
STAT1 / STAT2 activation
type I interferons activate STAT1 and STAT2 to induce resistance against viral infection
increase MHCI expression
activate NK cells
induce chemokines to recruit additional immune cells