7. Neuro Stroke and TBI
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
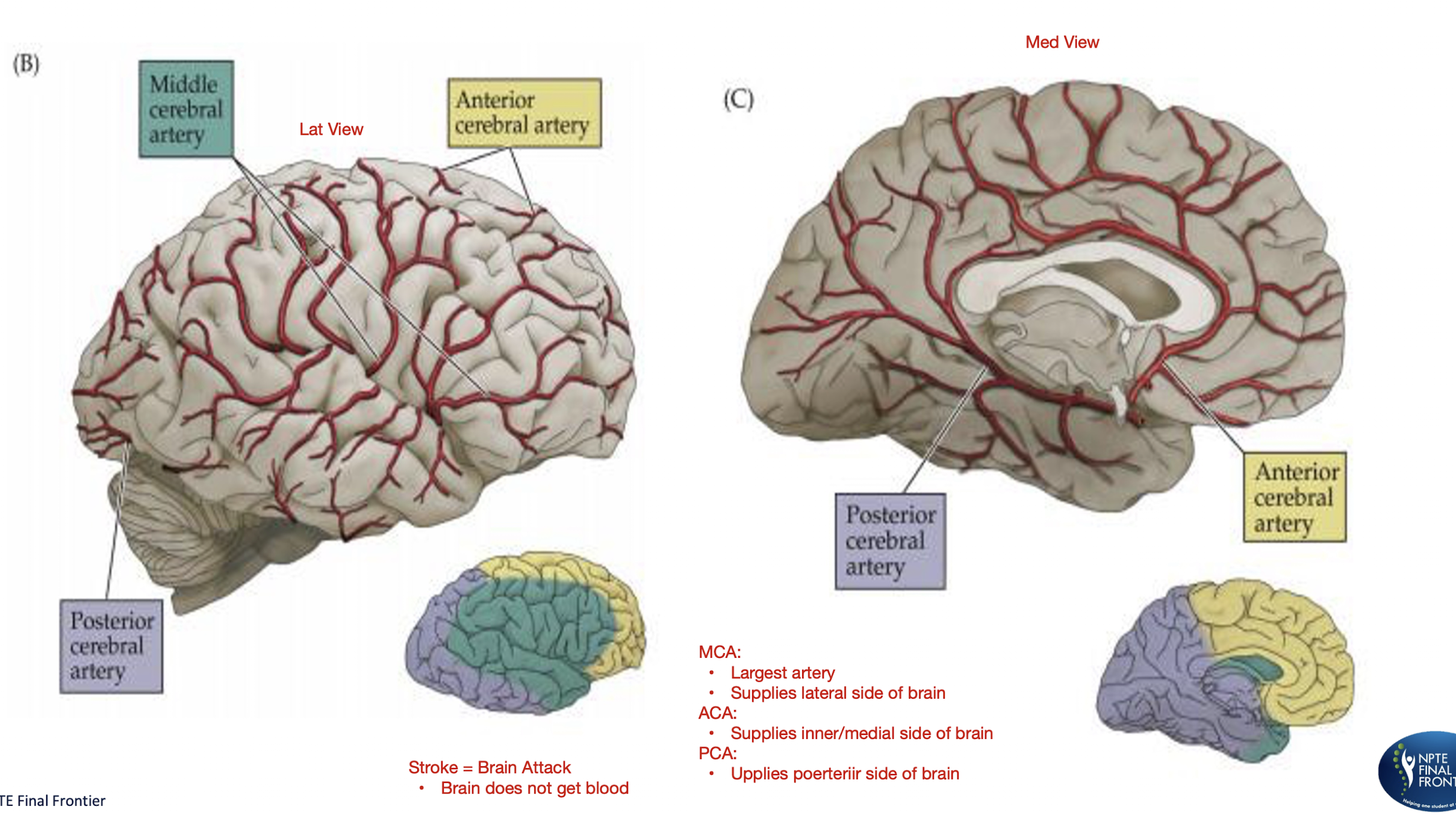
Brain Anatomy:
Stroke = ___ ___
What part of the brain does the… supply?
MCA:
ACA:
PCA:
Stroke = Brain Attack
3 Arteries
MCA: Lateral side of brain
Largest artery
ACA: Medial/Inner part of the brain
PCA: Posterior part of the brain
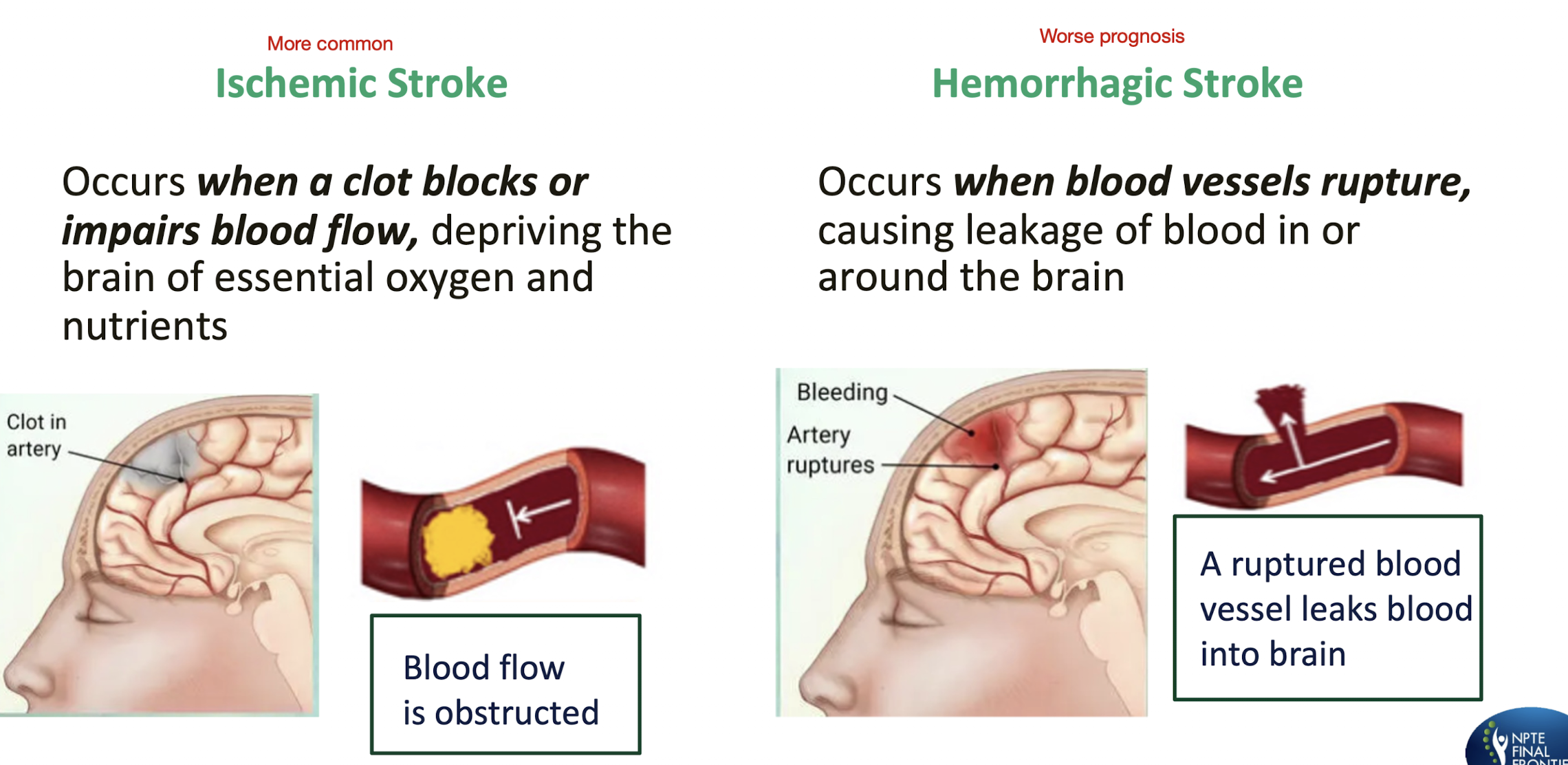
Types of Stroke:
Ischemic Stroke:
Hemorrhagic Stroke:
Which type of stroke is:
More common:
Have WORSE prognosis:
Ischemic:
Occurs when a CLOT blocks or impairs blood flow » depriving brain of essential oxygen and nutrients
Hemorrhagic:
Occurs when blood vessels RUPTURE » causing leakage of blood in or around brain
MC: Ischemic
Worse Prognosis: Hemorrhagic
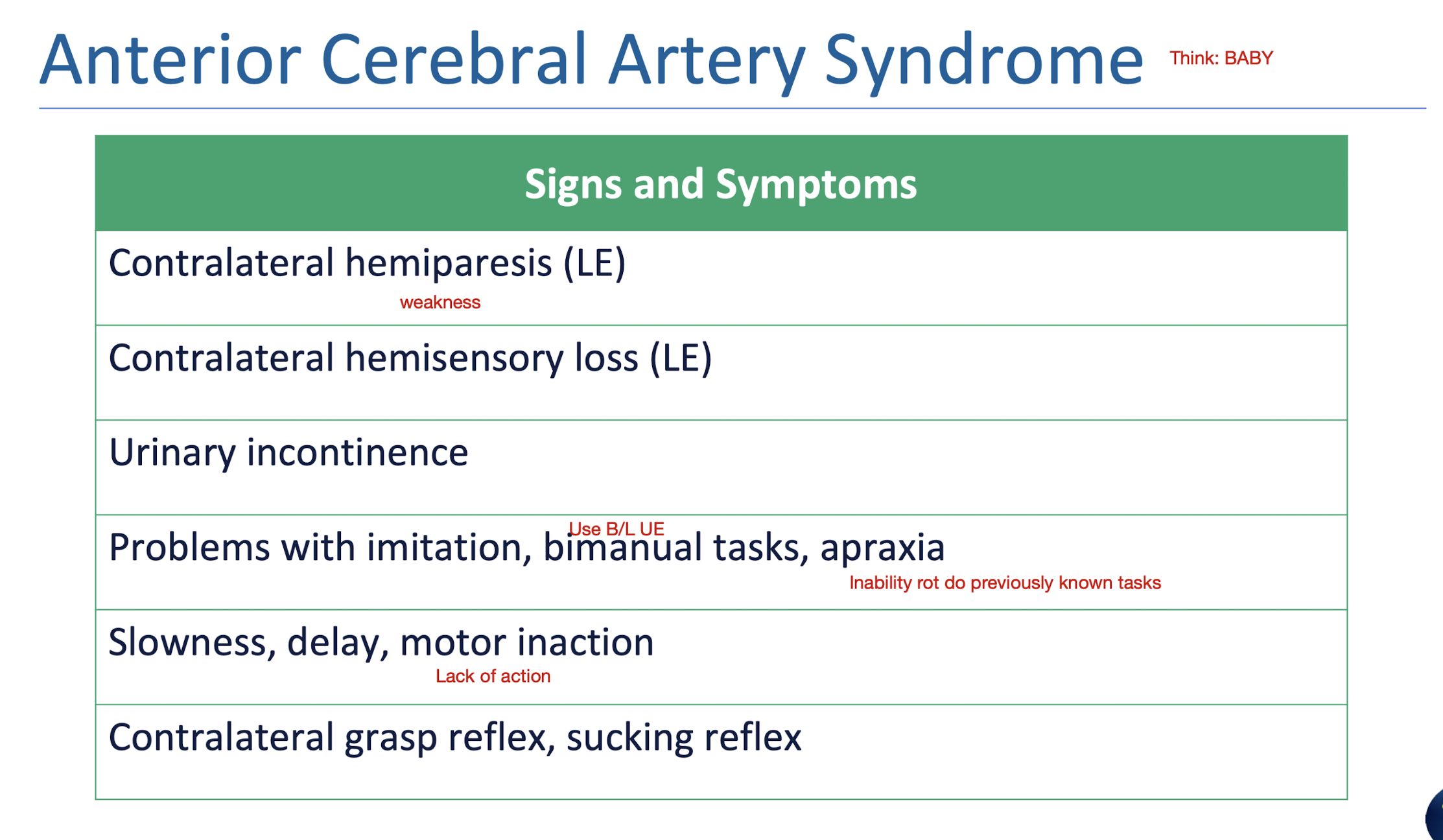
ACA: S/S
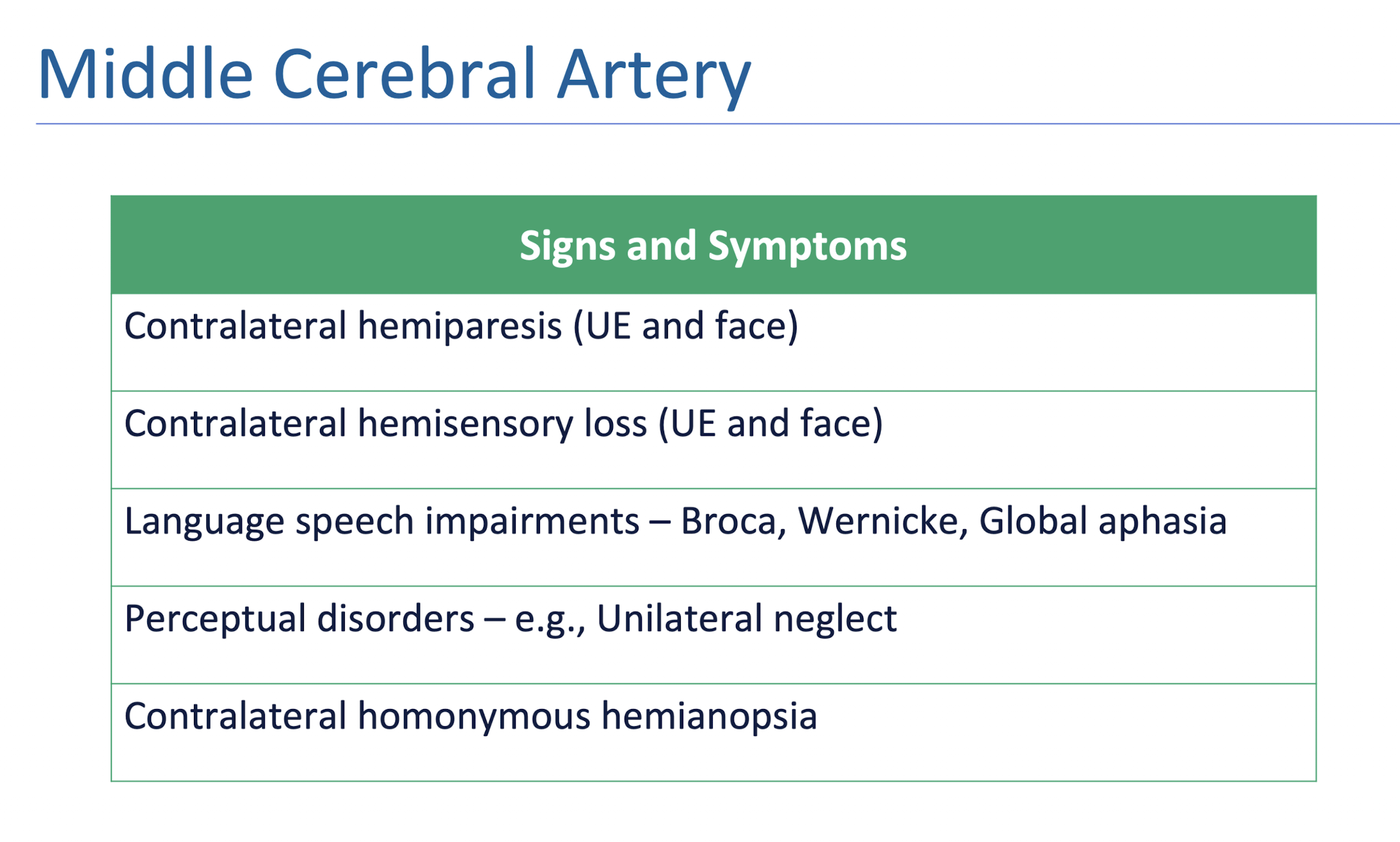
MCA: S/S
MCA Branches:
Lesion to the SUPERIOR BRANCH of MCA causes:
Lesion to the INFERIOR BRANCH of MCA causes:
Lesion at the MCA STEM causes:
Sup: Broca’s Aphasia
Inf: Wernicke’s Aphasia
Stem: Global Aphasia
L MCA Stroke:
Describe:
Broca’s Aphasia:
4 Characteristics:
Location:
Tx:
4:
Broken Speech
Expressive Aphasia
Non-Fluent Aphasia
Slow, Hesitant Speech
Location:
Frontal Lobe
Tx:
Yes/No Questions
L MCA Stroke:
Describe:
