3.3 Muscle Fibers and Energy
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
What are 2 different types of muscle fibers?
fast, slow twitch
Fast twitch muscle fiber will have ___ myosin ATPase and ____ calcium ATPase.
fast
Slow twitch muscle fiber will have___ myosin ATPase and ____ calcium ATPase.
slow
Oxidative or aerobic involves what size muscle fibers?
small
Glycolytic or anaerobic invovles what size muscle fibers?
large
Which muscle fiber type is weaker? (anaerobic or aerobic)
aerobic
Although glycolytic/anaerobic muscle fibers are stronger, they ___ through their fuel fast.
burn
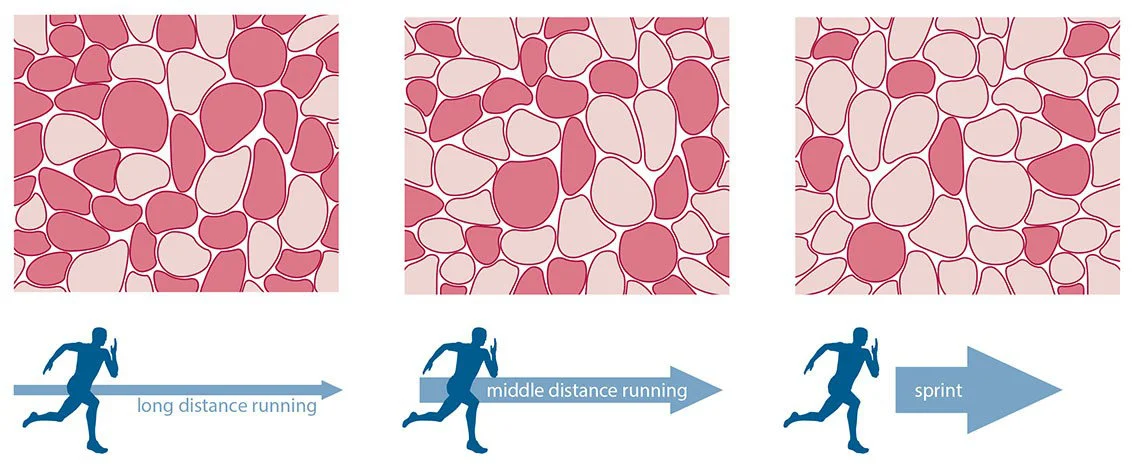
Which muscle fiber has less myoglobin?
anaerobic
Which muscle fiber has lots of myoglobin?
aerobic
Which muscle fiber has many mitochondria; which has fewer?
aerobic; anaerobic
Which muscle fiber fatigues quickly; which is slow to fatigue?
anaerobic; aerobic
What type of metabolism does glycolytic muscle fibers use?
glycolytic (anaerobic) metabolism
What is the pros of glycolytic metabolism? (2)
simple and fast
What is the con of glycolytic metabolism?
less efficient (less atp produced)
What metabolism do oxidative muscle fibers use?
oxidative metabolism
What is the pro of oxidative metabolism?
produces more atp per glucose molecule
What is the con of oxidative metabolism?
slow
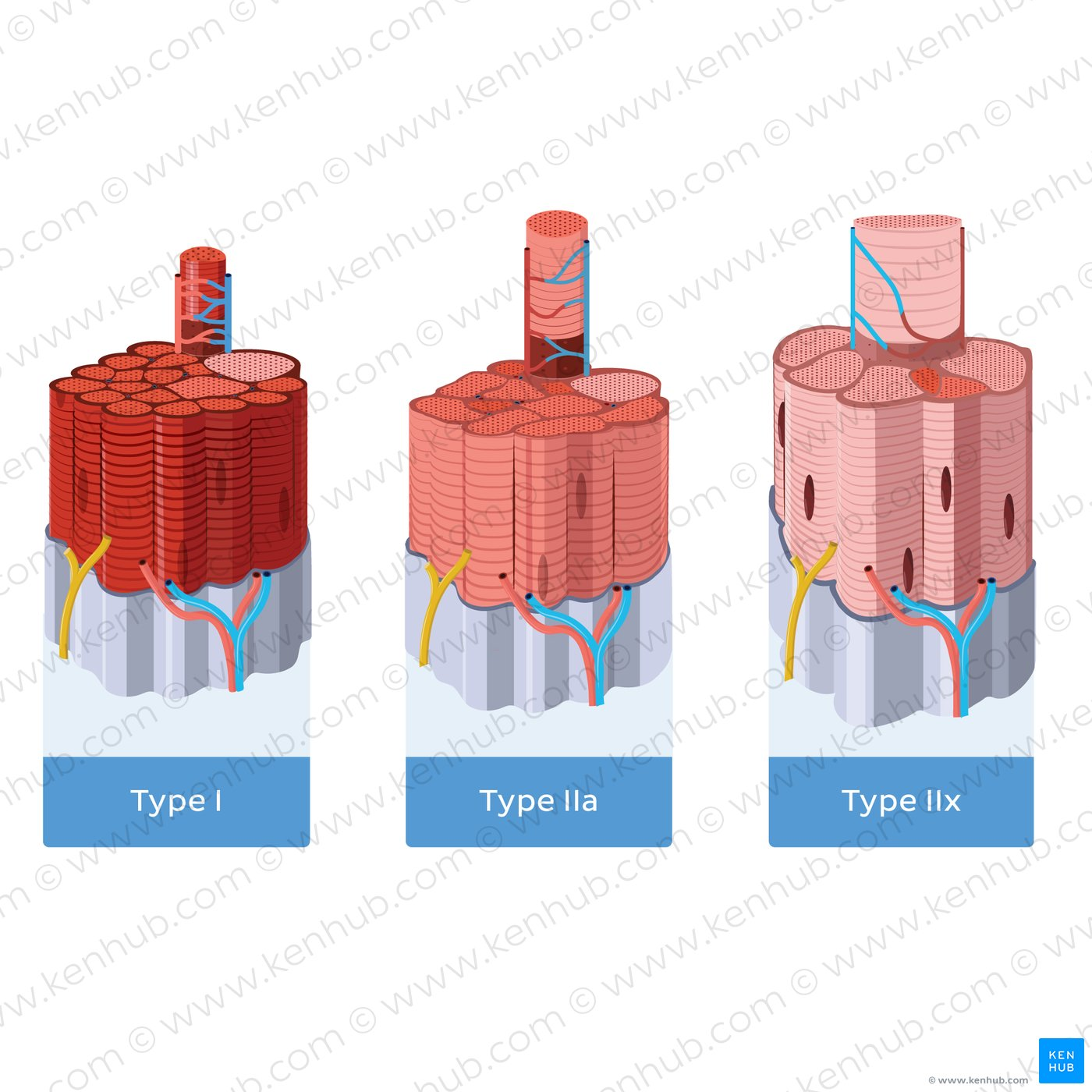
Why can glycolytic muscle fibers be larger than oxidative muscle fibers?
