Flashcard Format of the Practice Test Questions
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Every question, answer, part, and explanation from the Quiz 6 Practice Test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
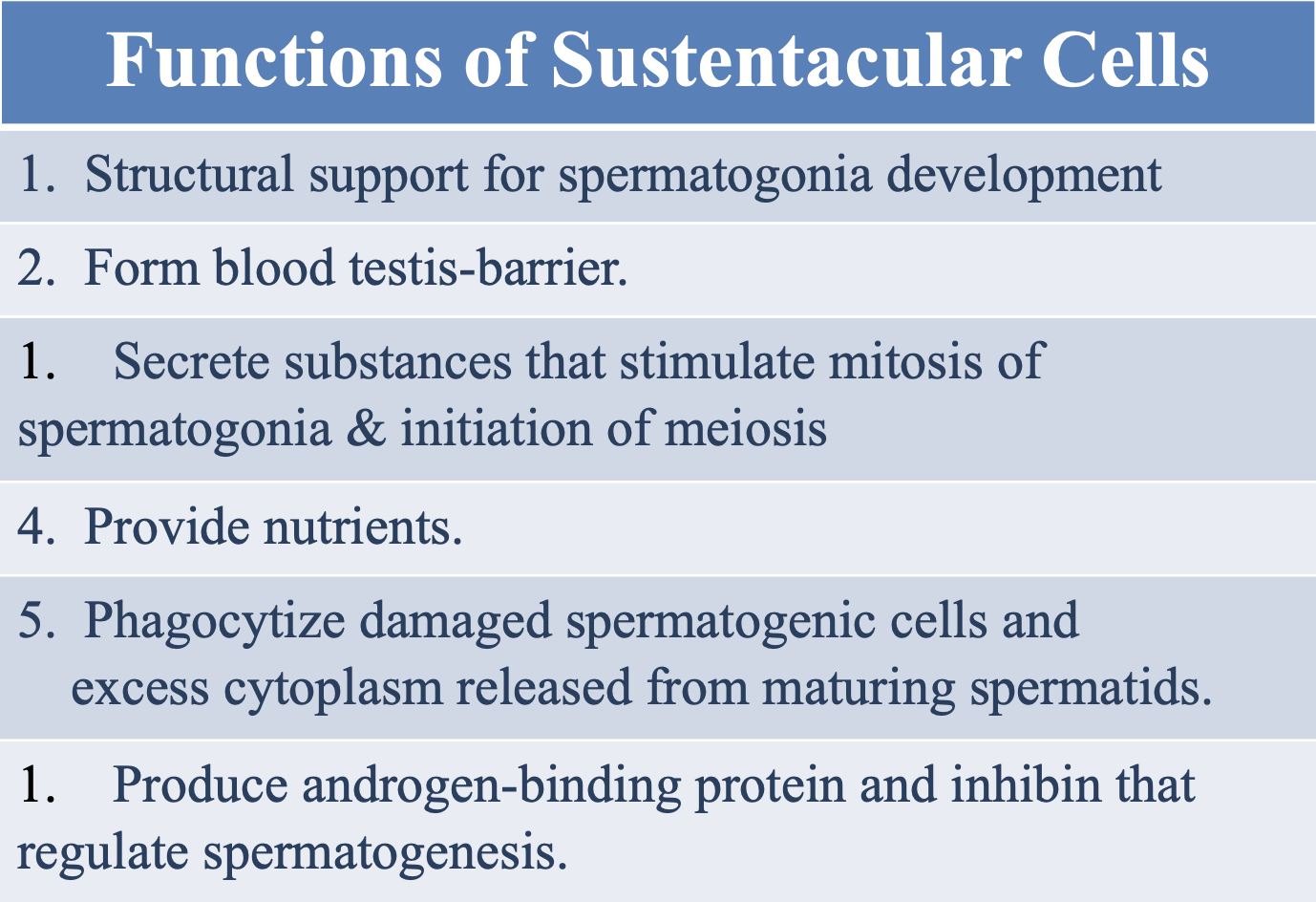
What are the 6 functions of sustentacular cells?
Provide structural support for spermatogonia development
Form the blood testis-barrier
Secrete substances that stimulate the mitosis of spermatogonia and the initiation of meiosis
Provide nutrients
Phagocytize damaged spermatogenic cells and excess cytoplasm released from maturing spermatids
Produce androgen-binding proteins and inhibin that regulate spermatogenesis
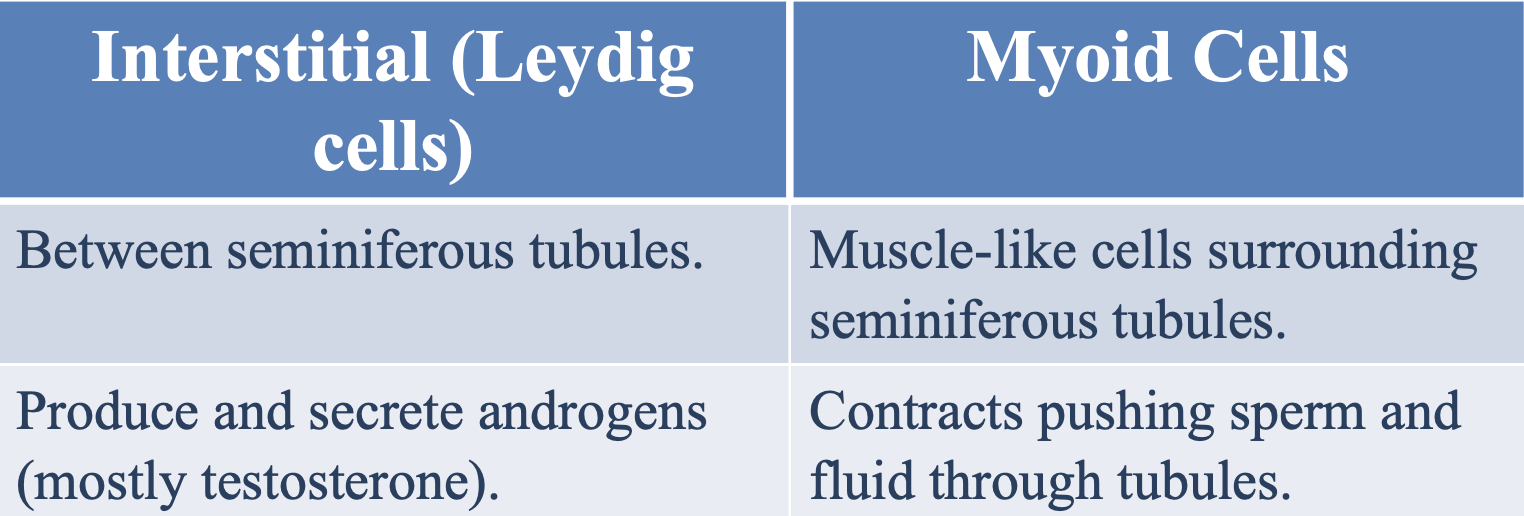
Where are leydig cells located?
Between seminiferous tubules
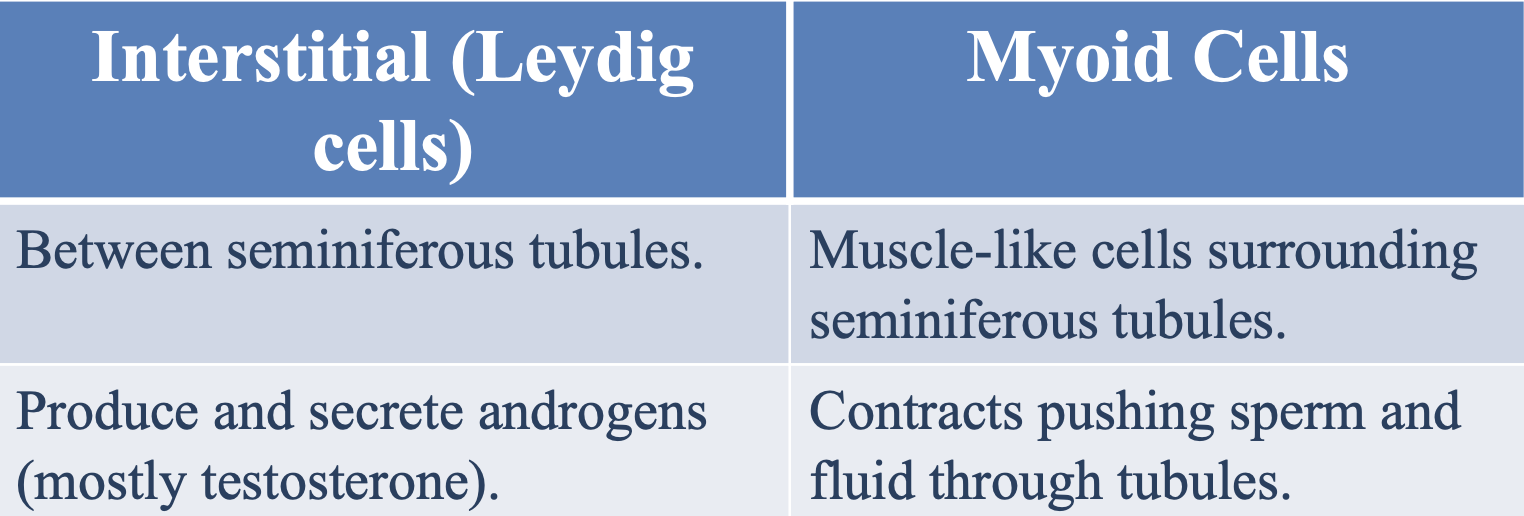
What is the function of leydig cells in the seminiferous tubules?
To produce and secrete androgens (mostly testosterone)
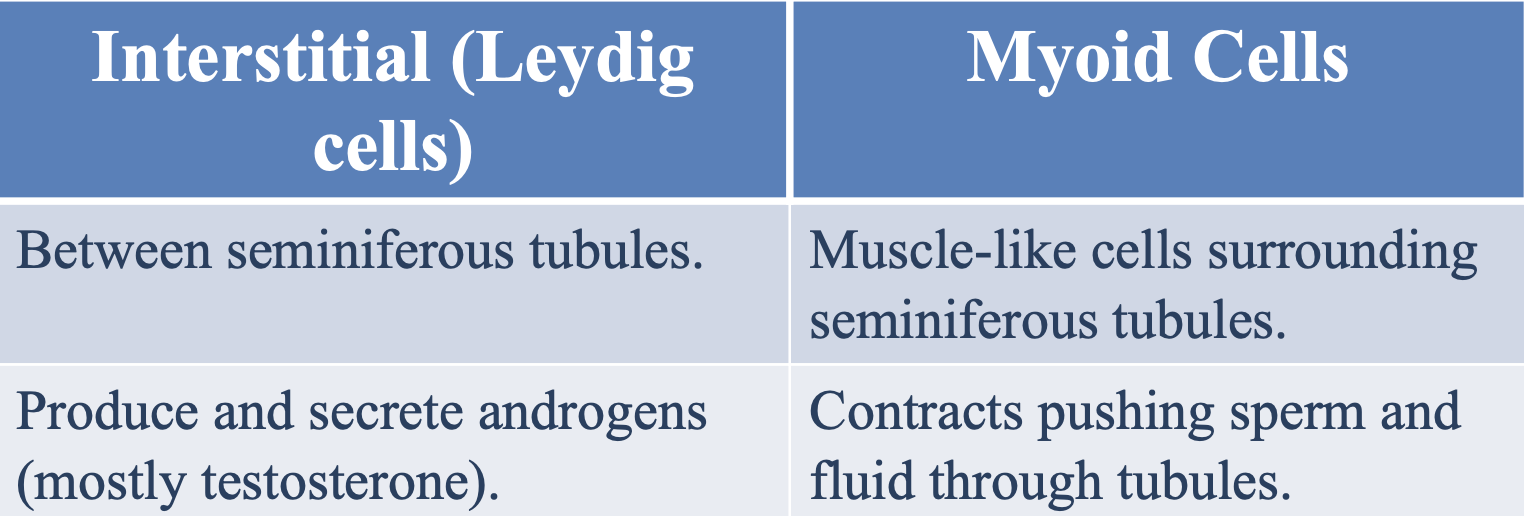
What type of cells are myoid cells and where are they located?
Muscle-like cells located surrounding the seminiferous tubules
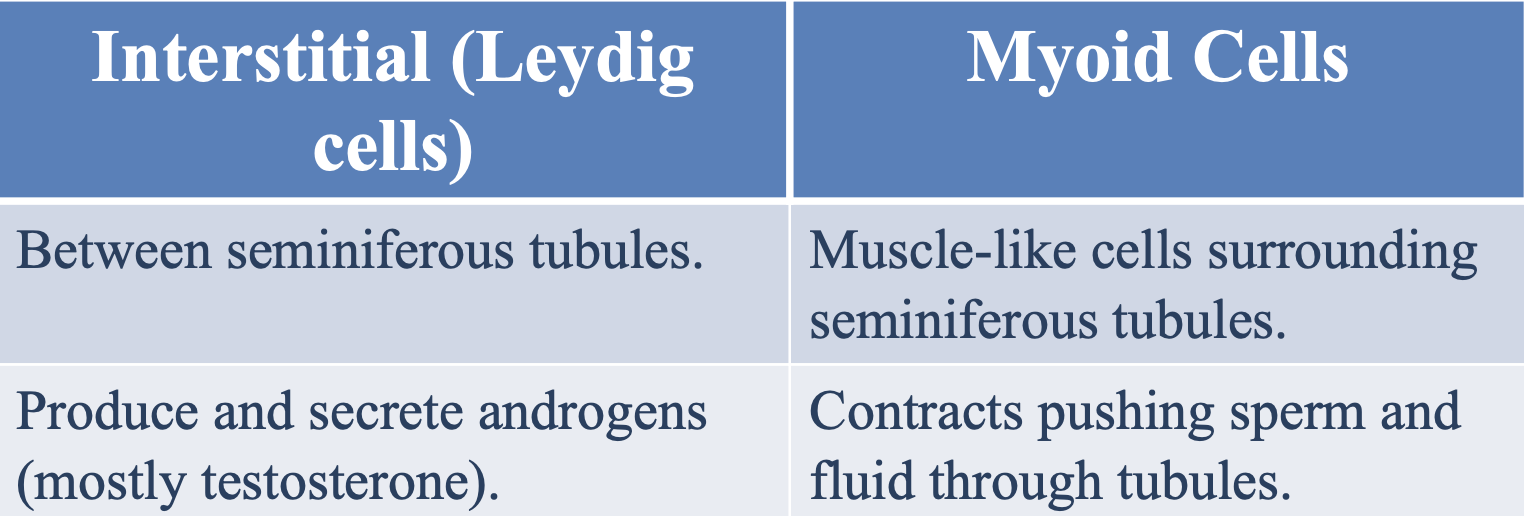
What is the function of myoid cells in the seminiferous tubules?
Contract to push sperm and fluids through the seminiferous tubules
When does an erection result?
When erectile tissue in the penis becomes engorged with blood

