Cerebral Perfusion and Traumatic Brain Injury Overview
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Cerebral Perfusion
Blood flow to brain tissues for function.
TBI
Traumatic brain injury from external force.
Primary Brain Injury
Immediate damage from trauma to brain.
Secondary Brain Injury
Delayed damage from biochemical processes.
Glasgow Coma Scale
Assessment tool for consciousness level.
Level of Consciousness
Awareness and responsiveness of a patient.
Pupillary Reaction
Pupil response to light and stimuli.
MAP
Mean arterial pressure; vital sign indicator.
Apraxia
Inability to perform purposeful movements.
Ataxia
Lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements.
Dyskinesia
Abnormal, uncontrolled movements.
Hemiplegia
Paralysis of one side of the body.
Nystagmus
Involuntary eye movement, often rhythmic.
Anesthesia
Loss of sensation in a body part.
Paresthesia
Abnormal sensation, such as tingling.
Blunt Trauma
Injury without skin penetration.
Penetrating Trauma
Injury with skin penetration by an object.
Epidural Hematoma
Blood accumulation between skull and dura mater.
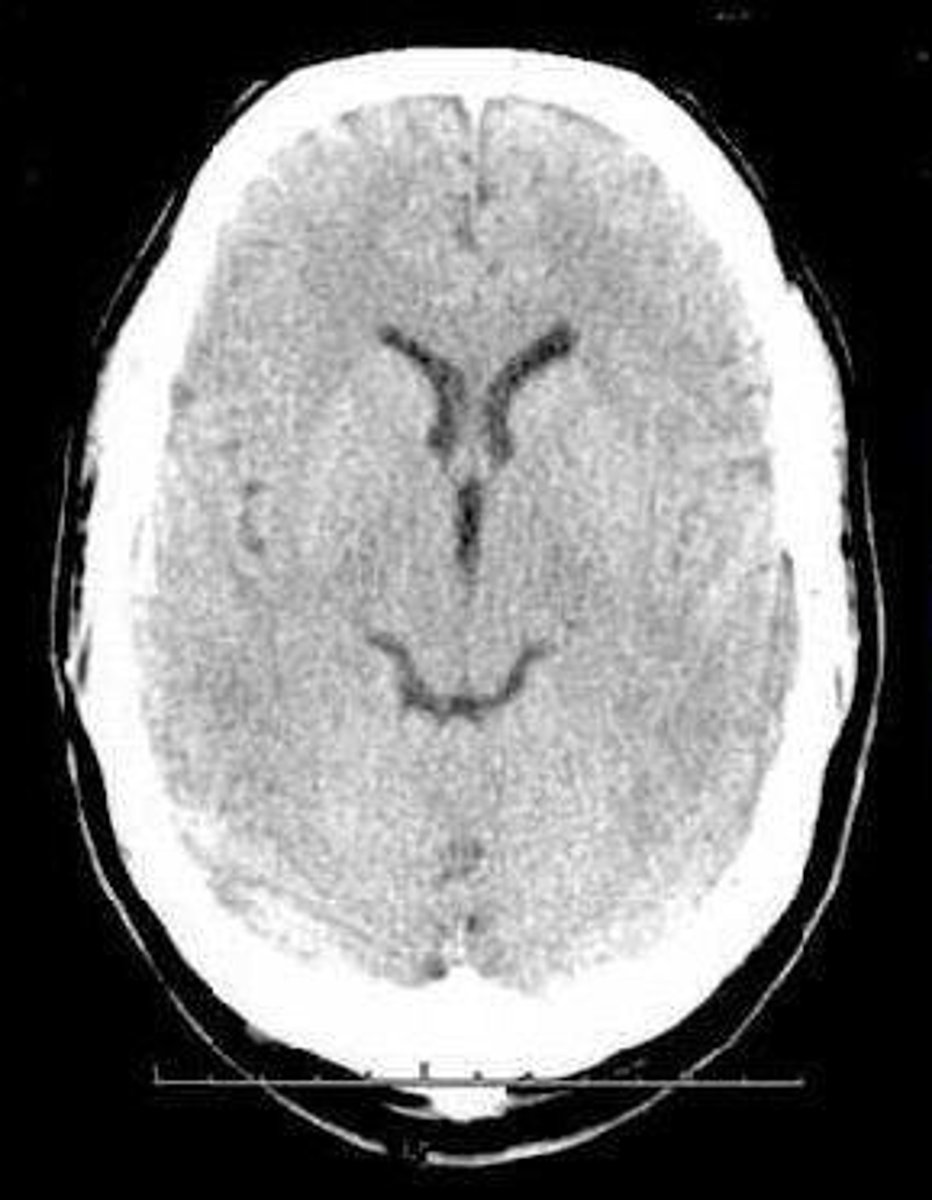
Subdural Hematoma
Blood accumulation between dura and arachnoid layers.
