Unit 11 Quiz
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Which of the following parts of the nervous system is an example of a control center?
spinal cord
Examples of effectors in the nervous system include:
muscle fibers in the biceps brachii
Outputs of the nervous system may include:
increased heart rate
Examples of receptors in the nervous system include:
cells in the retina of the eye
Inputs (afferent information) to the nervous system may include:
pH of blood
A ______________ is a collection of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system.
ganglion
______________ plexuses are found on the walls of digestive organs.
Enteric
Alpha motor neurons (α motor neurons) innervate:
skeletal (striated) muscle
In general, motor pathways are _________________ to the central nervous system.
efferent
Which of the following is part of the peripheral nervous system?
sciatic nerve
The central nervous system includes:
brain and spinal cord
In the cerebrum, gray matter is ______ to the white matter.
superficial
This glial cell type forms borders in the central nervous system: the endfeet of this cell type makes up the pia mater and these cells work with the endothelial lining of blood vessels to form the blood-brain barrier.
astrocytes
This type of glial cell is responsible for the immune defense of the brain.
microglia
Astrocytes are to central nervous system as ________________ are to peripheral nervous system.
satellite cells
Myelinated axons in the peripheral nervous system are surrounded by
Schwann cells
_________________ cells support regrowth of cut nerve axons. Oligodendrocytes do not.
Schwann cells
In the spinal cord, the gray matter is ___________ and the white matter is ___________.
deep; superficial
In terms of bony structures, the spinal cord ends and the cauda equina begins at the ___________.
Lumbar spine, somewhere between L2-L4
