NUFS 373 - Redox and antioxidants - topic 1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is oxidation?
The transfer of electrons (electron loss) or gaining oxygen atoms and increase in oxidation state.
What is reduction?
Gain of electrons or H+ gain, and decrease in oxidation state.
What is the most electronegative atom?
Fluorine
Since fluorine has high electronegativity, how does this affect its reduction potential?
It has a high reduction potential (strong tendency to gain electrons).
This also means it is the strongest oxidizing agent.
Which element is the strongest reducing agent?
Lithium (easily oxidized)
α-tocopherol has a lower standard reduction potential than PUFA. How does this contribute to antioxidant activity?
α-tocopherol can become oxidized by PUFA to turn it into radical. Which can help protect against lipid oxidation.
For an antioxidant to protect another compound from oxidation, where does its reduction potential have to be?
Lower than the compound it is protecting.
What is an FRS?
Free radical scavenger
Display a balanced equation of how free radical scavengers interact with oxidizing agents:

How does resonance help stabilize lipid hydroperoxyl radicals (ROO•)?
Can gain H•, which can convert it into hydroperoxide (ROOH).
How do phenolic antioxidants act in rosemary extracts?
Once added to the rosemary oil, it takes electrons and delocalizes it to protect the extract from fatty acid oxidation.
Name a few examples of phenolic antioxidants found in rosemary extract:
Carnosic acid, carnosol, rosemarinic acid
Draw the resonance forms of ascorbic acid:
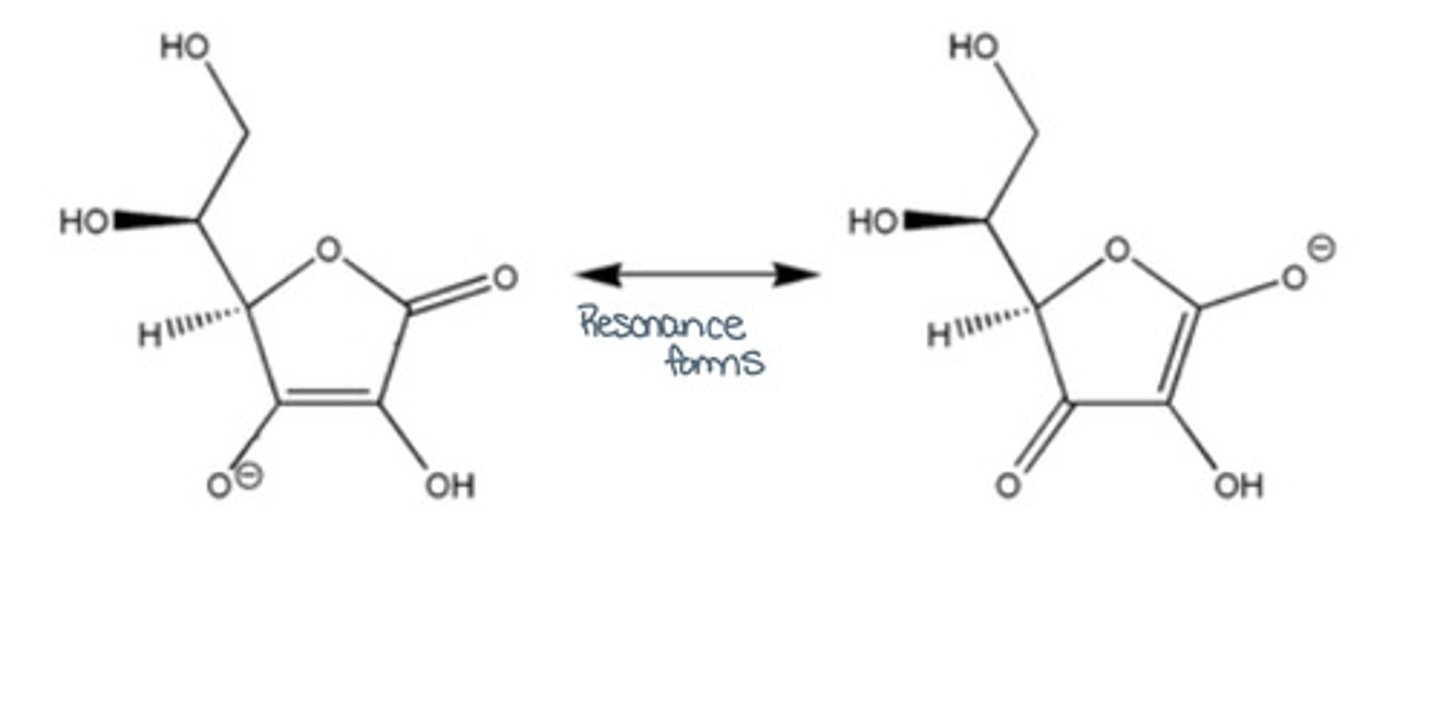
Based on this information, is ascorbic acid soluble in oils or not? What is the exception?
