1.1 Biological compounds
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
what is a carbohydrate
organic molecules composed of three elements: carbon, oxygen and hydrogen
what is the general formula for carbohydrates
(CH2O)n where n is the number of carbons
what are the three main groups of carbohydrates
-monosaccharide (one sugar molecule)
-disaccharide (two sugar molecules)
-polysaccharides (many sugar molecules)
what is the name based on for monosaccharides
number of carbons
what form do monosaccharides when they dissolve in water
ring structure
what are the different types of monosaccharides and give examples
-triose (3 carbons): glyceraldehyde
-tetrose (4 carbons): oxabacetate
-pentose (5 carbons): ribose and deoxyribose-important constituents of RNA and DNA
-hexose (6 carbons): glucose, fructose and galactose
what are the differences in structure between glucose, galactose and fructose
glucose: OH below carbon four
galactose: OH above carbon four
fructose: CH2OH below carbon one
what is the definition of isomer
same molecular formula but different structural forms
what are the two forms of glucose and draw them
alpha and beta
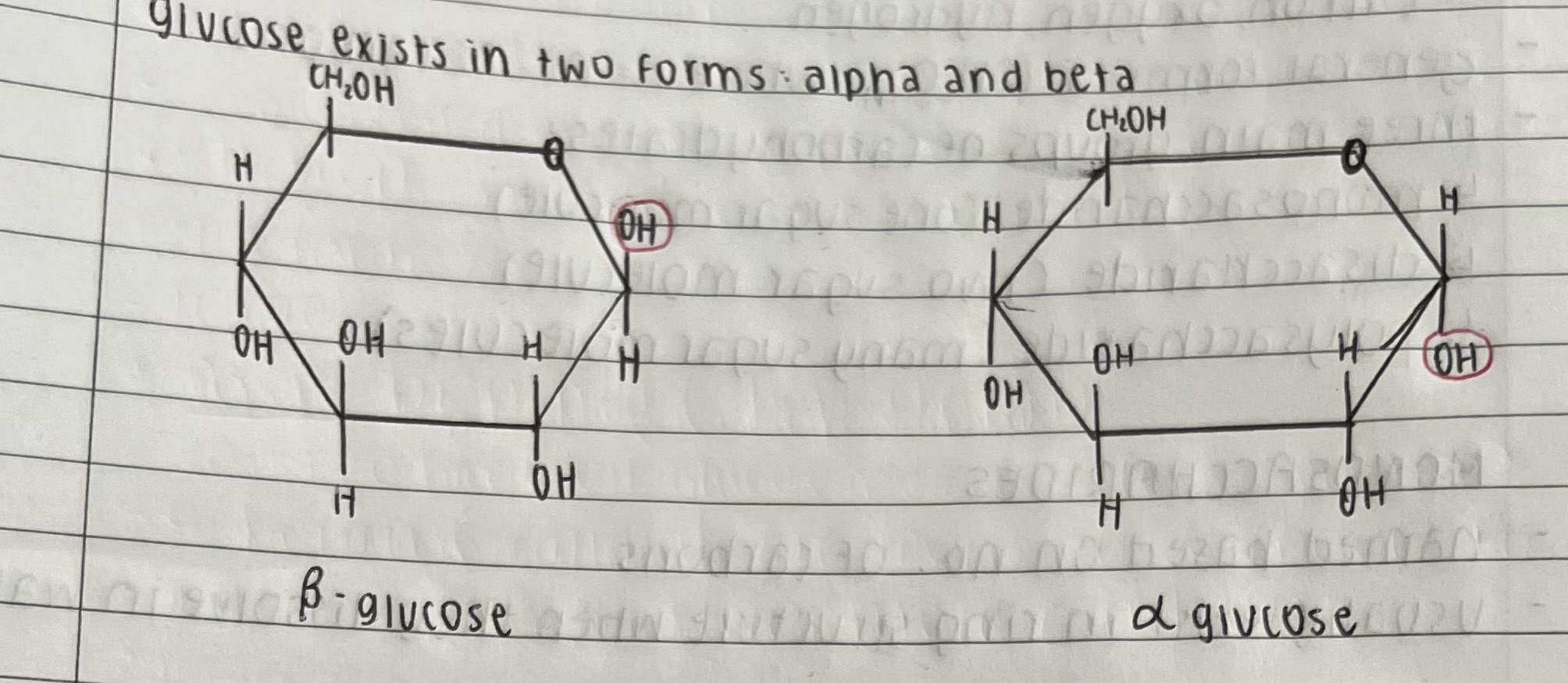
what is the difference between alpha and beta glucose structure
beta: hydroxyl group is above on carbon one
alpha: hydroxyl group is below on carbon one
how is glucose adapted to being an energy source
-soluble: hydroxyl group can form hydrogen bonds with water, so it can be transported around organisms
-bonds store a lot of energy- the energy is released when the bonds break
what is a disaccharide
sugars made of two monosaccharide units joined together in a condensation reaction
what is the formula for disaccharides
C12H22O11
what happens when two monosaccharide join together and give a general word equatio
-a glycosidic bond is formed
-a molecule of water is lost
monosaccharide + monosaccharide —> disaccharide + water
what are three word equations for monosaccharide into disaccharide
glucose + glucose ➝ maltose + water
glucose + fructose ➝ sucrose + water
glucose + galactose ➝ lactose + water
draw a diagram of two alpha glucose monosaccharide joining together
diagram:
What is the function of starch and how is it good for it
To store glucose in plants
-insoluble: does not affect osmotic balance in the cell
-large: cannot diffuse out of cell
-amylopectin side branches: allows enzymes to hydrolyse the glycosidic bonds easily and quickly to release glucose
-amylose being coiled: makes it compact so lots of glucose can be stored in smaller spaces
What is glycogen
Storage polysaccharide found in animals
What are some features of glycogen
-made of alpha glucose monomers
-1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
-larger and more branched than starch
How and why is glycogen good for storing energy
insoluble: does not dissolve in water, doesnt affect cell’s water balance
compact:packs a lot of glucose into a small space
more branched: allows enzymes to hydrolyse the glysosidic bond bonds easily
large: cannot diffuse out of the cel
