ANSC 113 - Outline Review
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What are the parts of the scrotum
tunica darots & tunica albigunia
what is the tunica dartos
the smooth muscle in the scrotum
what is the tunica albigunia
the connective tissue in the scrotum
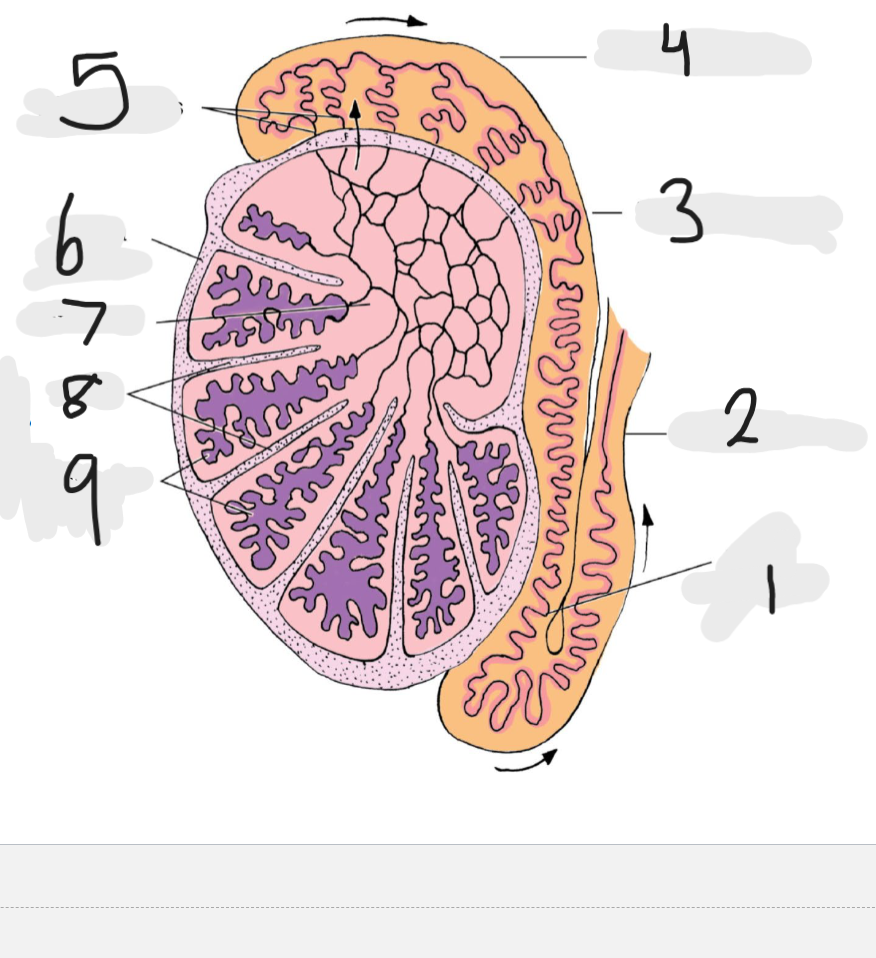
What is number 1
Tail of epididymis
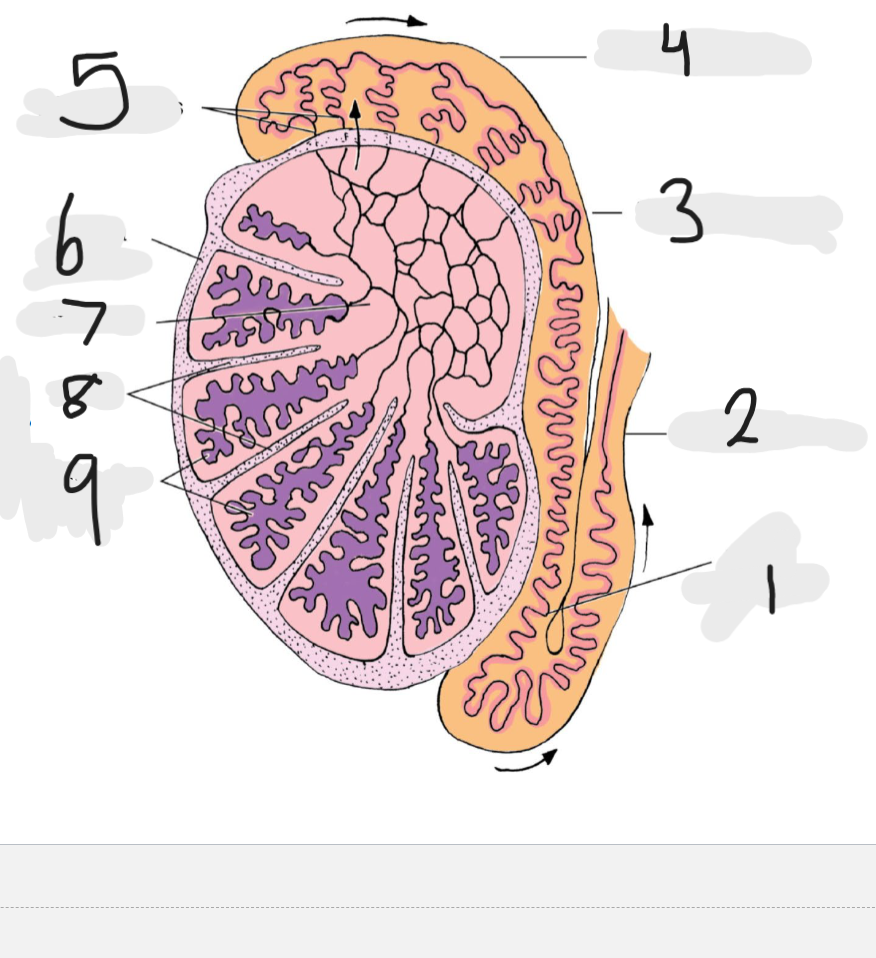
Number 2
Ducts deferens
