Ch 2 The Muslim World Expands
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Ghazis
Warriors for Islam

Osman
tribal leader who captured the Byzantine city of Bursa; the Ottoman Empire's name is derived from his

Ottomans
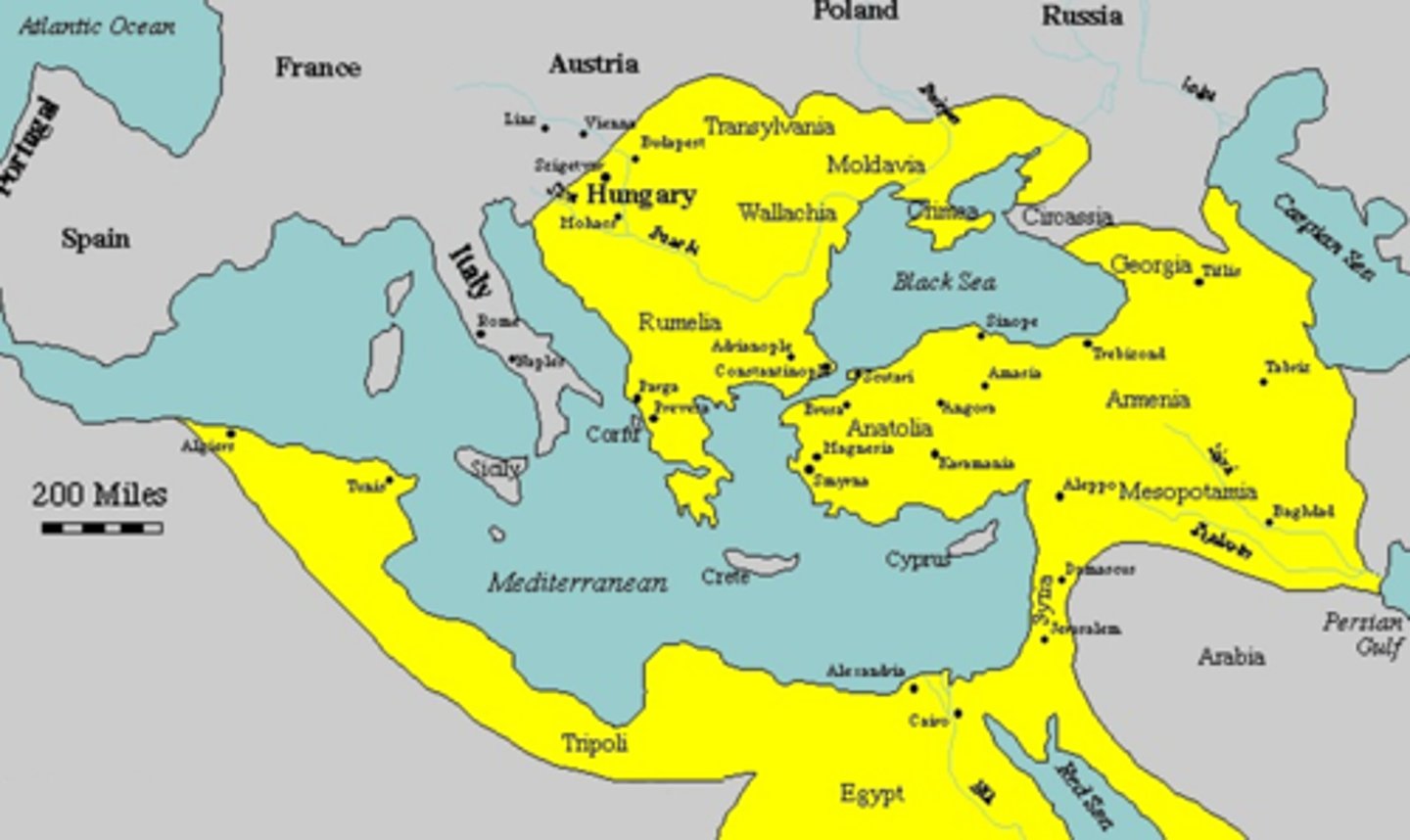
Turkic people who advanced from strongholds in Asia Minor during 1350s; conquered large part of Balkans; unified under Mehmed I; captured Constantinople in 1453; established empire from Balkans that included most of Arab world.
Sultan
Muslim ruler
Timur the Lame
Conquerer from Samar-kand who burned Baghdad down and crushed Ottomans at Battle of Ankara

Mehmed II
Ottoman sultan called the "Conqueror"; responsible for conquest of Constantinople in 1453; destroyed what remained of Byzantine Empire.

Constantinople
The capital city of the Byzantine Empire. It was a great location for trade because it was located along major waterways (Bosporus Strait) and it was at the crossroads of Europe and Asia.