Which of these structures is formed by cell bodies of autonomic neurons in the thoracic region of the spinal cord?
Lateral horn
A spinal nerve exits the vertebral canal through the:
intervertebral foramen
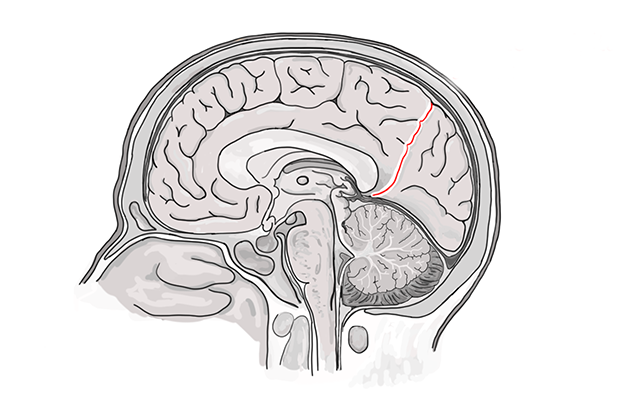
The structure indicated is the:
parieto-occipital sulcus
The combination of endothelial cells (capillary lining) and astrocyte end-feet found only in the brain is called the:
blood-brain barrier
The function of the pituitary gland is directly controlled by the:
hypothalamus
Most of the body's homeostatic loops are controlled, directly or indirectly, by the:
hypothalamus