What does the parasympathetic reflex of an erection release and what is its function?
Nitric oxide from endothelial cells to dilate the arterioles of the penis

Define ejaculation.
The expelling of semen from the penis

What kind of control is ejaculation under?
Sympathetic

What % of semen volume is contributed by the accessory seminal vesicles?
60-70%
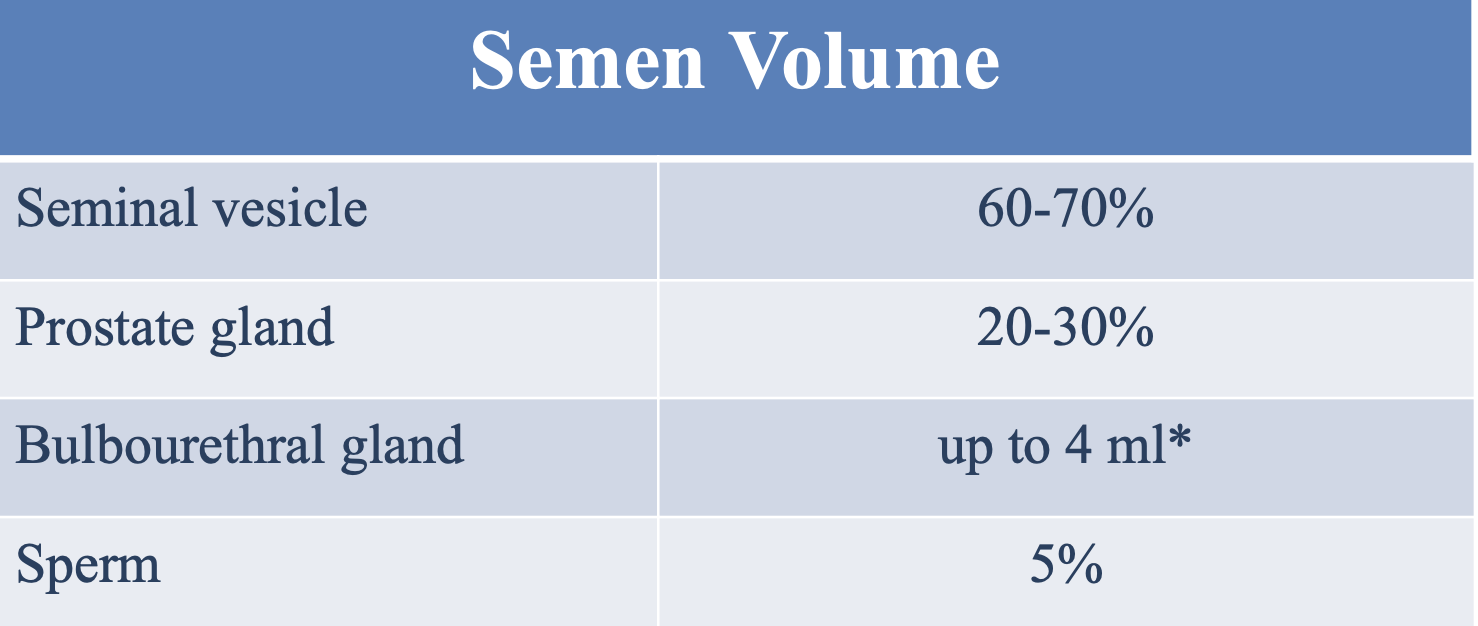
What % of semen volume is contributed by the accessory prostate gland?
20-30%
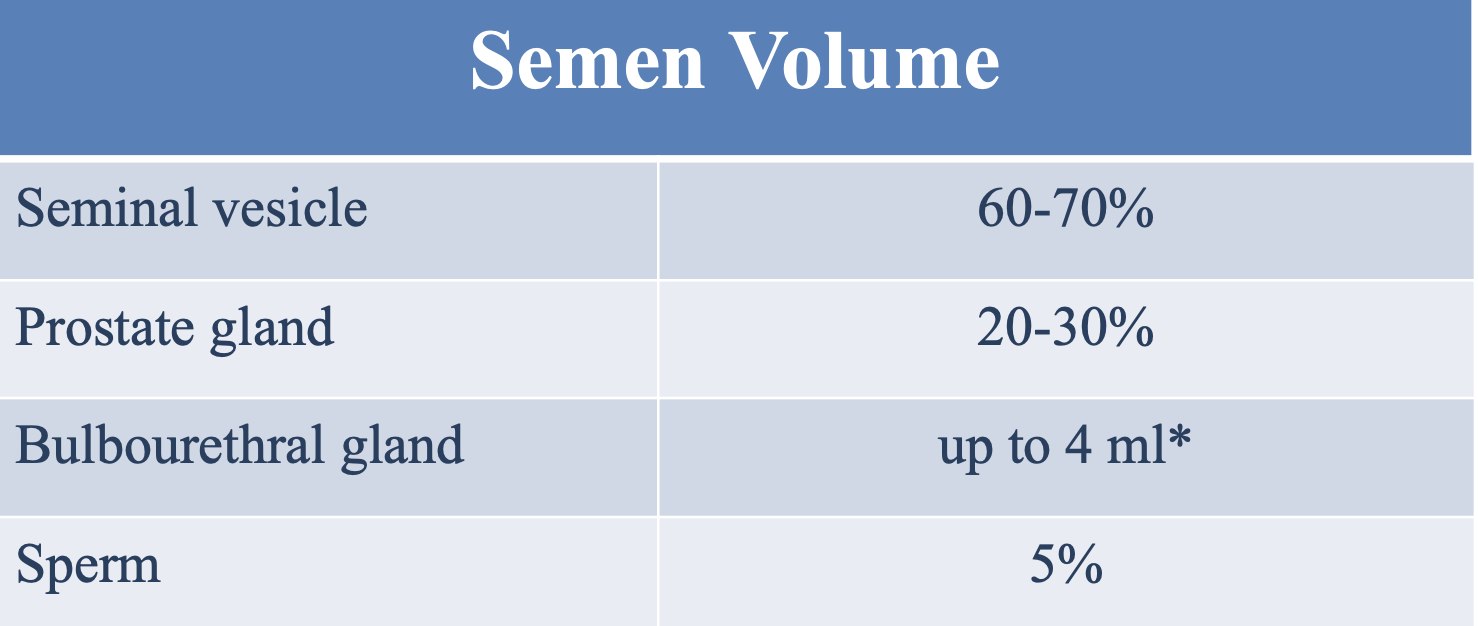
What % of semen volume is contributed by the accessory bulbourethral gland?
<5%, up to 4mL
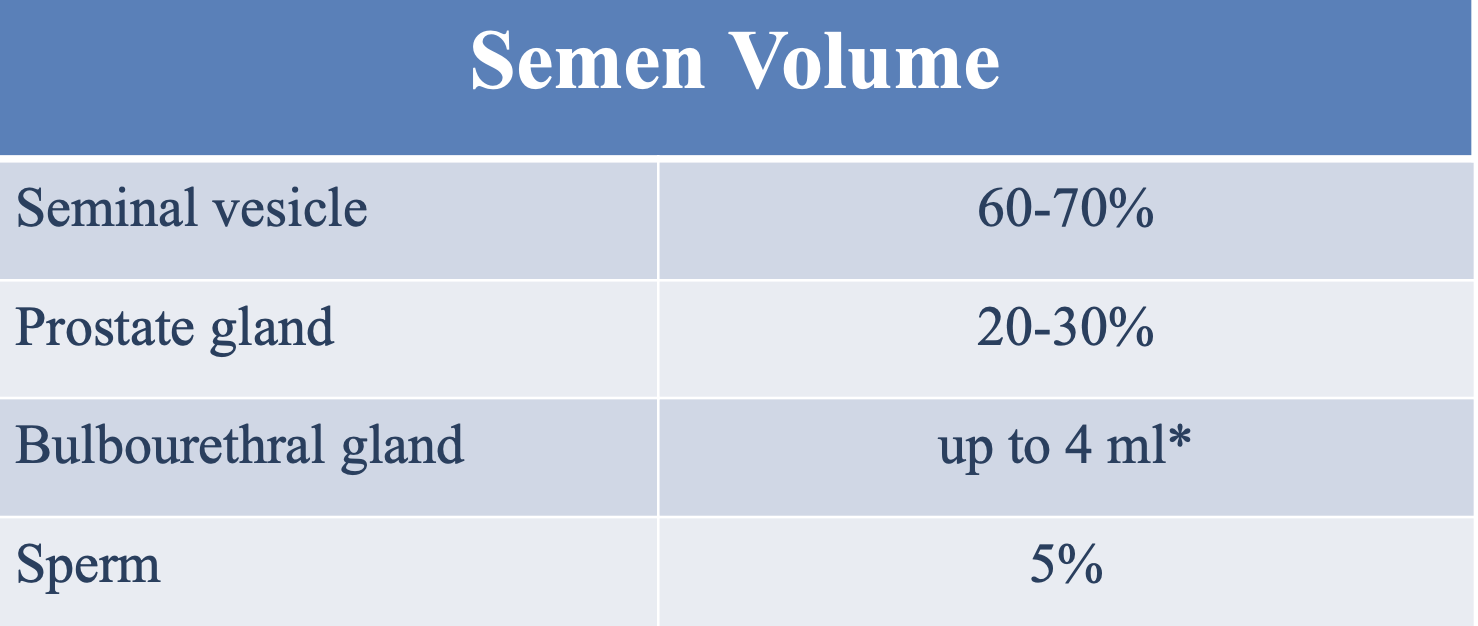
What % of semen volume is contributed by sperm?
5%
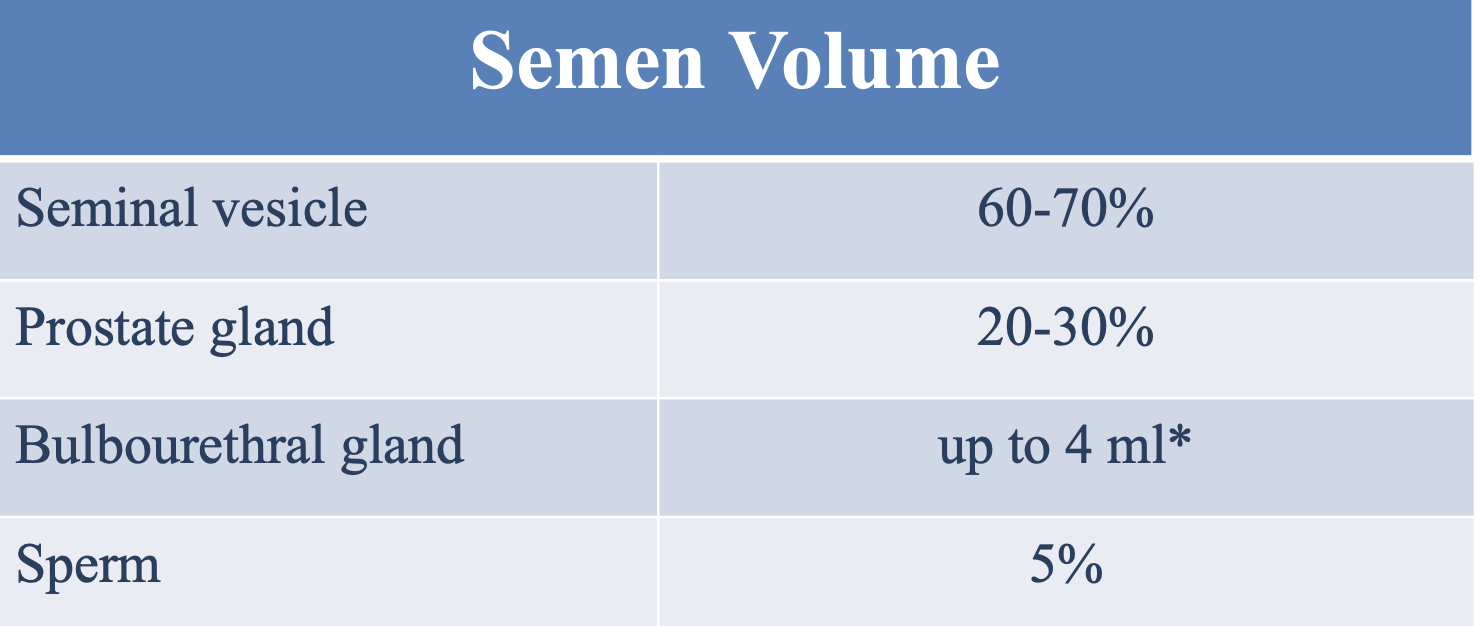