Suleyman I
Ruler of the Ottomans also known as the Magnificent. The height of the Ottoman Empire was achieved under Suleyman. Reformed taxes, overhauled the government bureaucracy, also improved Court System (law giver).

Devshirme
Ottoman policy of taking boys from Christian peoples to be trained as Muslim soldiers
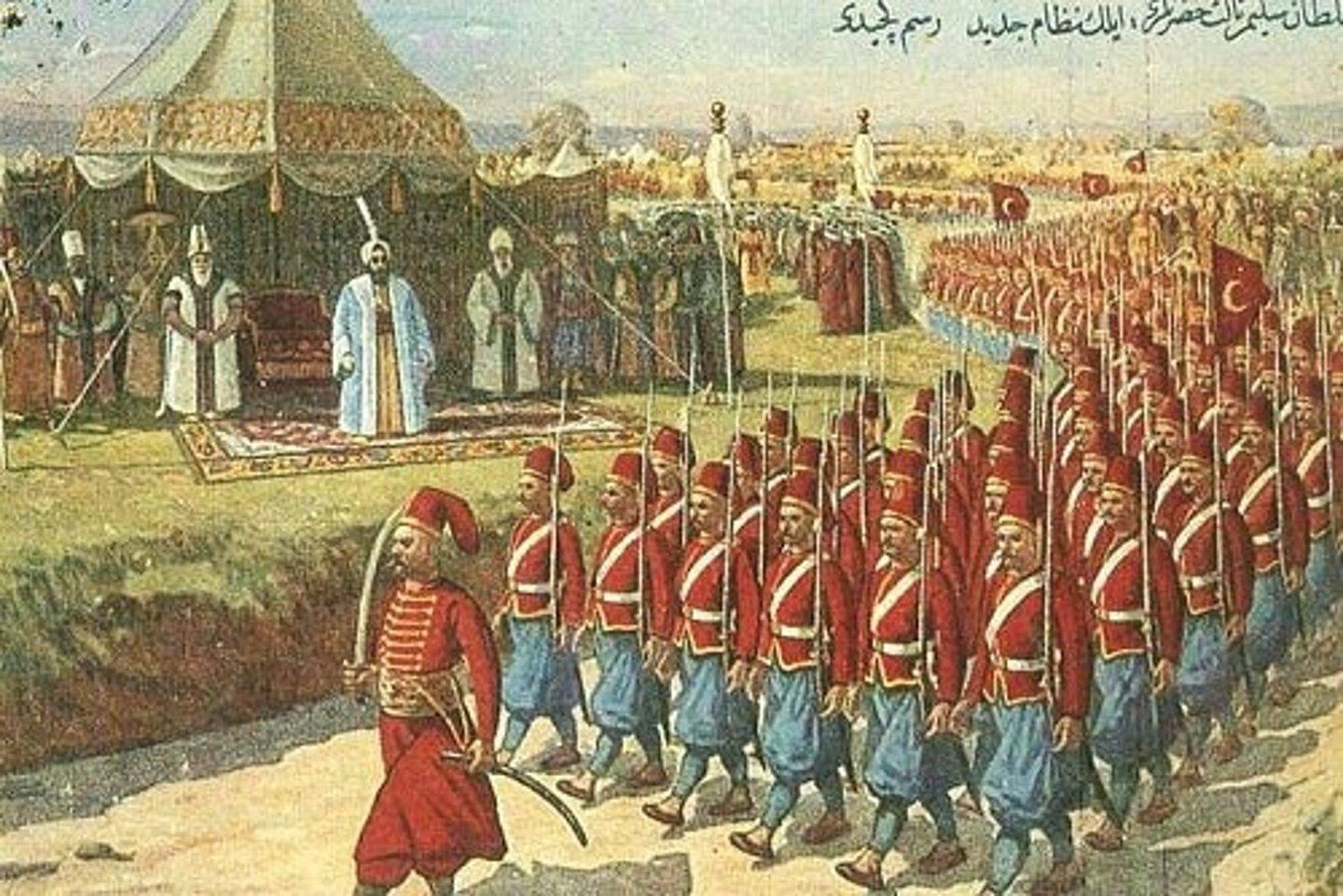

Janissaries
Infantry, originally of slave origin, armed with firearms and constituting the elite of the Ottoman army from the fifteenth century until the corps was abolished in 1826.

