muscle spindles and the reflex arc
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 2 week 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what is proprioception and what are examples
the skeletal muscle “tells” your brain where it is in space and your brain can perceive its location and generate movement
ex: not looking at your fingers as you type or looking at your legs as you walk
how is the this ability of skeletal muscle to brain communication possible
bc of the presence of special receptors in the muscle that sends signals back to the brain
these receptors include muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs
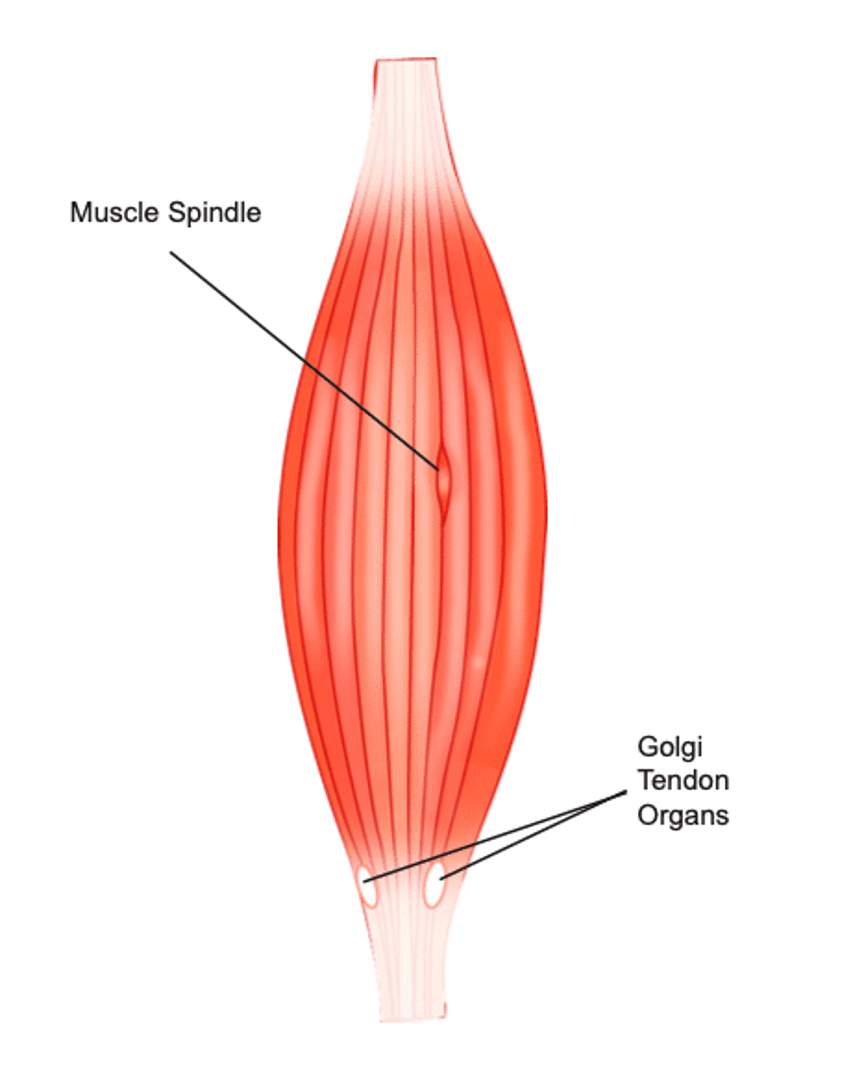
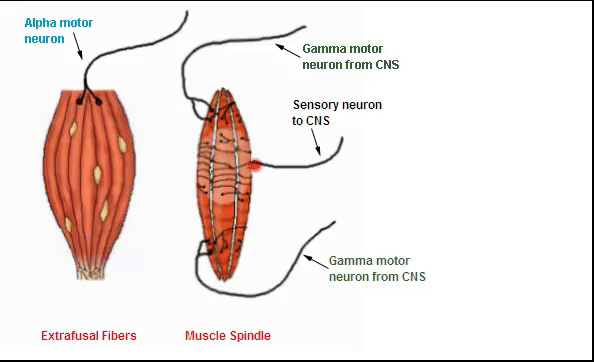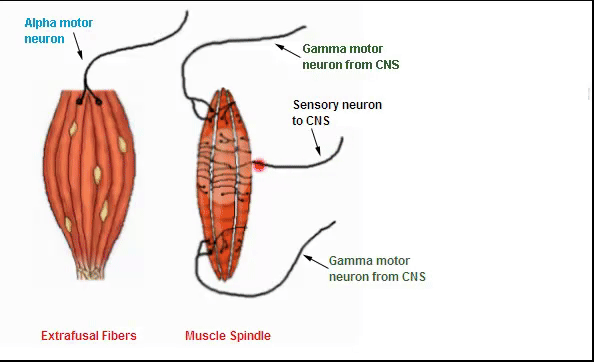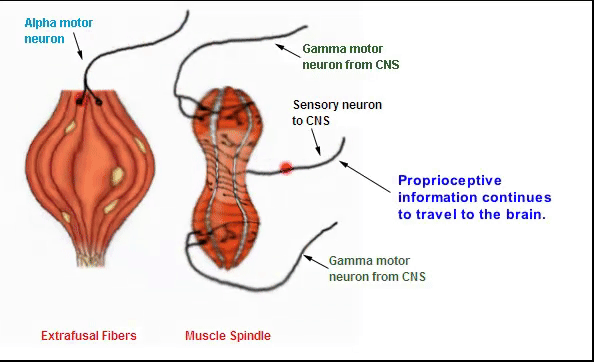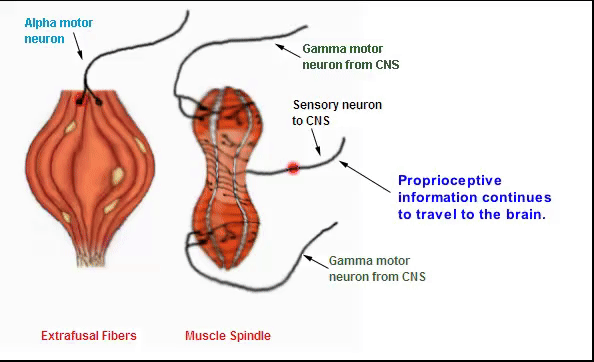
muscle spindles function and location
detect muscle stretch, muscle length, and the rate of change of muscle length
located between skeletal muscle fibers