No it is not soluble in oils.
The exception is ascorbyl palmitate (scavenging singlet oxygen) that can still inhibit lipid auto oxidation.
What is the sequence of ascorbate anion oxidation?
1. Ascorbate (reduced form) gets oxidized (1 electron loss) to an ascorbyl radical.
2. Ascorbyl radical gets further oxidized (2 electron loss) to L-dehydroascorbate (DHAA) or semihydroascorbate radical
- This has similar vitamin C activity (reduced form)
3. Dehydroascorbate gets hydrolyzed to 2,3-diketogulonate, losing its vitamin C activity.
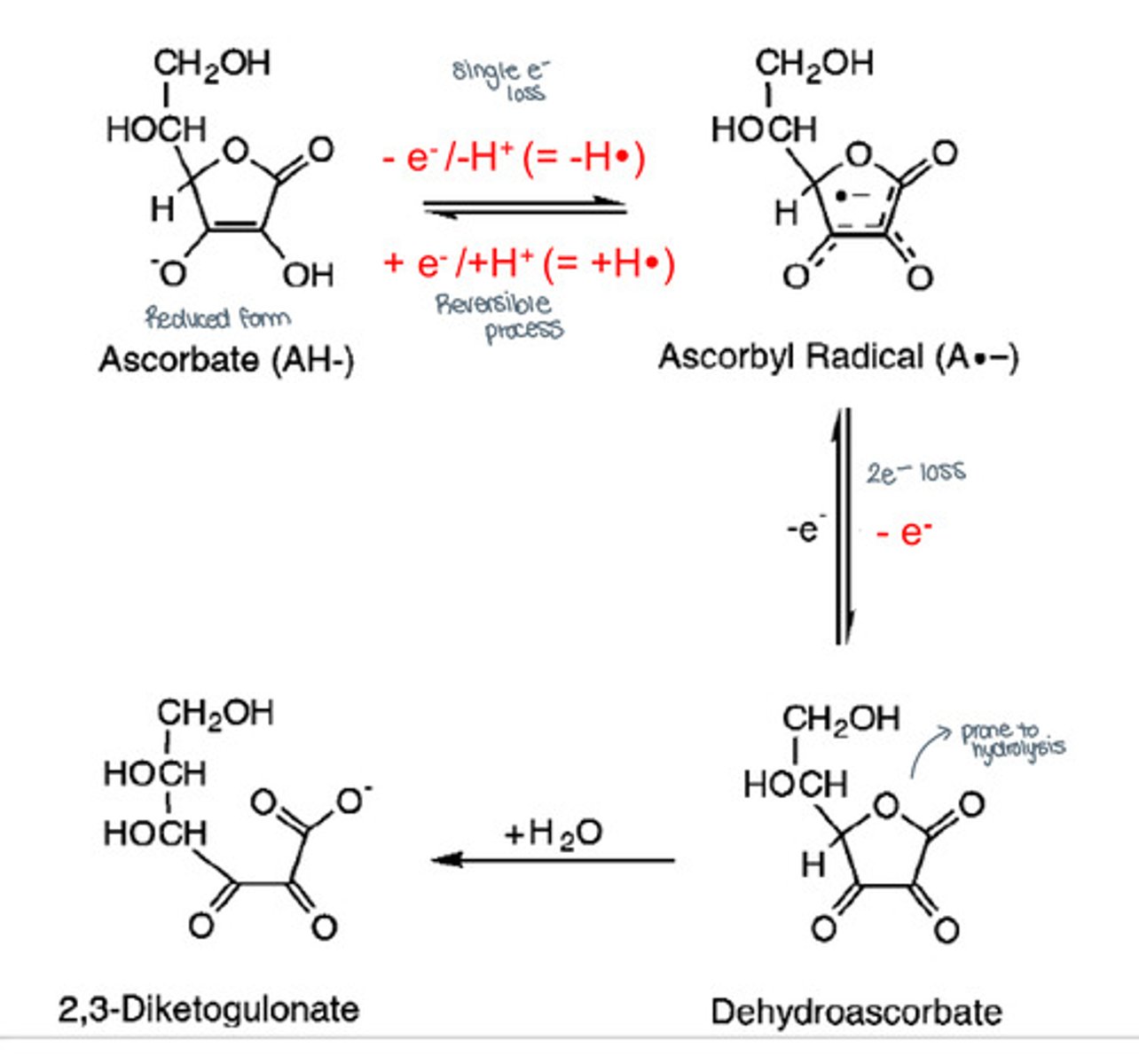
Based on the stability of ascorbic acid, what determines the loss of vitamin C activity?
