Blood Brain Barrier
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What makes up 95% of the blood brain barrier?
Capillary beds/cerebral vasculature
What does the cerebral vasculature allow?
Allows brain to take in nutrients such as glucose but get rid of waste such as CO2
What is the blood pathway in the BBB?
Carotid artery → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins
What are the 3 main cell types in the brain?
astrocyte
pericyte
endothelial cell
What is the diagram to show the composition of cells in the BBB?
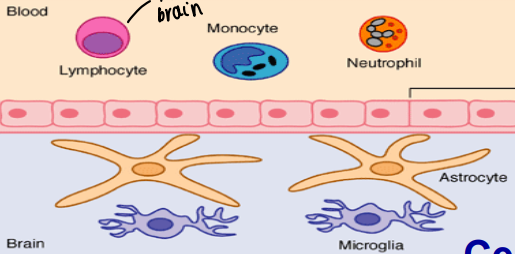
What is a pericyte?
Type of smooth muscle cell that contracts and controls the blood flow
Why does the BBB exist?
Ensures toxic compounds e.g., lymphocytes can’t enter the brain
What are the endothelial cells function in the brain?
Line the capillaries - has a basement membrane with collagen, fibronectin and laminin that surrounds endothelial cells
What do astrocyte foot processes do?
Secrete paracrine which promotes tight junction formation
What are tight junctions?
Prevent solute movement between endothelial cells
What is the structure of a pericyte?
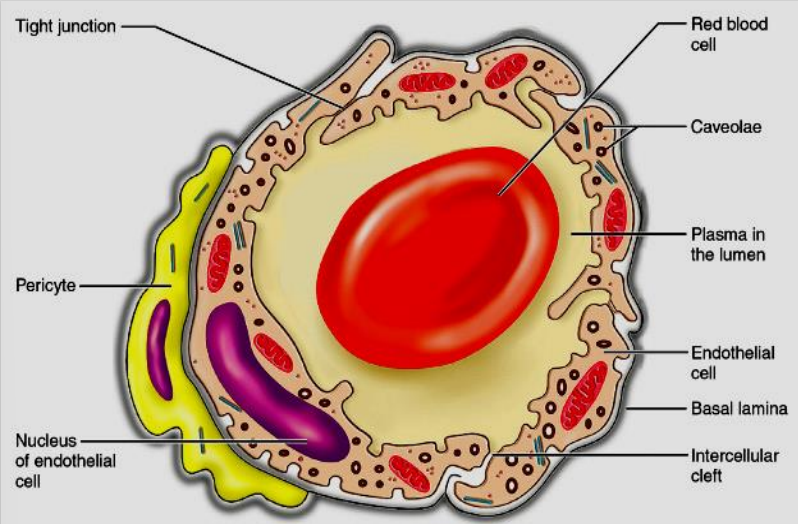
What types of junctions are in the BBB?
tight junctions formed by claudins and occludins that are attached to actin
adherens junctions sealed by cadherins
What are the integral membrane proteins in tight junctions?
Claudins, occludin and junctional adhesion molecules
What are the cytoplasmic accessory proteins?
ZO - zonula occludens and cingulin
What are the differences in neural vs non-neural capillaries?
Tight junctions in the brain, in usual capillaries there is an intercellular cleft and pinocytotic vesicles
More mitochondria in the brain capillaries as more metabolism need
What is the comparison of BBB and peripheral organs structure?
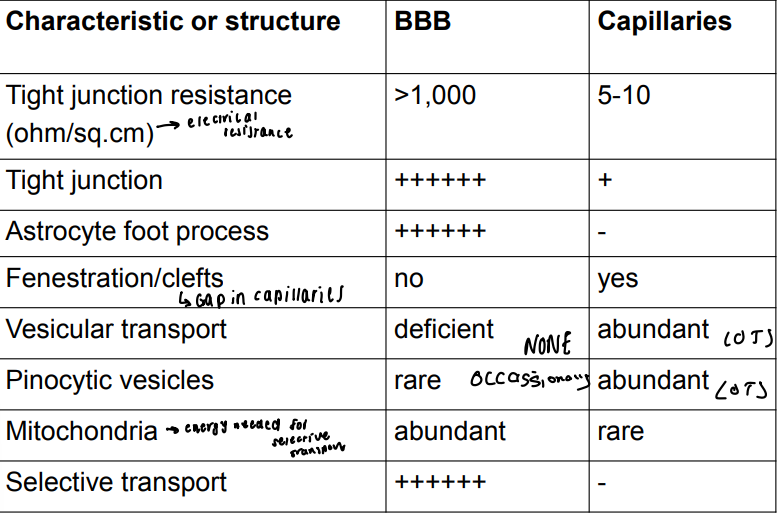
What are the 3 levels of barrier in the brain?
capillaries - 95%
Blood - CSF in the ventricles and tight junctions, along with endothelial cells
Subdural space - arachnoid cells that secrete CSF from the blood
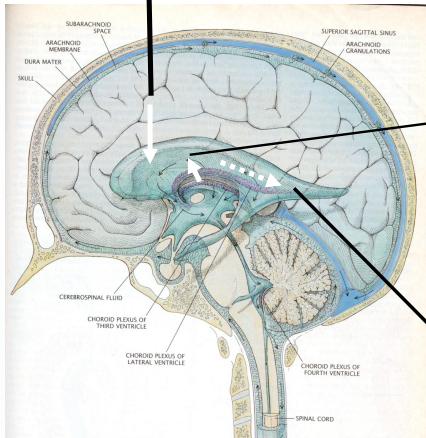
What is the diagram to show the choroid plexus in the brain?
