ITM chapter 5
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
database
well designed, organized, and carefully managed collection of data
data
raw facts
information
collection of organized and processed data and has additional value beyond the value of individual facts
knowledge
provides awareness and understanding of a set of information, and shows how information can support a specific task or be used to reach a decision
high-quality data
accessible, accurate, complete, economical, relevant, reliable
benefits gained from high quality data
improved decision making, increase of costumer satisfaction, increase in sales, innovation improvement, raises productivity, ensures compliance
accessible data
information should be easily accessible by authorized users so they can obtain it in the right format and at the right time to meet their needs
accurate data
error free and in some cases, inaccurate information is generated because inaccurate data is fed into the transformation process from data to information. called garbage in, garbage out.
complete data
contains all the important facts. for example, an investment report that does not include all important costs is not complete.
economical data
should also be relatively economical to produce. decision makers must always balance the value of information with the cost of producing it
relevant data
important to the decision maker. information showing that lumber prices might drop is probably not relevant to a computer chip manufacturer
reliable data
can be trusted by users. in cases the reliability of the information depends on the reliability of the data-collection method. a rumor from an unknown source that oil prices might go up may not be reliable.
timely data
delivered when it is needed. knowing last week’s weather conditions will not help when trying to
decide what coat to wear today
verifiable data
you can check it to make sure it is correct, perhaps by checking many sources for the same information.
data hierarchy - entity
person, place, or thing for which data is collected, stored and maintaine
data hierarchy - file
collection of entities
data hierarchy - attribute
characteristic of an entity
data hierarchy - domain
range of allowable values for a data attribute
data hierarchy - data item
specific value of a data attribute
data hierarchy - record
collection of attributes about a specific entity
data hierarchy - primary key
attribute or set of attributes that uniquely identifies the record
data hierarchy - foreign key
attribute in one table that refers to the primary key in another table
database management system
a group of programs provided by the DBMS supplier, programs used to access and manage a database, and provides an interface between the database and its users and other application programs
schema
a description that defines the databases’ logical and physical structure, and identifies the tables and the attributes in each table, also identifies the relationships between attributes and tables, DBMS can reference a schema
relational database
data is organized into relations, rows are entities, columns are attributes
selecting
eliminating rows according to certain criteria
projecting
eliminating columns in a table
joining
combining two or more tables through data attributes to create a new table
data normalization
eliminates data redundancy
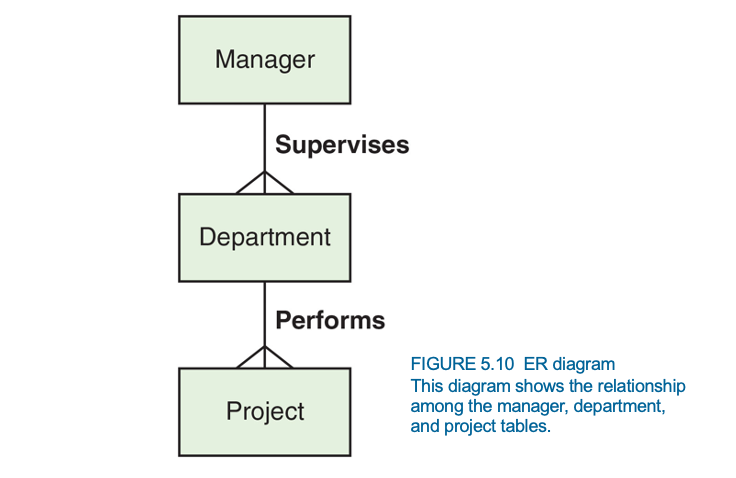
relational database MODEL
the manager supervises, the department proforms, and it ends in the project
SQL
special purpose programming language used for accessing and manipulating relational database data
SQL database
conform to ACID properties
SELECT ClientName, Debt FROM Client WHERE Debt > 1000
displays clients (ClientName) and the amount they owe the company (Debt) from a database table called Client; the query would only display clients who owe the company more than $1,000 (WHERE Debt > 1000).
data management
integrated set of functions that defines the processes by which data is obtained. certified fit for use, stored, secured and processed.
database administrator
skilled and trained IS professional that holds discussions with business users and defines their data needs
data steward
a non IS employee that manages critical date entities or attributes
database lifecycle management (DLM)
a policy based approach, manages enterprises data flow
concurrency control
the process of coordinating multiple transactions to make sure they are executed properly