The rate of ascorbate anion converted to L-dehydroascorbate
How does ascorbic acid act as a free radical scavenger?
Wants to form the stable radical anion and gets regenerated by reacting with other reducing agents such as glutathione and NADH + H+.
How is it possible that the ascorbic acid anion radical remains stable?
Due to extensive delocalization.
How does ascorbate in vegetables become affected by blanching (high temperature and water)?
As heat increases, this causes the cell to rupture which releases ascorbate oxidase enzyme. As blanching occurs, the level of ascorbate in the vegetable decreases, while increasing in the water. Ascorbate oxidase enzyme oxidizes ascorbate to dehydroxyascorbate.
Dehydroxyascorbate levels rise, but eventually fall due to enzyme deactivation. Deactivation will slowly allow ascorbate levels in the vegetables to pick up again.
What are other factors that affect ascorbic acid oxidation?
- Transition metal catalysis accelerates this process (Cu2+, Fe3+)
- Heat, light
- Dissolved oxygen and water
- When pH rises above 8 as the pKa of [A-2H]^2- form is controlled by a 11.4 pKa value.
At what pH is ascorbic acid most stable at?
pH close to 4, because in foods, most AA pKa is 4.04.
What are the roles of ascorbic acid as a reducing agent in foods?
- Inhibits enzyme browning by reducing ortho-quinones to ortho-phenolics
- Inhibition of oxidation in foods
- Reductive action in dough conditioners
- Protects compounds most susceptible to oxidation such as folates