what is cellulose
structural polysacccahride found in plant cell wall
what is some features of cellulose
-beta-glucose monomers
-1,4 glycosidic bonds
-every other beta-glucose is flipped
-difficult to digest since there are a lot of hydrogen bonds between chains
→high tensile strength meaning cells are less likely to burst
explain microfibrils and macrofibrils for cellulose
hydrogen bonds form between adjoining chains giving it its structural stability and the chains of glucose monomers linked this way are called microfibrils
several microfibrils group together into a macrofibril
where is chitin used
fungi: used to strengthen cell wall
insects: gives strength to exoskeleton (the hard part outside the body)
what is the structure of chitin
similar in structure to cellulose:
-B-glucose monomers
-1,4 glycosidic bond
-every other flips
contains acetylamine groups, forming a mucopolysaccharid
what are some properties of chitin
-waterproof
-lightweight
-the nitrogen on the acetylamine group means more hydrogen bonds can form and so it has a higher tensile strength
what do lipids consists of
consists of three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
→but it has a lot less oxygen than carbohydrates
are lipids polar or non polar
non-polar→hydrophobic in water but soluble in organic solvents such as alchohols
what are the two types of triglycerides and what is the difference
fats: solid at room temp (tend to be longer chained)
oil: liquid at room temp (tend to be shorter chained)
what are triglycerides made of
made of one molecule of glycerol and three fatty acid
how are triglycerides broken down and what are they broken down into
triglyceride + 3 water → glycerol + 3 fatty acids
(hydrolysis)
what are the differences between saturated and unsaturated triglycerides
saturated:
-no carbon-carbon double bond
-all carbon attached to max hydrogen
-generally from form fats at room temp since they are straight and pack closely together and so have stronger forces of attraction
unsaturated:
-at least one C=C double bond
-C=C causes a kink and so cannot pack closely together which means the forces of attraction are less and generally from oils at room temp
what are waxes
its a type of lipid that melt at temperatures above 45 degrees Celsius
what is the function of waxes for animals and plants
waterproof - reduces water loss from insect exoskeleton or plants
what are the different roles of triglycerides and explain each
-efficient energy storage: contains more carbon-hydrogen bonds than carbohydrates (since carbohydrates have more oxygen and so less carbons and hydrogen) it releases twice more energy than carbohydrates
-thermal insulation: when stored under the skin it acts as an insulator against heat loss
-protection: fats often are stored around delicate internal organs such as kidneys providing protection against physical damage
-metabolic water: they produce a lot of metabolic water when oxidised. Important for desert animals like Kangaroos which survive on metabolic water from the respiration of its fat intake.