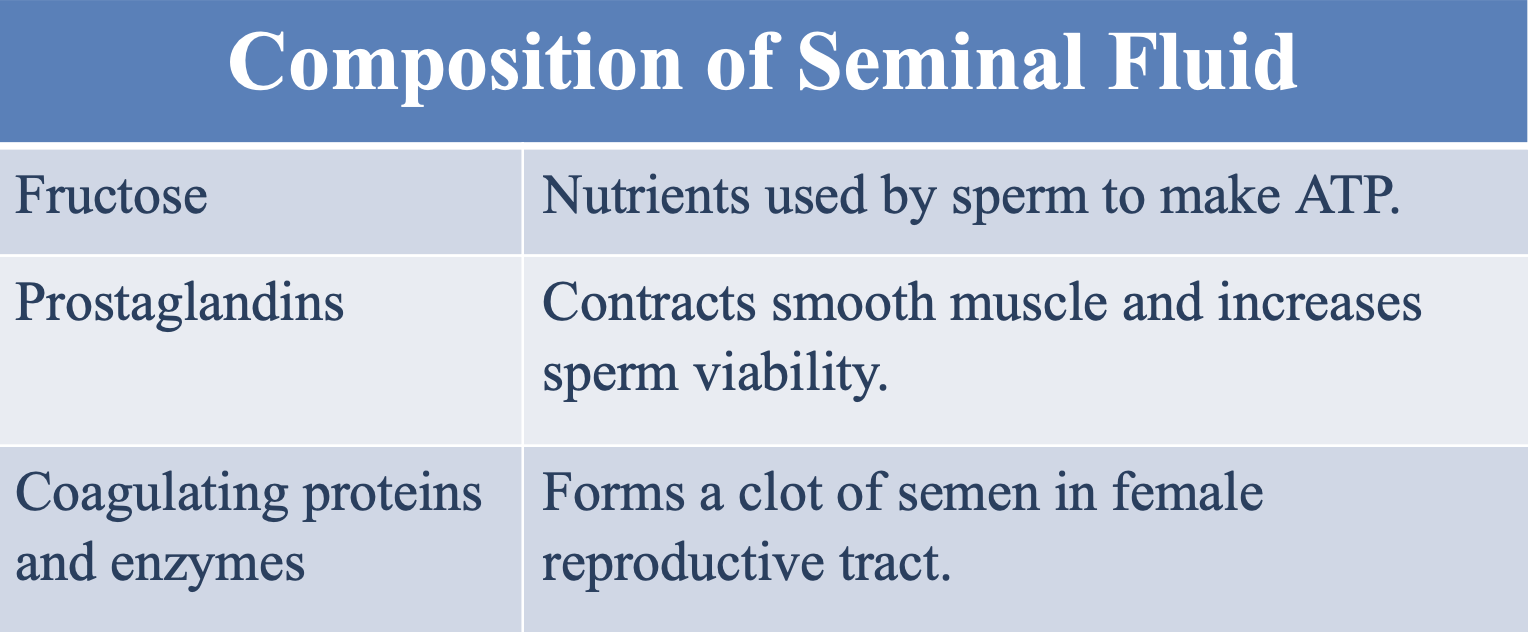
What 3 components compose the seminal fluid?
Fructose
Prostaglandins
Coagulating proteins and enzymes
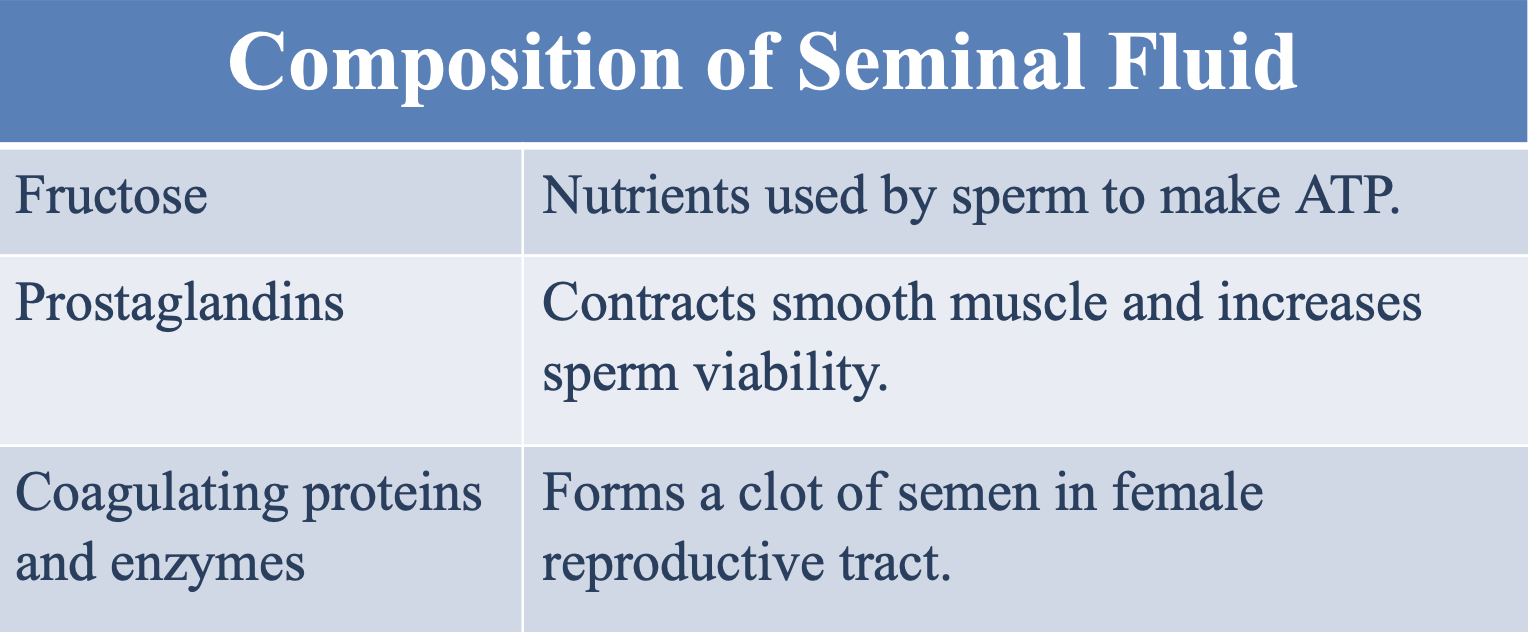
What is the function of fructose in the seminal fluid?
A nutrient used by sperm to make ATP
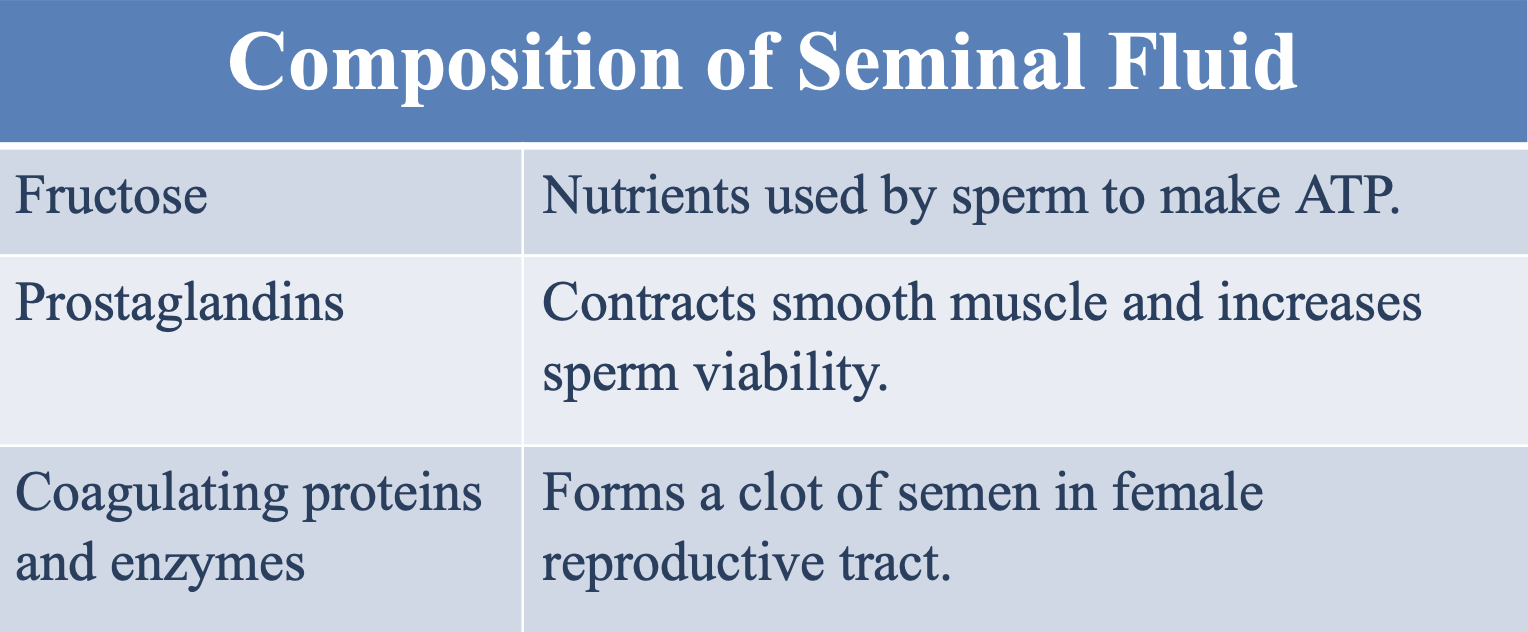
What is the function of prostaglandins in the seminal fluid?
Contract smooth muscle and increase sperm viability
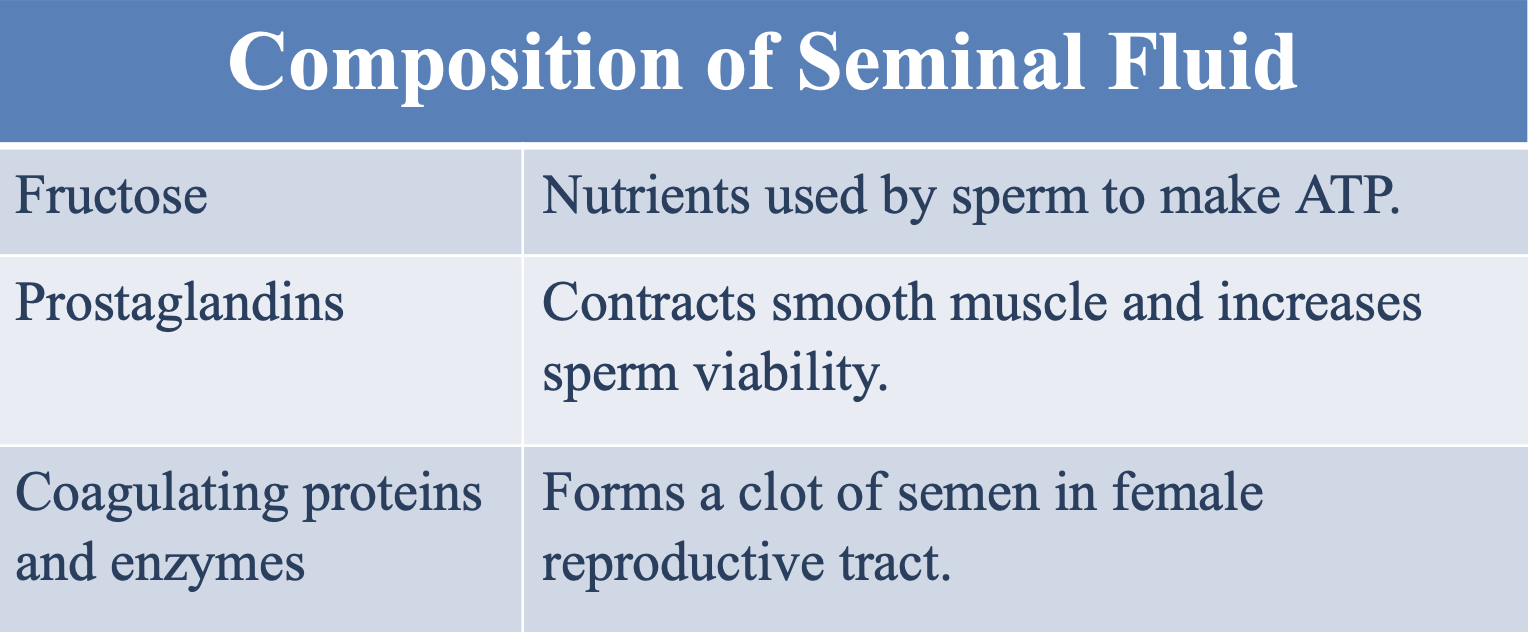
What is the function of coagulating proteins and enzymes in the seminal fluid?
Form a clot of semen in the female reproductive tract
Define cryptorchidism.
A disorder in which the testes fail to descend into the scrotum, causing no sperm to be produced