because they can store more glycogen
Why else are anaerobic muscle fibers stronger than aerobic?
more myofibrils
What’s myoglobin?
oxygen storage and transport protein
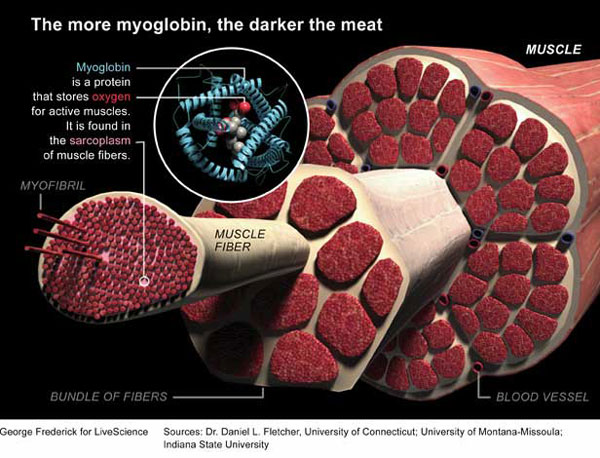
What color is myoglobin?
bright red
Where is more myoglobin seen? (which muscle cell/fiber)
oxidative/aerobic muscle cells
Definition of muscle fatigue
when a muscle fiber is no longer able to generate the force that it normally would from an action potential