Millets
Communitites within the Ottoman Empire where Christians & Jews were allowed to follow their own culture, religion and land.
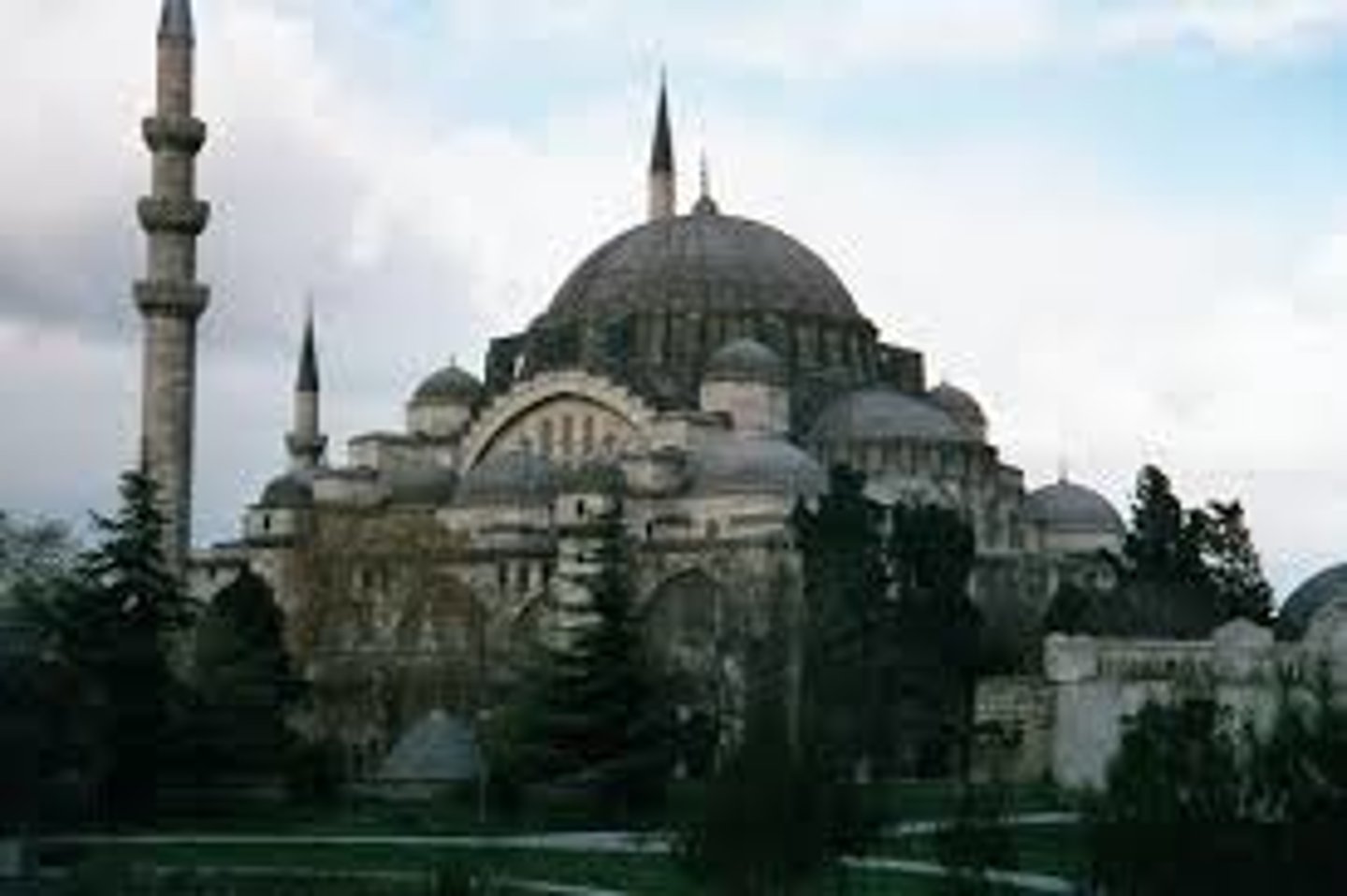
The Mosque of Suleyman
Combines tall, slender minarets with large domed buildings in the style of the Hagia Sophia.

Cultural Blending
this interaction of two or more cultures produces new languages and new ideas in art religion and society
The Safavid Empire
An empire that was a result of cultural blending. This empire drew from the traditions of Persians, Ottomans and Arabs
Isma'il
A great Safavid ruler who, at the age of 14, conquered much of the territory that became the Safavid Empire. He was a religious tyrant who made Shi'ia the state religion.

Shah
The title given to kings who ruled Iran
Shah Abbas
A Safavid king of Persia who centralized government, created a powerful military, encouraged the growth of industry and reduced taxes of farmers/herders

Golden Age of the Safavid Empire
The empire was able to establish a relationship with Christians and other members of the European community. They established trade, invited Chinese artists, and established a strong government.
Esfahan
Safavid capital built by Shah Abbas
Mughals
Islamic dynasty that ruled India from the sixteenth through the eighteenth centuries; the construction of the Taj Mahal is representative of their splendor; with the exception of the enlightened reign of Akbar, the increasing conflict between Hindus and Muslims was another of their legacies.
Babur
Founder of Mughal dynasty in India; descended from Turkic warriors; first led invasion of India in 1526; dies in 1530

Akbar
Most illustrious sultan of the Mughal Empire in India (r. 1556-1605). He expanded the empire and pursued a policy of conciliation with Hindus.