- Can break disulphide bonds
- Inhibition of nitrosamine formation in cured meat
- Reduction of metal ions
What is niacin?
Water soluble vitamin that can act as a coenzyme (NAD, NADP) and is widely distributed in foods (generally stable)
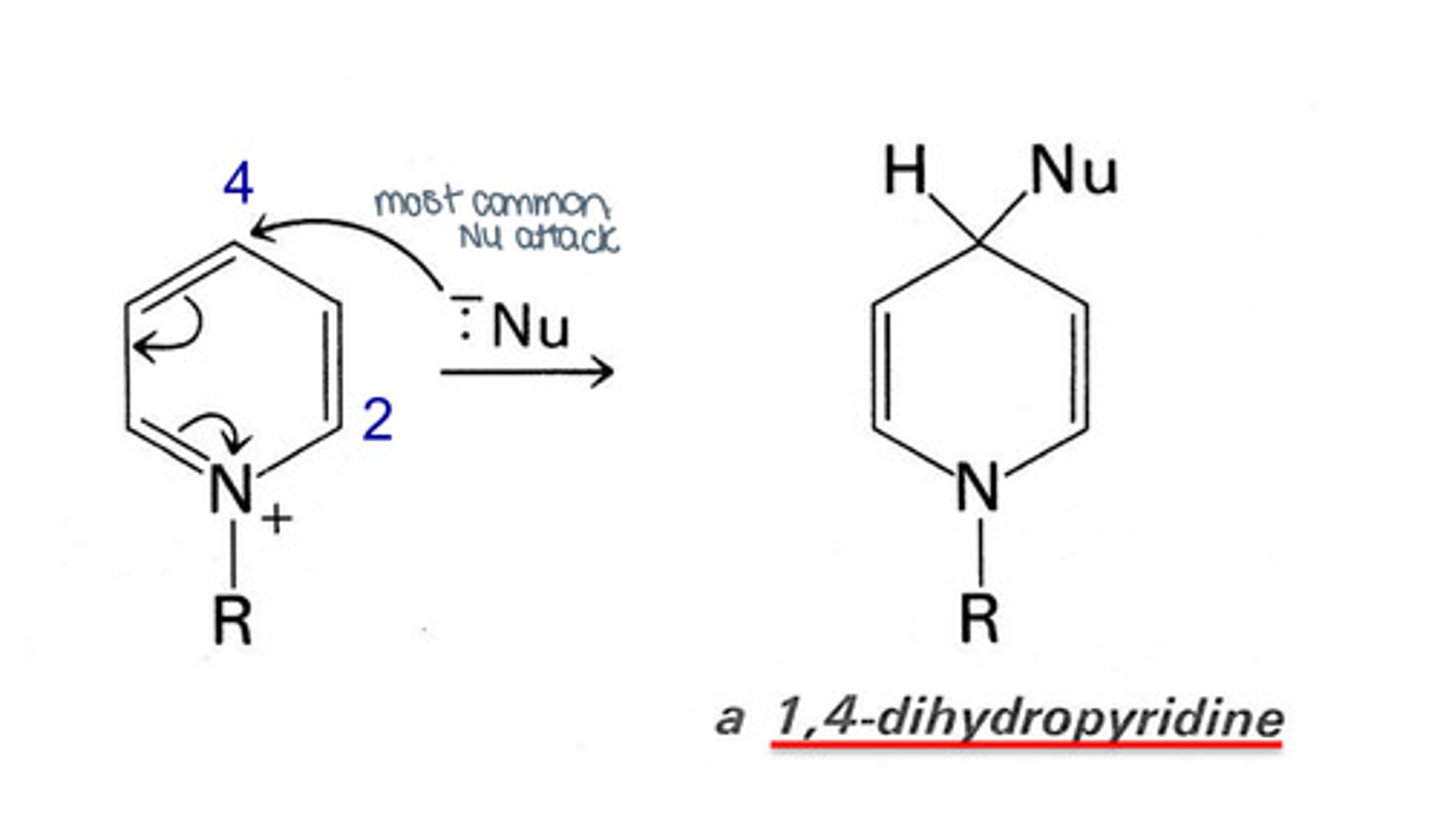
Even though pyridine is aromatic, it cannot participate in pi-bonding. What does it form instead?
Pyridinium ions/salts.
How do pyridinium ions interact with nucleophiles?
Susceptible to nucleophilic attack at positions 2 and 4 (most common), which typically turns it into 1,4-dihydroxypyridine (NADH).
This is done under the influence of alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme.
How is NAD+ regenerated?
Oxidation involving cytochromes