Definition of mitochondria
organelles which have the right structures and enzymes for aerobic respiration
DO glycolytic muscle fibers still have mitochondria? (2)
yes, just less
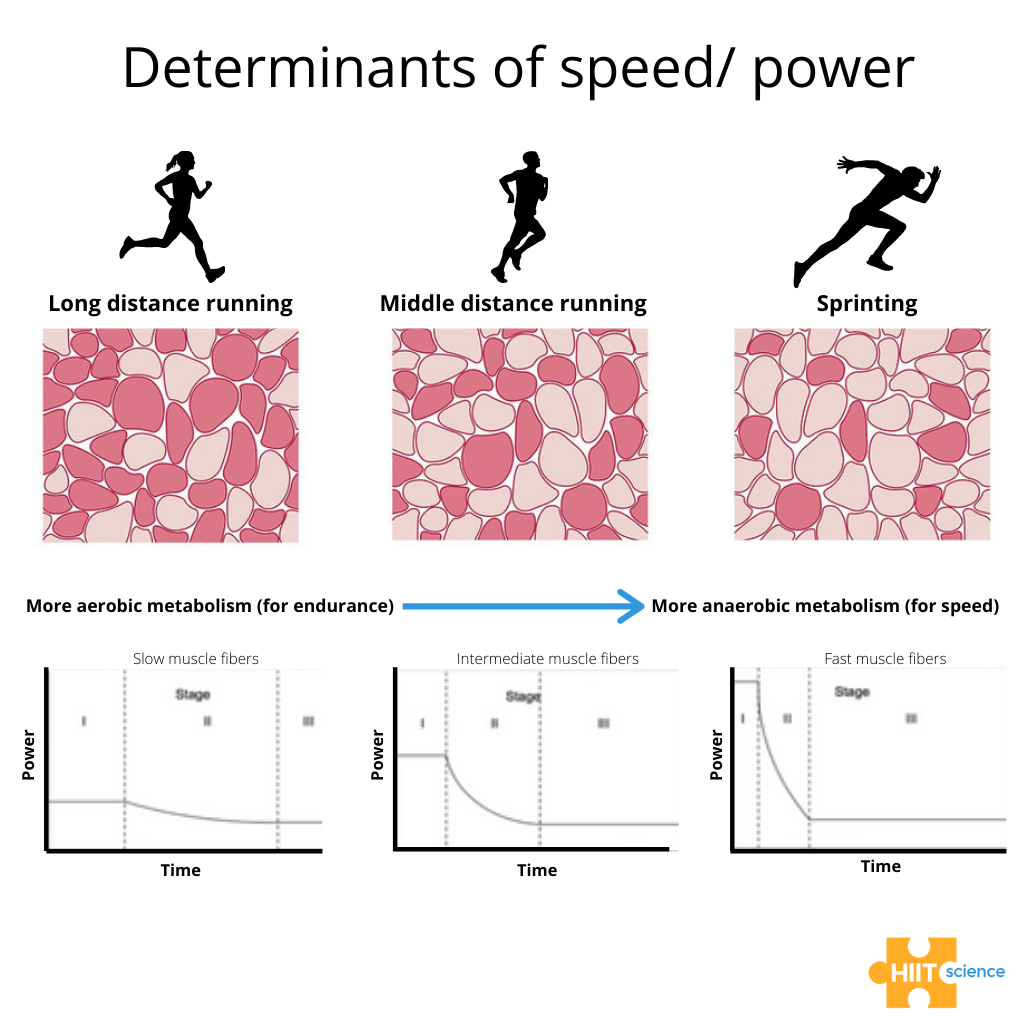
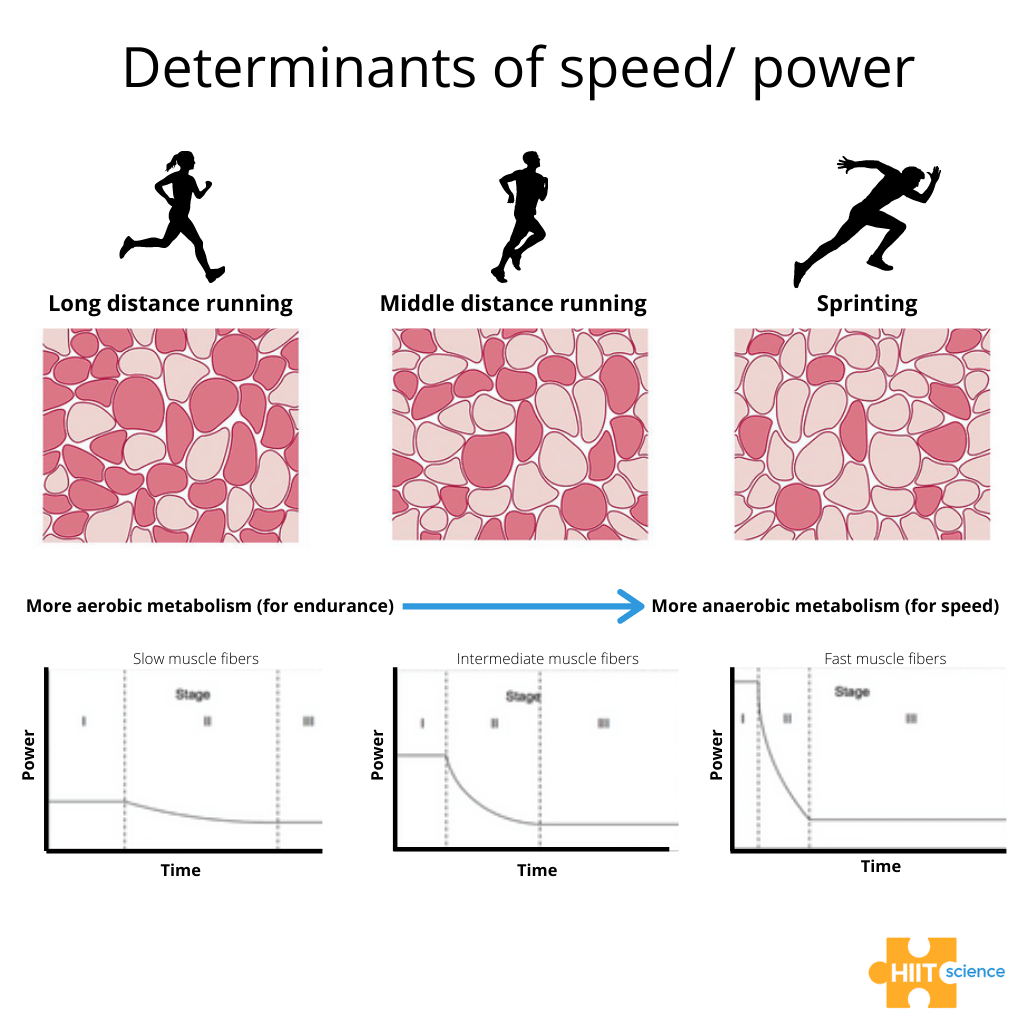
What type of muscle fiber uses oxidative metabolism and has slow twitch?
Type I
What type of muscle fiber uses oxidative metabolism and has fast twitch?