role is sense when a muscle is over stretched and send signal to brain to increase force production to prevent damage
stretches along with muscle fibers bc its parallel with extrafusal fibers
Golgi tendon organs function and location
detects muscle tension
located in the muscle tendon junction and detects changes in muscle tension and force produced by contraction
can override the signals from the muscle spindles and signal minute changes in muscle tension for better control of force generated
protect the muscle from overload, especially during activities that require large force
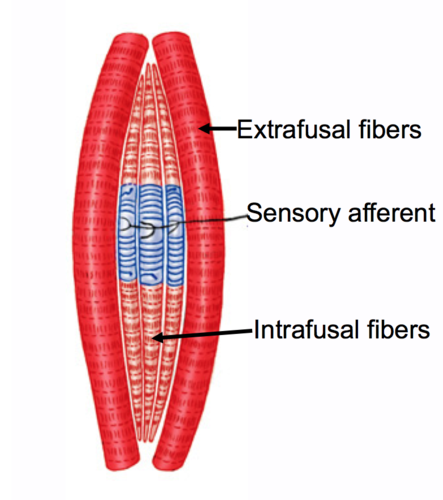
muscle spindles are collections of… and they do not generate… but
6-8 specialized fibers. they themselves do not generate force but rather signal changes in length and the rate at which these changes occur
because of the muscle spindles _____ shape, they are referred to as ___.
fusiform (spindle shape), intrafusal (intra-location fusal - shape of cell) fibers.