What process is the cellular-level event that produces memories?
long-term potentiation
Damage to Broca's area causes:
aphasia (problems with producing speech and other symbolic language)
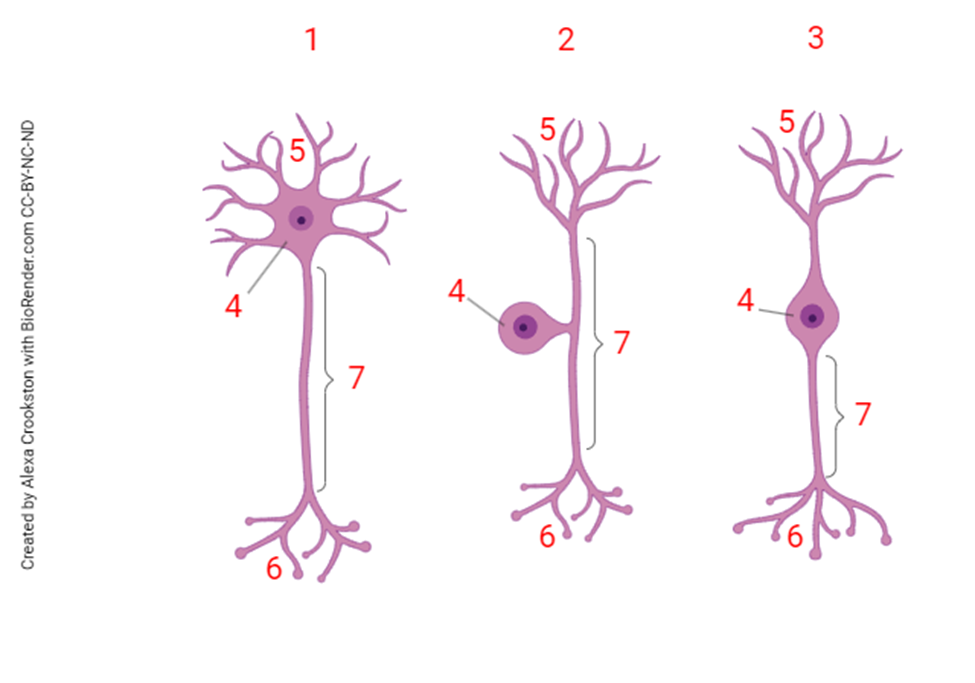
The neuronal structure shown at "6" is the
axon terminals
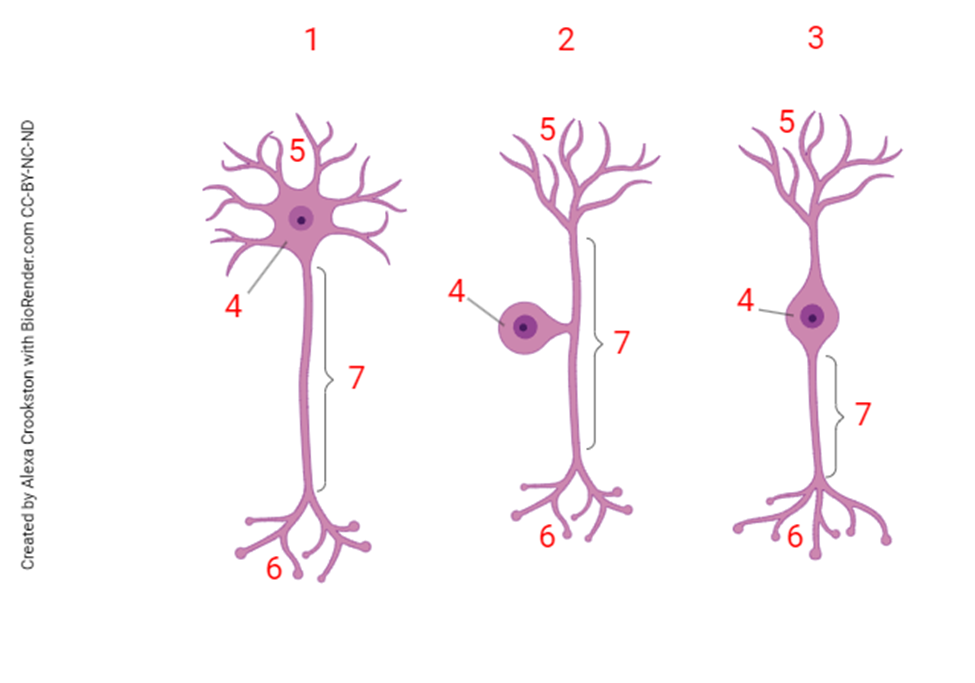
neurons typically receive information at the structure marked:
5
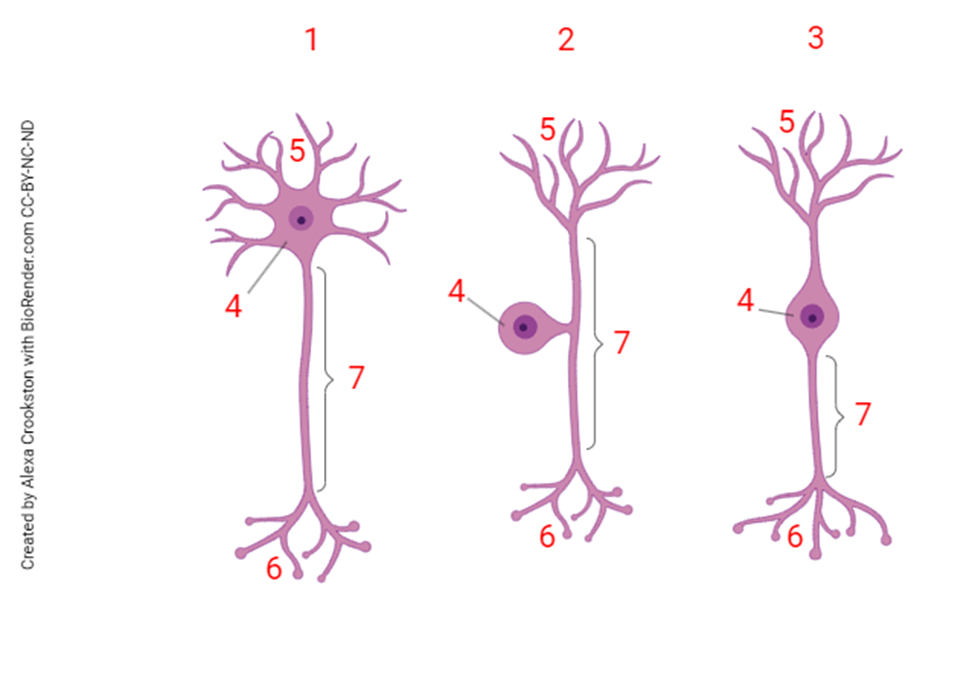
The structure shown at “5” is the
dendritic tree
the structure shown at “7” is the
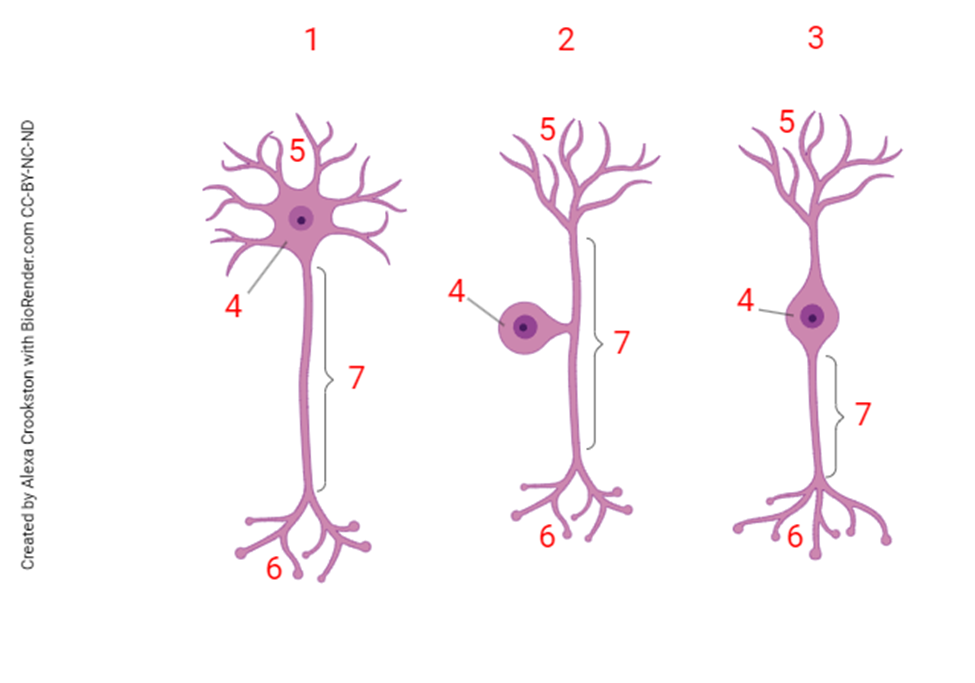
the structure shown at “7” is the
axon
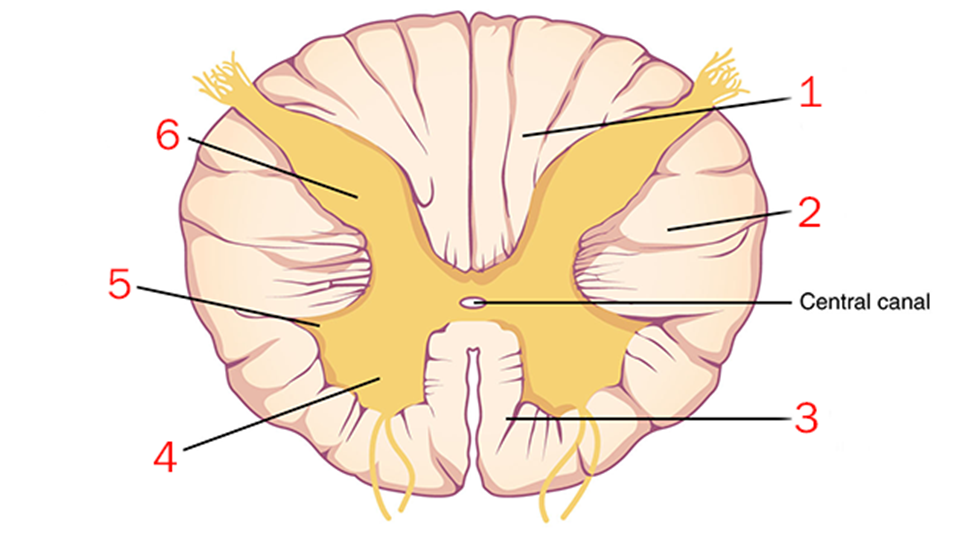
The structure shown at “6”