type IIa
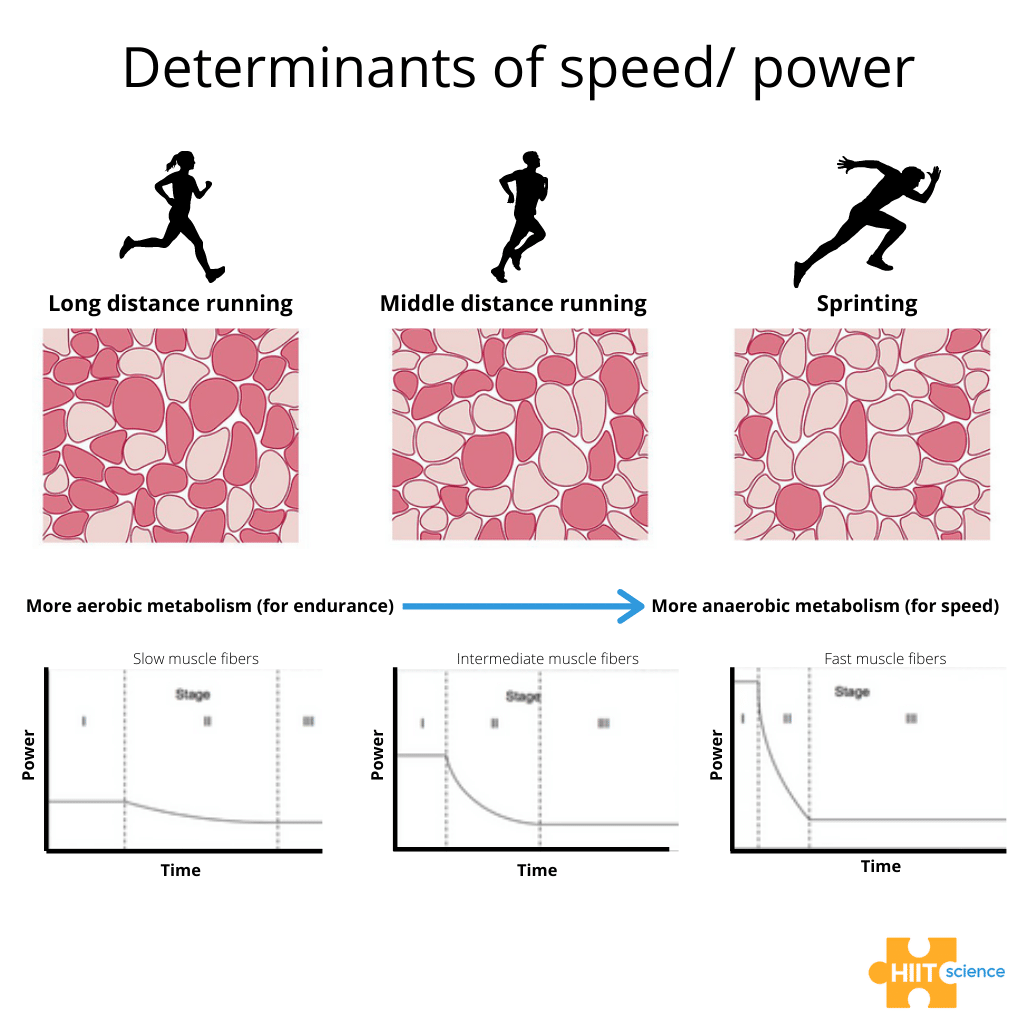
What type of muscle fiber uses glycolytic metabolism and has fast twitch?
type IIx
Are entire muscles made up of one type of fiber?
no (made up of all 3)
Although the muscle fibers are made up of all 3 fibers, there will be ____ proportion of certain kinds depending on the muscle.
more
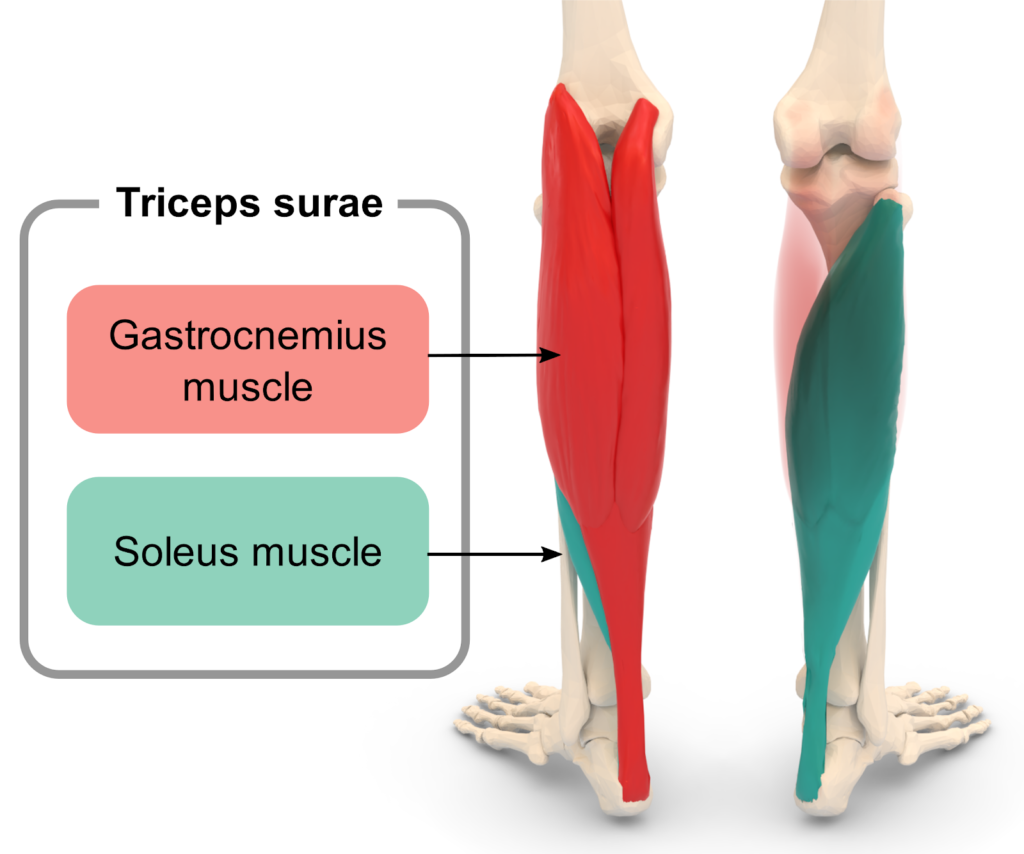
Examples of Muscle fiber proportions:
What % of type I muscle fiber is the Soleus muscle made of?
80% (can sustain contraction for long time)
Examples of Muscle fiber proportions:
What % of type I muscle fiber is the Quadriceps muscle made of?
50%
Examples of Muscle fiber proportions:
What % of type I muscle fiber is the Orbicularis Oculi muscle made of?
