Exam Two- homework and quizzes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/241
Earn XP
Last updated 1:51 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
242 Terms
1
New cards
viruses possess genetic material composed of DNA or…
RNA
2
New cards
to what does the term viral species refer?
a group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and structure
3
New cards
viruses that use RNA as a template for transcribing DNA include…
retroviridae
4
New cards
a virus may contain any of the following EXCEPT…
ribosomes
5
New cards
some viruses have a membranelike structure on their surface, composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. this is called an…
envelope
6
New cards
the potential use of viruses that infect bacteria to treat bacterial infections in humans is known as…
phage therapy
7
New cards
which of these factors is NOT used in classifying viruses?
disease symptoms
8
New cards
which type of microscope is needed to view a virus in the laboratory?
an electron microscope
9
New cards
members of the Adenoviridae cause…
the common cold
10
New cards
which of the following terms are NOT correctly matched?
Poxviridae; chickenpox
11
New cards
Influenza viruses are classified according to their hemagglutin and BLANK proteins
neuraminidase
12
New cards
which of the following is NOT a characteristic of viruses?
viral nucleic acid is surrounded by plasma membrane
13
New cards
a double-stranded, enveloped DNA virus that contains reverse transcriptase belongs to which family?
Hepadnaviridae
14
New cards
the protein coat of a virus is called the …
capsid
15
New cards
which statement about viruses is FALSE?
viruses will usually infect any available cell; regardless of the cell type
16
New cards
What is the usual size range of viruses?
30 to 300 nanometers
17
New cards
which method CANNOT be used to culture viruses in a laboratory?
nutrient agar culture medium
18
New cards
what is the name given to the viral DNA incorporated into a lysogenic cell?
prophage
19
New cards
after the attachment and entry of a virus into a host cell, what is the next step in the multiplication of animal viruses?
uncoating
20
New cards
during BLANK, the phage remains latent
lysogeny
21
New cards
which of these statements is NOT true?
attachment of animal viruses to host cells is random and nonspecific
22
New cards
cell lines derived from transformed (cancerous) cells are called…
continuous cell lines
23
New cards
the toxin production by Corynebacterium diphtheria carrying a template phage is an example of…
phage conversion
24
New cards
which two virus families make DNA from an RNA template?
Hepadnaviridae and Retroviridae
25
New cards
how might a virus pick up a human oncogene?
specialized transduction
26
New cards
consider a virus whose genome is composed of minus (-) sense RNA (for example, the rabies virus). what would be the first step in the biosynthesis of that virus?
synthesize mRNA from the - sense RNA genome
27
New cards
how would you know that viruses were multiplying in a confluent lawn of E. coli on a solid culture medium?
there would be a small zone of clearing in the bacterial culture
28
New cards
retroviridae use an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase called BLANK to transcribe DNA from an RNA strand.
reverse transcriptase
29
New cards
some viruses leave a cell by pushing through the cell membrane (rather than lysing the cell). when this happens, a portion of the membrane wraps around the viral capsid, becoming the envelope. what is the name for this process?
budding
30
New cards
in polio virus replication, the function of the antisense (-strand) RNA is to…
serve as a template for the production of sense (+strand) RNA
31
New cards
which of the following is the preferred method for cultivating many animal viruses?
growing them in animal cell cultures
32
New cards
why may you be asked whether you are allergic to eggs before receiving a vaccination?
some viruses are grown and isolated in embryonated eggs; especially those used for vaccines.
* the egg proteins may still be present in the viral vaccine preparations
* the egg proteins may still be present in the viral vaccine preparations
33
New cards
during the bacteriophage lysogenic cycle, …
phage DNA is inserted into the host chromosome
34
New cards
which of these processes of viral multiplication is most likely to damage the host cell?
release of nonenveloped viruses
35
New cards
which of these viruses can incorporate the molecule serving as mRNA into its capsid?
picornavirus
36
New cards
which of these enzymes is necessary for the replication of a +strand RNA virus?
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
37
New cards
the following steps occur during bacteriophage replication. what is the second step?
penetration
38
New cards
all of the following are prion diseases EXCEPT…
Wiles-Davidoff syndrome
39
New cards
which of the following is NOT an oncogenic virus?