Intracerebral Hematoma
Bleeding within the brain tissue.
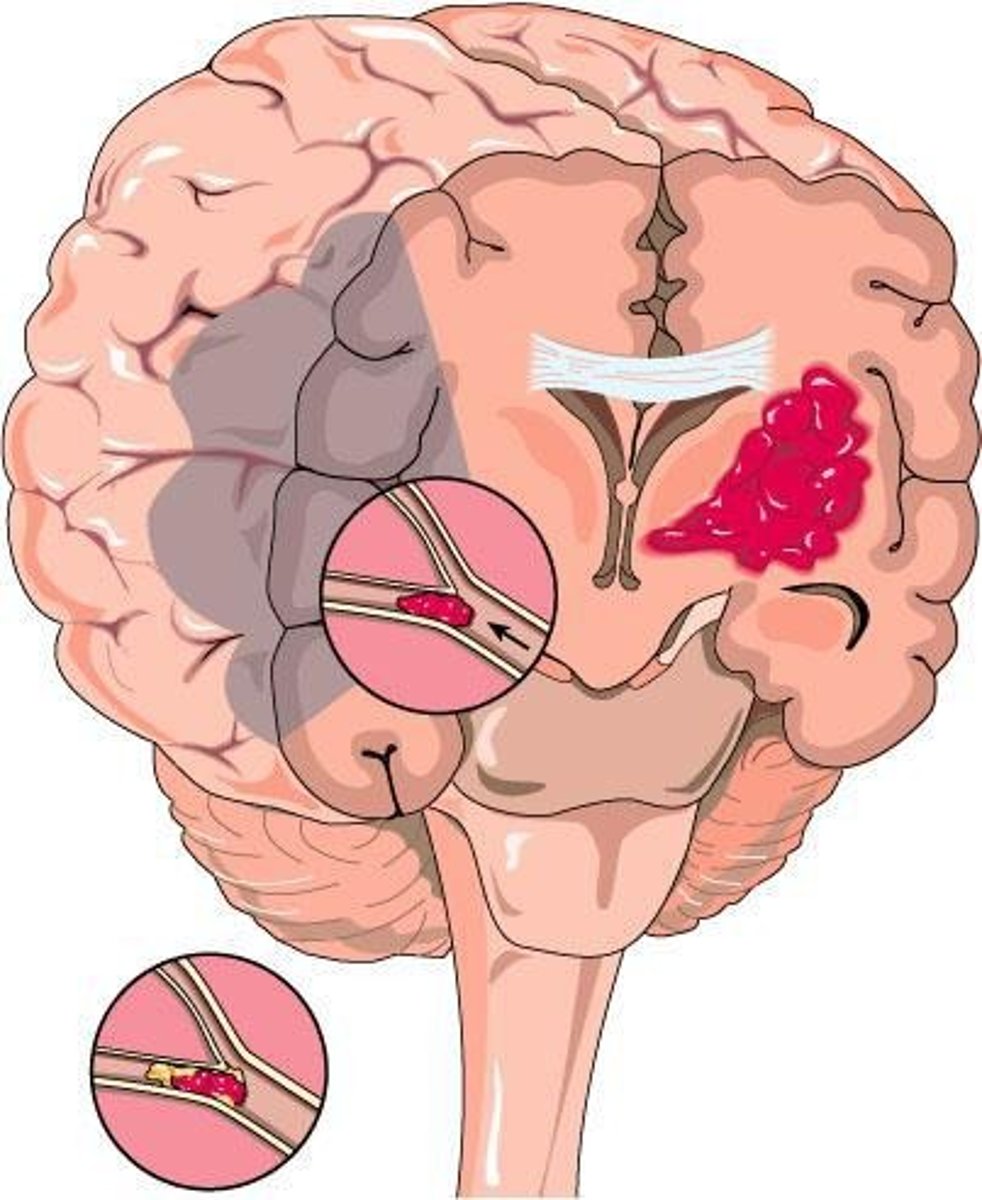
Skull Fracture
Break in skull bone due to trauma.