Wernicke’s Aphasia:
4 Characteristics:
Location:
Tx:
4:
Unable to understand
Receptive Aphasia
Fluent Aphasia
Word Salad
Location:
Temporal Lobe
Tx:
Gestures/Demonstration
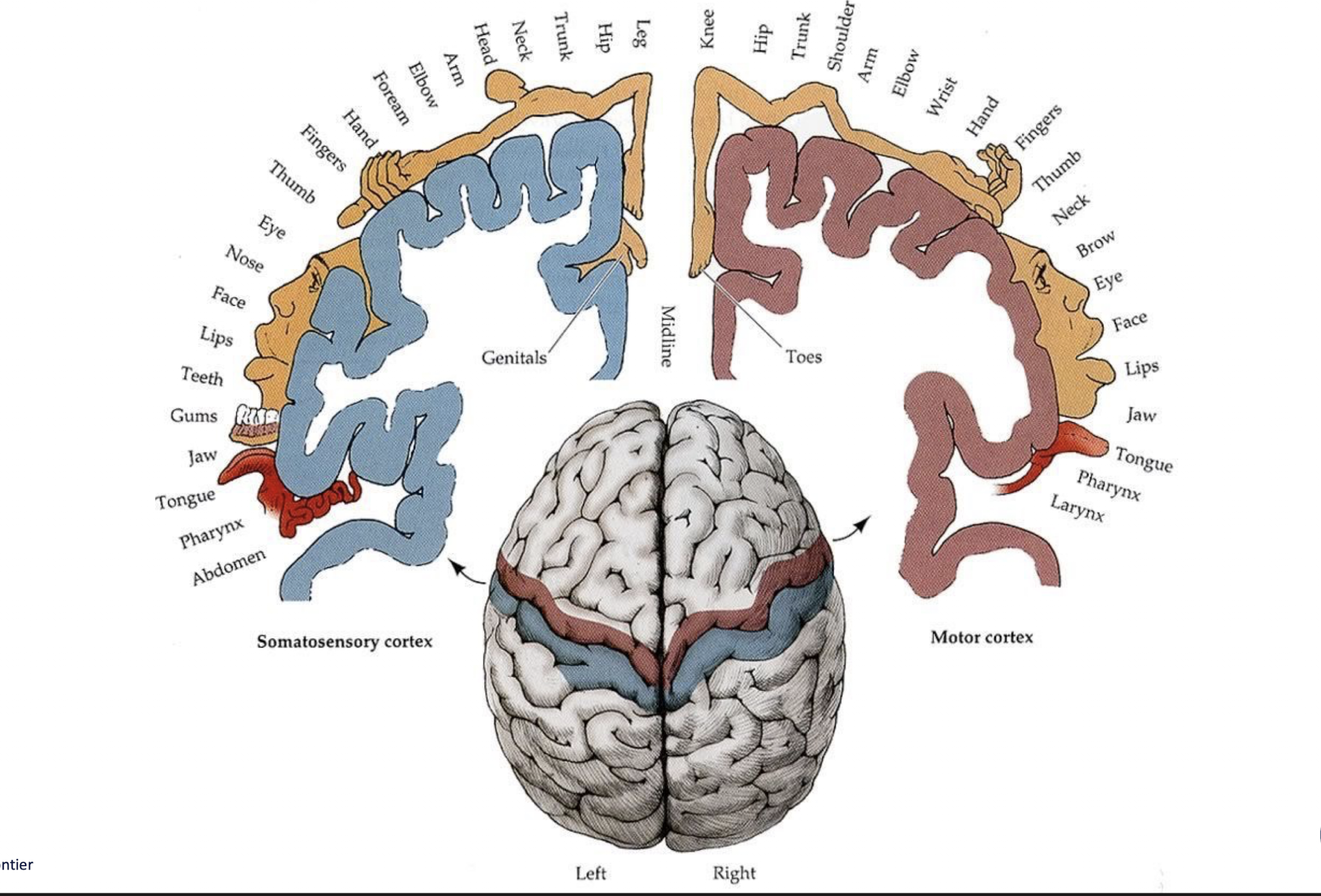
R MCA Stroke: Unilateral Neglect
What is Unilateral Neglect?
Seen with what type of CVA?
Tx: (2)
What is it:
Lack of awareness of weak side
Type:
R CVA (MCA)
Tx:
Encourage attention and use of environment on hemiparatic side and use of hemiparetic extremity
Active Visual Scanning:
Turning of the head and axial trunk rotation onto more involved side
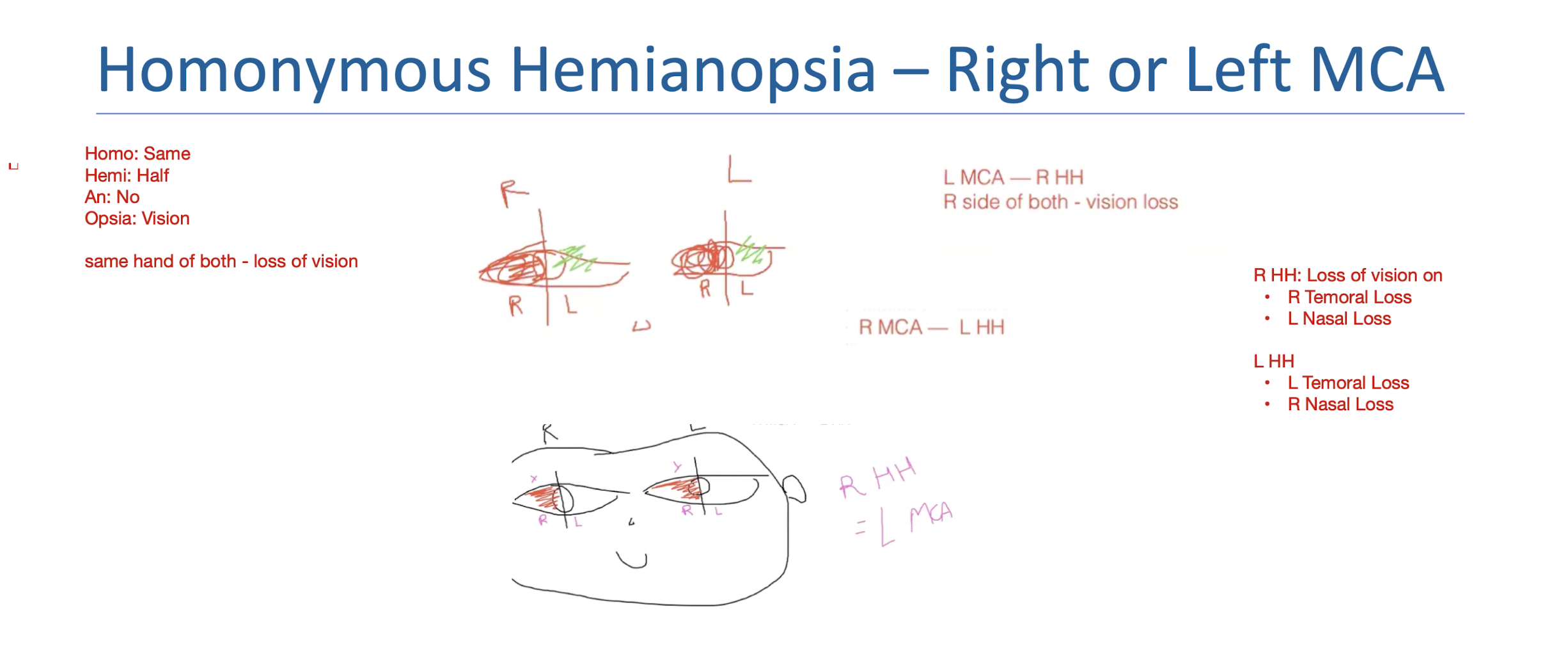
Homonymous Hemianopsia:
What is it?
