NEUROSCIENCE Midterm 1 (set 1)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1-3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Why study sensation and perception?
To repair sensual functions- like when spatial neglect occurs after stroke to right parietal lobe
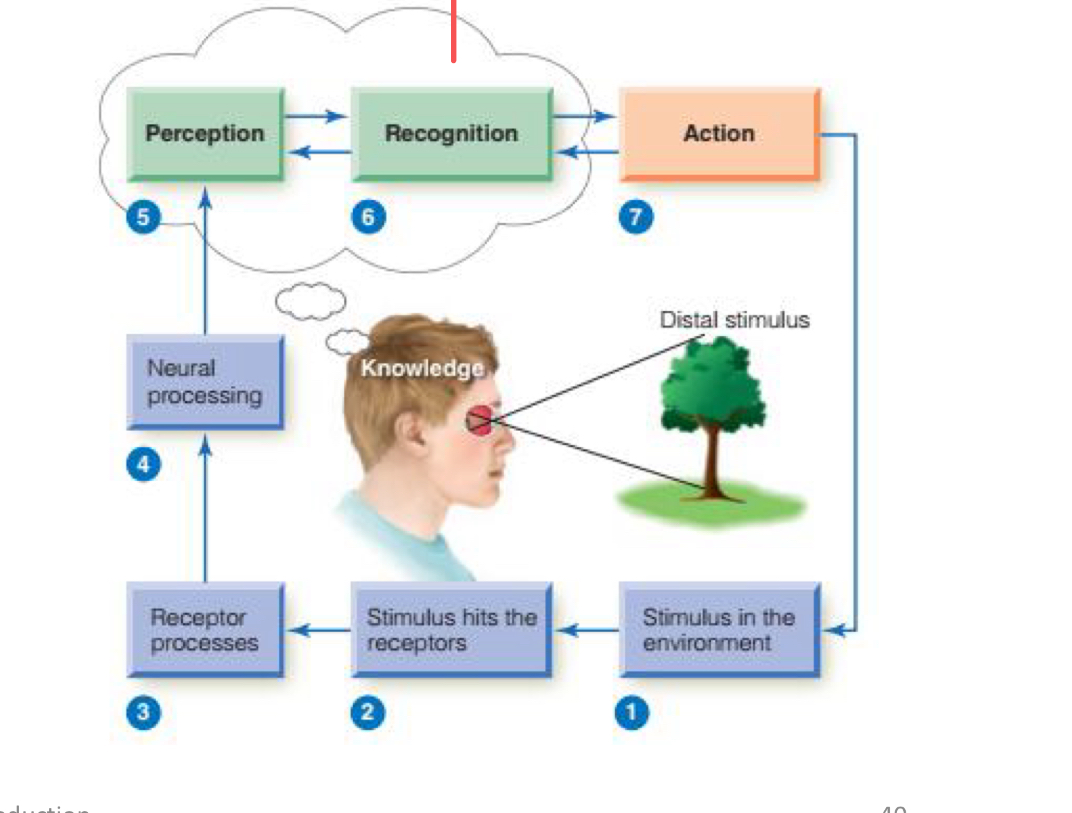
(Q) What is considered a stimulus? Give some examples of stimulus as well as the chart:
Something capable of interacting with the senses.
Molecules in the air (smell)
Sound vibrations from the leaves
Photons of light bouncing off a tree
What is not a stimulus?
Anything that does not interact with the sensory/we lack sensory receptors for: like light from a tree which you can’t even see
What wavelength of light can we perceive?
400-700nm
What decibel of sound can we perceive?
20-20 kHz. We start with a max of 20k, and then it gets worse as we age.
Can we feel wetness?
No, we don’t have a sensory receptor for that. We use cues from touch and temperature to assume wetness.
(Q) What is transduction?
This is when physical stimuli are converted into neural impulses. After transduction, the neural impulses are carried through networks of neurons to the brain
__ sends signals to the_
Thalamus (the brain's main relay station, processing and sending sensory information), amygdala (fight/flight/fear response)
What is perception?
The conscious experience of stimulus.