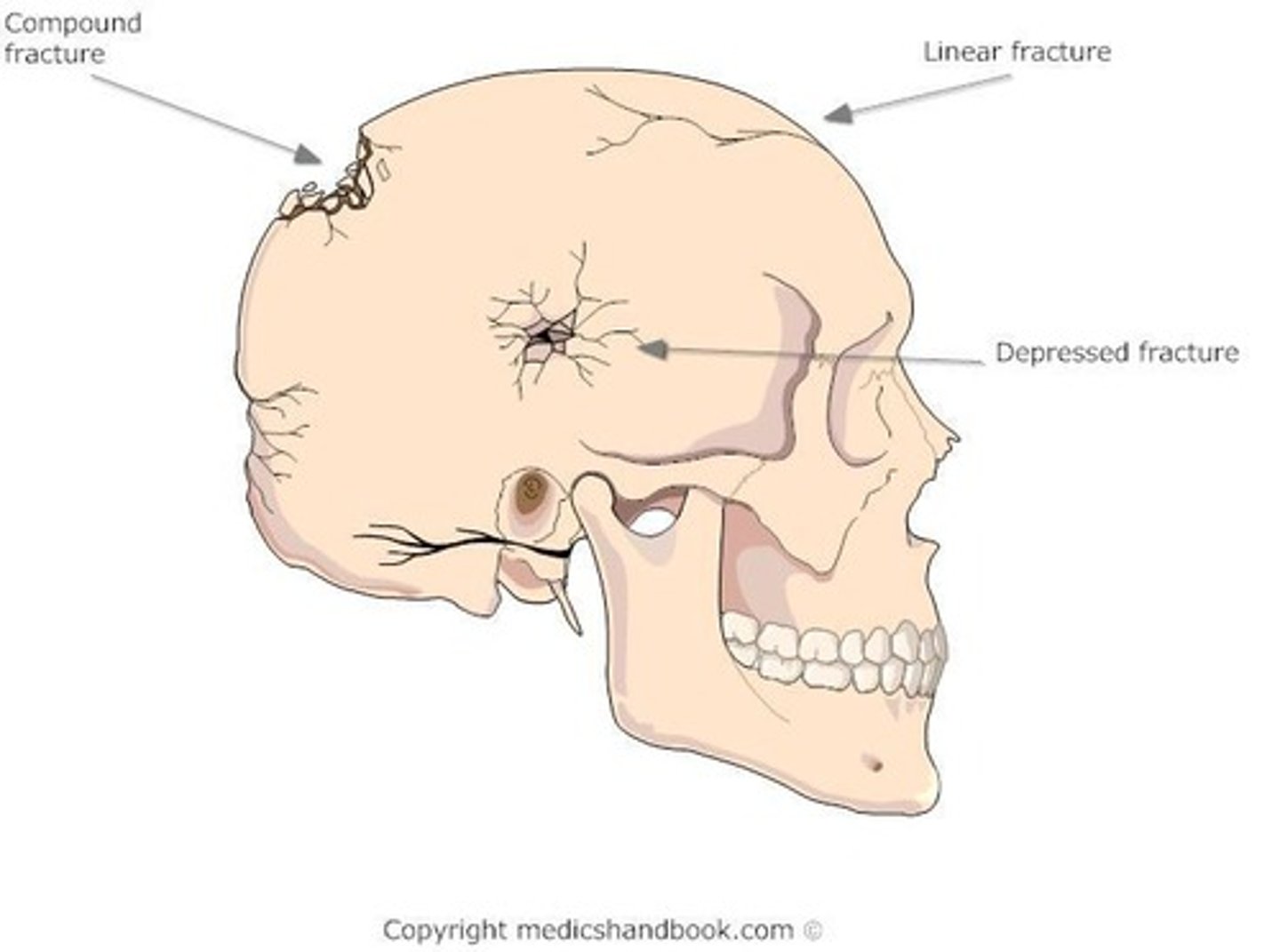
Linear Skull Fracture
Non-displaced fracture from low-velocity impact.
Depressed Skull Fracture
Inward indentation of skull from high-impact injury.
Severe TBI Mortality Rates
GCS 3-5: 60-80% mortality risk.
Comminuted Fracture
Multiple bone fragments from high-impact injury.