R HH =
L HH =
What:
Vision loss on same side of both eyes
R HH = L MCA
R Temporal Loss
L Nasal Loss
L HH = R MCA
L Temporal Loss
R Nasal Loss
Practice Q 1:
A patient with a diagnosis of left middle cerebral artery infarct is MOST LIKELY to have which of the following signs and symptoms?
A. Excessive weakness of the right lower extremity
B. Neglect of the left side of the body
C. Left homonymous hemianopsia
D. Inability to understand words spoken by the therapist
D. Inability to understand words spoken by the therapist

PCA CVA:
Peripheral Territory S/S:
Central Territory S/S:
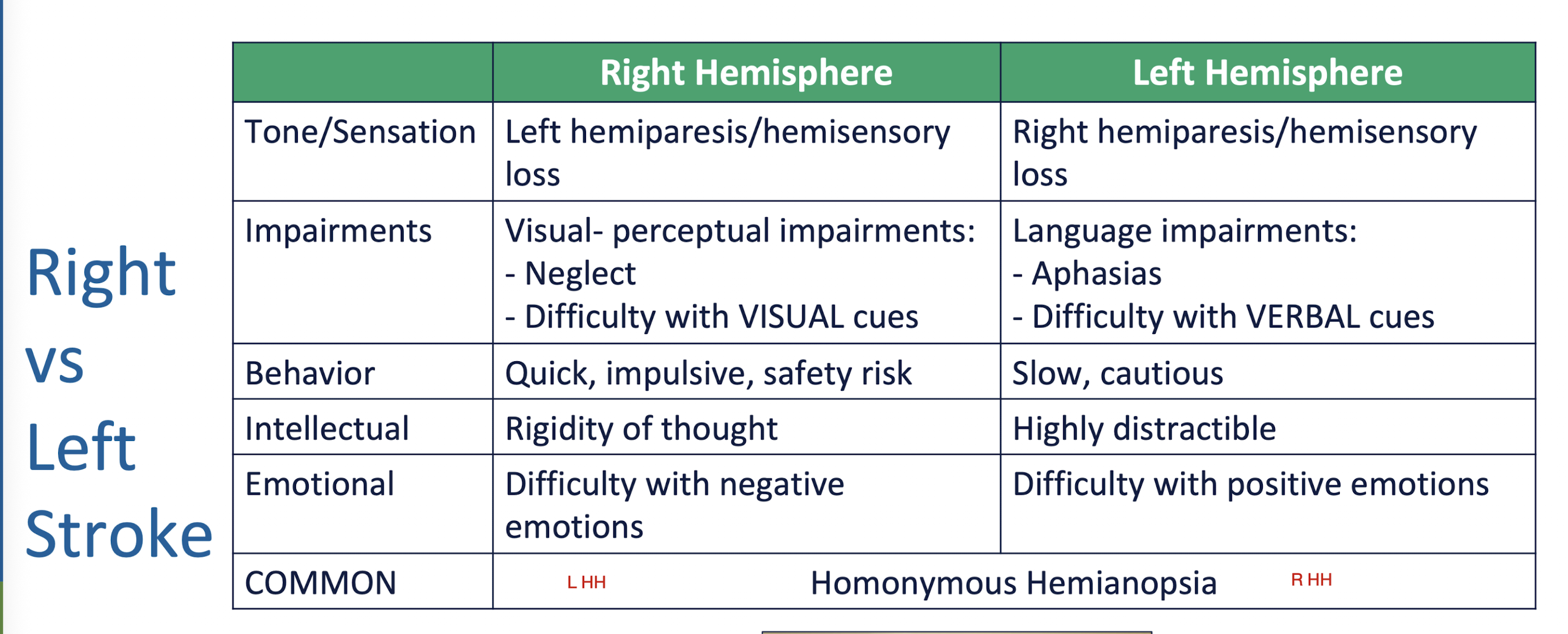
R v L CVA S/S:
Practice Q 2:
A patient presents with sudden onset of weakness on one side of the body. When asked, they were unable to name their friend who accompanied them to the hospital. During assessment, they were able to write a sentence perfectly but was unable to read their sentence. A lesion in which of the following is the MOST LIKELY cause of this symptom?
A. Superior division of Middle Cerebral Artery
B. Central territory of Posterior Cerebral Artery
C. Inferior division of Middle Cerebral Artery
D. Peripheral territory of Posterior Cerebral Artery
D. Peripheral territory of Posterior Cerebral Artery
What is the DIFFERENCE between:
Spasticity:
Synergy:
Spasticity » Increase in tone
Velocity Dependent
Seen at REST
Assessment:
PROM
Synergy » Combined patter of movement
Seen c MOVEMENT
Assessment:
AROM
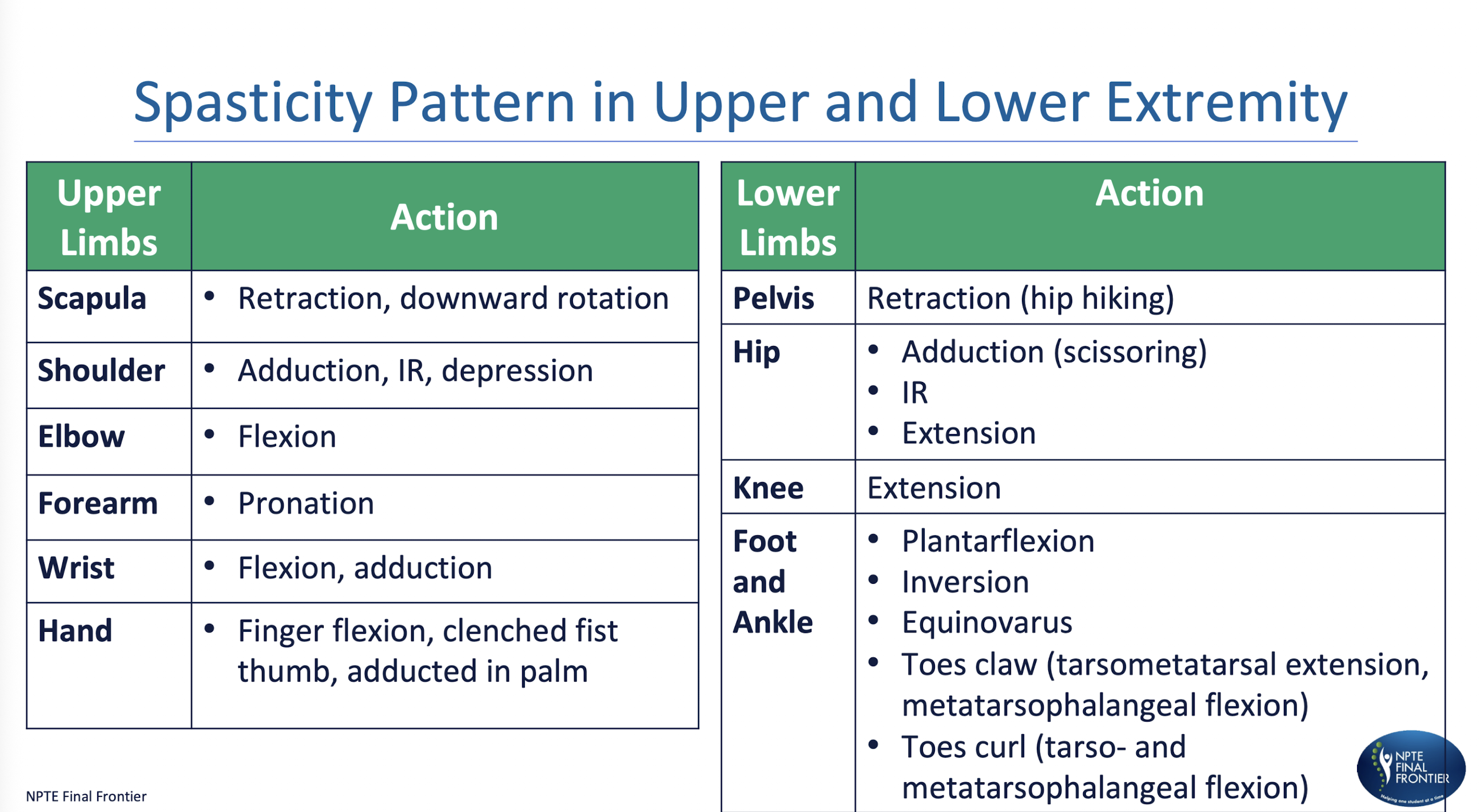
Spasticity Pattern in UE and LE:
OCCURS AT REST
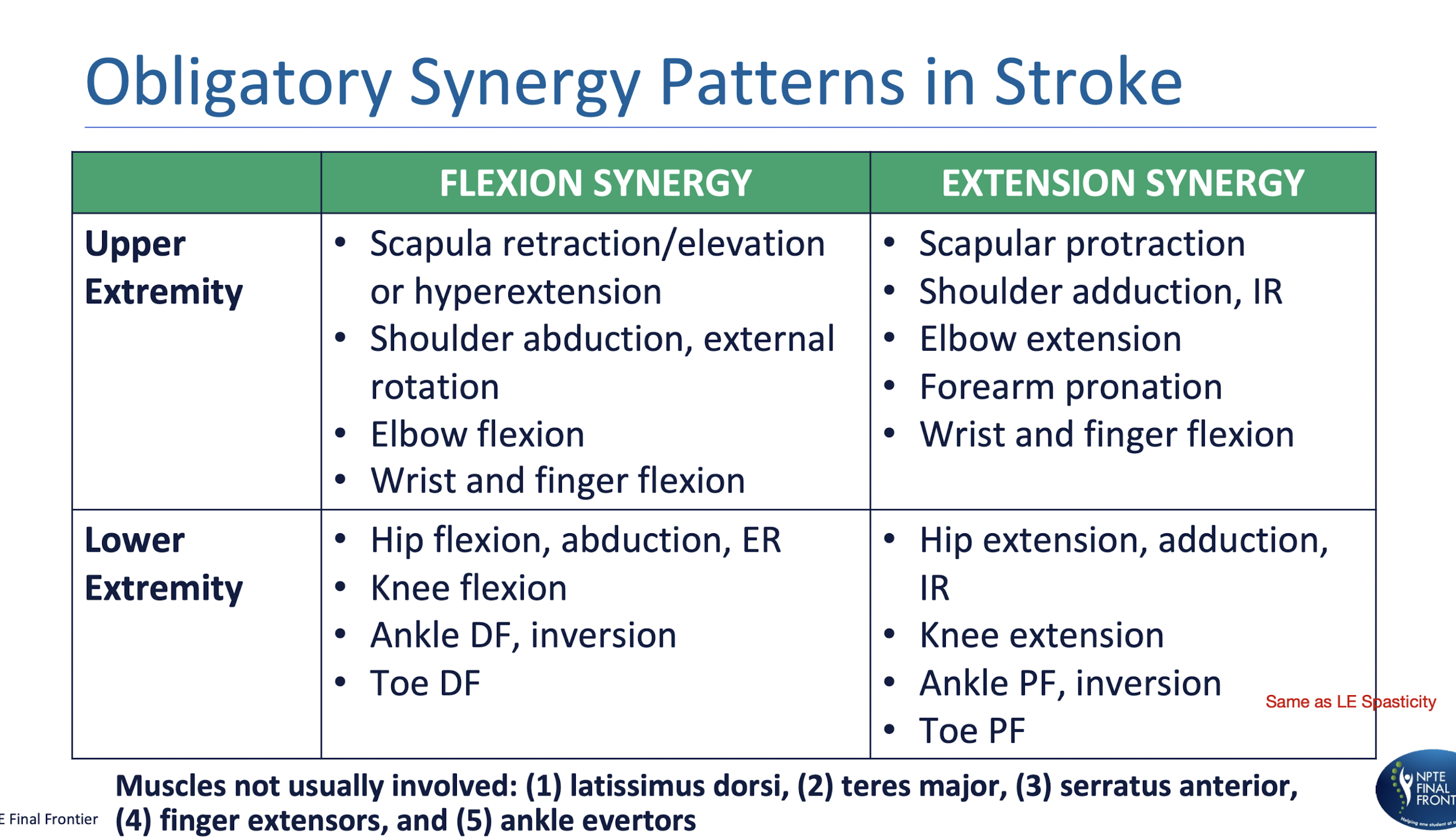
Obligatory Synergy Patterns in Stroke:
OCCURS WITH MOVEMENT
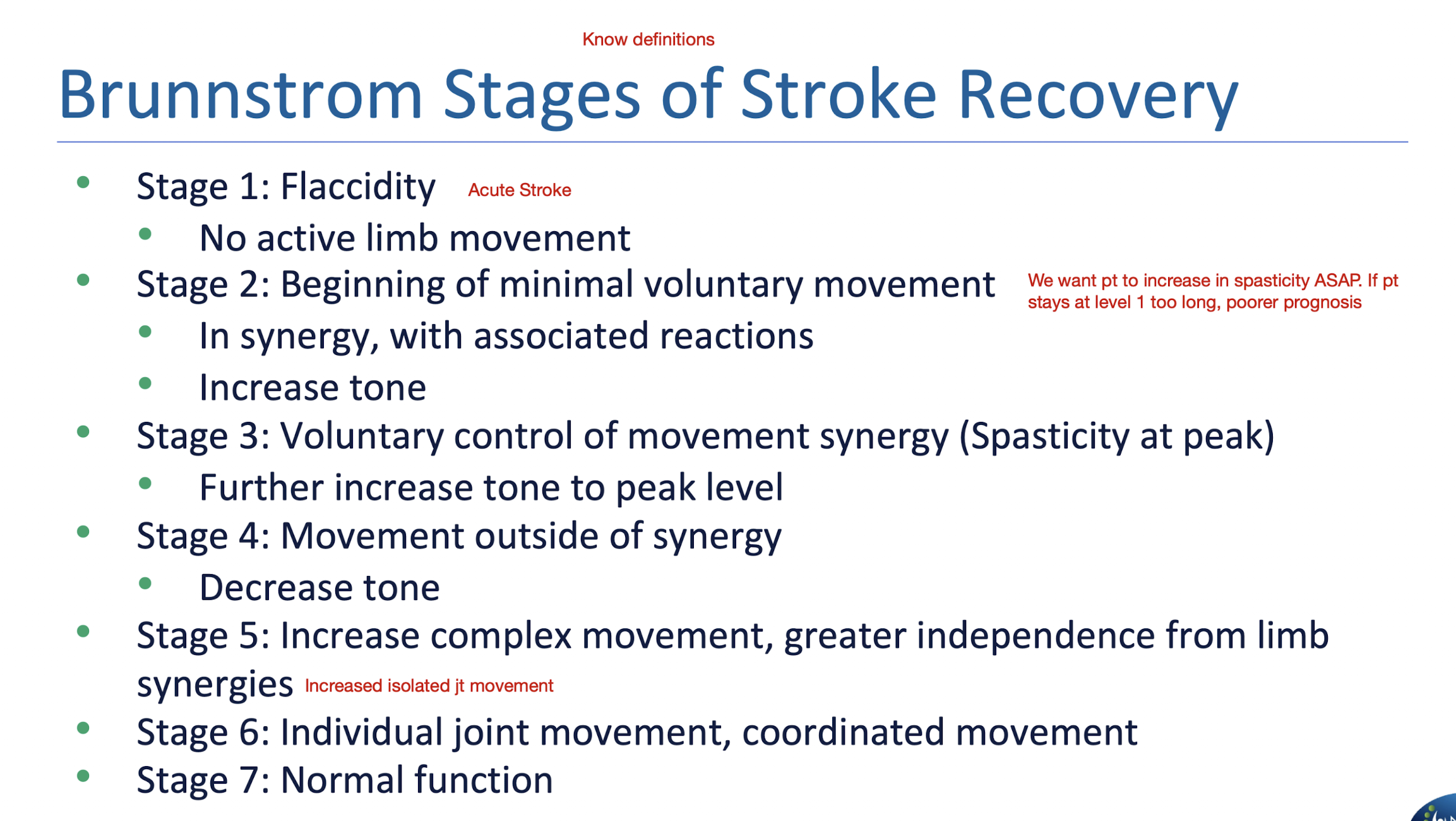
Brunnstrom Stages of Stroke Recovery
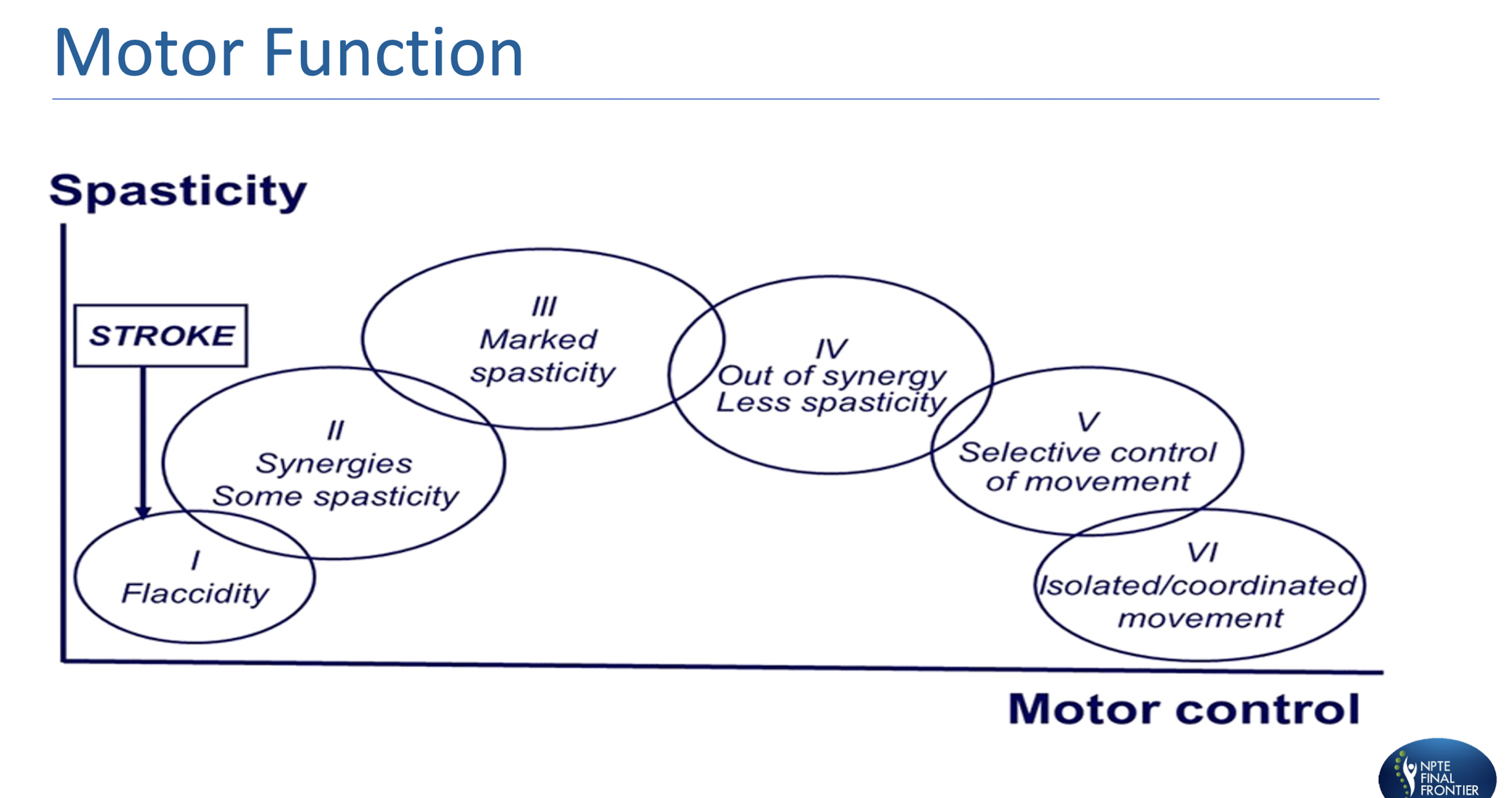
Flip for bell curve » Motor Function

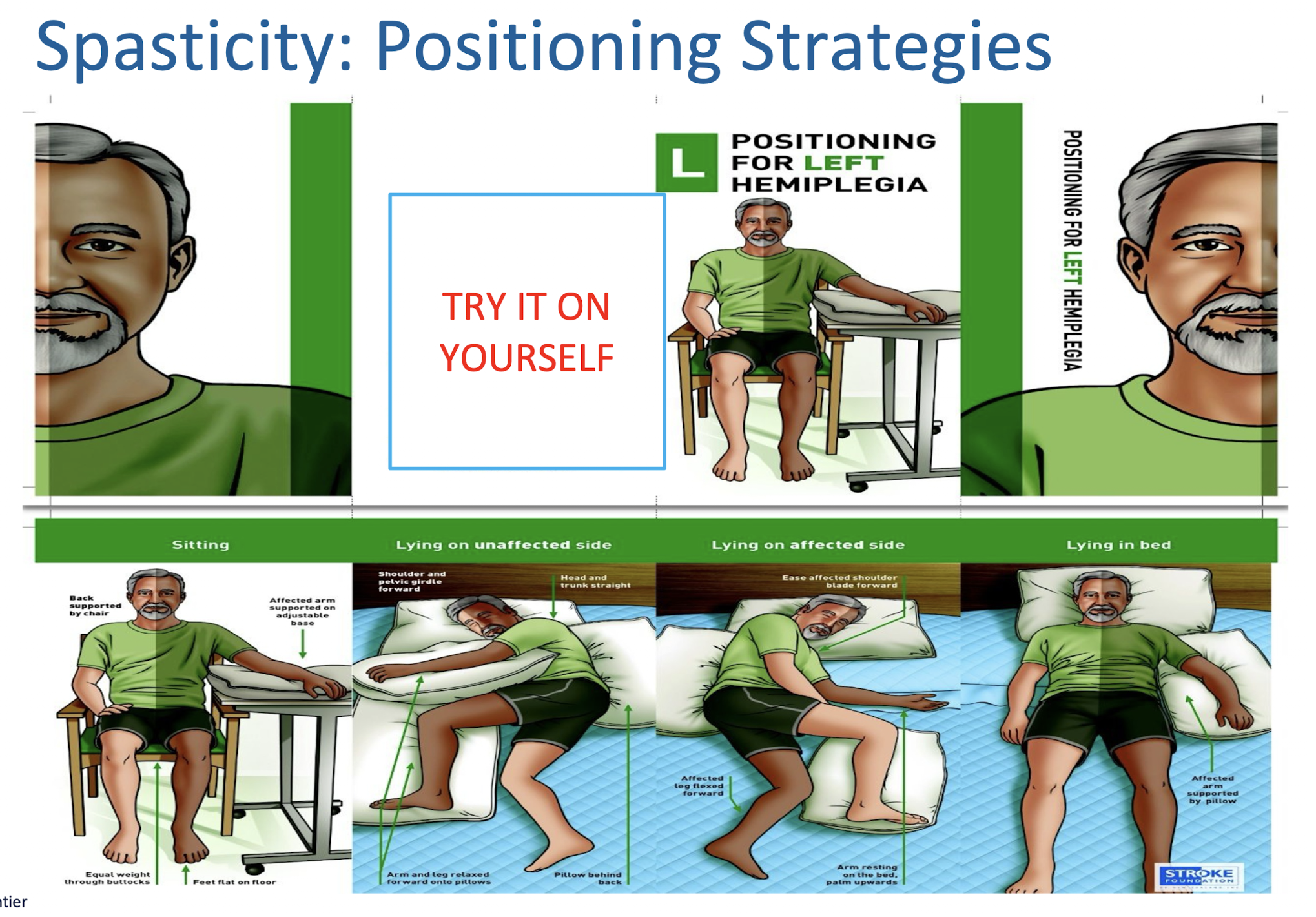
Spasticity: Positioning Strategies

Scenario Based Q 1:
With respect to the upper extremity, which of the following MOST ACCURATELY describes the position at rest?
