Psyc 410 Midterm Study Guide: Intimate Relationships
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
created 3/7/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Correlational Study
Examines relationships between variables without manipulation.
Experiment
Manipulates variables to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
Independent Variable
Variable manipulated to observe effects on dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
Variable measured to assess impact of independent variable.
Plagiarism
Using someone else's work without proper attribution.
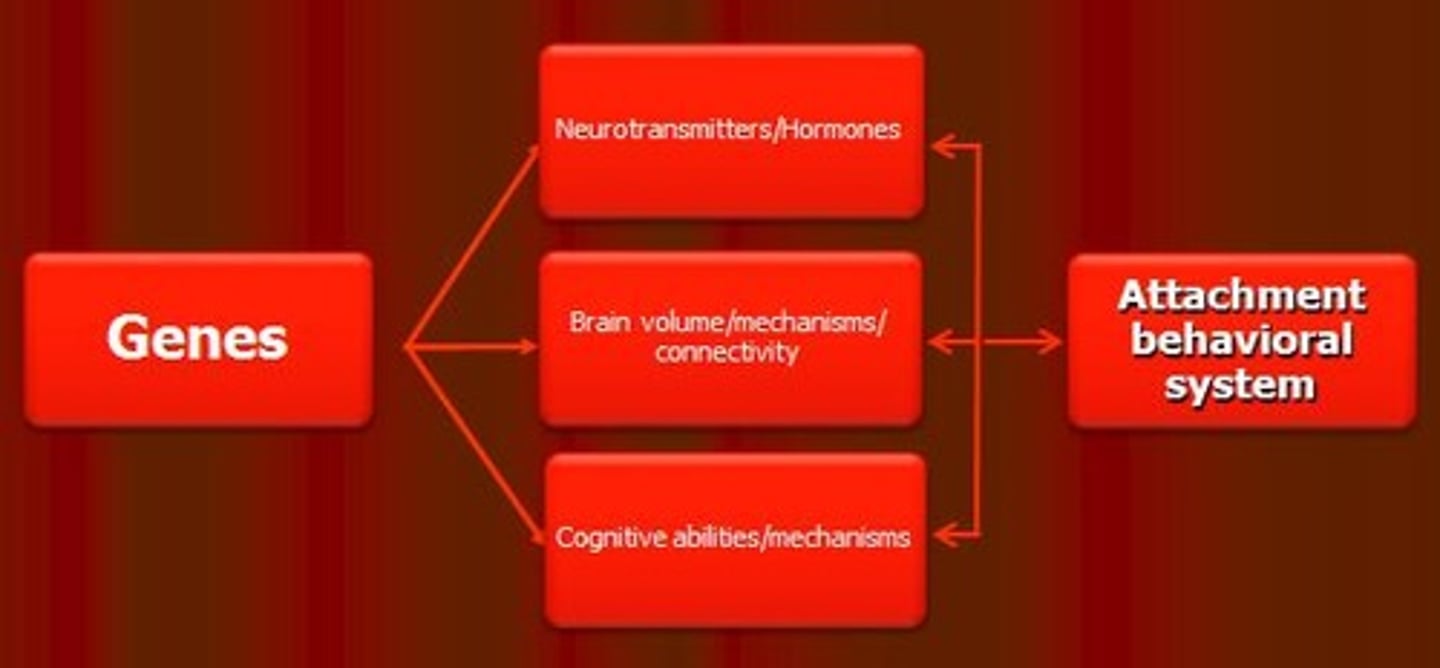
Attachment Theory
Explains emotional bonds between individuals, especially caregivers.
John Bowlby
Pioneer of attachment theory, focused on child development.
Mary Ainsworth
Expanded Bowlby's work; developed Strange Situation procedure.
Strange Situation
Assessment of infant attachment styles through separation/reunion.
Attachment Styles
Patterns of attachment behavior categorized in infants.
Secure Attachment
Characterized by trust and comfort in relationships.
Anxious Attachment
Involves fear of abandonment and excessive worry.
Avoidant Attachment
Involves emotional distance and self-reliance.
Internal Working Models
Mental representations of self and others based on experiences.