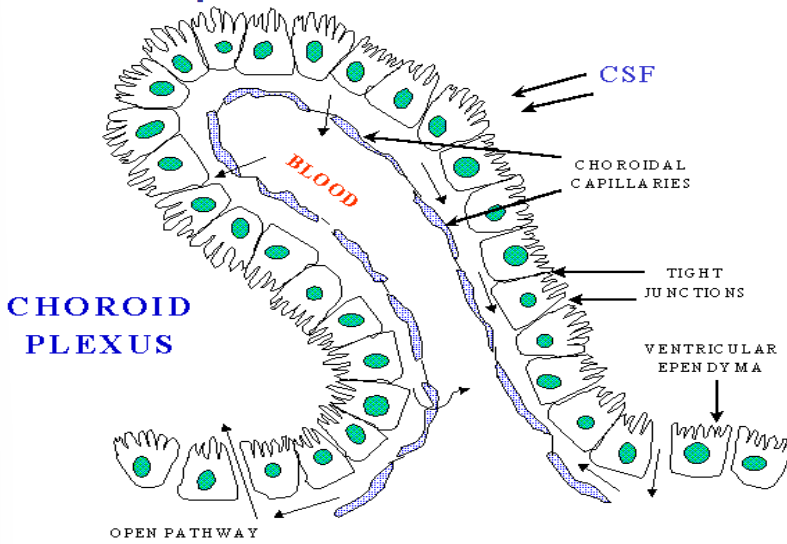
What is the rate of CSF replacement in the brain?
4-5x a day
Where is CSF made in the brain?
Choroid plexus
Where is the choroid plexus in the brain?
What are the functions of the CSF?
mechanical protection
stable extracellular environment
remove some waste products
nutrition
convey messages such as hormones/neurotransmitters
What is the BBB NOT?
A WALL! Not a solid barrier
What are the transport mechanisms in the brain?
passive diffusion
transporter diffusion
solute carriers
transcytosis - receptor or adsorptive mediated
mononuclear cell migration
Why are 95% of drugs not suitable for use in the brain?
Brain will efflux them out - can leave the brain
How does diffusion work in the BBB?
High to low concentration
Aqueous to lipids, small lipophilic molecules of <300Da
What are the 2 methods of carrier mediated transport in the brain?
Facilitated diffusion and active transport - against conc gradient
What are the different transporters in the brain?
Glucose (GLUT1)
Lactate - MCT1
Essential amino acids - L1
Organic anion transporter OATP3
Which carrier mediated transporters can move in and out of the brain?
Glucose, lactate and amino acids
What is transcytosis?
Movement of large molecules using vesicles across the BBB. Endocytosis and exocytosis
What are the 2 ways of transcytosis in the BBB?
Receptor mediated e.g., insulin, erythropoietin and transferrin and adsorptive mediated transcytosis e.g., albumin
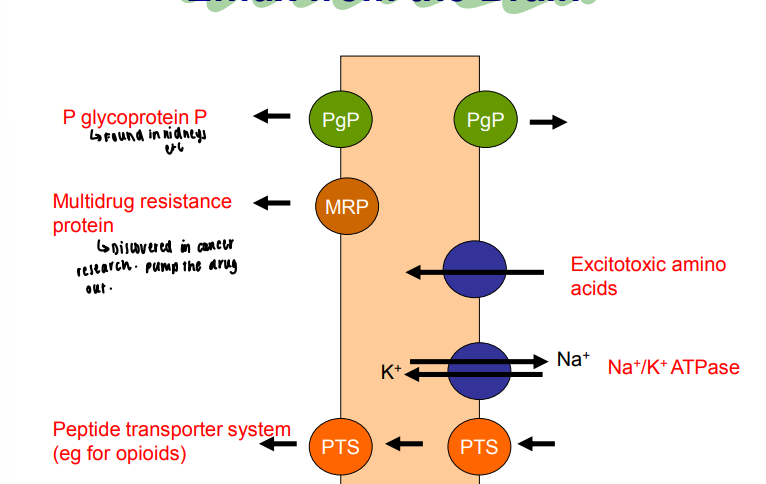
What larger molecules effluxes out of the brain?
P glycoprotein p in the kidneys
Multidrug resistance protein - pumps the drug out
excitotoxic amino acids
sodium potassium ATPase
peptide transporter system
What molecular properties mean molecules CAN’T enter the brain easily?
larger molecules - over 400Da
Low lipid fat soluble molecules
High electrical charge molecules
What are the functions of the BBB?
Protects brain from foreign substances that can harm it
Protects brain from hormones and neurotransmitters in the rest of the body
transports nutrients into the brain’
moves out toxins of the brain
maintains a constant environment for the brain
essential for brain normal functions
Why are there problems delivering drugs into the brain?
BBB likes smaller and lipophilic molecules but larger molecules can’t be transported unless it has an active transport system and there are effective efflux systems
What are the go through strategies for drug delivery to the brain?
endogenous system - use transporters and make drugs with similar structures
disrupting BBB osmotically - increase conc of reagents and temporarily disrupt the barrier
prodrugs - becomes a drug when metabolised
What are some examples of go behind strategies in the brain for drug delivery?
intraventricular/intrathecal - inject into spinal cord or ventricles
olfactory - drugs given in the nose via olfactory nerve
interstitial - direct injection