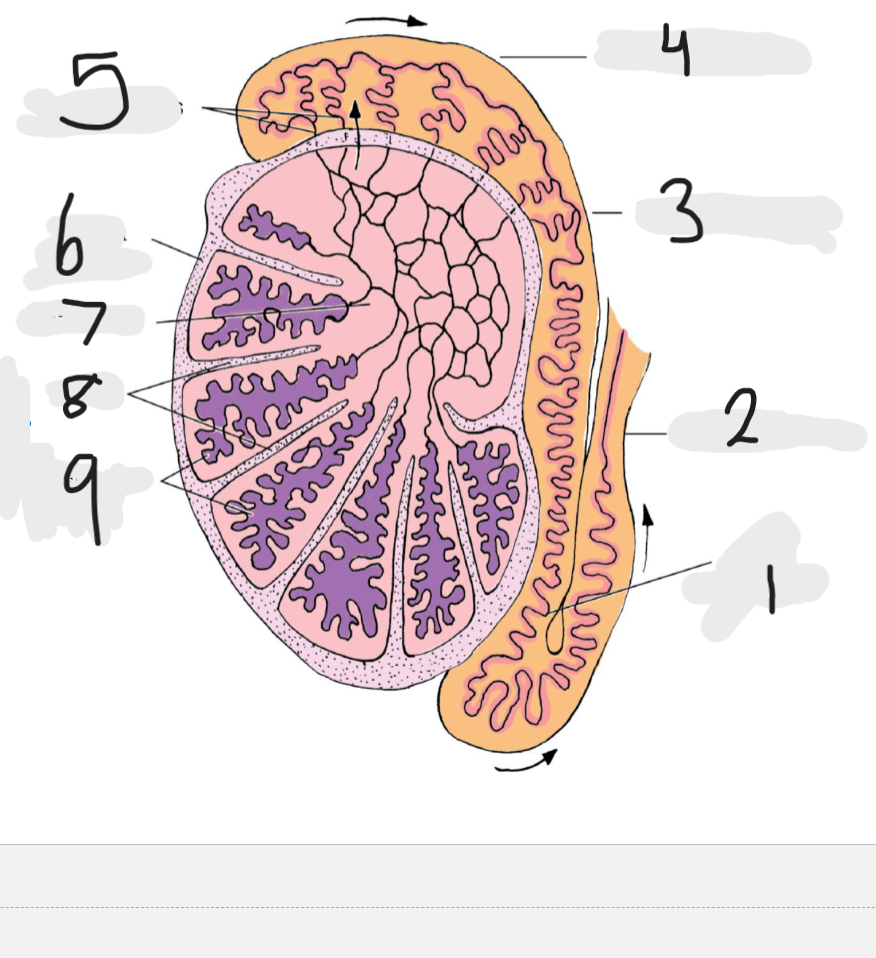
Number 3
body of epididymis
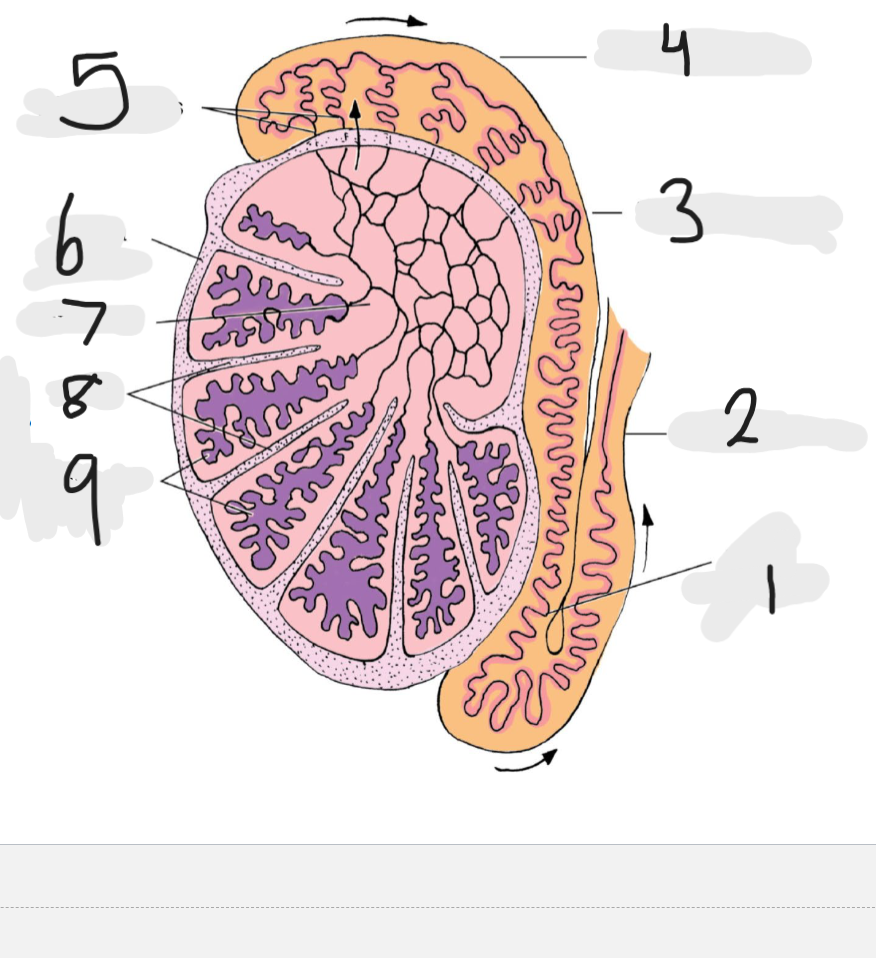
Number 4
head of epididymis
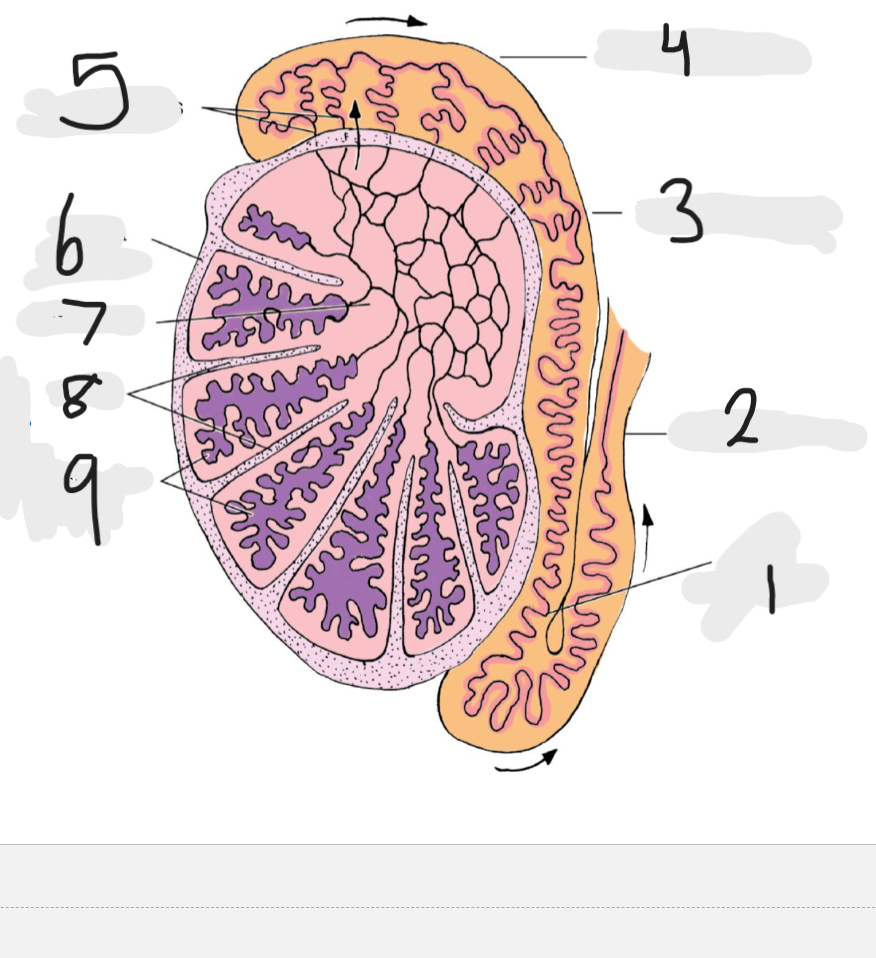
Number 5
Efferent ducts
