nervous syestem
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
sensory function
sensory receptors detect internal stimuli such as decreases un sugar levels or increases in acidity and external stimuli such as rain. neurons carry sensory information from cranial or spinal nerves called afferent nerves.
integrative function
the nervous syestem processes sensory information and decides the approperate responce. majority of neurons involved in integration are interneurons these are small axons that conctact the nearby brain spinal or ganglion neurons
moter funnction
the nervous syestems moter function involves responding to intergation decision. the neurons that serve thts function are efferent neurons that cary info away from the brain.
neuron
a functional unit of the nervous syestem that is specalised in transmiting signals from one cell to another.
how is communication achived between neurons
with the help of neurotransmiters such as acetylcholine and through electrical excitability
electrical exitability.
the ability to produce action potentals or impulses to a stimuli
what features do all neurons have
cell body, dendrites, axons. myelin sheath and synaptic terminals
what is the cell body
the main part of the neuron, it contains the nucleus and other cell organelles . there are 2 different types of process (fiber extentions) extention from the cell body and axons.
dendrite
branched structure which conveys signals from their tips to the cell body
axon
carry mesages away from the cell body to other cells
myelin sheath
insulates the layer that accommodates high speed sigals
node of ranvier
gaps between mylein sheath
axon terminals
make contact with other neurons or target effector cells
affernt neurons (sensory neurons)
Carry impulses from receptors to the central nervous syestem.i
interneurons
integrate sensory imput and moter output, make up synaptic connections - acco
efferent neurons (moter neurons)
carry impulses away from CNS to effector cells.
somatic nervous syestem
moter neurons carry signals to skeletal muscles in responce to external stimuli- voluntary.
autonomic nervous syestem
signals control internal eviorment such as cardiac.- involentary
sympathetic nervous syestem
when expenditure is necessary (fight or flight responce) inreases heart rate and blood pressure stimulates the secretion of adrenline and increases bloos flow to skeletal muscles,
parasympathetic nervous syestem
returns our body back to homeostais, it kicks in when energy reserves can be conserved and saved for later use. increases salvation digestion and storage of glucose and can slow down heartrate and decrease respiration.
supporting cells
do not generate electrical impusles but are essetial for structural integrity - account for aprox 90% of CNS
types of glial cells
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
ependymal cells
shwann cells
satelite cells
astrocytes
star shaped with many process and help form the blood brain barrier
anchor neurons to blood supply and regulate extange of neutrients
regulate extracellular fluids by removing ions and excess neurotransmiters
secrete growth factors and guide the growth of neurons.
ependymal cells
line the ventricles of the brain ans central canal of the spinal cord
produce cerebrospinal fluid and cili aid in its movement
microglia
protect cns cells from disease by engulfing invading microbes
also migrate to areas of injured tissue and clear away debris of dead cells
oligodendrocytes
wrap their flat extensions around nerve axons to form myelin sheaths in the cns
schwann cells
flatenned cells that form mylenated sheaths in the pns
satallite cells
protective cushioning cells
neuroglia vs neurons
neuroglia divide, neurons do not
most brain tumors are gliomas and involve the neuroglia not neurons.
resting membrane potential
cells under resting conditions have a potential difference across their plasma membrane this is called______
magnatude of the resting membrane potential is determined by 2 factors
differences in ion concentration in intra and extracellular fluid
differences in membrane permeabilities to different ions
Ion channels
an integral membraine protien which is a pathway for movement of charged particles through a cell membrane facilitated by integral membrane protiens which have selected water filled conductive channels that permit or exclude passage of charged particles based on size and charge. these pathways my be gated and regulated or non gated and always open or leaky
non gated ion channel (leakage ion channel)
Ion channel within a cells outer cell membrane which is allways open and permits the diffusion of one or more ions in the direction in accord with their concentration and charge gradients
gated channel
opens and closes in responce to stimuli eg voltage hormones pressure or light
voltage ion channel
opens and closes in responce to a stimulus which is a change in membraine potental (voltage)
chemical gated channel
opens and closes in responce to a stimulus which is the arrival and binding of a specific ligand ot signal molecule (hormone neurotransmitter). responsible for impulse initiation- inital depolorization repolarization or hyperpolarization of a cell depending on circumstances.