Varicellovirus
40
New cards
which of the following are possible strategies for treating viral infections?
* blocking viral attachment to host cell receptors
* blocking uncoating of the virus after entry
* blocking insertion of viral DNA into the host cell chromosomes
* blocking biosynthesis of viral nucleic acids
* blocking uncoating of the virus after entry
* blocking insertion of viral DNA into the host cell chromosomes
* blocking biosynthesis of viral nucleic acids
41
New cards
which of the following may cause a persistent viral infection?
measles virus
42
New cards
which of the following pairs is NOT correctly matched?
viroid; infectious DNA
43
New cards
shingles is a medical condition that usually occurs years after chickenpox, even though no illness is present in the intervening period of time.
* this occurs because human herpes virus-3 (HHV-3) is capable of…
* this occurs because human herpes virus-3 (HHV-3) is capable of…
latent infection
44
New cards
which of these viruses is known to cause a persistent viral infection?
measles virus
45
New cards
infectious agent known as BLANK cause Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
prions
46
New cards
which of the following is NOT an oncolytic virus?
retrovirus
47
New cards
prions cause disease by…
altering normal proteins
48
New cards
an example of a latent virus infection is…
shingles
49
New cards
what type of infectious agent causes potato spindle tuber disease?
viroid
50
New cards
which of the following body sites typically does NOT have normal microbiota?
kidney
51
New cards
germ-free animals often are more susceptible to infections and serious diseases than are animals with a typical complement of the normal microbiota
* based on this observation, which of the following would be an appropriate conclusion?
* based on this observation, which of the following would be an appropriate conclusion?
normal microbiota stimulate the development of the immune system
52
New cards
P. aeruginosa and other gram-negative bacteria tend to be difficult to control with antibiotics because of their BLANK, which carry genes that determine resistance to antibiotics.
R factors
53
New cards
microorganisms that typically colonize a host without causing disease are referred to as the…
normal microbiota
54
New cards
in the human intestinal tract, E. coli produces vitamins beneficial to the host and can inhibit pathogen growth. in turn, the bacterium is supplied with nutrients and an environment for growth.
* this symbiotic relationship between E. coli and its host is an example of …
* this symbiotic relationship between E. coli and its host is an example of …
mutualism
55
New cards
what is the difference between normal and transient microbiota?
normal microbiota are permanently present
56
New cards
which of the following is NOT an example of microbial antagonism (also known as competitive exclusion)?
microbes producing vitamins and growth factors that can be utilized by the host
57
New cards
BLANK pathogens are those that do not cause disease in their normal habitat but may do so in a different environment
opportunistic
58
New cards
which of the following is nOT necessary to satisfy Koch’s postulates?
the organism must cause disease through toxin production
59
New cards
which of the following is NOT a notifiable infectious disease?
pneumonia
60
New cards
Koch’s postulates are a set of guidelines to follow if you want to …
prove that a specific infectious disease is caused by a specific microorganism
61
New cards
in a healthy human, resident microorganisms would be found in all of the following areas EXCEPT the…
bloodstream
62
New cards
which of the following best defines the term pathology?
the structural and functional changes in an individual that are brought about by disease
63
New cards
women who have a healthy population of Lactobacillus spp. as part of the normal vaginal microbiota are less likely to get yeast infections
* which of the following terms is used to explain this observation?
* which of the following terms is used to explain this observation?
competitive exclusion
64
New cards
which of the following is the third stage of a disease?
period of illness
65
New cards
which of the following is NOT a predisposing factor of disease?
all of the listed choices can be predisposing factors of disease
* lifestyle
* occupation
* gender
* climate
* lifestyle
* occupation
* gender
* climate
66
New cards
which of these diseases does not have a human reservoir?
tetanus
67
New cards
in order to understand the full scope of a disease, we take its occurrence into account. the BLANK of a disease is the number of people in a population who develop a disease at a specific time
prevalence
68
New cards
a disease that is constantly present in a population is called an…
endemic disease
69
New cards
the occurrence of streptococcal bronchopneumonia in an individual recovering from influenza is an example of a…
secondary infection
70
New cards
during the BLANK, a person recovers from a disease and the body returns to its pre-disease state
period of convalescence
71
New cards
the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream is referred to as…
bacteremia
72
New cards
\n On October 29, Barbara participated in a study group for her microbiology class. On November 1, Barbara had a “scratchy throat” when she swallowed. On November 2, Barbara had a headache, runny nose, and watery eyes. She was fully recovered on November 7. During which time was Barbara in the prodromal period?
november 1
73
New cards
the protection from infection received when individuals susceptible to a particular disease live in a population where many individuals are immune is referred to as…
herd immunity
74
New cards
which of the following is part of a plan established by the CDC, NIH, and WHO to address and prioritize issues related to EIDs?