Define oogenesis.
The production of female gametes

Where does oogenesis occur?
In the follicles of the ovarian cortex

Where are the gametes of oogensis produced?
Within ovarian follicles

What are the 4 functions of the uterus?
The pathway of sperm for fertilization
The site of implantation of ovum
Provides nutritional support for the fetus
Provides contractions during birth

What type of gland are the mammary glands?
Modified sweat glands

What is the function of the mammary glands?
Milk production

What is the female perineum and where is it located?
A diamond-shaped region located between the pubic arch, coccyx, and ischial tuberosities

Where is the female clinical perineum located?
Between the vagina and anus

What is the female clinical perineum often the site of?
Incision during childbirth, called the episiotomy

What is the outermost serous layer of the uterus called?
Perimetrium

What is the thick middle smooth muscle layer of the uterus called?
Myometrium

What is the innermost mucous membrane layer of the uterus, composed of simple columnar epithelium, called?
Endometrium

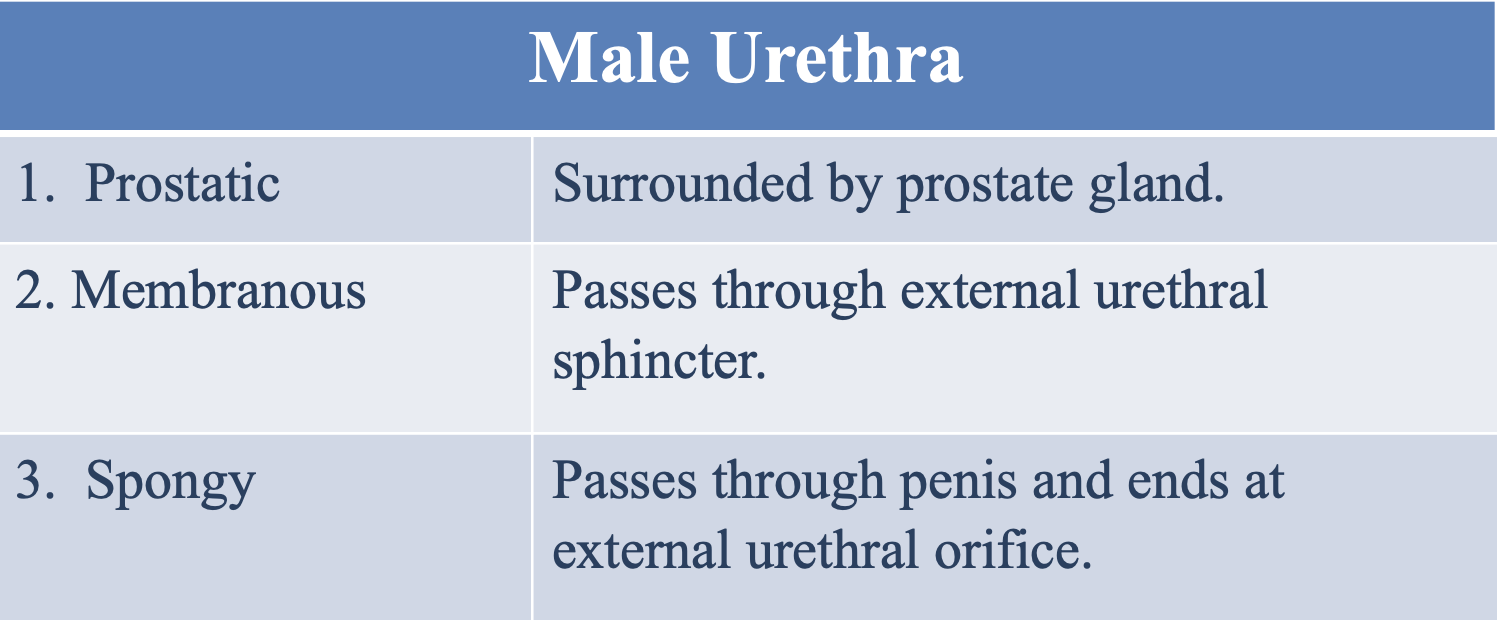
What is the prostatic male urethra surrounded by?
The prostate gland
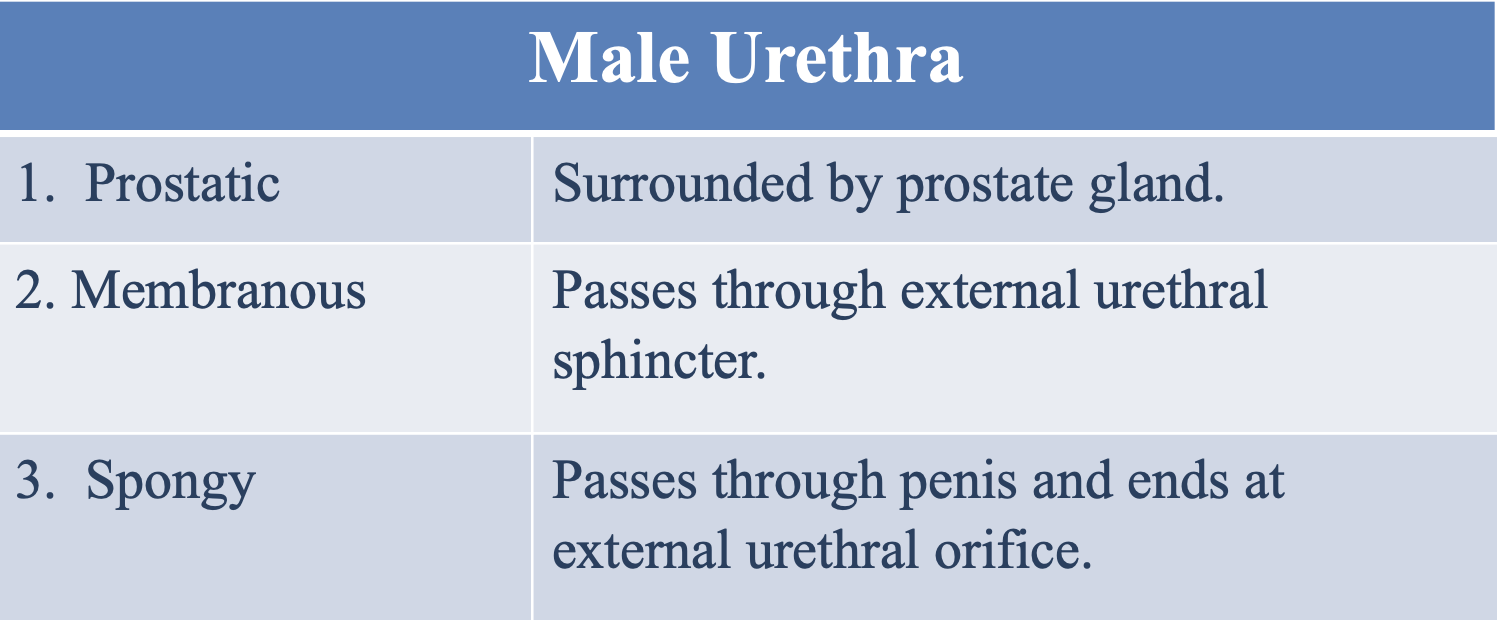
Where does the membranous male urethra pass through?
The external urethral sphincter
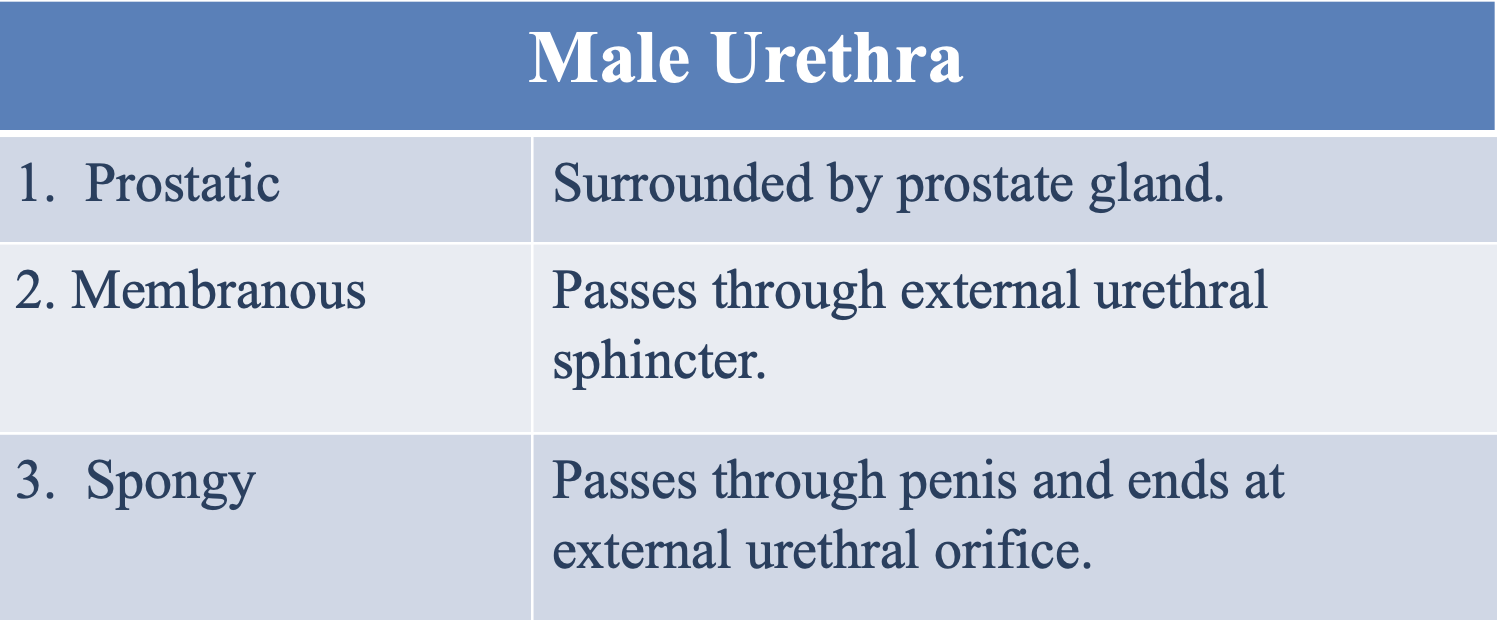
Where does the spongy male urethra pass through and end at?
Passes through the penis and ends at the external urethral orifice
What does the penile root connect to?
The pelvic bones

What does the body of the penis enlarge at the end as?
The glans penis

What structure covers the penis and is removed during circumcision?
The prepuce (foreskin)

