Physical Properties Part 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
two types of density measured in soils
particle density (ps)
bulk density (pb)
what is the soil particle density a ratio of
soil mass (oven dried) / volume of solids
does soil particle density account for pore space
NO
what is particle density mainly influenced by
density of soil minerals (< 2 mm)
what is range for soil particle density
2.60 to 2.75 g/cm3
what is the assumed value for soil particle density when not calculated
2.65 g/cm3
what is soil particle density not affected by variation in
parameters that alter volume of pores in soil
what are some soil factors that do not effect soil particle density
compaction, loss of structure, tillage
is soil particle density or soil bulk density always greater for the same soil
soil particle density
what is the ratio of soil bulk density between
soil mass (oven dried) / total soil volume (pores and solids)
what is the relationship between soil bulk density and total volume
soil bulk density increases = total volume decreases

what does soil bulk density reflect
amount of pore space in soil
what are four factors affecting soil bulk density
SOM content
soil structure
soil texture
compaction
OM density is ______
low (ranges from 0.9 to 1.4)
what does high SOM content cause in soil bulk density
direct reduction in bulk density
indirection reduction in bulk density
how does a high SOM content have direct and indirect reductions in soil bulk density
direct - OM has lower density than most mineral solids
indirect - OM promotes granular structure = increases pore space
how does soil structure affect soil bulk density
often increases in volume of pores = decreasing soil bulk density
what is the best structure for reducing soil bulk density
granular structure (high volume of pores)
what structures increase soil bulk density
columnar and platy
how does soil texture affect soil bulk density
non compacted soils high in sand have slightly higher soil bulk density than soils high in clay
do non compacted soils high in clay or sand have higher soil bulk density
sand
despite higher soil bulk density, sandy soils are not as _____ as clayey soils
restricting to root growth
why are sandy soils not as restricting to root growth compared to clayey soils
sandy soils have larger pore size than clayey soils
ideal bulk densities for soils depend on ______
texture
what is the ideal bulk densities for root growth
1.00 to 1.70 g/cm3
compare the ideal soil bulk density for fine/medium textured soils? coarse textured soils?
fine and medium - 1.20
coarse - 1.50
what are the root restricting bulk densities for clay texture class? loamy sand texture class?
clay texture class => 1.45
loamy sand texture class - >= 1.80
bulk soil density most affects root growth in _____ than ____ soils
dry and moist
what helps seed emergence in crusted soils
irrigation
what is the main cause of compaction
heavy vehicle traffic and improper tillage
what does compaction cause
subsoil compaction (hard pan forms below A horizon)
how can plow pan and traffic pan be corrected
by subsoiling operation
what are six effects of soil compaction
reduces soil pore volume = increases bulk density
reduces water retention and drainage
increases runoff and erosion
damages soil structure
reduces plant yield
reduces earthworm numbers (microbes)
what is porosity
the amount of pore space in soils
what is porosity influenced by
soil texture and structure
what is the ideal soil pore space
50% of soil volume half filled with water
what is total porosity a ratio between
volume of pore space (liquid + air) / total soil volume (dry soil)
what is the equation for total porosity
Pb = oven dry mass of soil / total volume (pore and solids)
Ps = mass dry soil / volume of solids
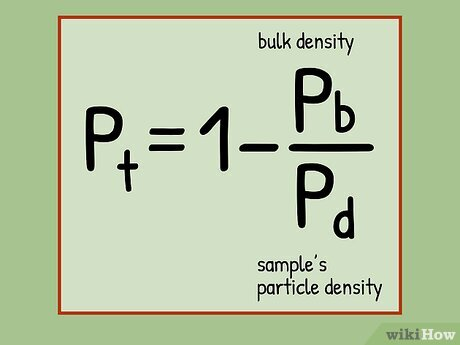
what are factors that affect soil porosity
any factor affecting bulk density also affects porosity
what is the relationship between bulk density and porosity
as bulk density increases = decrease in porosity
what two things can be used to evaluate the compactness of soil
porosity and bulk density
if pore spaces are limited what are plant roost limited in
access to air, water and nutrients
soil compaction does what to pore size and space
decreases size and space
macropores are _____ mm
> 0.08
what type of pores are most effective in translocation of air and water
macropores
what is water holding capacity
soil capacity to store water against gravity
what primarily controls water holding capacity
soil texture and OM
what is available water holding capacity
portion of water stored in soil that can be used by the plant roots
is all water stored in soils available to plants
NO
what is true of a soil with good tilth
well aggregated
has good infiltration, drainage, water holding capacity
what is the consistence of tilth
friable to very friable
what is soil tilth
physical condition of soil, which influences ease of tillage, seedbed preparation, seedling emergence and root growth