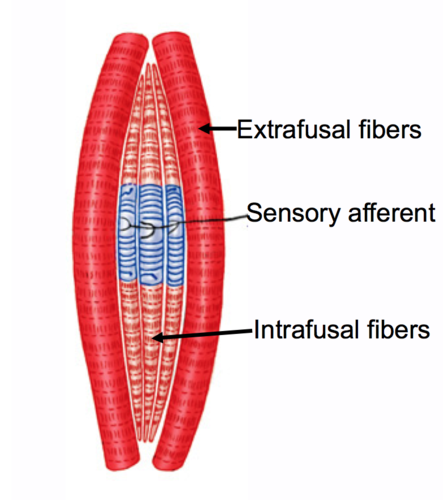
extrafusal fibers
the majority of muscle fibers that allow the muscle to generate power and muscle spindles are located parallel to extrafusal fibers
golgi tendon organ what is it and its location
specialized receptor
located between the muscle fiber and the tendon
located in series with the muscle
signals info abt the load or force applied to muscle
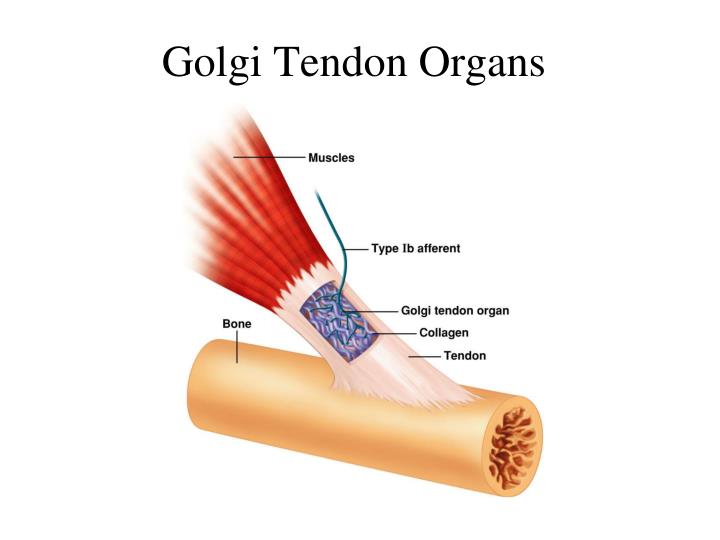
what is the golgi organ made of and what is it innervated by
a capsule containing collagen fibers and is innervated by primary afferent nerves (ib fibers, to distinguish them from the la fibers we find in muscle spindle)
when force is applied to the muscle, the golgi tendon organ is
stretched,
causing the collagen fibers to squeeze
distorts the plasma membranes of the primary sensory endings of the afferent nerves
as a result of squeezing, membrane of the afferent neuron depolarizes
fires an ap to signal the cns info abt the amount of force applied to muscle
what activates the intrafusal fibers
gamma motor neurons
when the whole muscle stretches, (whole process)
the sensory region of the spindles also stretches bc of it sensitivity to changes in shape
it triggers an ap in the sensory nerve, sending signals back to the brain
the more stretched the muscle, the more stretched the sensory region, the higher freq of ap thats sent back to cns
brain recieves info and can interpret how stretched the muscle is
it can then “know” the position of the limb in space (muscle attached to limb)
can then make a decision on the need to increase the freq of ap and number of motor unit activations going back to muscle
what is the concept of velocity
when the muscle spindle signals changes in length and how quickly/frequently these occur
when a muscle spindle signals changes in length, this info is sent where and through what
this info is sent to the cns thru two types of specialized sensory fibers that innervate the intrafusal fibers.