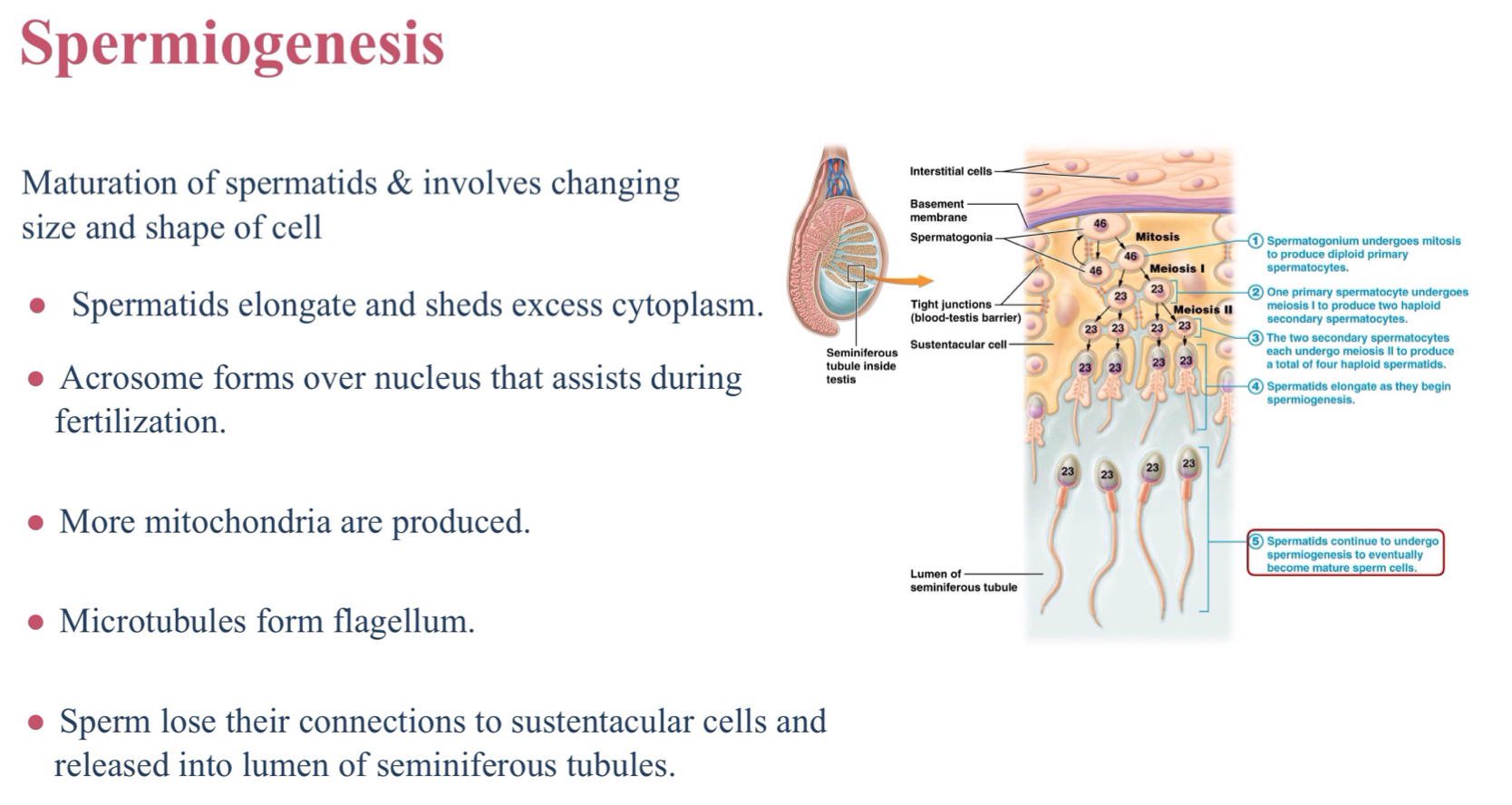
What are spermatogonium?
Stem cells that begin spermatogenesis
What does mitosis of the spermatogonium produce?
Primary spermatocytes
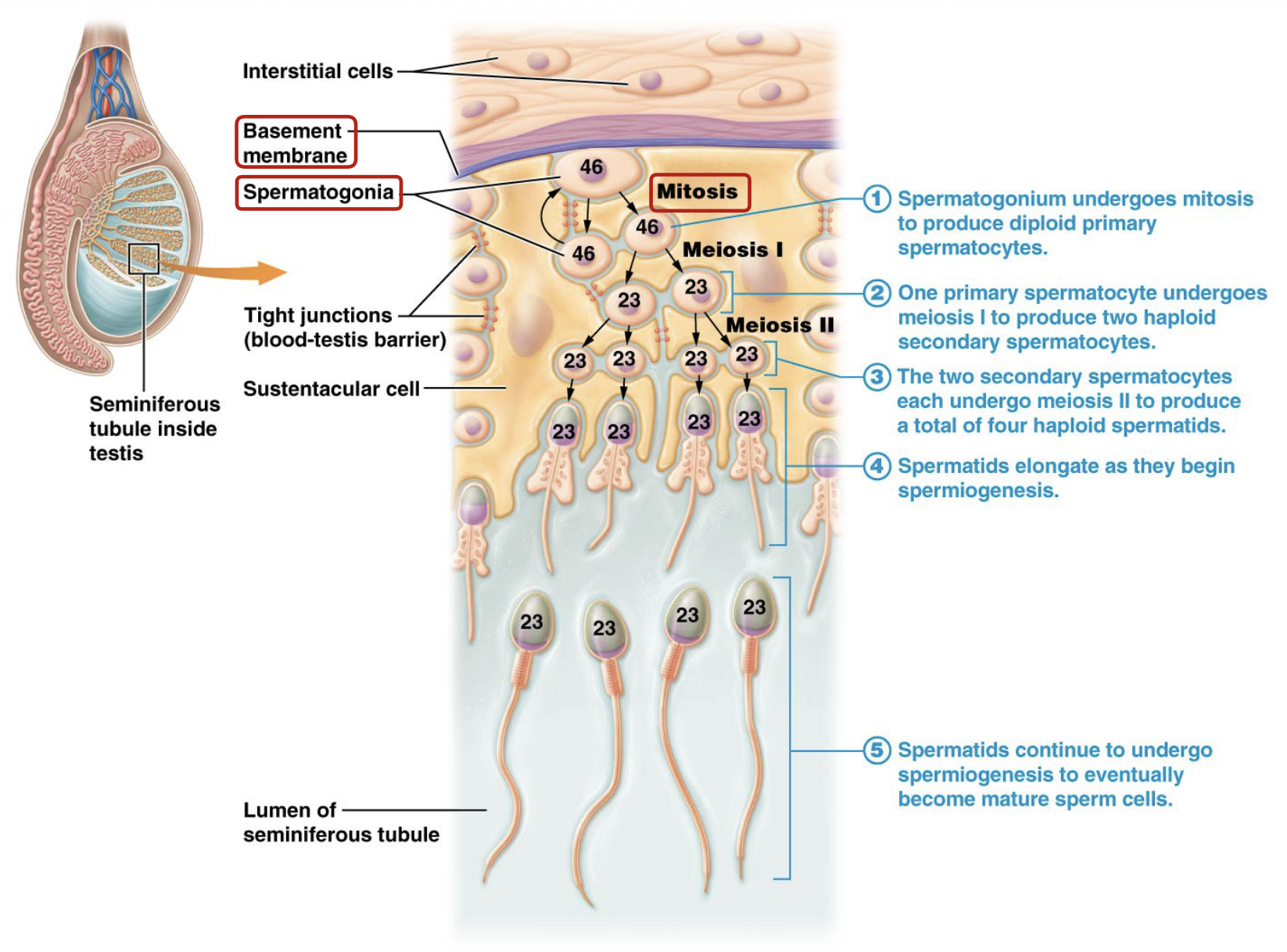
What does meiosis I of the primary spermatocytes produce?
Secondary spermatocytes
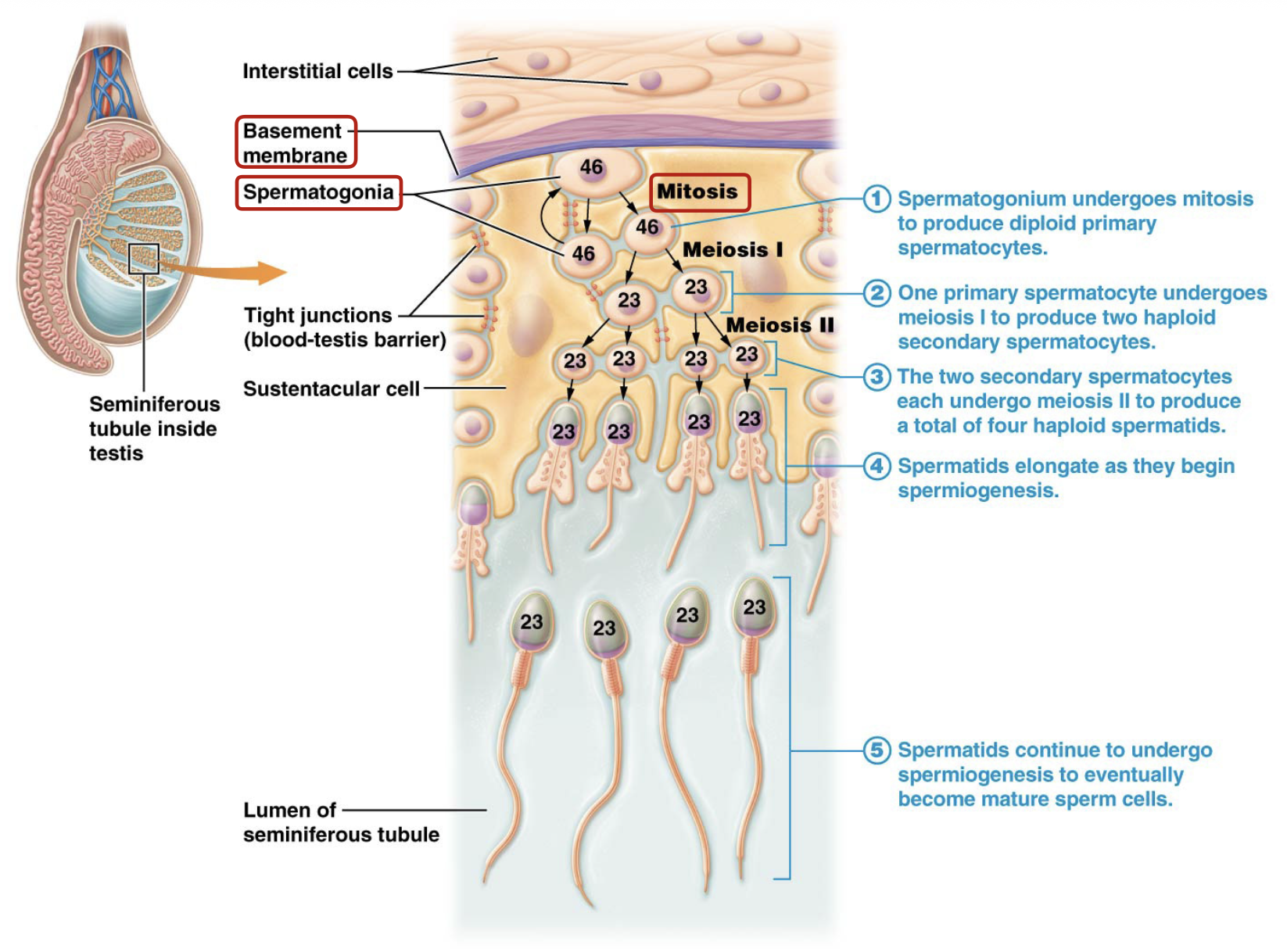
What does meiosis II of the secondary spermatocytes produce?