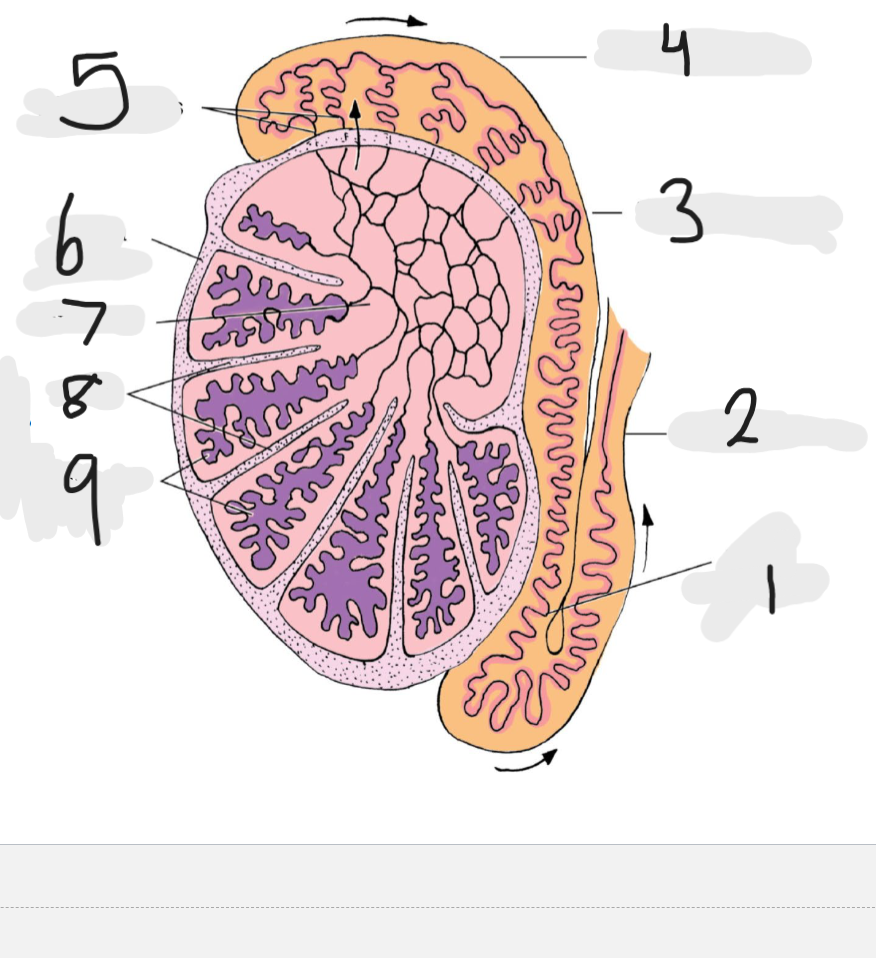
Number 6
Tunica albuginea
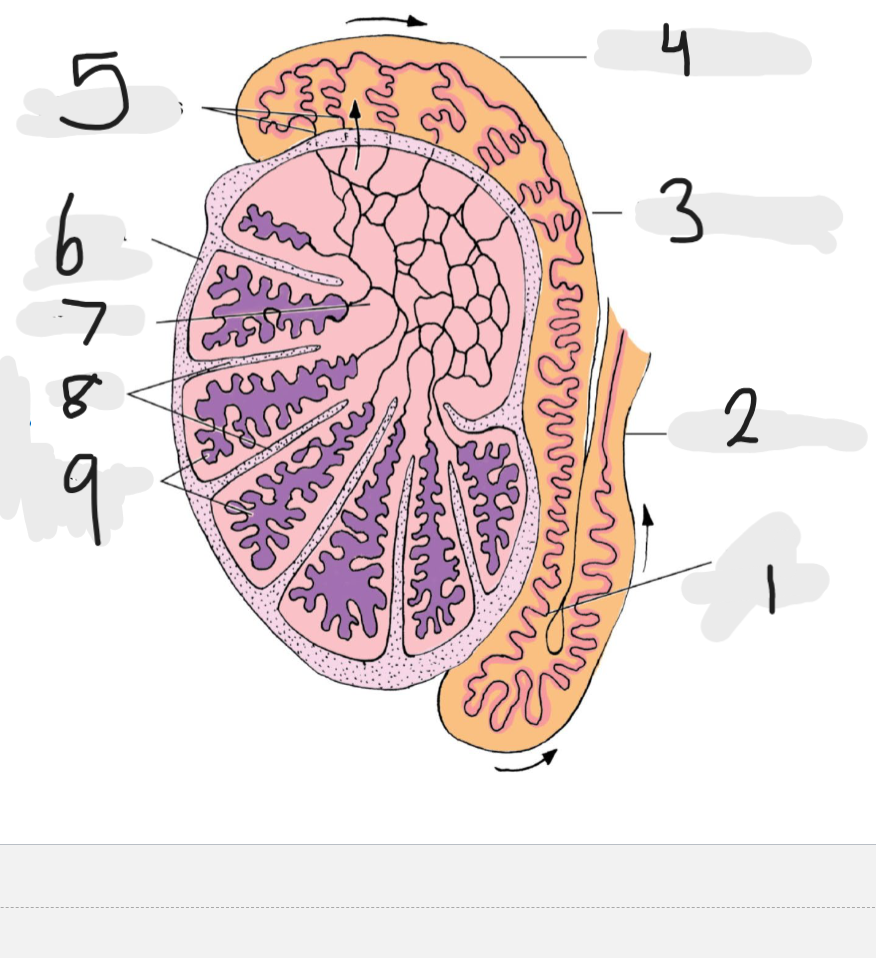
Number 7
rete testis
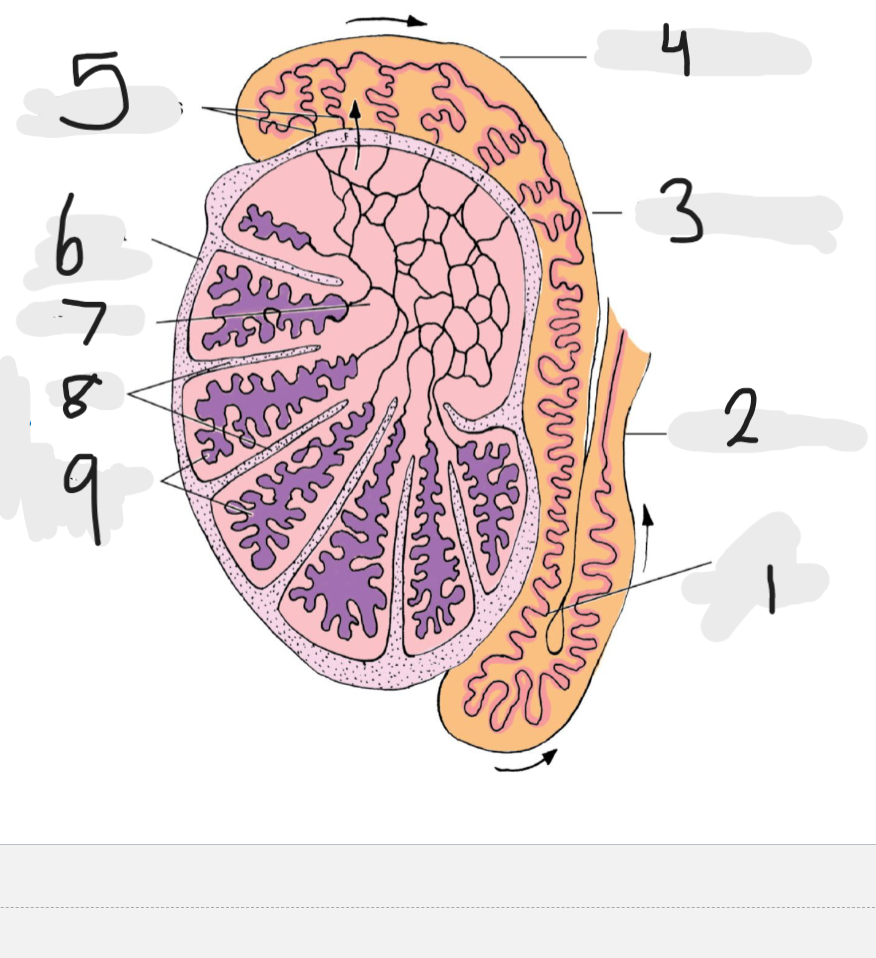
Number 8
septa
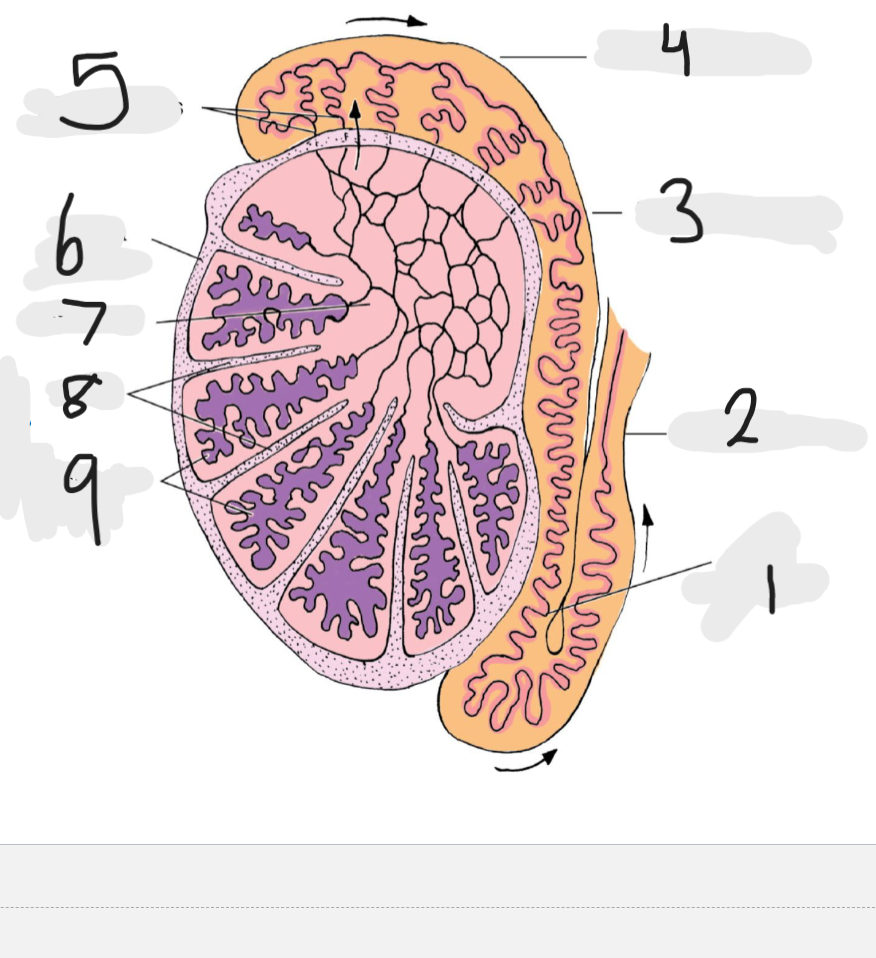
Number 9
seminiferous tubules
what is found on the INSIDE of the seminiferous tubules
Sertoli cells-support sperm
spermatogonia - cells at bottom of seminiferous tubules, starting cell for sperm
spermatocytes - slightly larger growing to sperm cells
spermatids - stage right before becoming spermatozoa
(keep the S’s together)
what is found on the outside of the seminiferous tubules in the testes?