15%
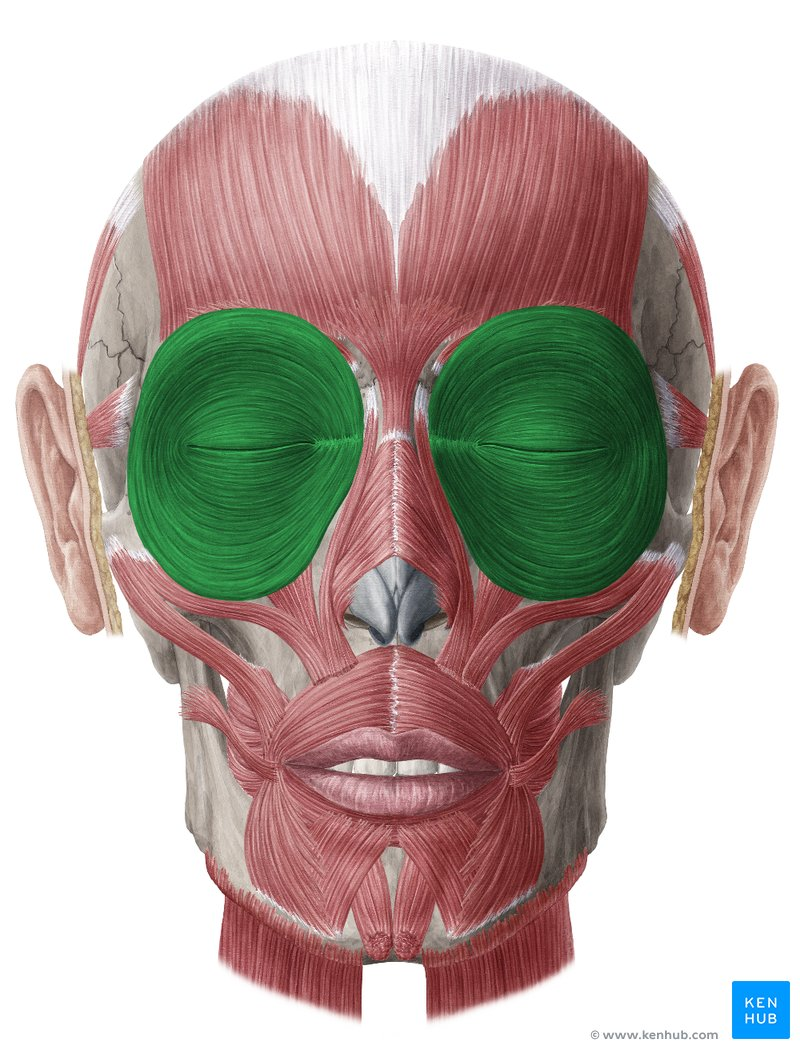
Why is the orbicularis oculi only 15% type I?
needs fast twtich muscle because makes quick movement
Can Type II fibers interchange between a and x (yes/no)? If so what is it dependent on (3)?
yes; dependent on size, myofibrils, mitochondrias
Example of type IIx becomming IIa → spend lots of time endurance training so, the IIx fibers get rid of ______ and get more _____.
myofibrils, mitochondria
Do genetics make a difference in muscle fiber?
yes (influence composition & performance)
Individual motor units that control certain muscle fibers will control the same OR different types of muscle fibers?
same
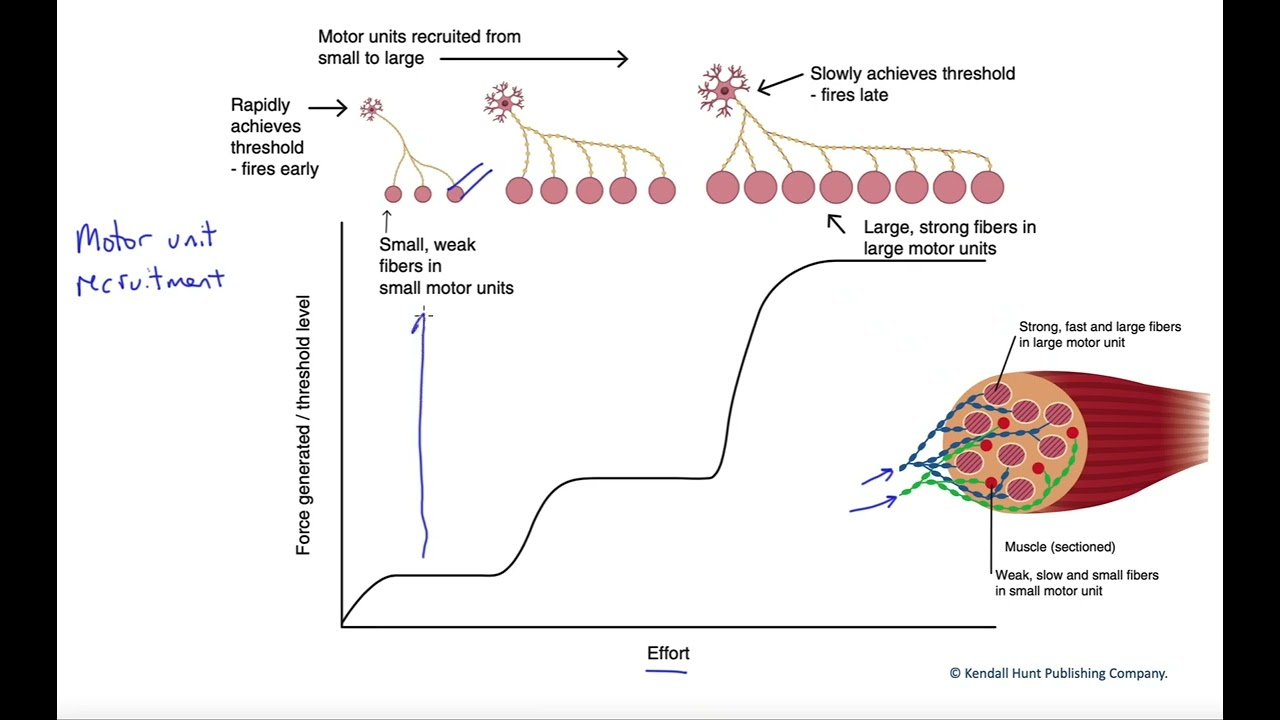
What’s the recruitment order for muscle fibers during asynchronous recruitment? (3)
type I, type IIa, type IIx (always last fiber to be used)
Muscle Trembling
You are holding/lifting a heavy dumbbell and need to call upon type IIx fibers; however, these don’t twitch, causing _____ _____. (2)
muscle fatigue
Muscle Trembling
When the type IIx give up because they’re out of energy, the muscle goes back to using type __ or type __ fibers.