Spermatids
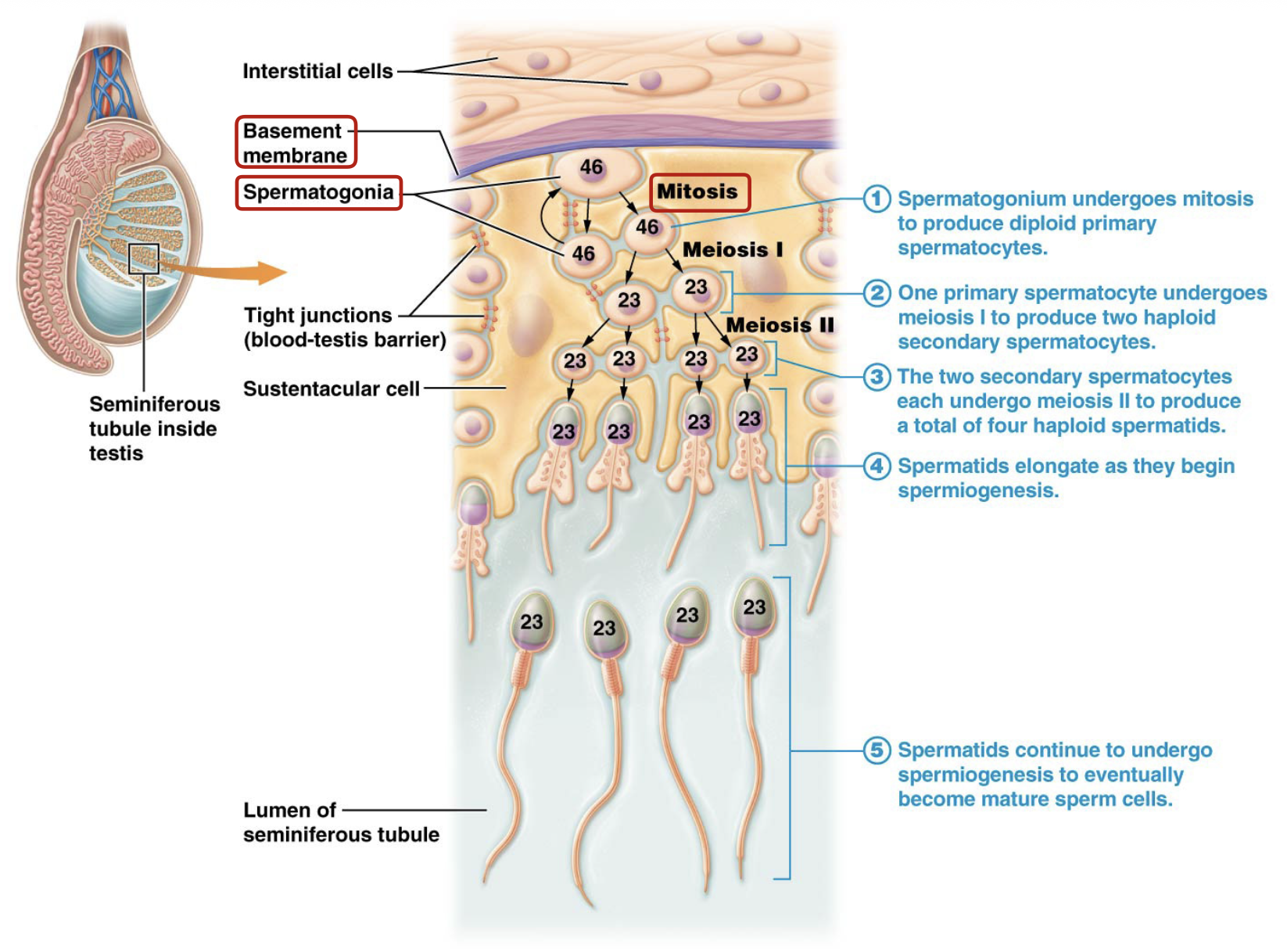
Define spermiogenesis.
The process of maturation of spermatids
What cells in the process of spermiogenesis elongate and shed excess cytoplasm?
Spermatids
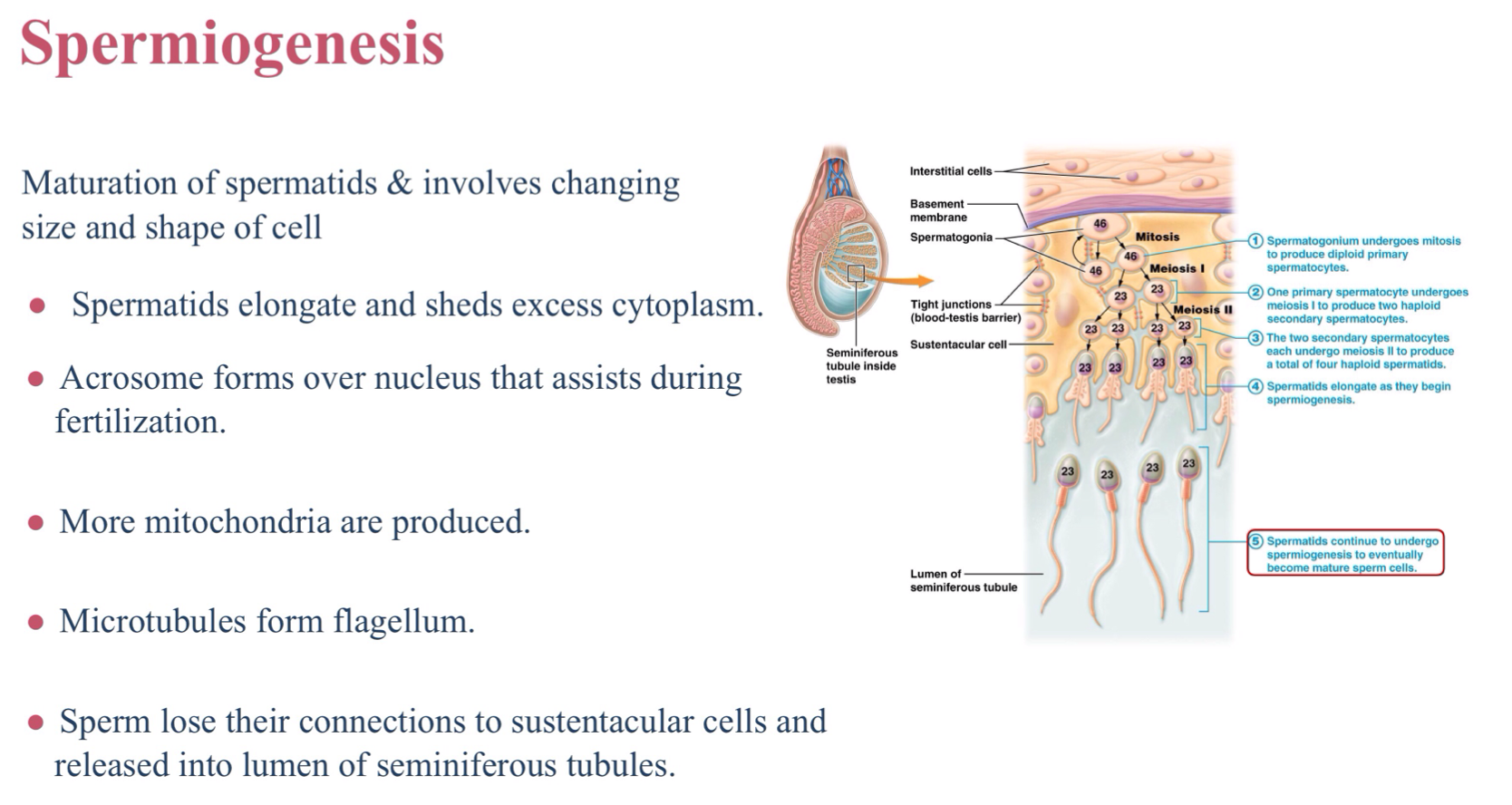
What organelle forms over the nucleus to assist during fertilization in the process of spermiogenesis?
Acrosome
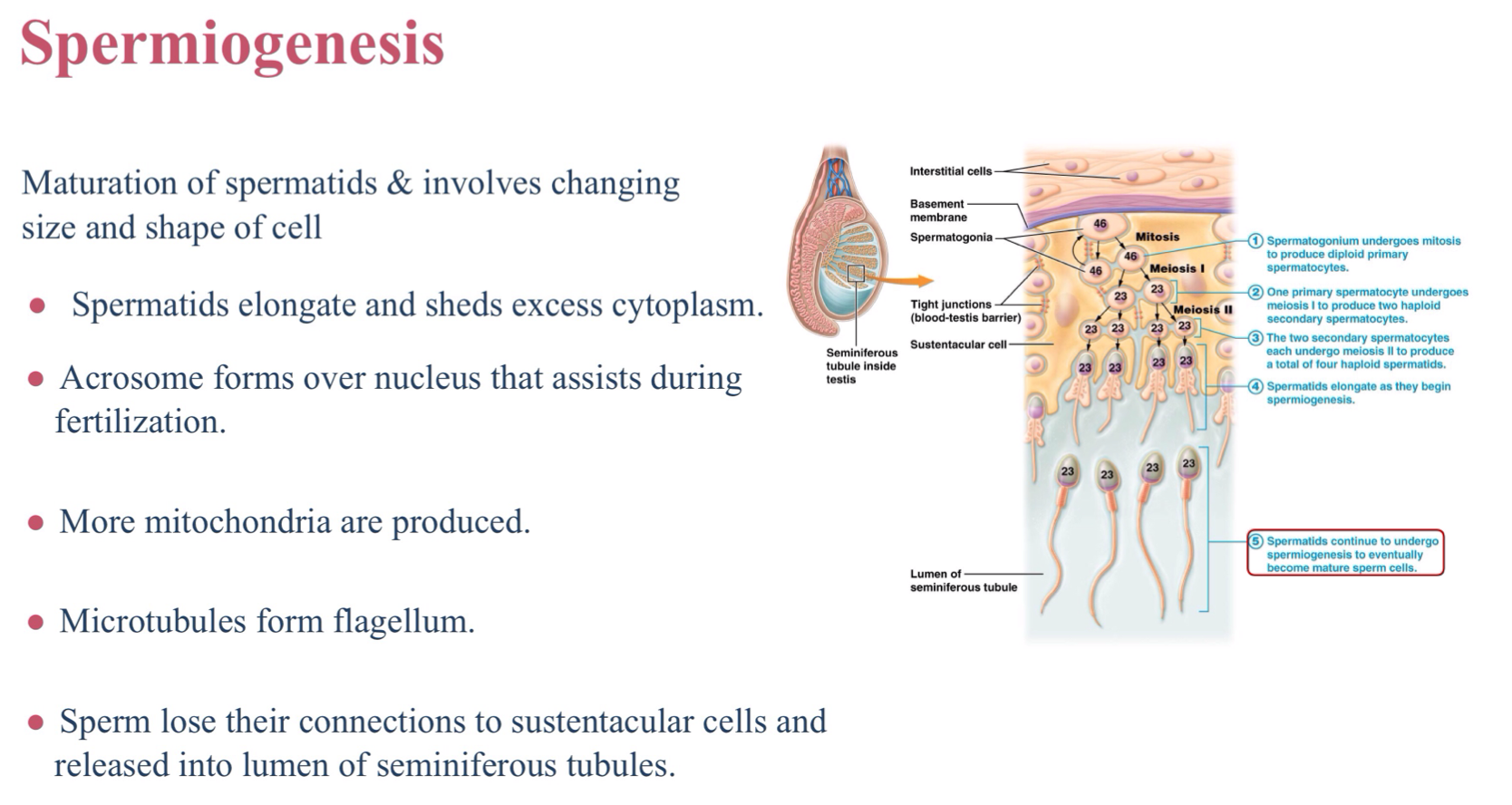