mechanicaly gated channel
opens or closes in responce to mechanical pressure or vibration. responsible for impulse initiation depolarization of an exitable cell such as mechanoreceptor(sencory cell responcding to touch vibration compression or strech)
light gated channel
photosensitive cell which opens in responce to a stimulus such as the arival of a photon of light energy. ie responding to light in the retina of the eye
hyperpolarization
an increase in voltage across the mebrane by the opening of potassium which increases the k+ outflow and causes the cell to become more negitve
depolarization
a reduction of voltage across the membrane by opening of the Na+ channels causing an increase in the flow of Na+ into the cell making the cell lest negitive
action potentials
rapid large alterations in the resting membrane potential used by excitable cells to comunicate or prefoem certain actions. they can travel long distances without dying out therfore are ideal for long/short communitcation.
if a region of a membraine is depolarized enough by graded potental an ________ ________ will occur
action potential
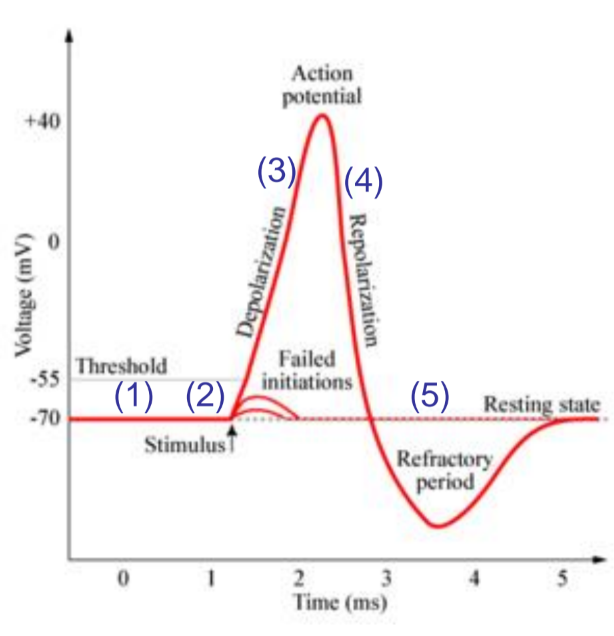
number 1
resting state, both Na+ and K channels are closed
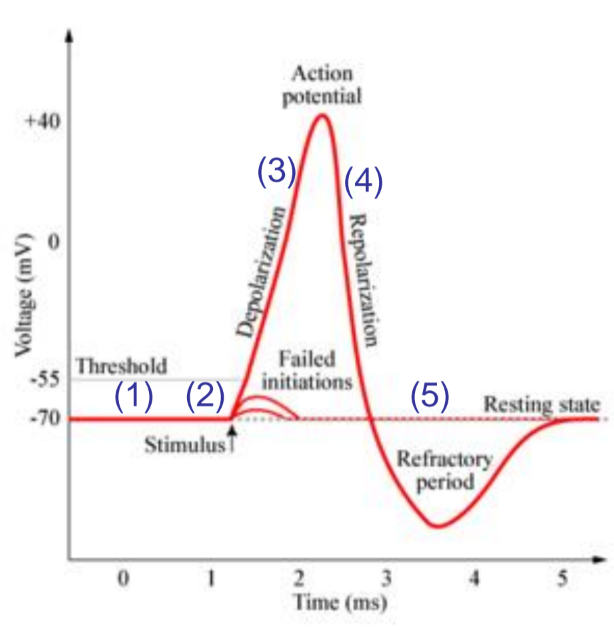
number 2
stimulus causes graded potential opening Na+ channels leading to depolarisation
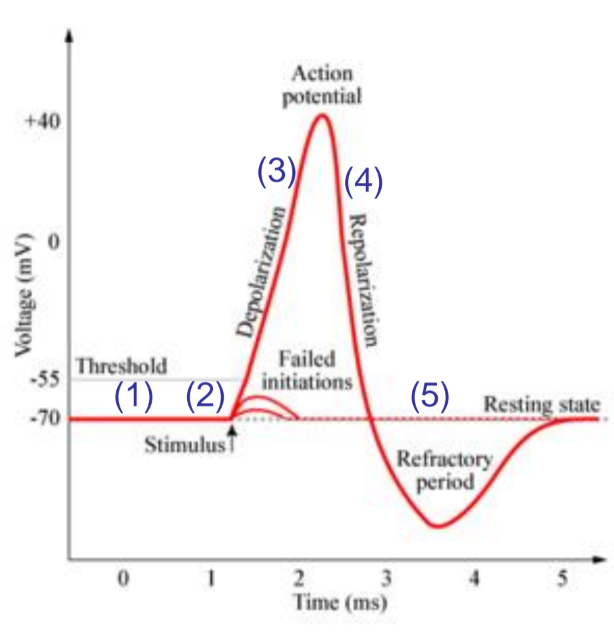
number 3
depolarisation: if stumulus is large enough and AP is initiated aditional Na+ channels (activation and inactivation gates) open and cell become more positive.