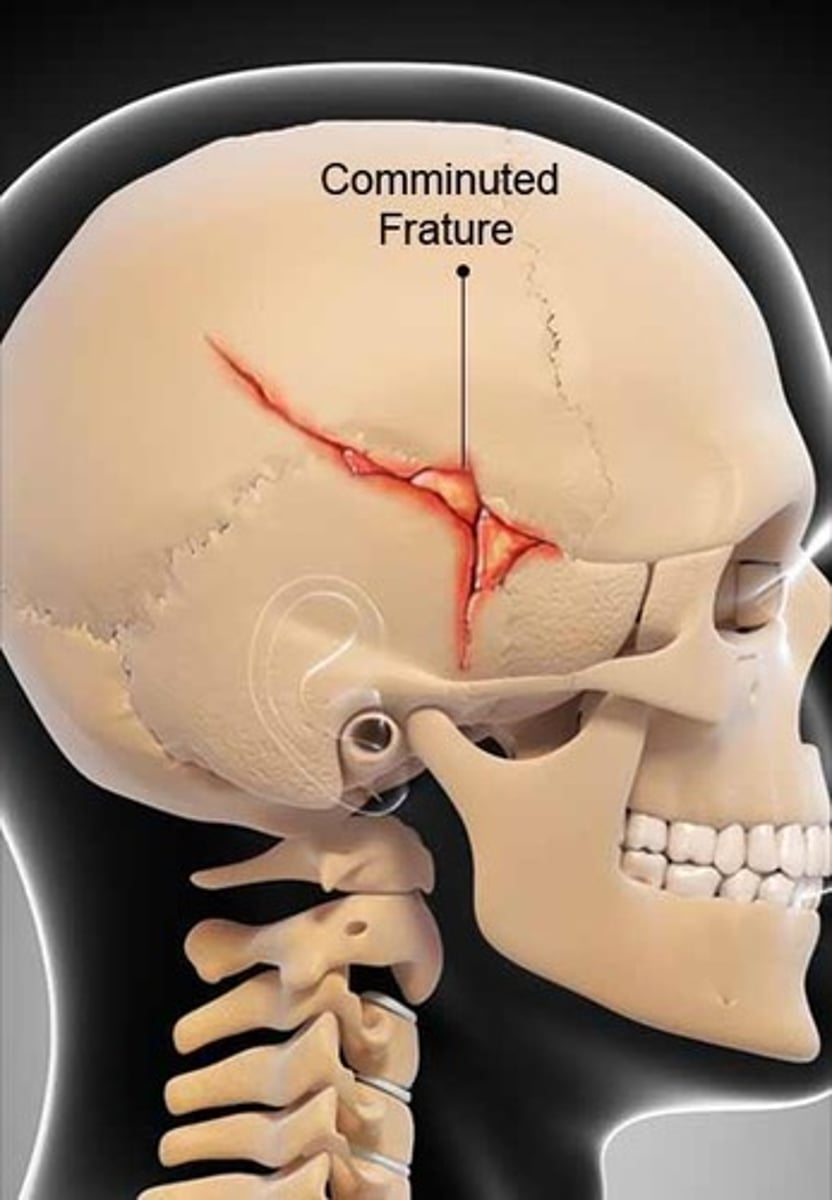
Compound Fracture
Depressed fracture with scalp laceration.
Basilar Skull Fracture
Fracture at the base of the skull.
Raccoon's Eyes
Periorbital ecchymosis indicating skull fracture.
Battle's Sign
Postauricular bruising indicating skull fracture.
Concussion
Brain movement within the skull from impact.