What two forms of riboflavin are coenzymes with redox activities?
FAD and FMN
Over 80% of what flavin forms are found in bovine and human milk?
Free riboflavin and FAD
What can the pyridine ring in NAD+ be used for?
Used as an oxidizing agent/coenzyme in many enzymatic reactions.
FMN and FAD are used as a food additive. What colour?
Orange-red
What form of flavin is the oxidized form? What colour is it?
Flavoquinone, yellow
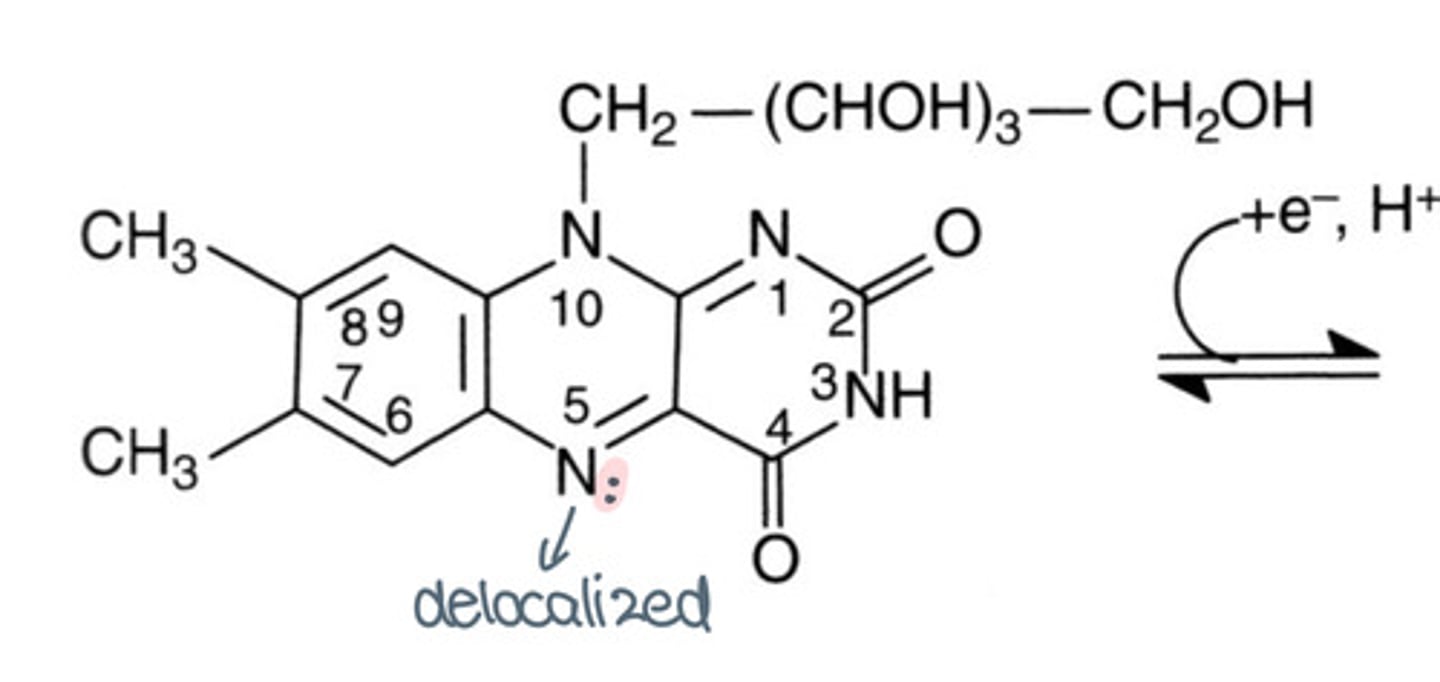
What is flavoquinone's radical form? What colour is it?
Flavosemiquinone radical, red
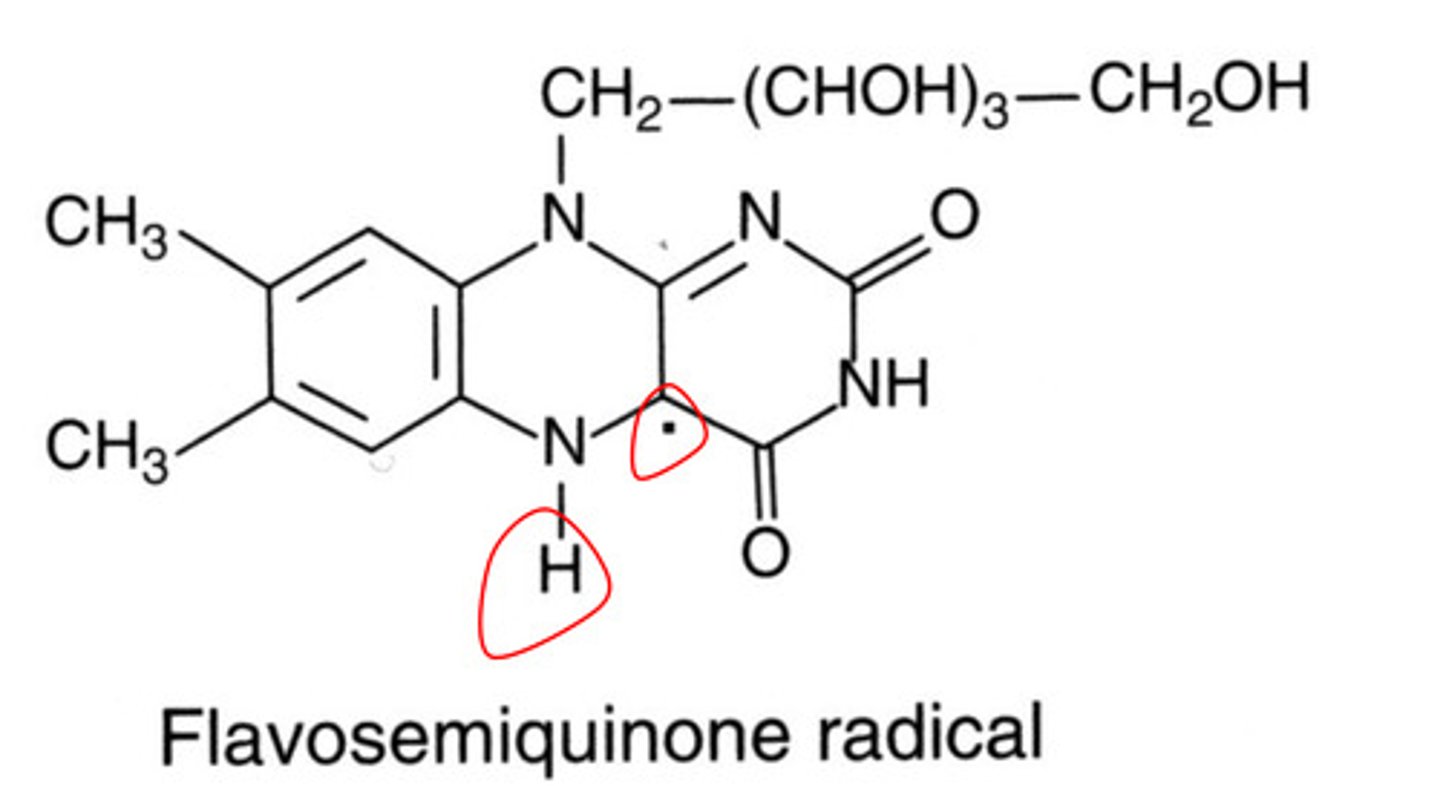
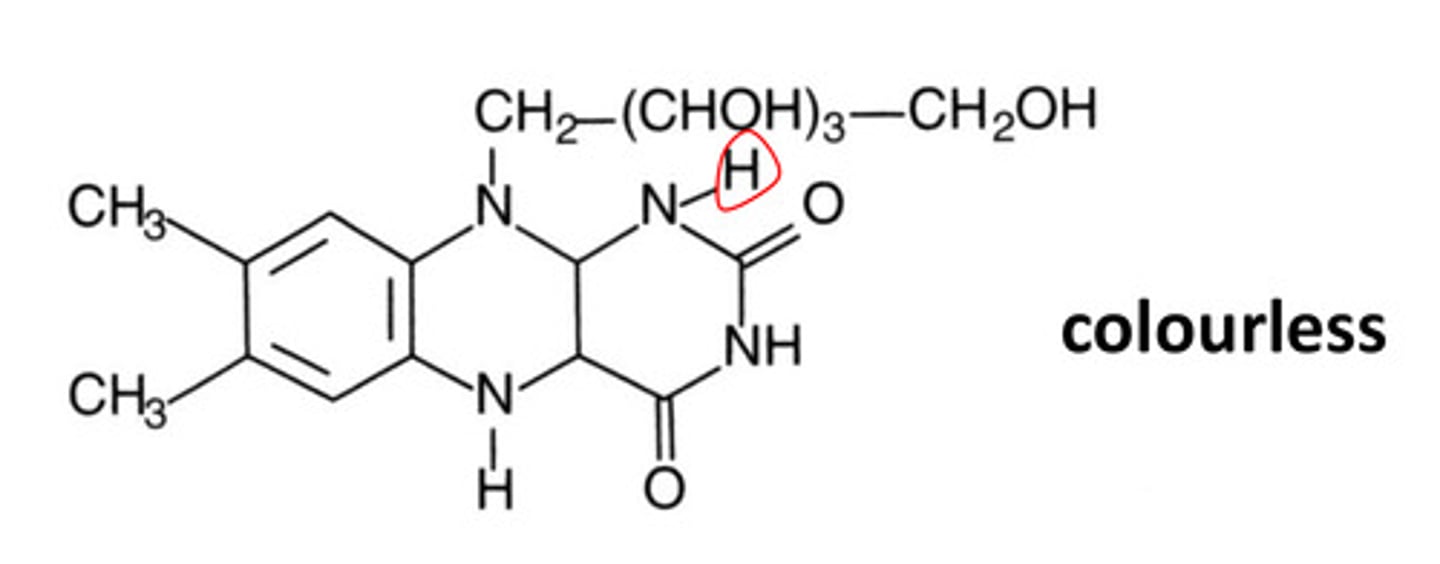
When the oxidized and radical forms of flavoquinone get reduced, what form is made? What is the colour?