Attachment Scripts
Cognitive frameworks guiding expectations in relationships.
Adult Attachment Interview
Structured interview assessing adult attachment styles.
Attachment Q-sort
Method assessing attachment through behavioral observations.
Self-report Measures
Surveys assessing individual perceptions of attachment styles.
Two-factor Model
Attachment conceptualized through anxiety and avoidance dimensions.
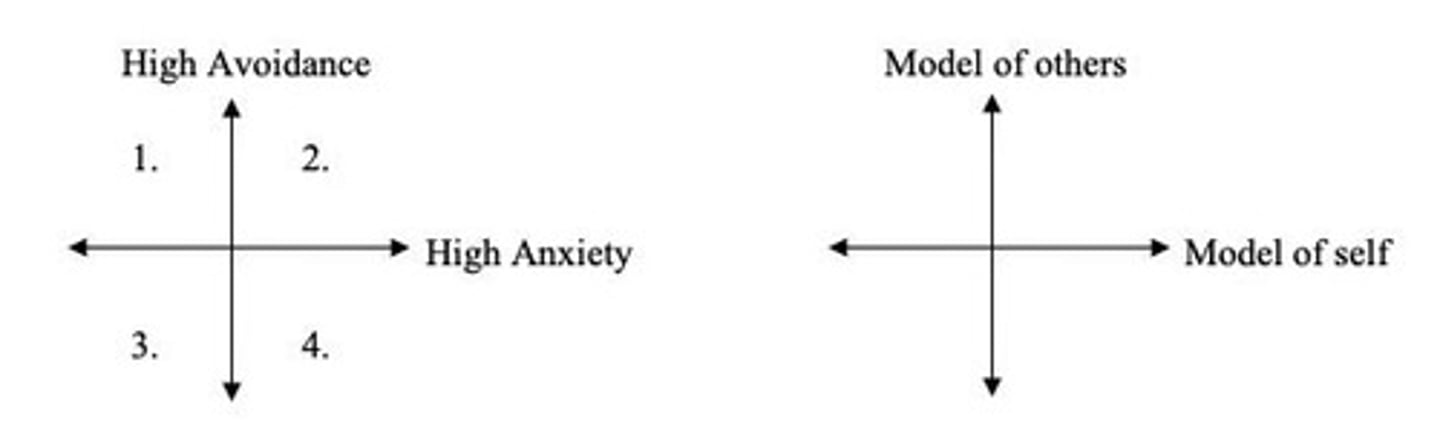
Four-factor Model
Includes secure, anxious, avoidant, and fearful attachment styles.
Attachment Stability
Consistency of attachment styles over time.
Attachment Change
Shifts in attachment styles due to life events.
Priming
Activating specific memories or associations to influence behavior.
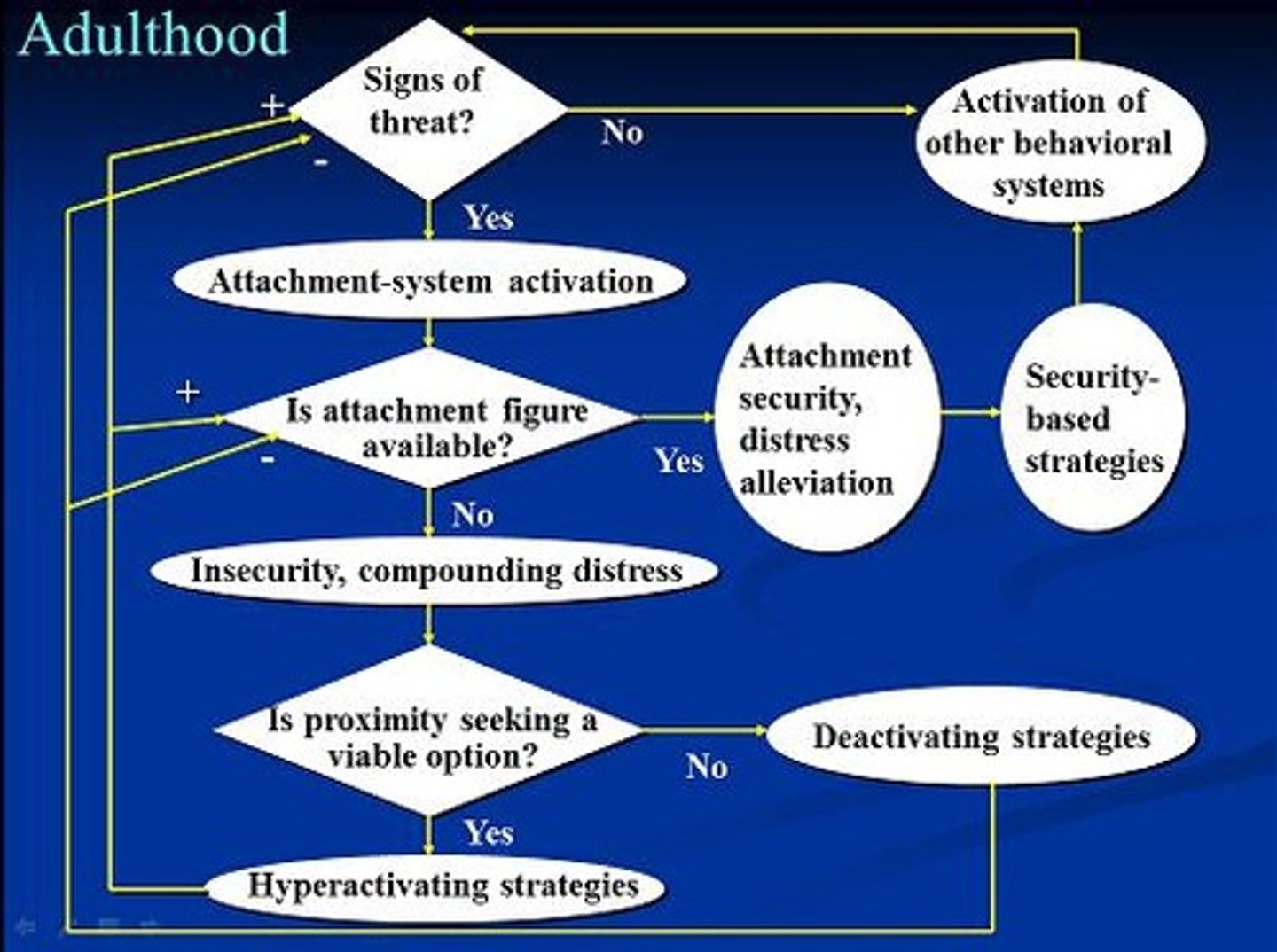
Behavioral Systems
Interconnected systems guiding behaviors like attachment and caregiving.
Trinity Model
Integrates attachment, caregiving, and sexual behavioral systems.
Oxytocin
Hormone associated with bonding and social behaviors.
Neuroimaging Studies
Examine brain activity related to attachment styles.
Cultural Differences
Variations in attachment styles across different cultures.
Earned Security
Achieving secure attachment despite past insecurities.
Disorganized Attachment
Characterized by lack of clear attachment behavior.
Emotionally Focused Therapy
Therapy focusing on emotional bonds in relationships.
Psychiatric Disorders
Mental health issues linked to insecure attachment.
Life Transitions
Major changes influencing attachment stability and change.
Attachment and Therapy
Explores how attachment styles affect therapeutic outcomes.
Attachment Security Priming
Enhancing feelings of security to improve mental health.
Mikulincer et al. Study
Research on attachment and cognitive accessibility under threat.
Bowlby's Metaphors
Dynamic processes describing attachment development.
Influence of Environment
Contextual factors affecting attachment stability and change.
Attachment Measurement
Methods used to assess attachment styles in adults.
Hazan and Shaver Measure
Self-report measure assessing adult attachment styles.
Bartholomew & Horowitz
Categorized attachment styles into four types.
Attachment Figures
Key individuals providing security and support in relationships.
Relationship Factors
Stage and length of relationship influencing attachment styles.
Gender Differences
Variations in attachment styles based on gender.
Racial/Ethnic Variations
Differences in attachment styles among diverse groups.
SES Variations
Influence of socioeconomic status on attachment styles.