-waterproofing: fats are insoluble in water (hydrophobic) which reduces water loss. Animals can coat their fur with it.
what bonds are present in triglycerides
ester bonds
health implication of fatty acids
-a high intake of saturated fats in the body can contribute to heart disease
-arteries contain endothelium which is a thin layer of cells that keep arteries smooth. Too much saturated fats raises cholesterol/LDL (low density lipoprotein) in the blood which can increase the chance of an atheroma forming which clogs up the artery.
-if the body contains a higher proportion of unsaturated fats the body will make more HDL which carries harmful fats away to the liver for disposal
what is the structure of phospholipids and what happens in water
-molecule of glycerol
-phosphate head which is a negative ion - hydrophilic (soluble in water)
-two fatty acid side chains - hydrophobi
what elements are present in protein
always made of these four
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
carbon
often sulfur is present and other elements too
what is the structure of an amino acid
-an amino group (NH2)
-carboxyl group (COOH)
-variable group (written as R sometimes)
show the reaction of two amino acids
-condensation reaction between amino acids.
-the carboxyl group of one reacts with the amino group of another
-molecule of water is lost and a peptide bond is formed
what is the definition of polypeptide and protein
polypeptide: 4-50 amino acids joined together
protein: over 50 amino acids joined together
describe the primary structure of a protein and state what bonds are present
-linear sequence of amino acids
-determined by the DNA sequence of one strand of the DNA molecule
-bonds: peptide bonds
describe the secondary structure of a protein and state what bonds are present
-folding of the primary structure into a 3D shape held together by hydrogen bonds
-alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
-bonds: hydrogen and peptide
describe the tertiary structure of a protein and state what bonds are present
-formed by the bending and twisting of the polypeptide helix into a compact 3D shape
-bonds: hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bridges and hydrophobic interaction
hydrogen bonds: where there are small differences in charge
ionic: between ionised R groups
disulphide bridges: between cysteine groups (contains -SH) of amino acids (type of covalent bond S-S)
hydrophobic interactions: the R group can either be hydrophobic or hydrophilic
describe the quaternary structure of a protein and state what bonds are present
-combination of two or more polypepetide chains in tertiary form
-haemoglobin is an example of protein with a Quaternary structure and it has 4 polypeptide chains
bonds: hydrorgen, ionic, hydrophobic interactions and sometimes disulphide bridges
what is an inorganic ion
ion that does not contain carbon
what is macronutrients and micronutrients
macronutrients: needed in small amounts like zinc
micronutrients: needed in minute amounts
what are the inorganic ions we need to know
magnesium
iron
calcium
phosphate
what is the role of magnesium
constituent of chlorophyll and so needed for photosynthesis
without it leaves appear yellow
what is the role of iron ions
constituent of haemoglobin so is involved in transport of oxygen
diet deficient in iron can lead to anaemia
what is the role of calcium ions
structural component of bones and teeth (phosphate also required)
what is the role of phosphate ions
needed for making nucleotides including ATP
a constituent part of phospholipids in cell membranes
why is water said to be dipolar
has a slightly positively charged end (hydrogen) and a slightly negatively charged end (oxygen) but has no overall charge
why is water able to dissolve sodium chloride
-dipolar (positive and negative)
-attracts polar molecules
-opposites attract
-oxygen will face sodium and hydrogen will face chlorine
what are all the properties of water and explain each of its biological importance
solvent: involved in many biochemical reaction (hydrolysis and condensation) and allows polar molecules to dissolve and acts as a transport medium
high specific heat capacity: large fluctuations in temp are prevented - aquatic environments
high latent heat of vaporisation: large amount of heat needed to vaporise water so often used as cooling mechanism (sweating in mammals)
metabolite: involved in many biochemical reaction (hydrolysis, condensation and reactant in photosynthesis)
cohesion: water molecules attract each other and form hydrogen bonds between themselves - allows water to be drawn up xylem vessels of trees and creates surface tension allowing insects like pond skater to be supported
high density: ice floats and can acts as insulator preventing water underneath from freezing
transparent: light passes through for photosynthesis