A. Forearm pronation with wrist and finger flexion and thumb abduction
B. Forearm supination with wrist extension finger flexion thumb adduction
C. Shoulder in adduction and internal rotation and thumb adduction
D. Shoulder abducted, externally rotated, elbow flexed, forearm supinated
C. Shoulder in adduction and internal rotation and thumb adduction

Scenairo Based Q 2:
The patient has extreme spasticity, and she demonstrates flexion synergy patterns of the upper extremity while attempting to move her upper extremity. Which of the following is MOST LIKELY to be seen when she lifts her arm and what is the appropriate classification per the Brunnstrom staging?
A. Shoulder ER, abducted, elbow and wrist flexed, and forearm supinated; Stage III
B. Shoulder IR, adducted, elbow and wrist flexed, and forearm supinated; Stage III
C. Shoulder ER, abducted, elbow and wrist extended, and forearm pronated; Stage IV
D. Shoulder IR, abducted, elbow and wrist flexed, and forearm pronated; Stage V
A. Shoulder ER, abducted, elbow and wrist flexed, and forearm supinated; Stage III
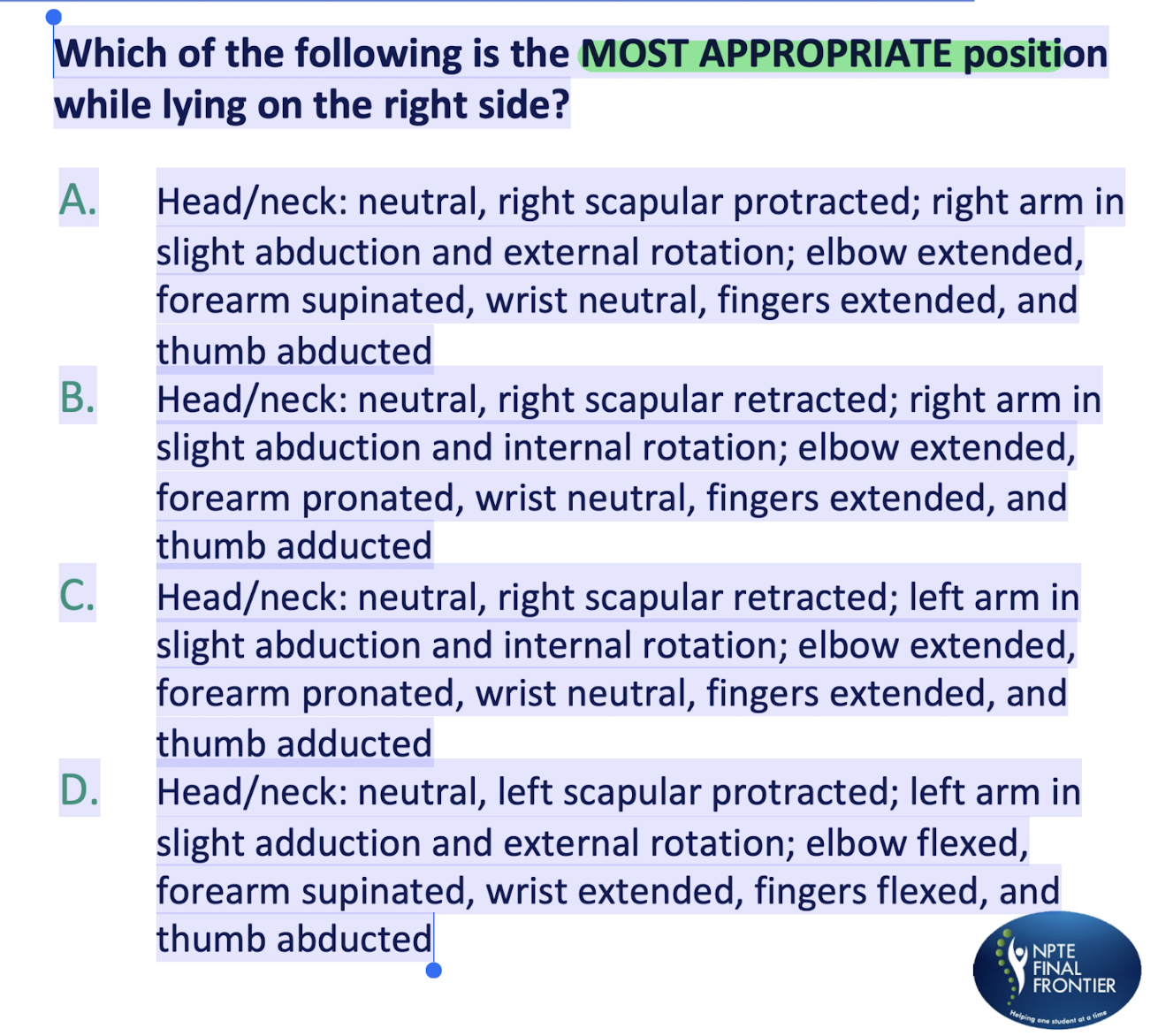
Scenario Based Q 3:

TBI

RLA: Levels I-III
RLA: Level I-III Management
What are 4 management strategies for RLA Level 1-3?
Positioning: Head neutral, prevent ulcer, sit (if stable)
Gentle PROM: Joint integrity, skin integrity
Respiratory care: Postural drainage, percussion, vibration
Educate family: What to expect, how to be more involved

RLA Level IV:
RLA Level IV: Management
How to appropriately manage Level IV in terms of:
Confusion:
Memory:
Agitated:
What is a good strategy to to perform on pts if they get too agitated?
CONFUSED:
Consistent: Same therapist, same staff, family introduce yourself daily. ESTABLISH A ROUTINE
Orient the patient: Calendar, clock
MEMORY:
NO CARRYOVER: Chart and graph to measure progress
AGITATED: Calm behavior. DO NOT confront!