I, IIa
Muscle Trembling
During the first part of the lifting, once the type IIx fibers “give up”, what’s occuring?
muscle tremble
Muscle Trembling
As your body uses the other fibers (that are already fatigued), your muscle starts ____ more.
trembling
When ATP → ADP + Pi ; what’s being released/is a product (due to bonds breaking)?
energy
When doing ADP + Pi → ATP, what’s added to allow this reaction?
energy
What are 4 ways to get ATP in skeletal muscle cells?
phosphocreatine, anaerobic metabolism, aerobic metabolism, fatty acids
When starting with a glucose molecule, what are the 2 metabolisms that can be used to get ATP from that?
anaerobic metabolism, aerobic metabolism
About how many twtiches of ATP can a muscle cell hold?
8 twitches worth of ATP
If we ever run out of ATP (in the muscle), what happens?
rigor mortis
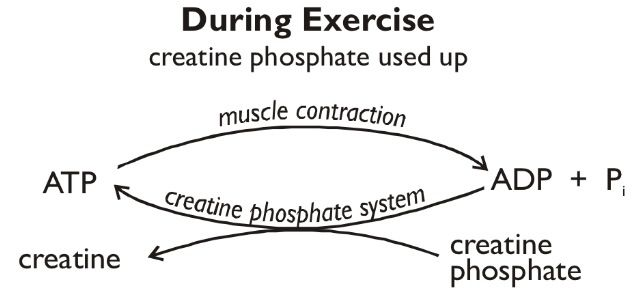
What does phosphocreating allow for?
rapid regeneration of ATP in short term
Phosphocreatine is only done while wating for ____ _____ ____?
glucose metabolisms’ ATP
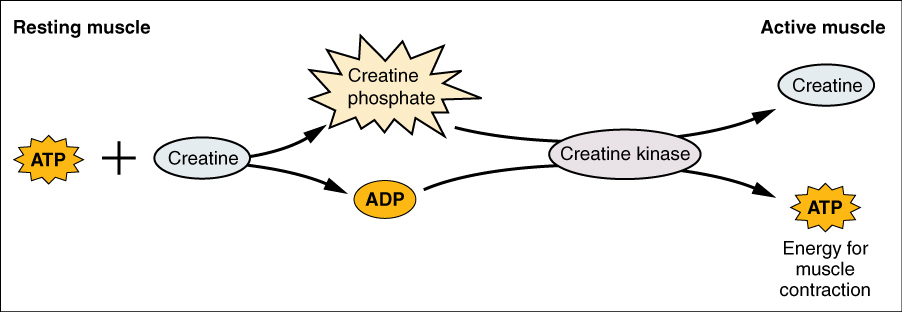
MUSCLE AT REST
If there’s excess ATP; what does it do during phosphocreatine?
gives one of its Phosphates to creatine molecule
MUSCLE AT REST
So ATP + Creatine = ? (2)
Phosphocreatine and ADP
What can happen to those ADP products from the ATP + creatine? (what other metabolism will use them, and what will it form?)
can be recycled to form ATP using glucose metabolism
so at muscle cell at rest; if there’s excess ATP, you can build up a stockpile of phosphocreatine. What analogy can be used to describe phosphocreatine?
like a portable charger (that stores energy for quick use)
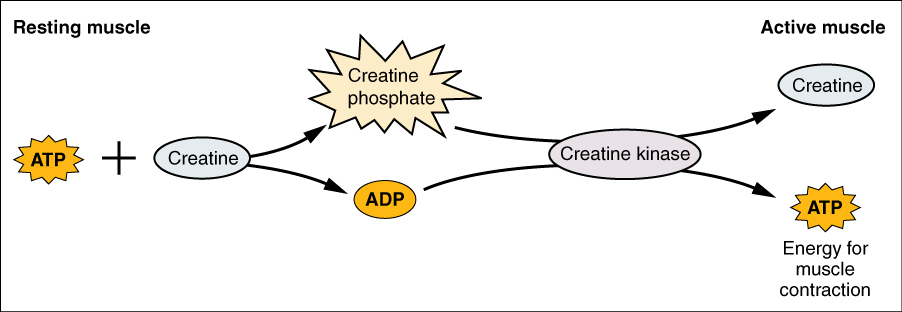
Muscle In Use
What occurs to the phosphocreatine when it needs to conver into ATP?
gives its phosphate to ADP to make ATP
Muscle in Use
So, ADP + Phosphocreatine → ? (2)
ATP, creatine
What is the enzyme that transfers the phosphate ←→ creatine?