the process of spermiogenesis produces more of which organelle?
Mitochondria
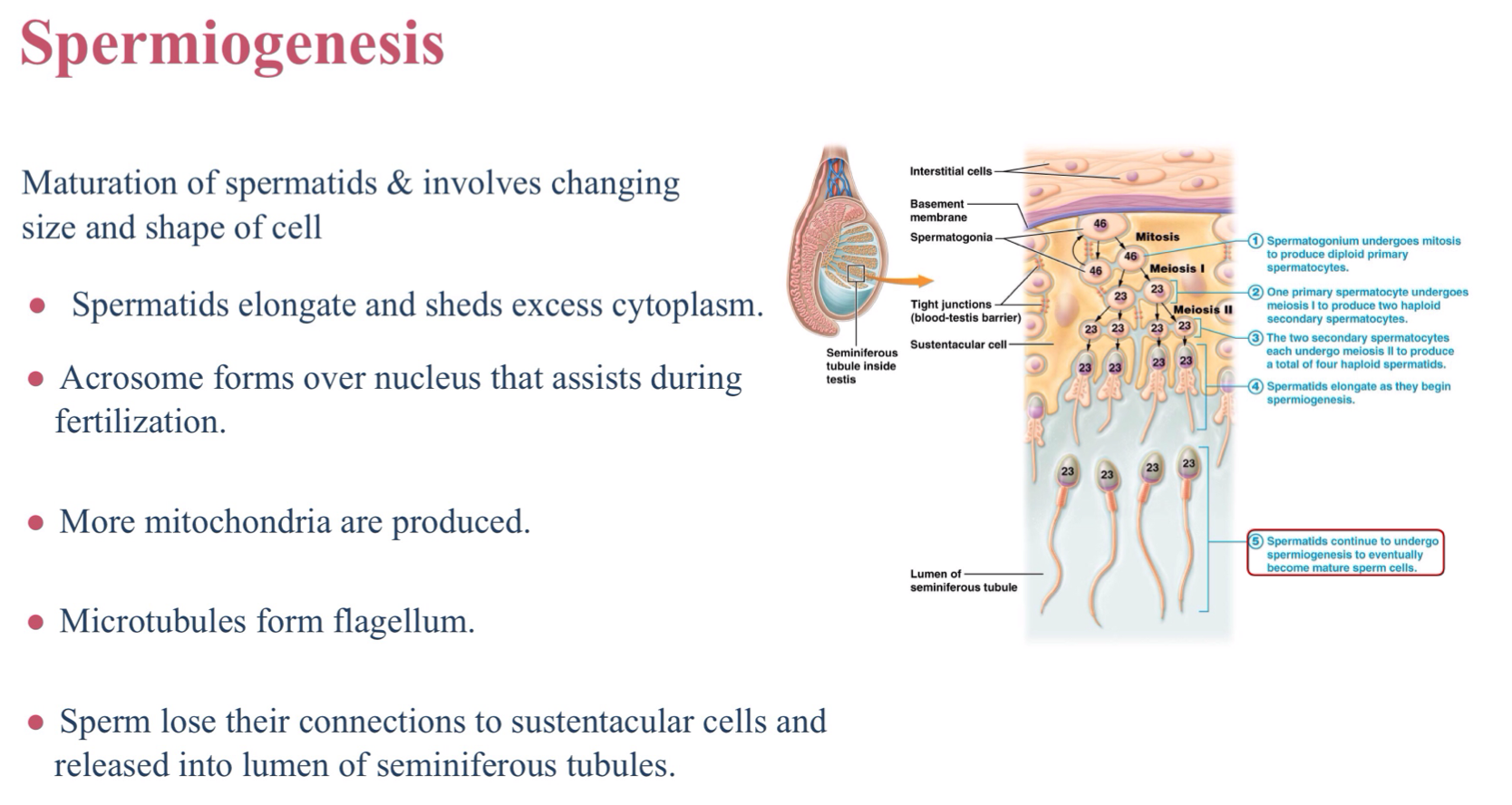
What happens to sperm in the process of spermiogenesis?
Sperm lose their connections to sustentacular cells and are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubules
What is the female gonad?
The ovaries
What structure connects the uterine tubes to the uterus?
The isthmus