List the primary processing areas and what they process
Occipital Lobe: Vision
Temporal Lobe: Hearing
Parietal Lobe: Skin senses (touch, temperature, pain)
Frontal Lobe: Smell/taste
Frontal Lobe receives…
inputs from other lobes
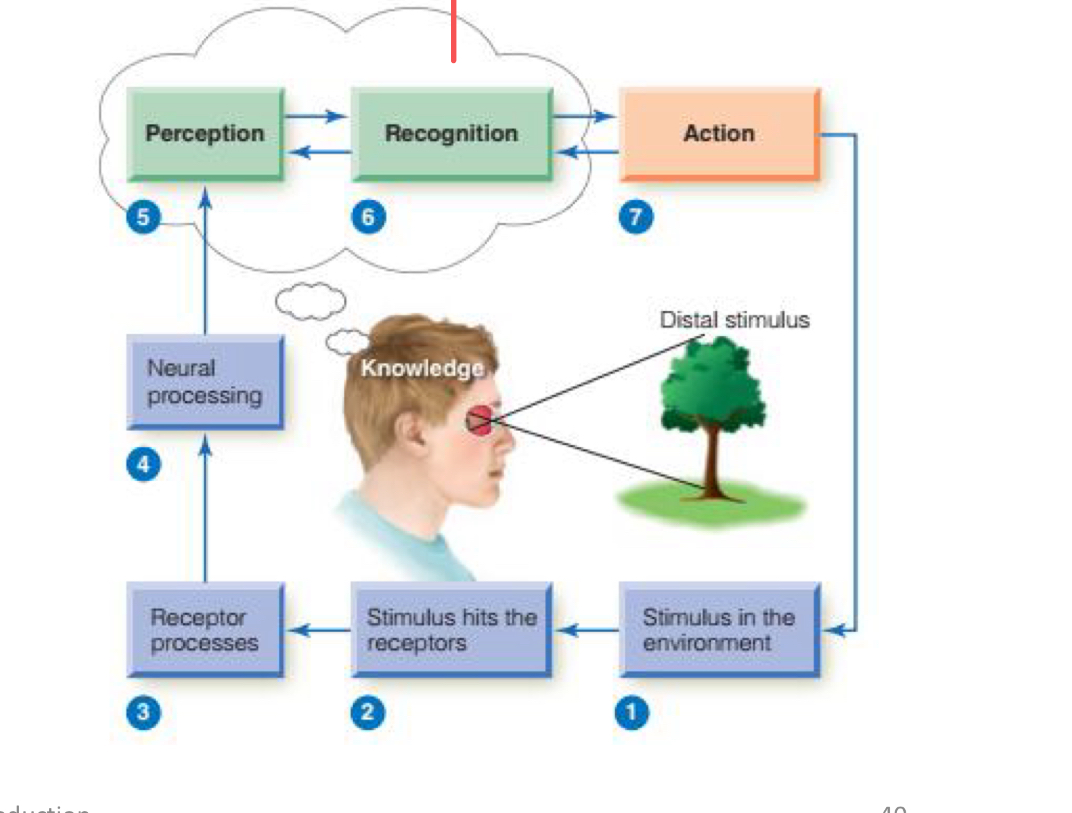
which steps does “sensation” occur in? And does it result in conscious awareness of the stimulus?