creatine kinase
During glucose Aerobic or Oxidative Metabolism, what are the 4 steps? (broad)
glycolysis, linking step, kreb’s cycle, oxidative phosphorylation
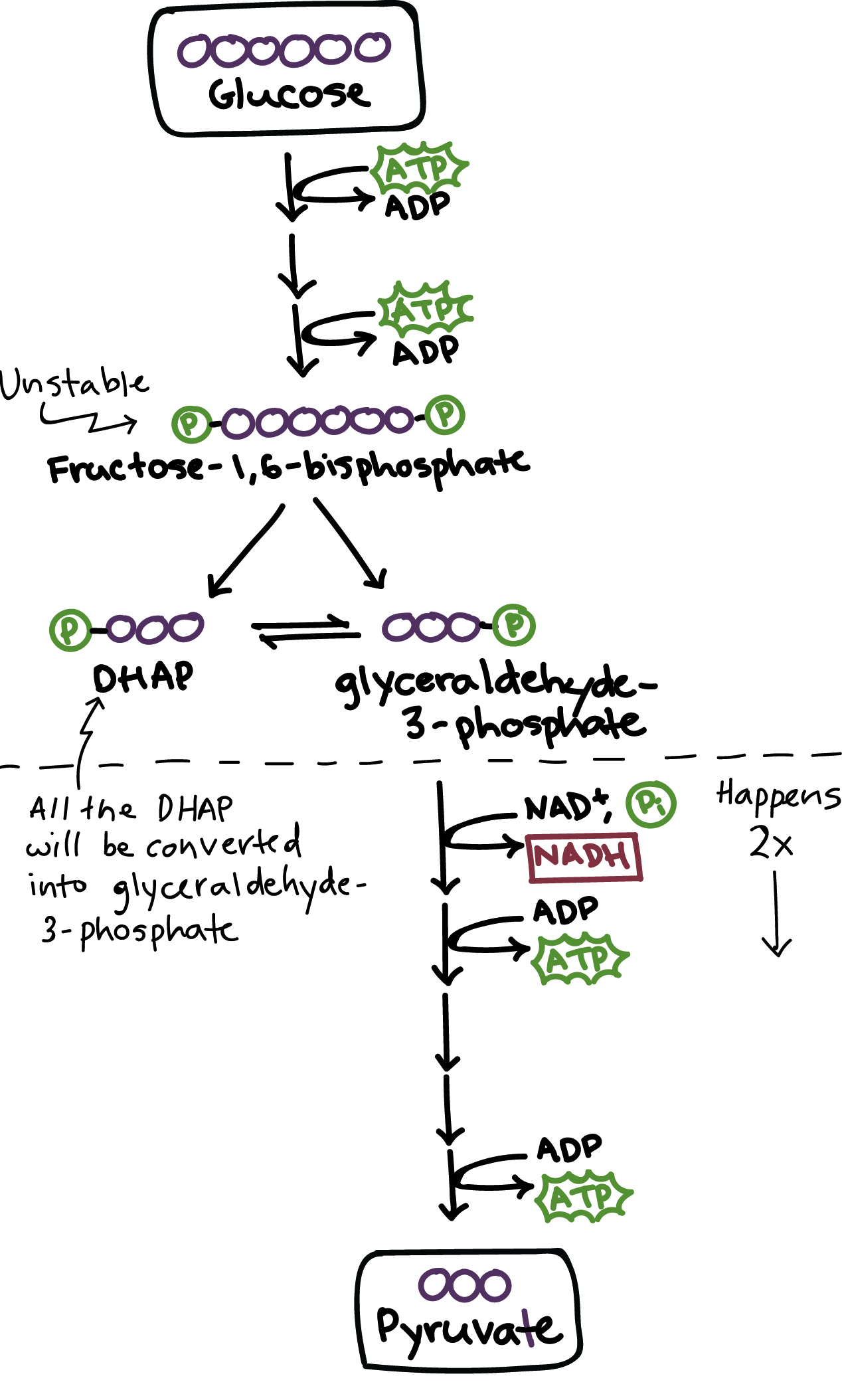
In glycolysis what is the starting and end product? (2, say quantity of each molecule)
1 glucose, 2 pyruvate
How many ATP are PUT into glycolysis; how many are gained?
2 atp; 4 atp
What’s the net ATP in glycolysis?
(4-2) 2 ATP
In glycolysis; what happens to the 2 NAD+? (say quantity)
(reduced) becomes 2 NADH
What’s the role of NADH?
carrying the energy (carries one H+ and one e-)
Do both anaerobic and aerobic metabolisms use glycolysis?
yes
In the Linking Step; the 2 Pyruvate turns into ____? (say quantity)
2 Acetyl-CoA
What’s the other product/byproduct in the Linking Step when turning pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA? (say quantity & molecule)
2 CO2
During the Linking step, 2 other NAD+ turn into? (quantity&molecule)
2 NADH
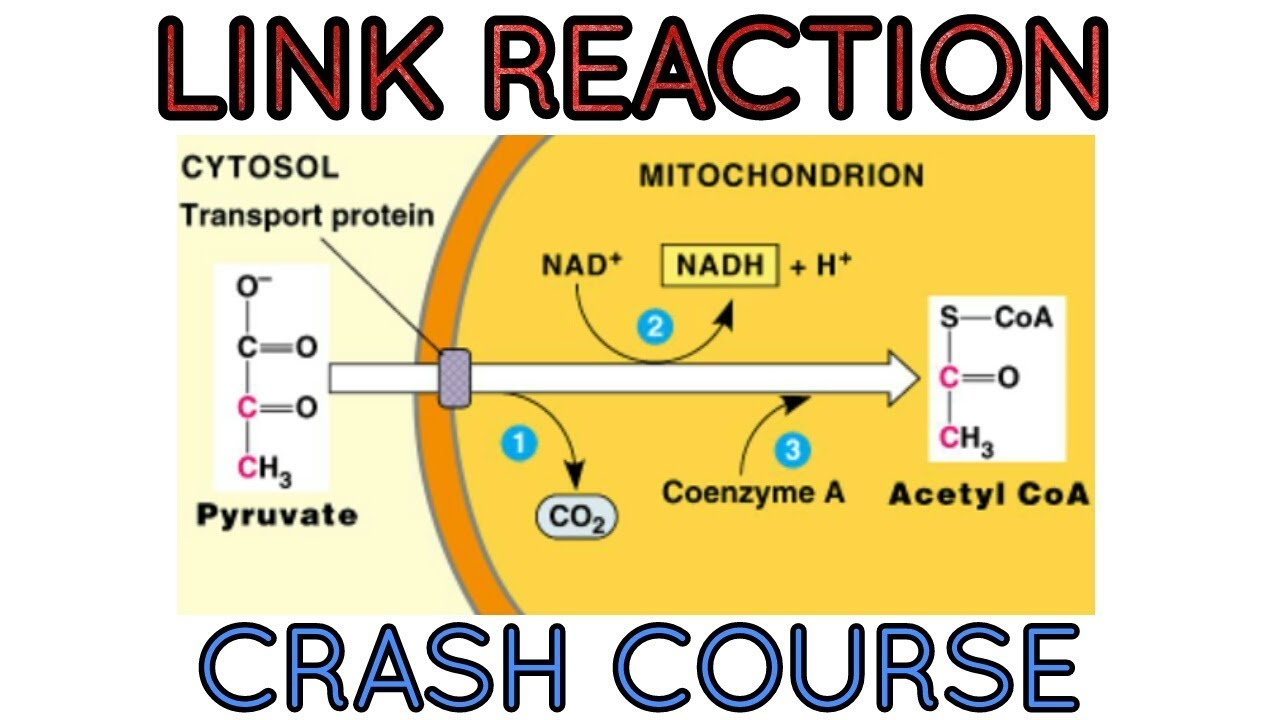
Where does the Linking Step take place? (intracellular structure)
mitochondria
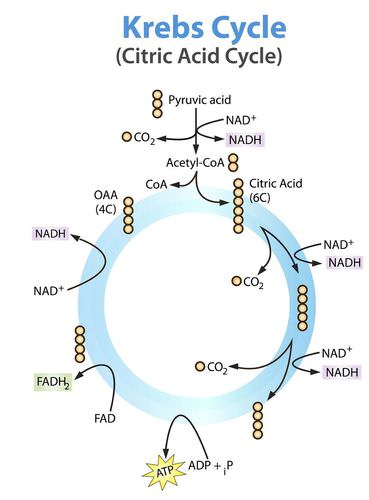
The 2 Acetyl-CoA then go to the ____ ____?
Krebs cycle
Do both (2) Acetyl-CoA molecules go through the Kreb’s cycle at the same time, or individually?
individually
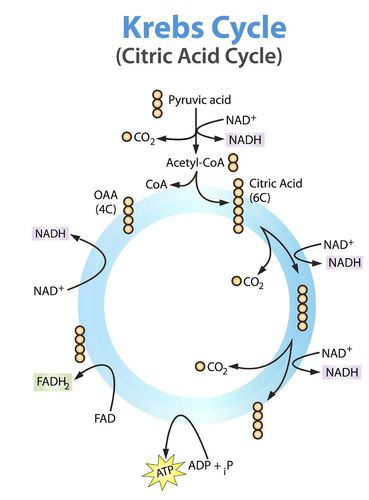
What are the products of 2 Acetyl-CoA molecules going into Krebs’ cycle? (4)
6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP, 4 CO2
Adding up the products from glycolysis, linking step, and krebs’ cycle→ how many products are there so far? (nadh, fadh2, atp, co2)
10 NADH, 2 FADH2, 4 ATP, 6 CO2
Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur? (intracellular location)
mitochondrial matrix
What occurs after the Kreb’s Cycle?
oxidative phosphorylation
What occurs to the NADH and FADH2 in oxidative phosphorylation?
they get oxidized and give their electrons to the electron transport chain
What’s the purpose of the ETC (electron transport chain)?