describe the specialized sensory fibers that innervate the intrafusal fibers
they have stretch receptors that open and close in response to changes in length of the intrafusal fibers
two types: primary afferens (la) and secondary afferens (ll)
they send info from the spindle to the cns (why theyre called afferent fibers)
this is how the brain interprets the position, stretch and frequency of muscle length change and can place your limbs into space
describe what the primary afferens do
provides info abt length changes and velocity
fire at high rate during stretching
firing rate depends on rate of change of the muscle length
firing decreases when the muscle is no longer stretching
describe what the secondary afferens do
provide info abt changes in length only
firing rate increases steadily during stretching
firing rate does not depend on the rate of change of the muscle length
it depends only on the immediate length of the muscle
two types of motor neurons
alpha motor neurons and gamma motor neurons
what do the alpha motor neurons do
innervate extrafusal fibers (muscle fibers that contract to generate power)
presynaptic neuron at the nmj is a alpha motor neuron
this is the neuron thats part of a motor unit as it can innervate multiple muscle fibers at the same time
gamma motor neurons
innervate intrafusal fibers
keep muscle spindle sensitive to stretch over a range of muscle lengths
allow the intrafusal fibers to stretch along with the extrafusal fibers
activating the sensory innervation and allowing it to continuously communicate with the cns
alpha-gamma co-activation needs to occur because…
for the muscle to function properly and for the brain to always know where the muscle is in space and how much power it needs to generate to perform an action, alpha-gamma co-activation occurs
what if there was no alpha-gamma coactivation
signals would be separated from each other and function in sequence
signal sent to the whole muscle from the cns, down thru the alpha motor neuron
to the skeletal muscle will cause the muscle to contract
extrafusal muscle fibers contract
intrafusal muscle fibers within muscle spindle would go slack and info from from spindle would stop
since no proprioceptive info reaching cns, brain doesnt know where muscle is in space
therefore wont know how much muscle contracts and if more force is needed
what happens when we go have alpha gamma co-activation
commands are simultaneously sent thru gamma motor neurons
to the intrafusal fibers to keep muscle spindles operating during contraction