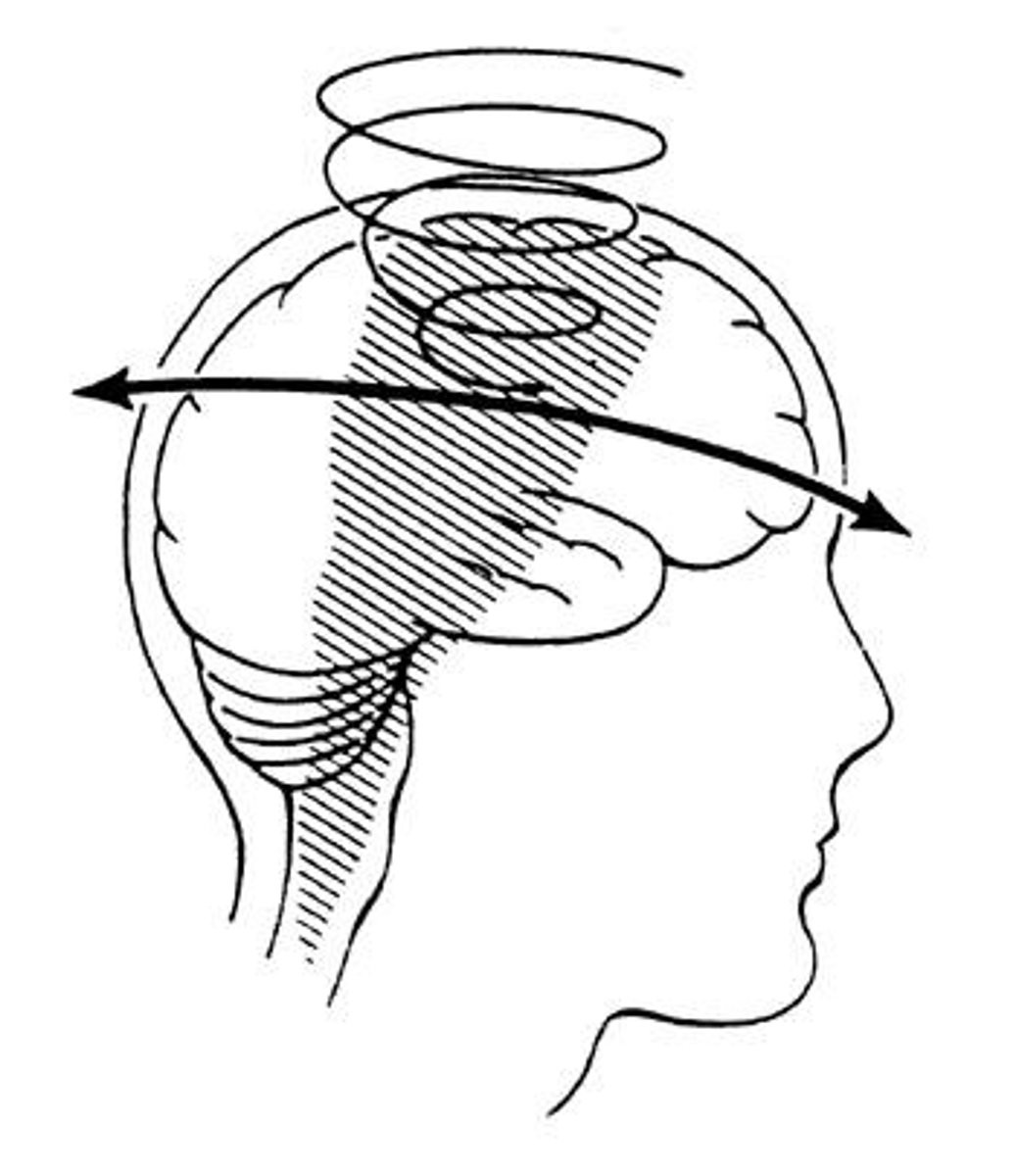
Contusion
Brain injury beneath impact site from force.
Coupe-Contracoup Injury
Injury from brain rebounding against skull.