Flavohydroquinone, colourless
What are flavoenzymes?
Redox proteins containing FMN or FAD that catalyze many biological reactions.
They also help with energy reduction, oxygenation, light emission, non-redox, biodegradation, chromatin remodelling, DNA repair, apoptosis, protein folding, detox, neural development, and biosynthesis.
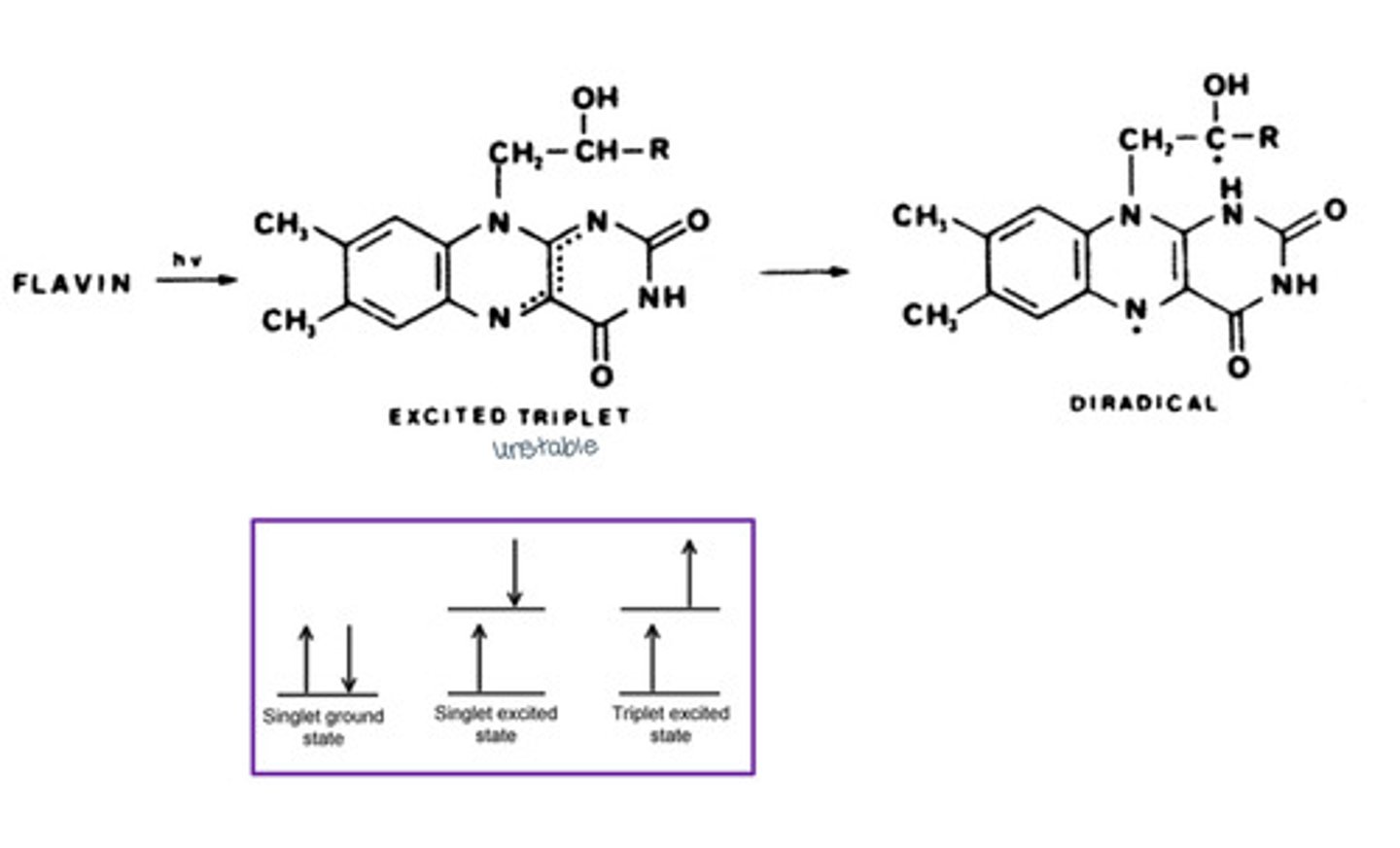
Describe the formation of the flavin diradical:
Describe what happens when flavins induce photochemical reactions:
Flavins can photosensitize the cis-trans isomerization of olefine compounds, which proceeds with a triplet-triplet energy transfer.