posterior (dorsal) horn
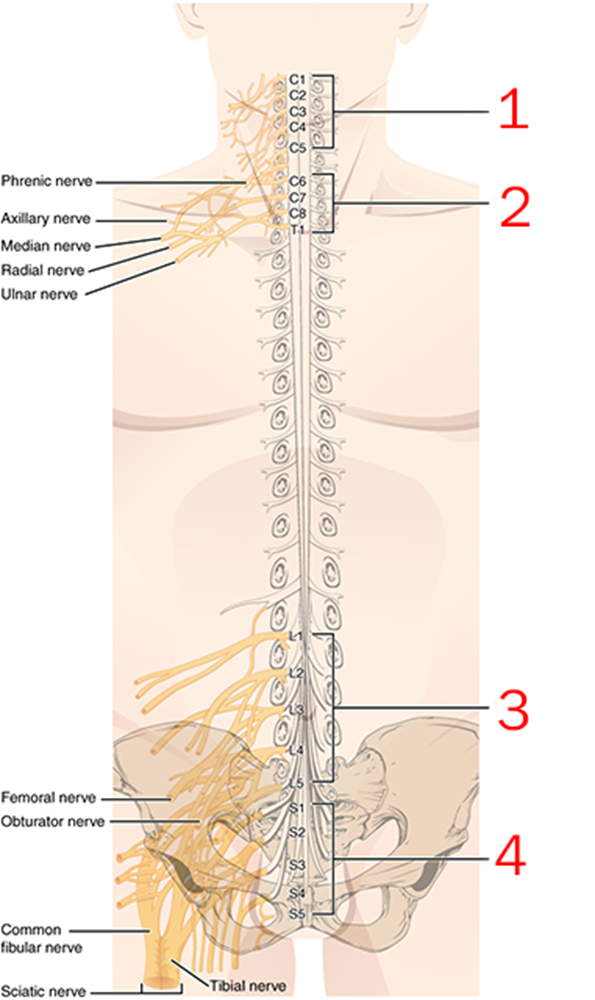
Which spinal nerve plexus is indicated
Brachial Plexus
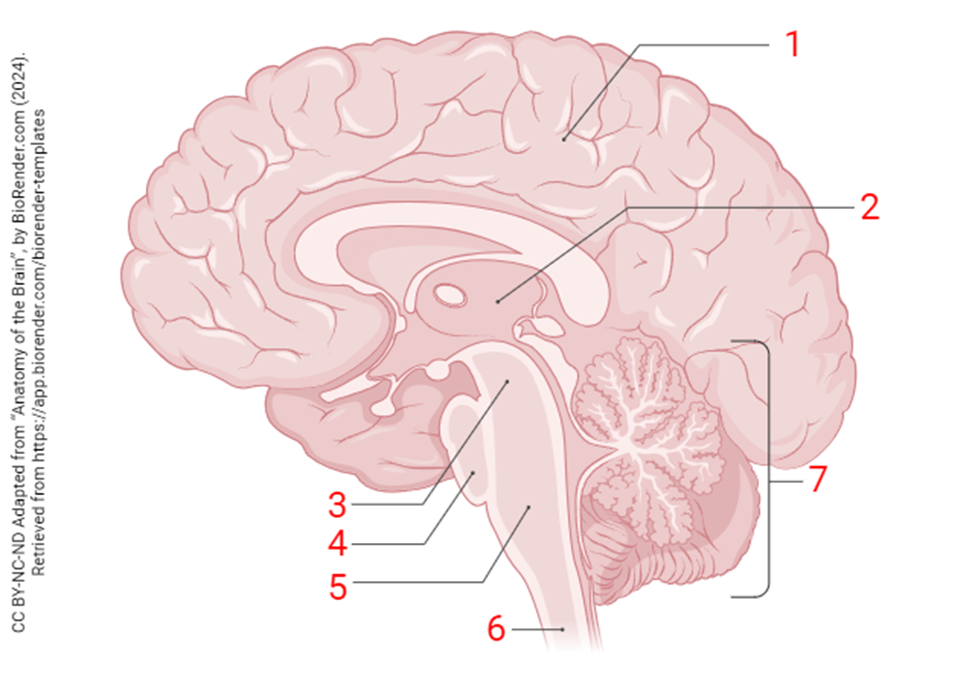
the region of the brain indicated by number 6 is the
spinal cord
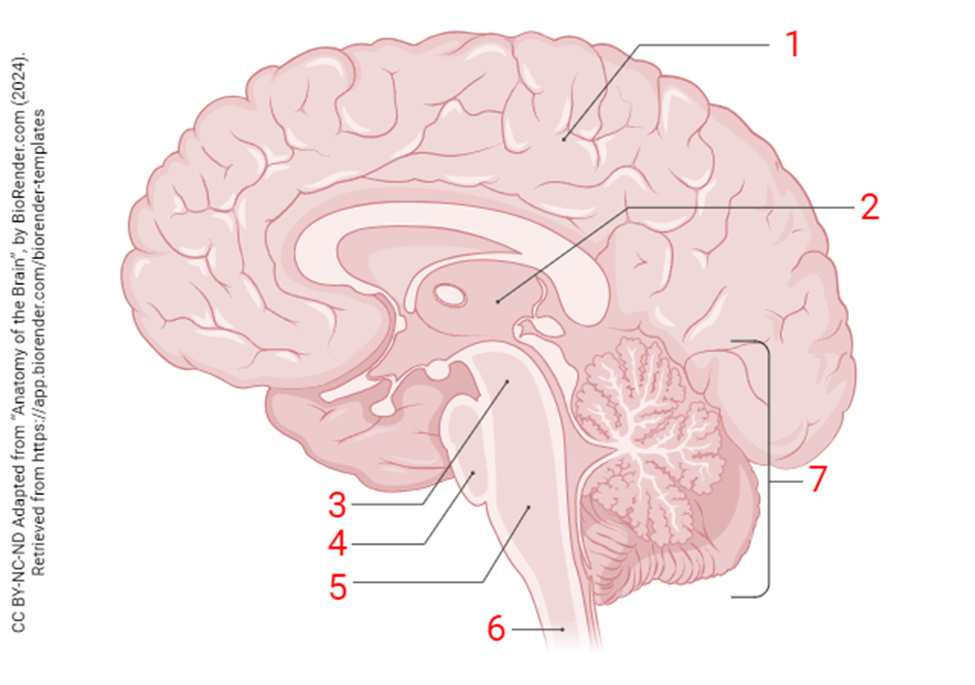
the region indicated by the number 5 is the
medulla oblongata
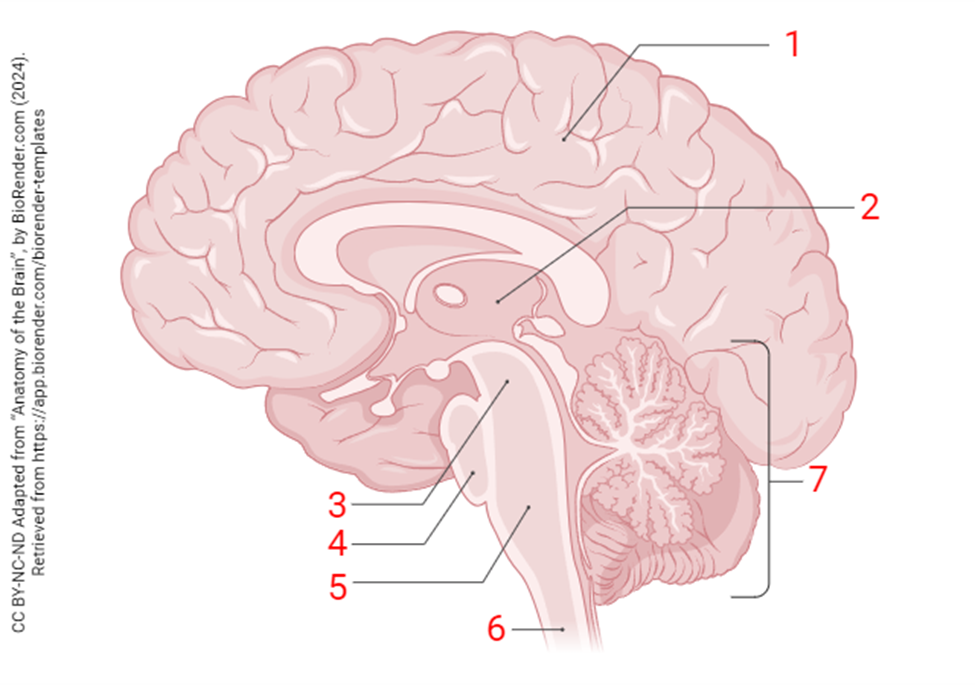
the region indicated by “7”
cerebellum
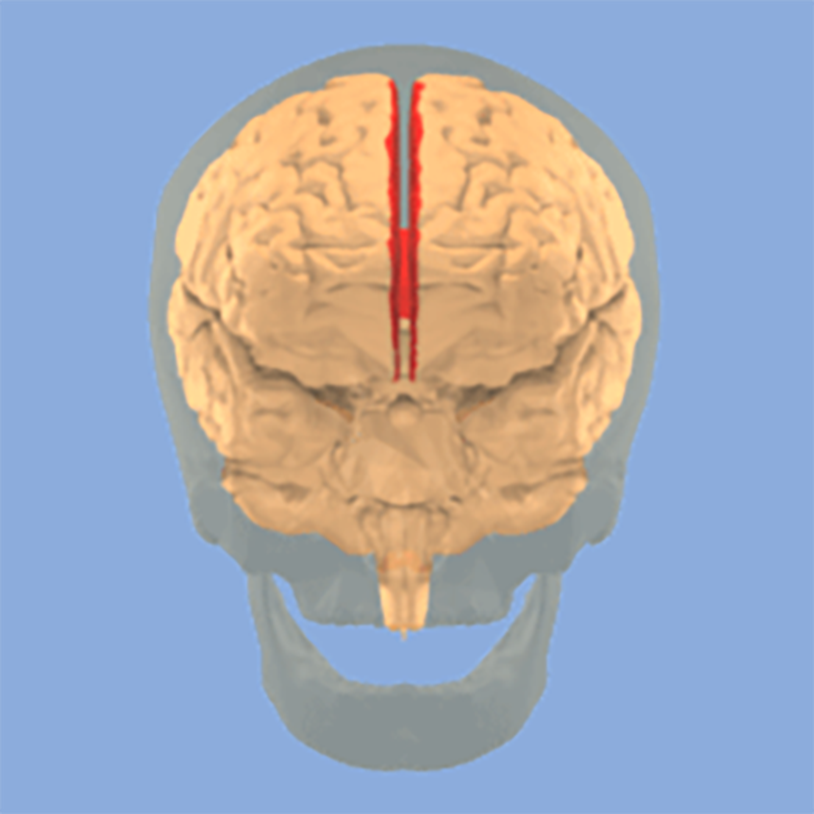
the structure indicated is
medial longitudinal fissure

the structure indicated at 3
central sulcus
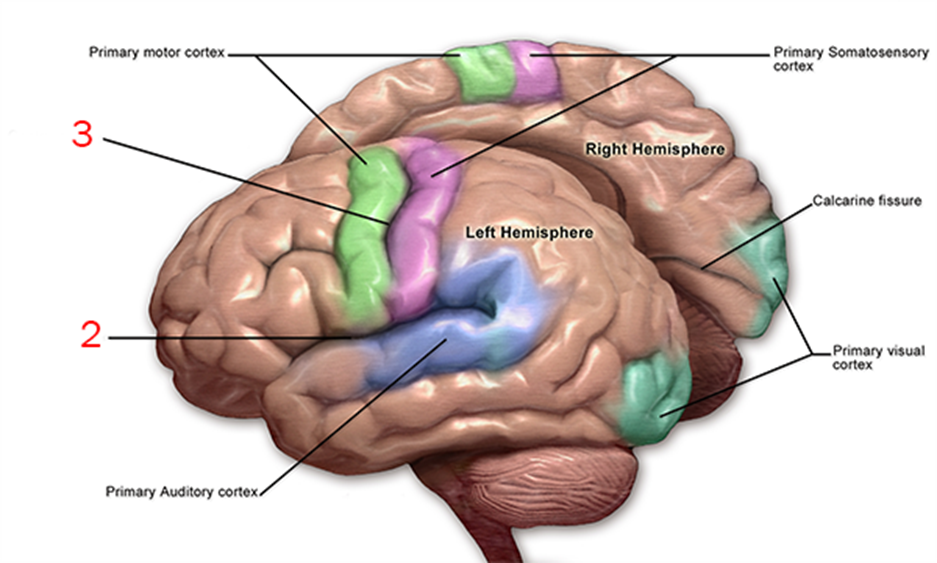
structure at “2”
lateral fissure (sulcus)