leydig cells - testosterone production
immune cells (fight bad things before they can get to sperm)
blood vessels (duh)
what do sertoli cells do?
Support sperm
life cycle for sperm
spermatogonium (large cells with no shape)
primary spermatocyte
secondary spermatocyte
spermatid (not fully developed head)
spermatozoa
What separates the inside and outside of the seminiferous tubules
basement membrane
what is found in the intersitial space (outside st)
leydig cells
blood vessels
immune cells
why is the basement membrane important?
provide structural support
acts as a barrier
facilitates signaling between cells
epididymis parts
head, body, tail
where are sperm viable in the epididymis
tail aka cauda
parts of the spermatic cord
pampiniform plexus
cremaster muscle
vas deferens
what does the pampiniform plexus do
counter-current heat exchange
what does the cremaster muscle do
it’s a skeletal muscle that raises and lowers the testicles
what is the vas deferens
transport of spermatozoa until it becomes the urethra
what are the accessory sex glands?
ampulla
seminal vesicles
prostate
bulbourethral
types of penis
fibroelastic & vascular
what type of penis does each animal have
fibroelastic
bull
ram
boar
Vascular
horse
what makes the fibroelastic penis different
retractor penis muscle
what is the part of the female reproductive tract that we see?
the vulva, it’s on the outside so visible
inside of female reproductive tract that is connected to the vulva
the vagina
main purpose of vagina
be protective
it’s keratinized to prevent abrasions
cervix difference in animals
sow - corkscrew inverse shaped
mare - straight shot
ewe- circles/rings
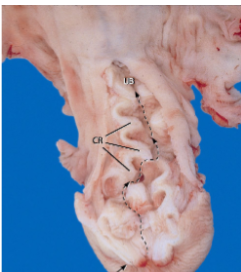
what species cervix is this
ewe (sheep)
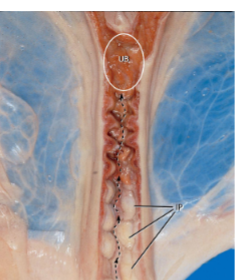
what species cervix is this
sow (swine)
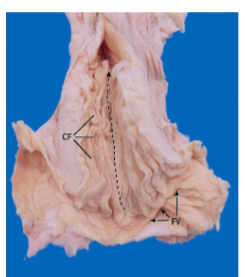
what species cervix is this
Mare (horse)
Purpose of cervix
secretory
acts as a barrier between uterus and vagina (and penis when it enters)
anatomy specific to species to accept male penis
Uterus purpose
aids in travel of sperm
secretory organ
has 2 horns/branches and 1 body
shape differs between species
why do different species have different uterus shapes
depending on how many offspring they typically have
ex: sow have larger/longer uterine horns bc they are litter bearing species
2 parts of the ovary, where are they located
cortex - outside (except horse)
medulla - middle (inside) (except horse)
cortex function
gametes
oocytes housed in follicles
medulla use
support, contains blood vessels and lymphatics

identify species w/ this ovary, why is it like this?
cow
cortex is on the outside, not litter baring so few follicles
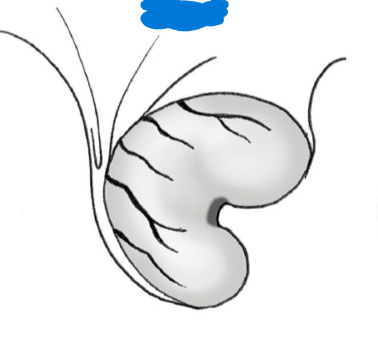
identify species w/ this ovary, why is it like this?