Environment – Closed – prevent harm to others
Distraction
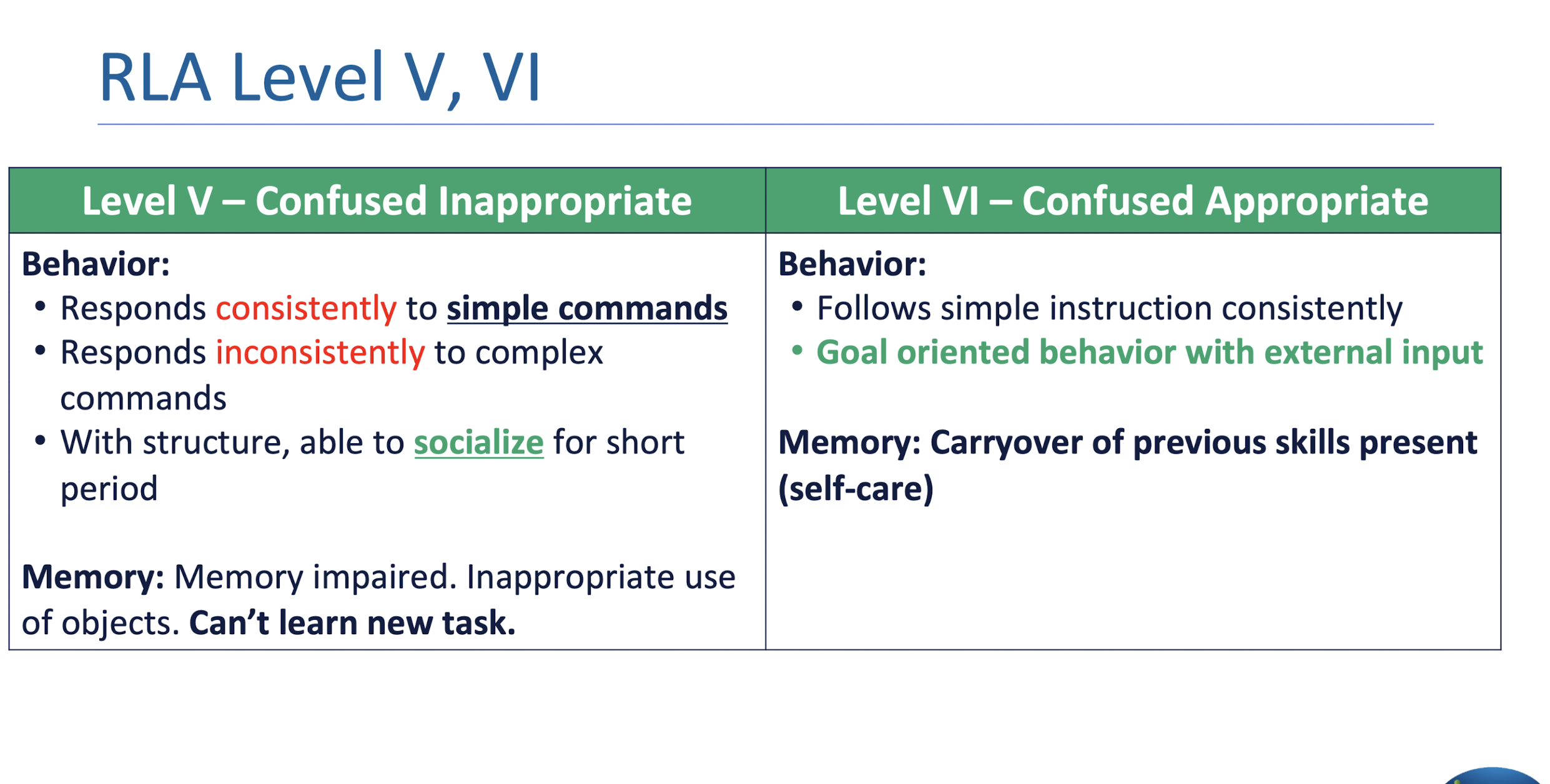
RLA Level V-VI:
RLA Level V-VI: Management
What are 2 main management strategies for RLA Level V-VI?
Follow goals from level IV
Complex commands cannot be followed - Avoid more complex open environments
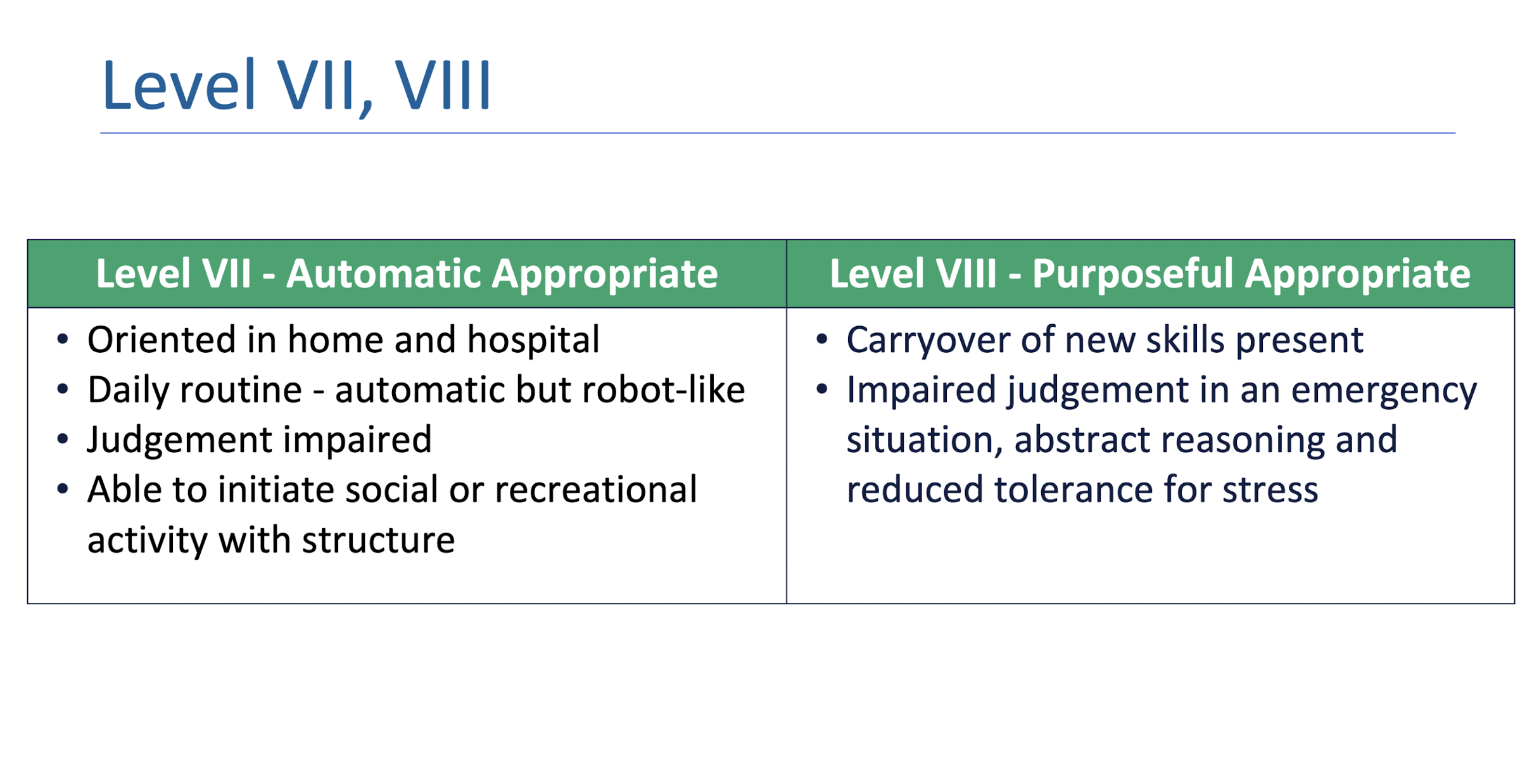
RLA Level VII -VIII:
RLA Level VII-VII: Management
What are 4 main management strategies for RLA Level VII-VIII?
Focus on re-entry to work and community
Emphasize skills related to problem solving, social interaction
Trial period of independent living
Adaptation at work or school to return to normal life

Glasgow Coma Scale:

Scenario Based Q 1:
Upon further examination, the patient seems to be in a heightened state of activity and is making up stories. They are not coordinating with the therapist at all. How would the physical therapist MOST LIKELY classify this patient’s level of cognition?
A. Level VI
B. Level IV
C. Level V
D. Level III
B. Level IV

Scenario Based 2:
Which of the following strategies will be MOST BENEFICIAL while working with the patient?
A. Having a different clinician work with the patient every day so he gets used to meeting new people
B. Involving patient in group therapy so he can make friends
C. Informing the patient two days in advance about what to expect in the next few physical therapy sessions
D. Giving the patient two options and having the patient select one
D. Giving the patient two options and having the patient select one
NOTE:
Give 2-3 options to make them feel in charge
NO Yes/No
NO open ended q’s

Scenario Based 3:
If the patient becomes agitated during a session, what is the best initial response?
A. Leave the patient alone to calm down on their own
B. Use calming techniques to distract the patient
C. Correct the patient to discourage aggressive behavior
D. Restraint the patient to calm them and avoid harm
B. Use calming techniques to distract the patient