causes contraction of intrafusal fibers (these contractions are not large enough to contribute to the force generated by skeletal muscle)
contraction in intrafusal fibers maintains stretch on central region where central receptors are located at the same rate as the whole muscle
during muscle contraction, alpha-gamma coactivation ensure that the muscle spindles continue to send info to brain abt muscle and limb position
why is gamma neuron activation important during muscle contraction
Gamma neurons stimulate intrafusal muscle fibers which send proprioceptive information back to the brain through sensory pathways
afferent pathway
take info from specific organs + tissues and send it to the cns for integration
when our body tries to maintain homeostasis by keeping our body in certain limits, info on over/under limit is sent to cns via afferent pathway
sensory innervation of muscle spindle is an afferent pathway
efferent pathways
also known as motor pathways
sends info from cns to effector organ (ex muscle)
alpha neuron that innervates skeletal muscle at nmj is an efferent (motor) neuron
gamma motor neurons are efferent neurons
reflex arc requires
a sensory receptor
a sensory (afferent neuron)
one or more synapses (generally in spinal cord)
1 or more interneurons
a motor (efferent) neuron
effector organ (skeletal muscle in this case)
reflex arc leads to ___ ____ . it would take much longer for_____
rapid response. the info to reach the brain, for the brain to integrate it and make a decision
stretch reflex (example of reflex arc) sequence
tapping patellar tendon produces a small stretch in the quadricep muscle
stretch of muscle leads to stretch of muscle spindles
which triggers an ap in the sensory/afferent neuron that enters the spinal cord
afferent sensory neuron synapses onto motor neuron of quad into spinal cord
motor nerve of quad is activated while innervation to opposing muscle, (hamstring), is inhibited due to reciprocal innervation
quad contracts and hammy relaxes, leading to lower leg kicking out
what is reciprocal innervation
contraction of one muscle resulting in relaxation of its oppsing muscle
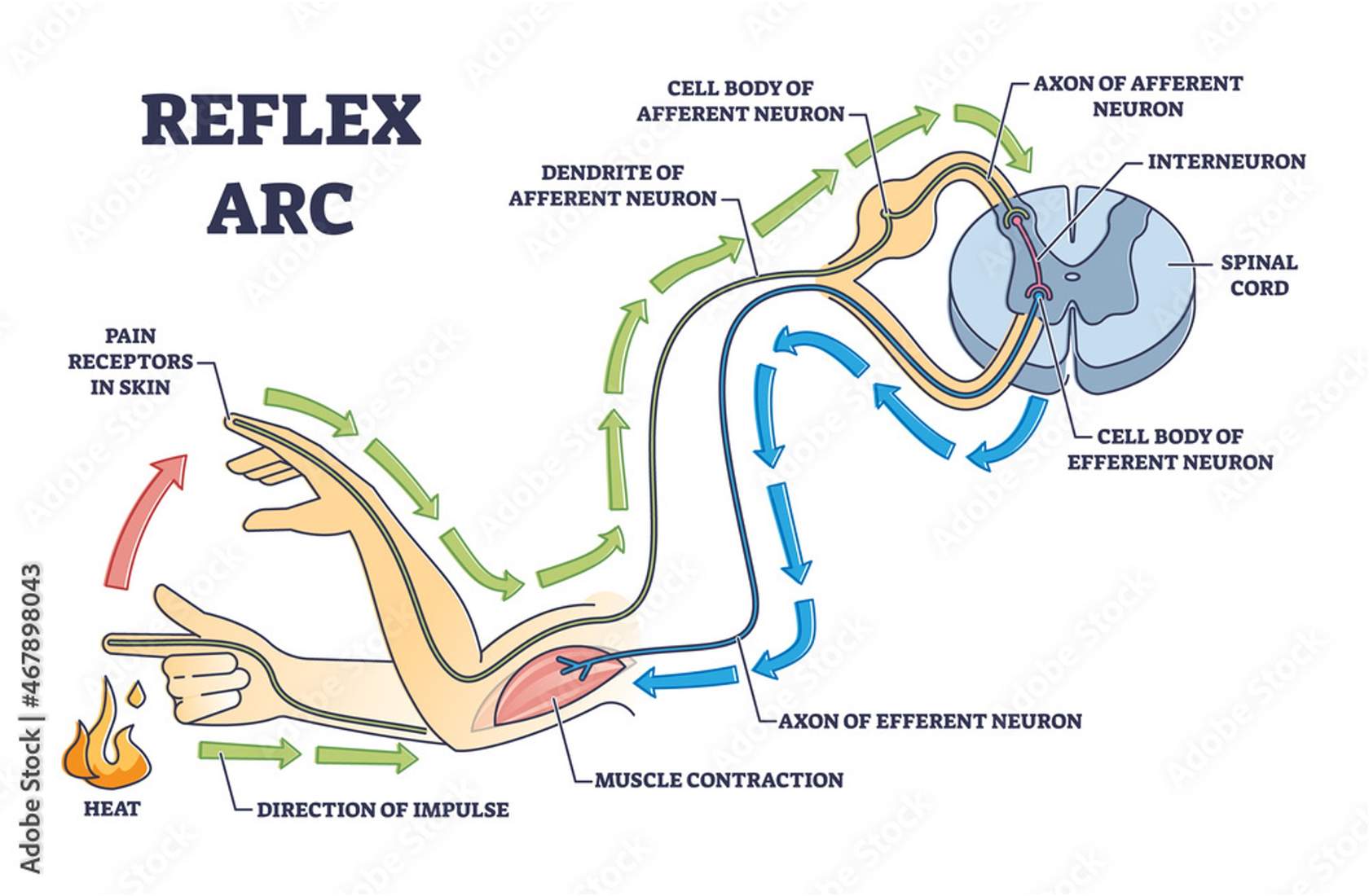
example of reflex arc situation
pain receptors in tip of finger send info to cns
sensory info from fingertip is sent to cns via afferent pathway
afferent neuron synapses with an interneuron (synapse in spinal cord, part of cns)
the interneuron synpases onto the efferent (motor) neuron (cell body of motor neuron in cns)
info travels down the motor neuron to effector organ (this case, skeletal muscle)
hand moves away from flame