Mare
medulla is on the outside so you can see the blood vessels
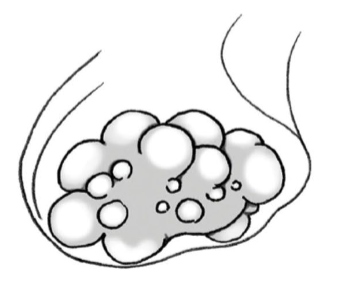
identify species w/ this ovary, why is it like this?
Sow, litter baring so more follicles released each ovulation
Because the cortex is on the inside for the mare what does is ovulate with
uses a specialized structgure called the ovulation fossa
where does FSH come from
granulosa cells
where does LH come from
Theca cells
what is different between a primary/secondary follicle and a tertiary/graafian follicle (visibly)
there is a presence of a visible antrum
what is the antrum
the inside the theca outside the zona pellucida, the liquid cells that grow from estrogen as the follicle begins to grow and get closer to ovulation
what do tertiary and graafian follicles produce a high amount of
estrogen
what makes a follicle capable of ovulation
surge of LH
end of estrus period
what hormone causes luteolysis
Prostaglandin
what is luteolysis
the process of the corpus luteum undergoing regression and ceasing its function
what does the corpus hemmoraghicum turn into?
Corpus luteum
during what stage does a corpus hemmoraghicum exist?
metestrus
during what stage does a corpus luteum exist?
diestrus
what does the CL produce
progesterone
what is a corpus albicans
destroyed corpus luteum
what is the cap on the top of the sperm that it uses like a helmet called
acrosome
what must occur for fertilization to be successful
the acrosome needs to be exposed
egg nucleus needs to stop in metaphase II
sperm matures in uterus
what does the sperm bind to in the oocyte
ZP3 on zona pellucida
what does the zona pellucida do
hardens as soon as sperm receptors are activated
prevents multiple sperms fertilizing the egg
what is polyspermy
when multiple spermatozo fertilize the egg
how does the nucleus stuff work
the sperm and egg will form respective nuclei and then come together for metaphase
fertilization stages
capacitation
binding to oocyte
acrosome reaction
what is capacitation
prepares sperm for release of acrosome enzymes
happens in female tract
removes outer plasma and acrosome membranes
what is the name for a zygote with 16 cells
morula
what is the name for a cell with 32 cells
blastocyst
what is different about a blastula
cells are compacted and form a cavity
what causes a blastula to hatch?
the cells divide enough to cause pressure to be placed on the Zona Pellucida causing it to hatch
what is the trophoblast
the outer layer of the placent
What is the yolk sac
the sac that holds nutrients in animals (literally the yellow part of the egg)
how early does the yolk sac form in placental formation
the first thing to form
what is the amnion
part of the placenta
protects fetus and promotes symmetrical growth
it’s the part that directly surrounds the fetus
what is the allantois
directly surrounds the amnion
fuses with the chorion
waste and nutrient reserve
what is the chorion
the outer most layer
fuses with endometrium
placentomes in ruminants
diffuse in horses and pigs
zonary in dogs and cats
discoid in humans
What type of chorion do horses & pigs have, how does it work
Diffuse, lots of small points of attachment
what type of chorion do dogs and cats have, how does it work
zonary, endotheliochorial (croissant looking one, fetal cells surround mom blood vessels)
what type of chorion do ruminants have, how does it work
cotledonary, has the large points of attachment (placentomes)
what type of chorion do primates have, how does it work
discoid, hemochorial (maternal blood directly touches the fetal cells, cell/blood diagram)
what are placentomes made of
caruncle + cotyledon
what is parturition initiated by
ACTH production
what does parturition cause in maternal hormones
release of oxytosin to coordinate contractions
what is stage 1 of parturition
positioning (superman)
what is stage 2 of parturition
delivery of fetus
what is stage 3 of parturition
expulsion of placental membranes.