Steps 2-4 and does not result in conscious awareness of the stimulus
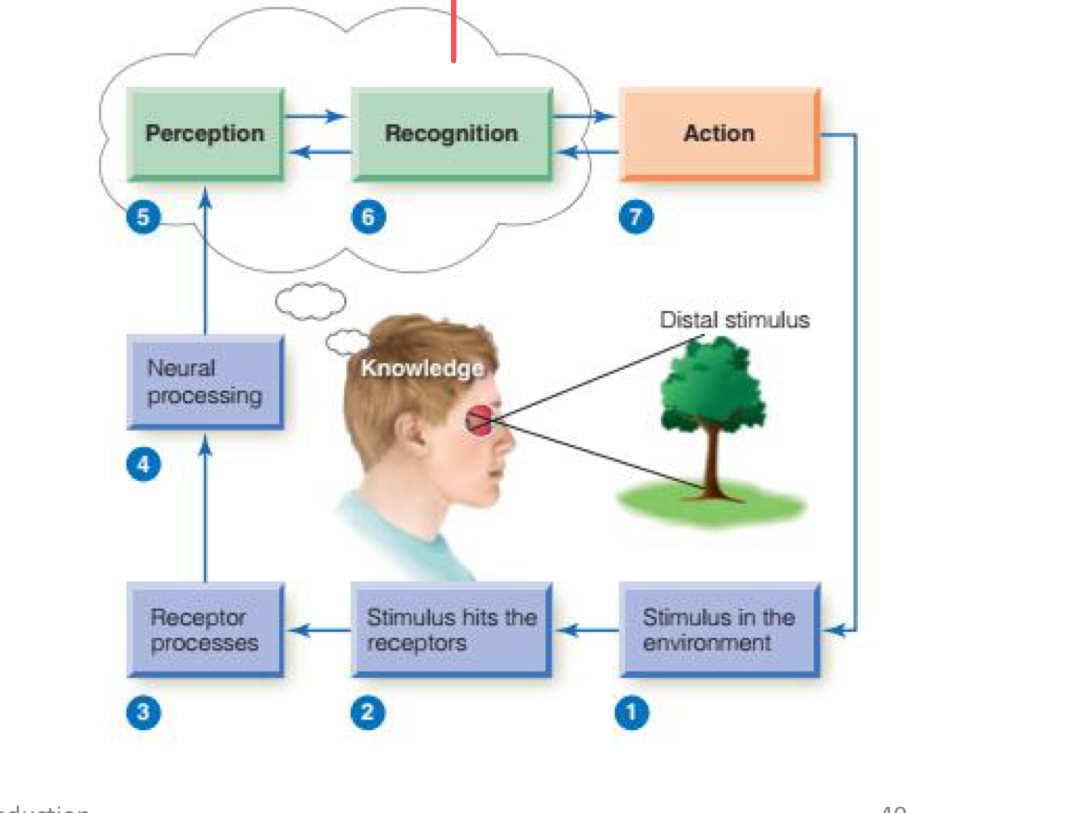
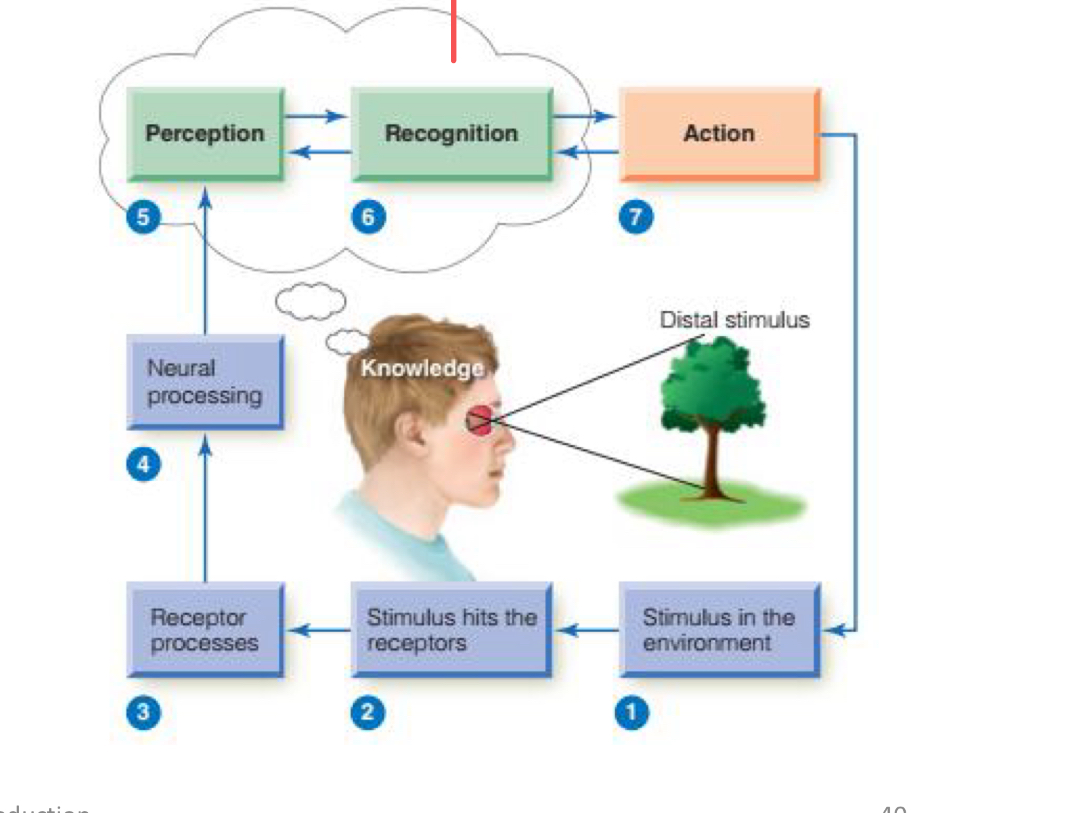
Which step starts perception of the stimulus and involves conscious experience of the stimulus?
Step 5.
Define recognition
Involves identifying the stimulus (knowing what it is). Requires top-down processes. (Step 5-6)