What structure covers the ovary at the end of the infundibulum?
Ciliated fimbriae

In which structure does fertilization usually occur?
The ampulla

What does blood from the testicular arteries fill during an erection?
The vascular spaces of the corpora cavernosa of the penis
Which 3 substances are secreted by the prostate gland?
Citrate
Prostate specific antigens and enzymes
Antimicrobial chemicals

What is the function of citrate secreted by the prostate gland?
A substrate used by sperm to make ATP

What is the function of the prostate specific antigens and enzymes secreted by the prostate gland?
Dissolve semen clots to allow sperm to move deeper into the female reproductive tract

What is the function of the antimicrobial chemicals secreted by the prostate gland?
Inhibit bacterial growth to decrease infections

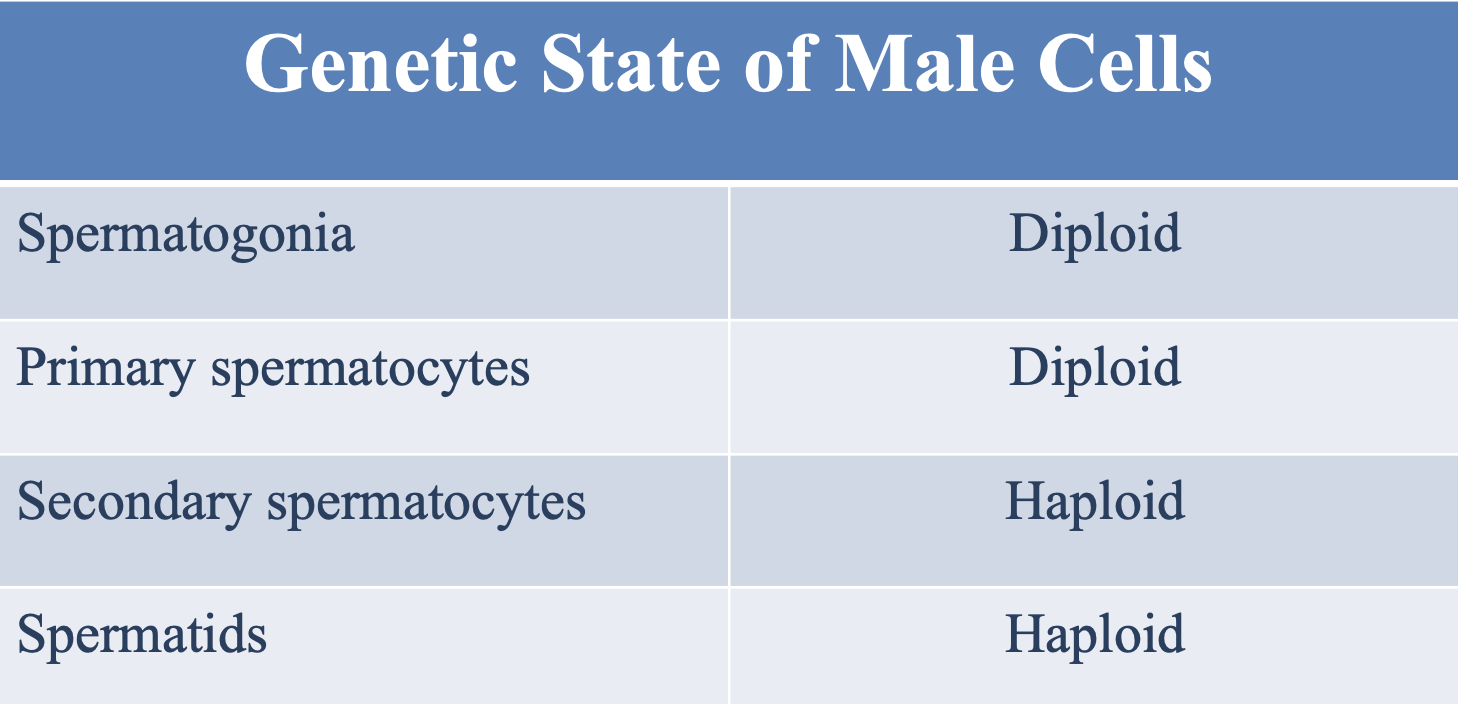
What is the genetic state (cell type) of the male spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes?
Diploid
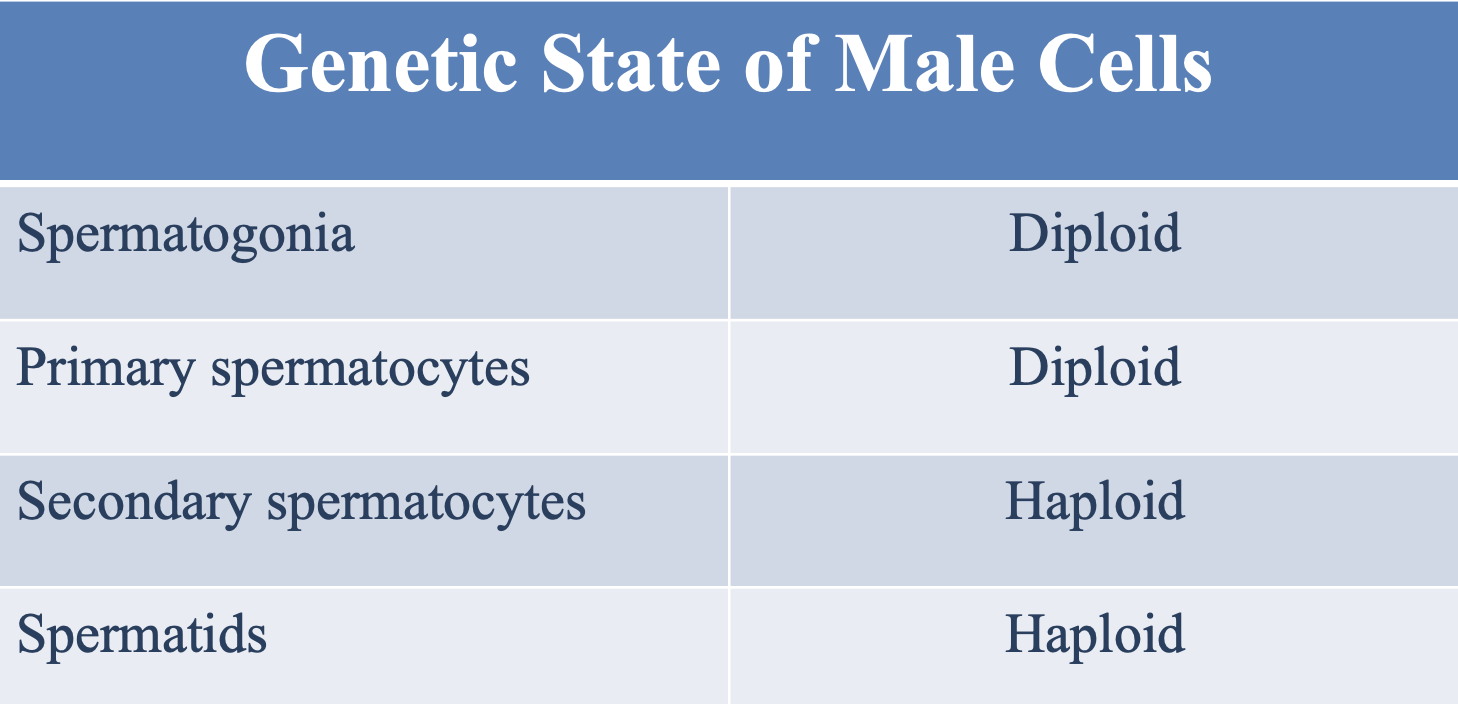
What is the genetic state (cell type) of the male secondary spermatocytes and spermatids?
Haploid
Which structure secretes fructose?
The seminal vesicles
Which structure secretes citrate?
The prostate gland
What portion of the female reproductive system is the clitoris a part of?
The vulvar vestibule
What is the small female reproductive structure that corresponds to the corpora cavernosa of the penis?
The clitoris
What type of female genitalia (external/internal) is the clitoris?
External
What is the function of the clitoris?
Engorges with blood during sexual activity
What nerve fibers innervate the clitoris?
Sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers
What 3 layers does the muscularis of the ductus (vas) deferens consist of?
1 circular layer and 2 longitudinal layers of smooth muscle:
Inner longitudinal layer
Middle circular layer
Outer longitudinal layer

What are the parts of the male duct system?
The epididymis, ductus (vas) deferens, ejaculatory duct, and urethra

What do the two terms emission and expulsion refer to?
The movement of sperm, testicular fluids, and secretions from the prostate gland and seminal vesicles into the male urethra