Miniatures
Small individual Indian paintings intended to be held in the hand and viewed by one or two individuals at one time.
Sikhs
Nonviolent religious group that blended Buddhism, Hinduism and Sufism
Shah Jahan
Mogul emperor of India during whose reign the finest monuments of Mogul architecture were built (including the Taj Mahal at Agra) (1592-1666)
Mumtaz Mahal
The translation of her name means "the beloved ornament of the palace" and she was the inspiration behind the construction of the Taj Mahal.
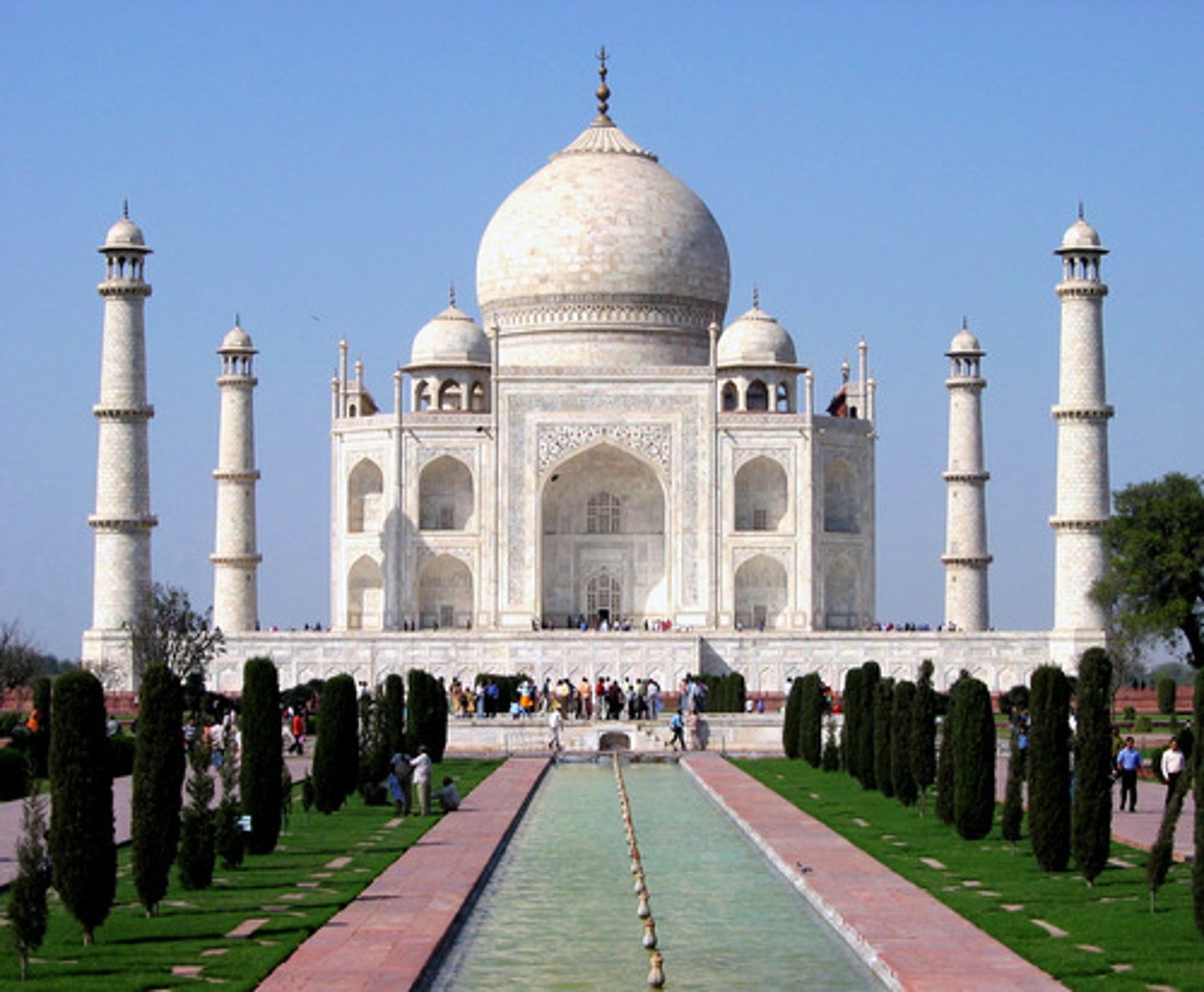
The Taj Mahal
A monument made by Shah Jahan for his wife who died during child birth

Aurangzeb
Mughal emperor in India and great-grandson of Akbar 'the Great', under whom the empire reached its greatest extent, only to collapse after his death.

Selim the Grim
Ottoman sultan who conquers the Safavids in 1514; he also conquers Mecca, Medina, and Cairo