How does photosensitized oxidation affect foods?
Degrades amino acids and other labile compounds, resulting in off-flavours.
What conditions are riboflavin sensitive to? Explain:
Light exposure: 3.5 hours of exposing milk to sunlight can cause complete loss of riboflavin
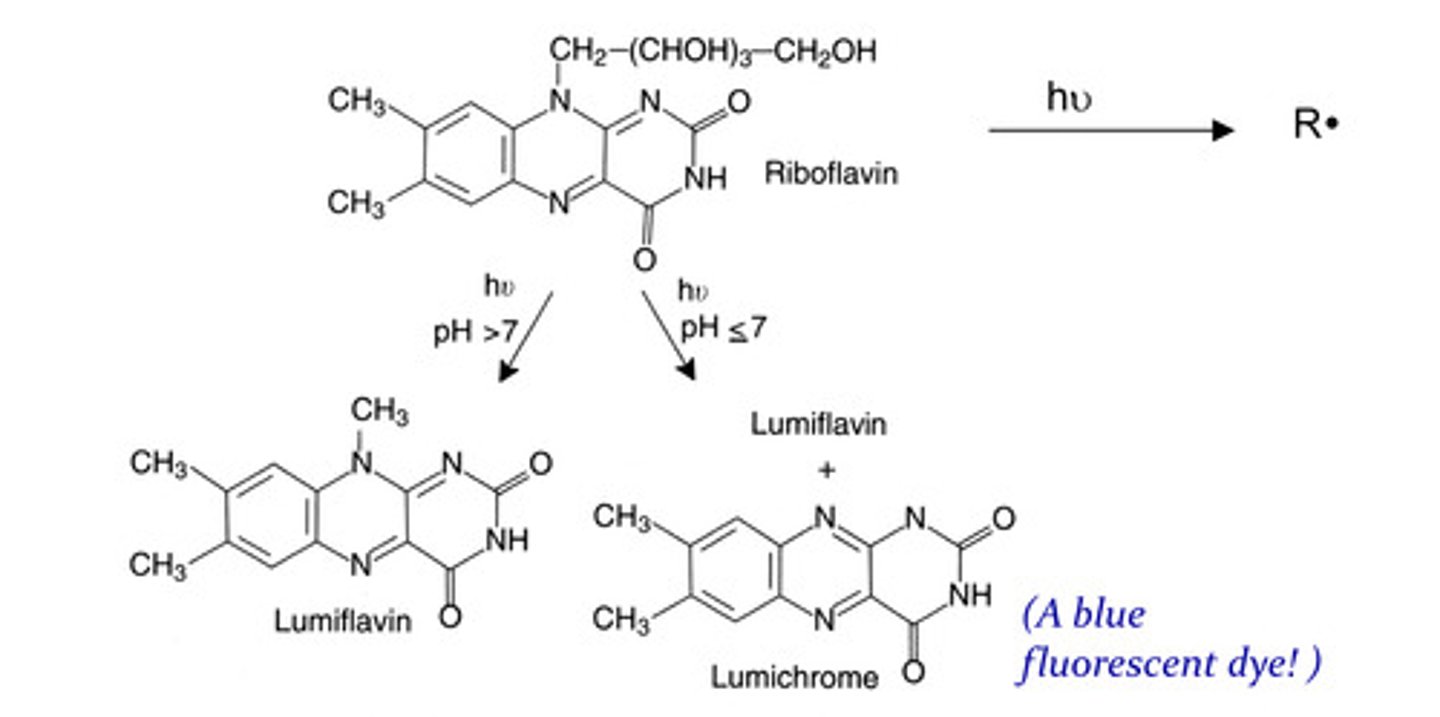
Changes in pH: over or under 7 can cause rise to inactive products and may proceed by formation of the diradical.
What products do changes in pH convert riboflavin to?
pH > 7 = lumiflavin
pH < or equal to 7 = lumiflavin and lumichrome (blue fluorescent dye)
Is riboflavin stable to heat? Explain:
Yes, it is relatively stable.
For example, meat loses only 0-25% of its riboflavin content when subjected to heat.
What are common sources of riboflavin?
Yeast, milk, meat (liver), fortified foods such as cereals.