* detect infectious pathogens, the disease they cause, and factors that influence their emergence
* expand basic and applied research on ecological and environmental factors that influence EIDs
* enhance the communication of public health information and the prompt implementation of prevention strategies regarding EIDs
* establish plans to monitor and control EIDs worldwide
* expand basic and applied research on ecological and environmental factors that influence EIDs
* enhance the communication of public health information and the prompt implementation of prevention strategies regarding EIDs
* establish plans to monitor and control EIDs worldwide
75
New cards
an infection that does NOT cause any signs of disease is a…
subclinical infection
76
New cards
which one of these diseases is NOT communicable?
botulism
77
New cards
which of these disease stages is most likely to be altered in length if the number of infecting organisms at the start of the infection is very high?
incubation period
78
New cards
infections in which the pathogen is distributed throughout the body are referred to as generalized infections or…
systemic infections
79
New cards
attachment of DNA-containing animal virus
requires a physical and chemical interaction between the surface of the virus and host cell surface
80
New cards
entry and uncoating of a DNA-containing animal virus
* this process disassembles the viral capsid and releases the viral DNA
* may involve receptor-mediated endocytosis
* may involve fusion of the viral envelope with the host cell plasma membrane
* may involve receptor-mediated endocytosis
* may involve fusion of the viral envelope with the host cell plasma membrane
81
New cards
biosynthesis of a DNA-containing animal virus

82
New cards
maturation of DNA-containing animal virus

83
New cards
what disease does the human herpesvirus-1 cause?
cold sores or fever blisters
84
New cards
a feature that may be found in viruses but never in bacteria is…
may contain an RNA genome
85
New cards
how do all viruses differ from bacteria
viruses are not composed of cells
86
New cards
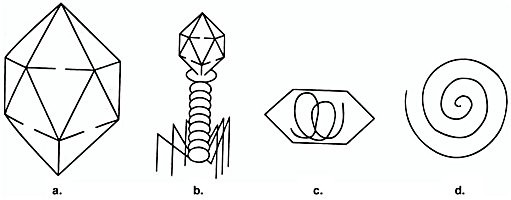
the morphological types of viruses illustrated in the figure are ultimately determined by the…
nucleic acid
87
New cards
viruses that utilize reverse transcriptase belong to the virus families…
Hepadnaviridae and Retroviridae.
88
New cards
which of the following is NOT utilized to culture viruses?
culture media
89
New cards
Each of the following can be used for the detection and/or identification of viruses except…
fermentation tests
90
New cards
Lysogeny can result in all of the following EXCEPT
immunity to reinfection by any phage.
91
New cards
An envelope is acquired during which of the following steps?
release
92
New cards
Which of the following places these items in the correct order for DNA-virus replication?
1. Maturation
2. DNA synthesis
3. Transcription
4. Translation
1. Maturation
2. DNA synthesis
3. Transcription
4. Translation
2, 3, 4, 1
93
New cards
Most RNA viruses carry which of the following enzymes?
RNA- dependent RNA polymerase
94
New cards
oncogenic viruses
cause tumors to develop
95
New cards
Which of the following statements regarding latent viral infections is true?
latent infections can persist for years in an individual without causing any symptoms
96
New cards
a persistent infection is one in which…
the disease process occurs gradually over a long period of time
97
New cards
an infectious protein is a …
prion
98
New cards
Which of the following statements concerning prion diseases is true
normal host cellular prion proteins are converted into scrapie proteins
99
New cards
from which phrase is the term “prions” derived
proteinaceous infectious particles
100
New cards
in what year did Stanley Prusiner discover prions?
1982