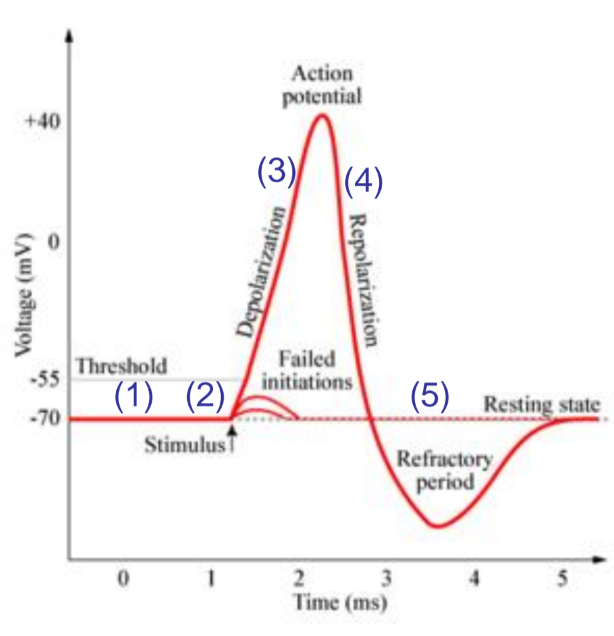
number 4
repolarization: na activation gates closes K+ gates open and K+ leaves the cell leading to a negitive charge.
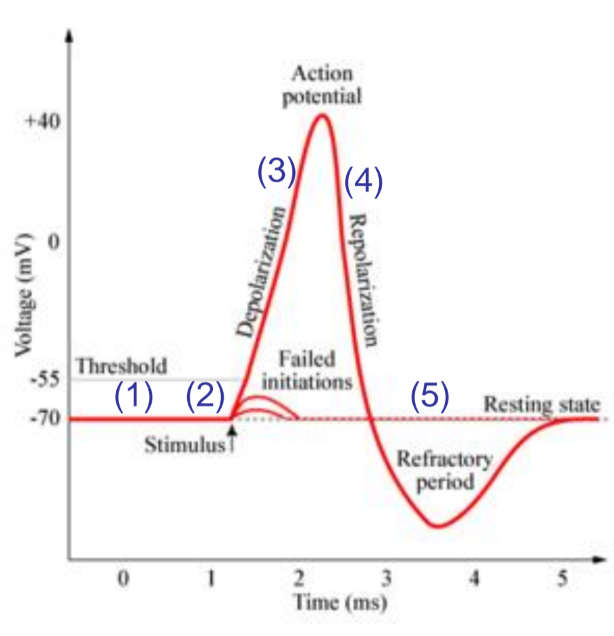
number 5
undershot: Na+ gates closed but K+ gates are still open as react slowly to repolarisation. cannot generate another action potental until retuened to resting state (refactory period)
propigation or conduction
for AP to functionas a long distance signal it must somehow travel along an axon to the far end of the cell. this is called_____ or_____ and its dependant on postitve feedback.
propigation of action potential (continuous conduction)
AP is generated as Na+ ions flow inwards at a triger zone (depolarization)
deporlarization opens adjactent Na+ gates and generates a second AP repolarization is now occuring at a triger zone,(outflow of K+)
seccond AP generates a third AP as third AP depolarizes second AP repolarizes .
saltatory conduction
the jumping of the AP from node to node- the AP dose not propigate itself between the notes rather the Na+ current generated by the AP travels along to the next node where it depolarises and stimulates a new AP
vertebrate axons are mylenated and voltage gates are concentrated in the nodes of ranvier (unmylenates)
benifts of saltatory conduction
faster conduction adn less associated energy costs for the cell.
synapese
allow information to be integrated and filtered, certain signas are transmited while others are blocked.
synapeses are also the sites of actions for many drugs that affect the brain.
axodendritic
from axon to dendrite
axosomatic
from axon to soma
axoaxonic
axon to axon
Electrical synapses
ionic current spreads directly from one cell to another through gap junctions each gap contains hundreds of tubular protien structures called connexons that form tunnels to conect the cytosol of two cells. common in visceral single unit smooth muscle cardiac muscle and a developing embryo
Advantages of electrical synapses
faster communication than chemical synapses since the impulses conduct across gap junctions.
synchronisation - achives cordnated contractions of the heart or smooth muscle.
allow for two way transition of impulses
chemical synapses
through exocytosis of the synaptic vessicles, a presynaptic neuron relases neurotransmitter molecules. after diffusing across the synaptic cleft, the neurotransmiter binds to receptors in the plasma membraine of the postynaptic neuron
steps of chemical synapse step 1
a nerve impulse is passed allong the axon of a nerve cells and terminates at the synaptic end bulb
Steps of chemical synapse step 2
the depolarizing stage of the nerve impulse opens voltage gates Ca+ channels resulting in the net flow of Ca+ inwards through the open channels
Steps of chemical synapse step 3
increase in Ca+ in the presynaptic cell triggers excotysosis of synaptic vesicles. as vescicles mrege with the PMm neurotransmiter mollecules within the vesicles are released into the synaptic cleft.