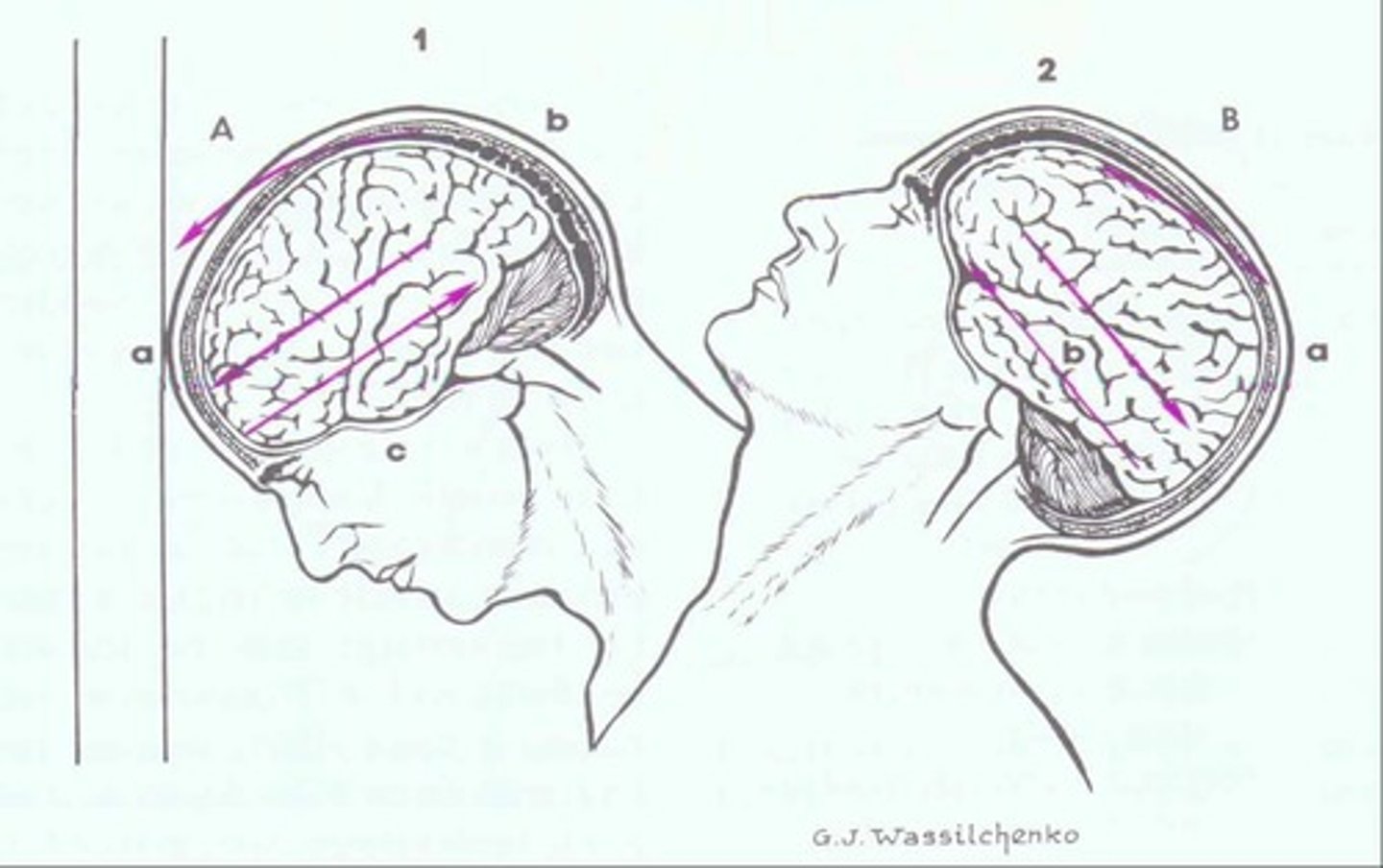
Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI)
Shearing damage to brain pathways from twisting.
Altered Cerebral Perfusion
Impaired blood flow to the brain.
Stroke
Sudden loss of brain function due to blood flow.
Ischemic Stroke
75% of strokes, caused by blood clots.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
25% of strokes, caused by blood vessel rupture.
Thrombosis
Formation of a clot within a blood vessel.
Embolism
A moving clot that obstructs blood flow.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Bleeding into the space surrounding the brain.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Bleeding within the brain tissue itself.
BE FAST
Stroke assessment tool focusing on balance and facial droop.
NIH Stroke Scale
11 assessments to quantify stroke severity.