transfers electrons down a set of proteins to push H+ across mitochondrial membrane
So what does the H+ gradient provide?
generates energy for ATP synthase to produce ATP
What does ATP synthase do?
contorts and links ADP and Pi together to make ATP
What is the acceptor that takes the electrons/H+ out of the ETC?
O2
If you have cyanide poisoning, what’s removed?
o2 acceptor
For 1 NADH how many ATP are produced?
2.5
For 1 FADH2 how many ATP are produced?
1.5
So with 10 NADH and 2 FADH2, how much ATP is generated from oxidative phosphorylation alone?
28
Adding up all the ATP from aerobic metabolism, how much is produced? (~)
32
What are the other inputs/byproducts of oxidative phosphorylation? (besides the ones mentioned)
o2; H2O
For anaerobic/glycolytic metabolism, what happens after glycolysis? (say the cycle/metabolism)
lactic acid fermentation
What occurs with Lactic Acid fermentation? Begin with what happens to NADH?
NADH turns into NAD+
Where does the electrons/hydrogens go from NADH → NAD+?
onto pyruvate
By putting the electrons/hydrogens onto pyruvate, what does it turn into? (product)
lactate (lactic acid)
so, how many ATPs does anaerobic metabolism get?
2
What’s a positive outcome of anaerobic metabolism?
fast
For Fatty Acid breakdown, what’s the first step?
beta oxidation
What occurs during beta oxidation? (describe)
fatty acids’ last two carbons are broken off from molecule
What are the products after beta oxidation? (3)
NADH, FADH2, acyl unit
What happens to the acyl unit?
becomes Acetyl-CoA
What does Acetyl-CoA go through (similar to aerobic)?
krebs cycle
For every ONE Acetyl-CoA that goes through the Kreb’s Cycle, what are the products? (amount as well; 3)
3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP
So from the beta-oxidation and Kreb’s cycle, how many NADH and FADH2 are there?
4 NADH, 2 FADH2
To find out how many ATPS there are; we multiply 4 NADH x ____ + 2 FADH2 x ____.
2.5, 1.5