Class 17 (Unit 7)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
How can the p-value can be found in a two-sided test?
2P(Z ≥ |test. stat.|)
absolute value
|z| = the positive version of z
Example (absolute value)
If we are conducting a two-sided test, and we calculate a test statistic of z =↘1.50, then the P-value is
2P(Z ≥ 1.50)
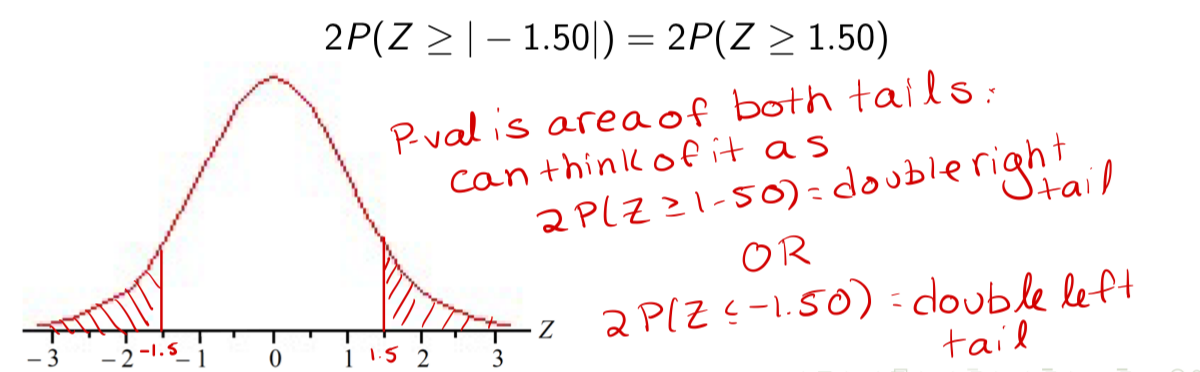
Summary of P-value for testing H0: μ = μο vs:
Ha : µ > µ0 is P(Z > z)
Ha : µ < µ0 is P(Z < z)
Ha : µ →= µ0 is 2P(Z > |z|)
When are the calculated P-values exact?
If the population is normal, and approximate for large sample sizes in other case (by the CLT)
P-value interpretation template
If the null hypothesis were true, then the probability of observing a sample mean at least as high/low/extreme as the sample mean observed would be P-value
Write Bold items in the context of the question
when do you write high? (P-value interpretation)
right-sided test
when do you write low? (P-value interpretation)
left-sided test
when do you write extreme? (P-value interpretation)
two-sided test
Verifying results
Notice that in the root beer example, we were very close to rejecting H0. Our P-value (0.0702) is only slightly higher than our level of significance (0.05)
Remember, the fact that we didn’t reject H0 doesn’t mean we have enough evidence to conclude that µ truly is 500 ml - it just means we didn’t have strong enough evidence to conclude with high enough certainty that µ differs from 500 ml.
Because we got a value of ¯ x that was very close to rejecting H0, the company might wish to take another sample of bottles, and conduct another test to verify the results
Some NO NO NO’s
“Our P-value of 0.0702 was almost lower than our level of significance ε = 0.05. Why don’t we just change α to be 0.10? Then our P-value is lower than α, and we can reject H0.”
Is it okay to do this???
mean ¯ x = 502, which is greater than 500. So it seems reasonable to think that if µ differs from 500, it is probably higher.
So why don’t we conduct an upper tailed test (i.e. right-sided test) of H0 : µ = 500 vs Ha : µ > 500? Then we would not have doubled the tail area, so that our P-value would have ended up being 0.0351. This is less than α = 0.05, and so we would be able to reject H0”
Is this okay to do???
Is it okay to change the level of significance?
No!!!!!!! It is unethical to make changes after a test has been completed
It is important that the level of significance is chosen before we conduct the test. It is not appropriate to change the level of significance after conducting the hypothesis test.
Is it okay to change a two-sided test into a upper tailed test? (
Still NO!!!! This is not appropriate! We were originally interested in determining whether µ differs from 500 in either direction.
Why can’t we change a two-sided test into a upper tailed test
The fact that ¯ x was greater than 500 doesn’t mean we can change our alternative hypothesis, as though suddenly we were only interested in µ being greater than 500
The hypotheses need to be determined before we conduct the test. It is unethical to change the hypotheses or the level of significance to get a certain desired outcome.
What is the other method for conducting a two-sided hypothesis test
confidence interval method
what two conditions must be satisfied to use a confidence interval to conduct a hypothesis test.
The test must be two-sided, and
The confidence level and level of significance must add up to 1
E.g. if we are conducting a two-sided test with a 1% level of significance, we need to use a 99% confidence interval
When does a two-sided test reject the null hypothesis (confidence interval method)
A two-sided test with significance level ε rejects the null hypothesis if µ0 falls outside the 100(1 - α)% confidence interval. If µ0 falls inside the interval, we fail to reject H0
Does this decision rule/ confidence interval method make sense?
YES!!! Think: we are supposed to be reasonably confident that our confidence interval contains the true value of µ.
If µ0 is outside our confidence interval, then it is not reasonable to believe that µ= µ0. Thus we reject H0.
If µ0 is inside of our confidence interval, that it is reasonable to believe that µ could be equal to µ0. Thus we fail to reject H0.
Confidence interval method steps
Statement of level of significance
Statement of hypotheses
Statement of decision rule:
Reject H0 if µ0 is not in the 100(1 - α)% confidence interval.
Calculation of 100(1≤ α)% confidence interval
Conclusion
Example (Confidence Interval Method)
Perform a hypothesis test for the root beer example, using the confidence interval method and α = 0.05
Statement of level of significance
Let α = 0.05
Statement of hypotheses
H0 : µ = 500 vs Ha : µ ≠ 500
Statement of decision rule:
Reject H0 if µ0 = 500 is not in the 95% confidence interval for µ
Calculation of 100(1≤ α)% confidence interval
The 95% confidence interval for µ is
Conclusion
Since µ0 = 500 falls within the 95% confidence interval, we fail to reject H0. At the 5% level of significance, we have insufficient evidence that the true mean volume of all bottles in the shipment differs from 500 ml.

Note (Confidence Interval Method)
For a 2-sided test, it shouldn’t matter which method you use: both methods (P-value or confidence interval) should bring you to the same conclusion
Conclusion Template (Confidence Interval Method)
Since µ0 = µ0 falls within/does not fall within the C% confidence interval, we fail to reject/reject H0. At the α% level of significance, we have insufficient/sufficient evidence that Ha is true.
Write the Bold items in the context of the question