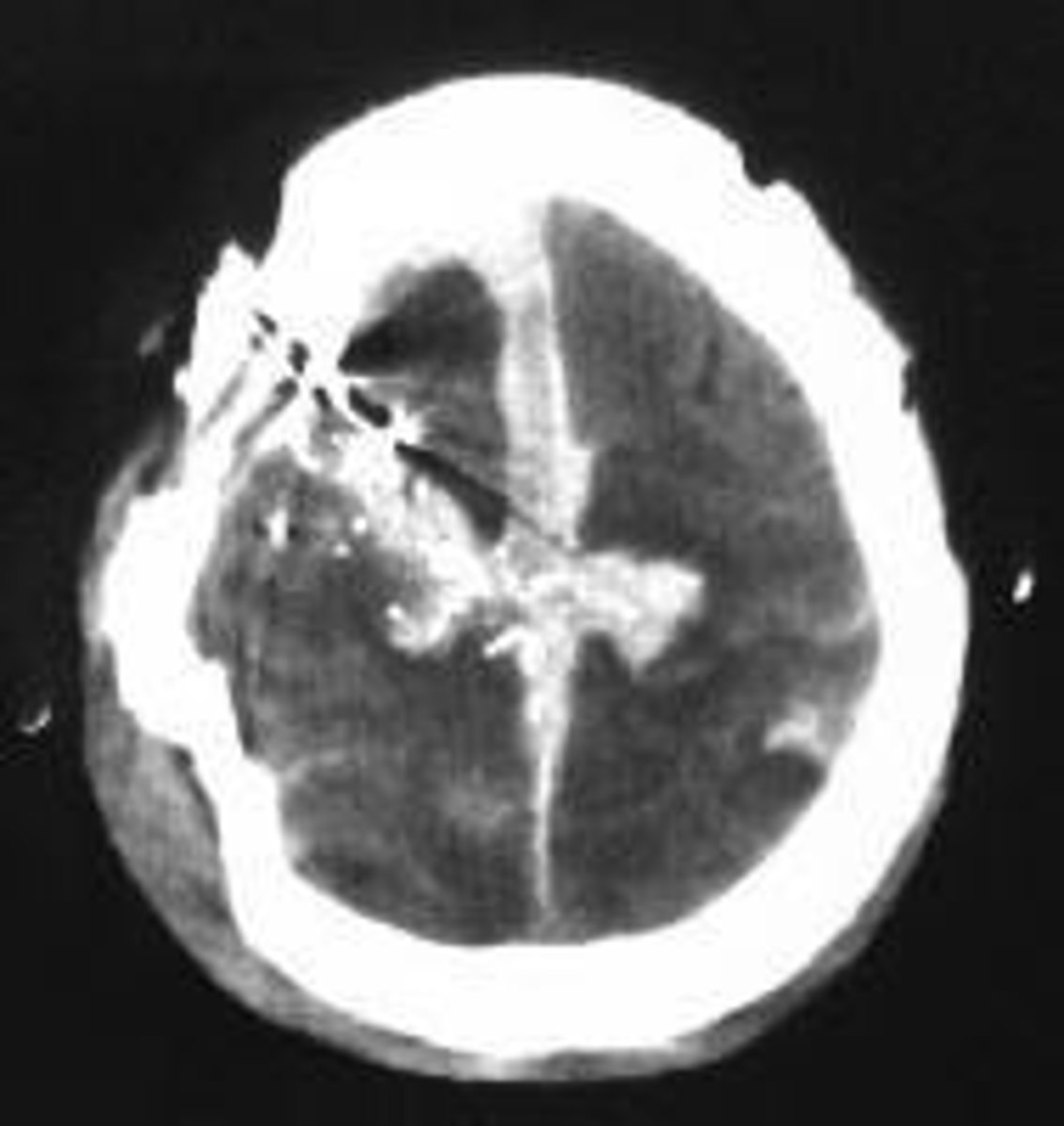
CT Scan
Imaging test for diagnosing brain injuries.
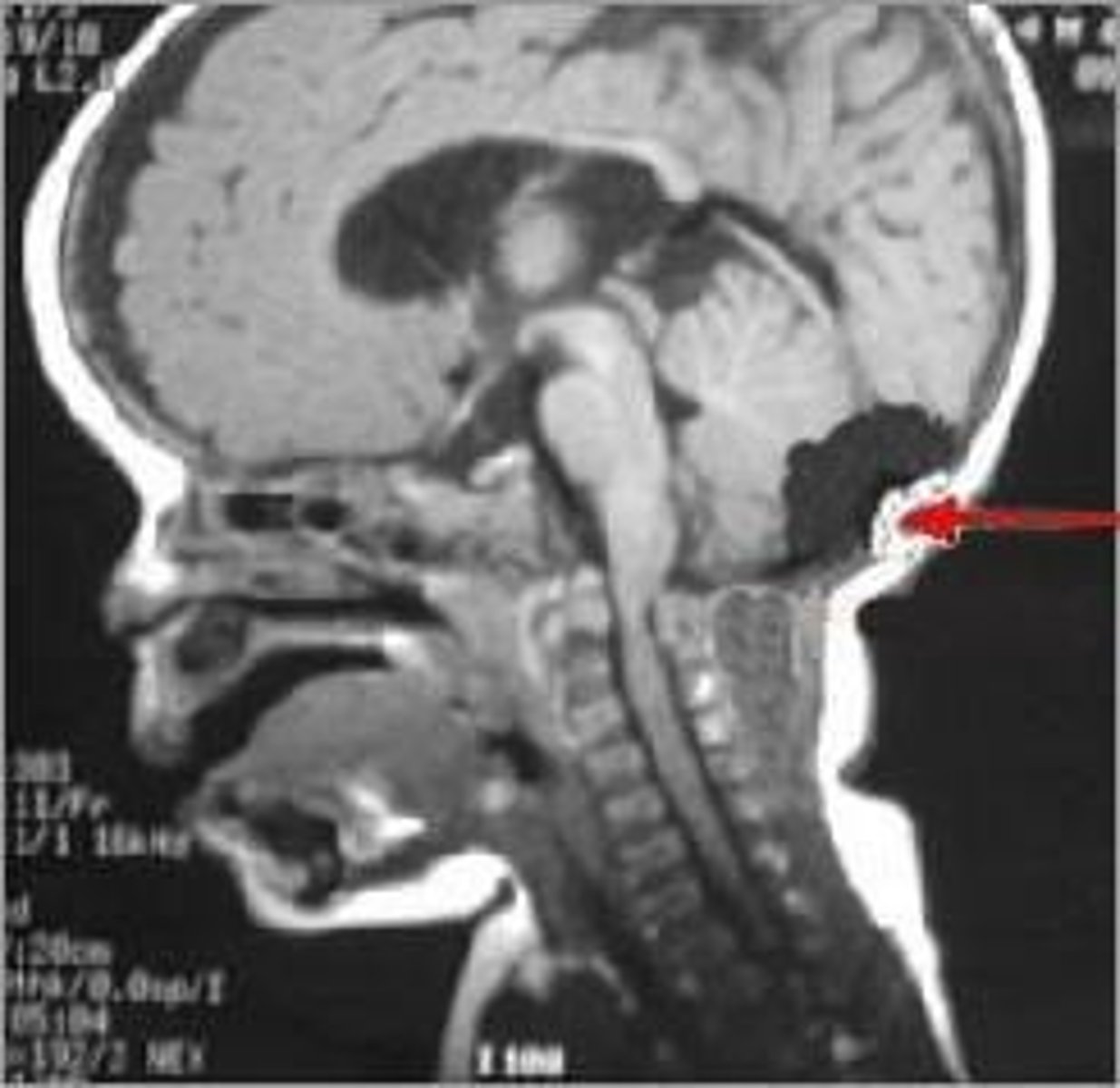
MRI
Magnetic imaging for detailed brain examination.
Echocardiogram
Ultrasound to assess heart abnormalities.
Blood Pressure (BP)
Vital sign indicating cardiovascular health.
Temperature (Temp)
Body's measure of heat, vital for homeostasis.
Stroke Risk Minimization
Strategies to reduce chances of stroke recurrence.
Anti-coagulant Medications
Drugs that prevent blood clot formation.
Anti-platelet Medications
Drugs that inhibit platelet aggregation.
Aspiration Prevention
Measures taken to avoid inhalation of substances.
Physical Therapy (PT)
Rehabilitation to improve movement and function.
Occupational Therapy (OT)
Therapy to enhance daily living skills.
Seizure Precautions
Safety measures to prevent seizure-related injuries.
Ischemic Stroke
Stroke caused by blocked blood flow to the brain.
rtPA (tissue plasminogen activator)
Medication to dissolve blood clots in strokes.
Mechanical Thrombectomy
Surgical procedure to remove blood clots mechanically.
Cerebral Edema
Swelling in the brain due to fluid accumulation.
Mannitol
Osmotic diuretic used to reduce cerebral edema.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Stroke caused by bleeding in the brain.
Vasospasm
Narrowing of blood vessels, reducing blood flow.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Medications that relax blood vessels and lower BP.
Nimodipine
Calcium channel blocker used for vasospasm treatment.
External Ventricular Drain (EVD)
Device to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid.
Craniotomy
Surgical opening of the skull to access the brain.
Craniectomy
Surgical removal of a portion of the skull.
Subdural Hematoma
Bleeding between the dura and arachnoid layers.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Bleeding into the subarachnoid space.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Internal bleeding within the brain tissue.
Monroe-Kellie Hypothesis
Principle stating cranial volume components must balance.
Brain Herniation Types
Various shifts of brain tissue due to pressure.