Steps of chemical synapse step 4
neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to neurotransmitter receptors on the post synaptic PM.
Steps of chemical synapse step 5
binding of receptor and neurotransmitter opens channels allowing partictular ions to flow allong their concentration gradients.
Steps of chemical synapse step 6
as ions flow in the the voltage across the membrane changes resulting in a postsynaptic potental which can be depolarizing or hyperpolarizing depending on ions flowing
Steps of chemical synapse step 7
When the depolarizing potental reaches threshols (55mV) an impulse is triggerd.
neurotransmitter removal
neurotransitters need to be removed from synaptic cleft or could influcece the post synaptic neuron muscle fiber or gland cell indefinitey
diffusion
Neurotransmitter diffuses away from synaptic cleft therefore cannot effect/bind to receptors
enzymatic degradation
neurotransmitter can be degrafed so they no longer function
uptake by cells
many neurotransmitters are activly transport back into the cells that released them
spatial summation
summation of the result of neurotransmitter released simultaneously by several persynaptic end bulbs
tempreal summation
summation by the result of neurotransmitter released by a single presynaptic end bulb in quick succession
EPSP
if the total excitatory effect > the total inhibitory effect but less than thereshould the result is ans ESP that dose not generate a nerve impulse. subsequent stimuli can gernerate an impulse more easily however (membraine depolarised)
Nerve impulse
if the totoal excitaory effects > total inhibitory effect and greater than threshoold the result is an EPSP tha dose generate a nerve impulse. impulse continue until EPSP drops below threshold.
IPSP
if total inhibitory > total excitary membrane hyperpolarises and postsynaptic neuron has an inablity to generate nerve impulses.
small molecule neurotransmitters
acetylcholine, amino acid neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine
neuropeptided
endophin,dinophin and substance p
acetylcholine
major neurotransmitter in the pns also presnet in cns
enzymaticlly removed from postynaptic neuron by acetylcholineterase chorine recycled to presynaptic cells. simple deffusion also occurs
amino acids
used to synthesise neurotransmitters but also act alone
are the mosy prevalent neurotransmitters in the cns and produced here
excitaory amino acids includr gluamare and asparate and function in learning memory and neurol development
serotonin
releases in the cns and controls sleep mood and movements
deficency assoceated with depression
conecntrated in the brainstem neurons and act on virtuaooy all structures in the brain and spinal cord
inhibitory effects on pathways mediating senesations
medulla oblongata
is continuation of spinal cord. it controls autonomic functions such as heart rate,blood pressure and digestion
pons
controls breathing and connects right and left hand side of cerevebelli,
midbrain
extends from pons to diencephalon also conects 3rd and 4th ventricles and procesese audio and video information and controls sleep ans consciousness
olfactory
sensory nerve
bipolar neurons
dendrites in nasal mucosa
axons end in olfactory bulb
optic
sensory nerve
retinas to thalamum
oculomoter
mixed nerve
moter fibers
to four extrinsic muscles of eye
trochlear
mixed nerve
moter fibers
sensory
trigeminal
largest cranial nerve
sensory fibers from the face
touch
temp
pain especially teeth
motor fibers to chewing muscles
Accesspory
to trapezius musscles
hypoglossal
to muscles of toung for swallowing speech
cerebellum
coordinates sleletal muscle activity, balance and equlibruim and delicate movements
thalamus
coordinates skeletal muscle activity and has a key role in awarness
hypothalamus
command centre for homeostatic and endocrine coordination
centre for drived and emotion
regulatres petutary gland
regulates circadian rhythms
epithalamus
small region consisting of pineal gland
limbic system
emotional brain, pleasure, docility and anger
cerevrospinal fluid
contributes to homeostasis in 3 ways
mechanical protection: shock absorption and flotation
chemical protection: optimal chemical enviorment for neurons
circulation allows for extange of neutrients/waste
blood brain barrier
enothelial cells by tight junctions from the bbb
controls the package of solutes between blood and cfs
water soluble substances can pass across the bbb while other insoluble substances such as protiens and antibiotics cannot
limits entery of microbes to the brain.