Multiple Choice 5
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
A ball is attached to a string and swung in a horizontal circle. Which of the following would decrease the acceleration of the ball? Select all that apply
Double the length of the string without changing the speed of the ball
Double the length of the string while halving the speed of the ball
A car travels around a curved section of road at a constant speed. Which of the following changes would increase the magnitude of the frictional force the road would need to exert on the car in order for the car to drive around the curve without skidding
Decreasing the radius of the curve, increasing the mass of the car, increasing the speed at which the car is driving
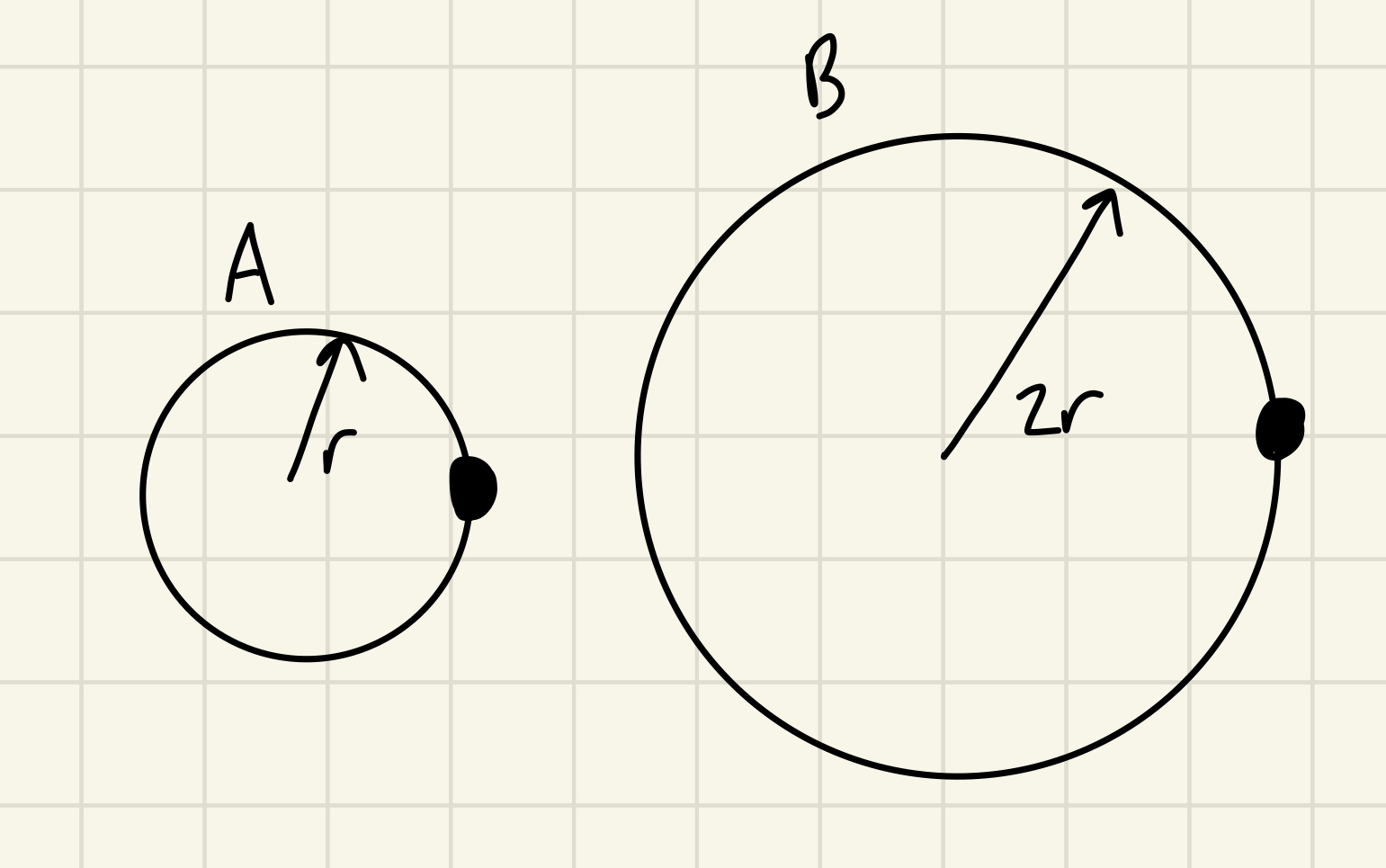
Identical objects move at constant speed around the two circular paths shown below. Both objects take the same amount of time to complete one full revolution around their respective circle
aA=1/2aB
If you put a penny on the center of a rotating turntable, it does not slip. However, if you place the penny near the edge, it is likely to slip off. Which answer below explains this observation?
The radial acceleration is greater at the edge and the friction force is not enough to keep the penny in place
Planet X has two moons. Moon 1 has twice the mass of Moon 2. Both moons orbit at the same distance from Planet X and take the same time to complete an orbit. Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply
The force Planet X exerts on Moon 1 is twice as strong as the force Planet X exerts on Moon 2
Both moons have the same acceleration
Which of the following should you do to decrease the likelihood that your car will skid when turning on icy roads?
Increase the coefficient of friction (by putting snow chains on your tires)
Decrease the speed at which you take turns
Why is it difficult for a high speed car to negotiate an unbanked turn?
The magnitude of static friction force might not be enough to provide the necessary radial acceleration
A pendulum bob is attached to a string and allowed to swing. Which of the following statements is true with correct reasoning about the magnitude of the force the string exerts on the bob Fs on B and the magnitude of the force Earth exerts on the bob Fe on B at the very bottom of the pendulum’s swing?
Fs on B>Fe on B because the bob is accelerating upward at the bottom of its swing
Where on Earth’s surface would you expect to experience the greatest radial acceleration as a result of Earth’s rotation?
The equator
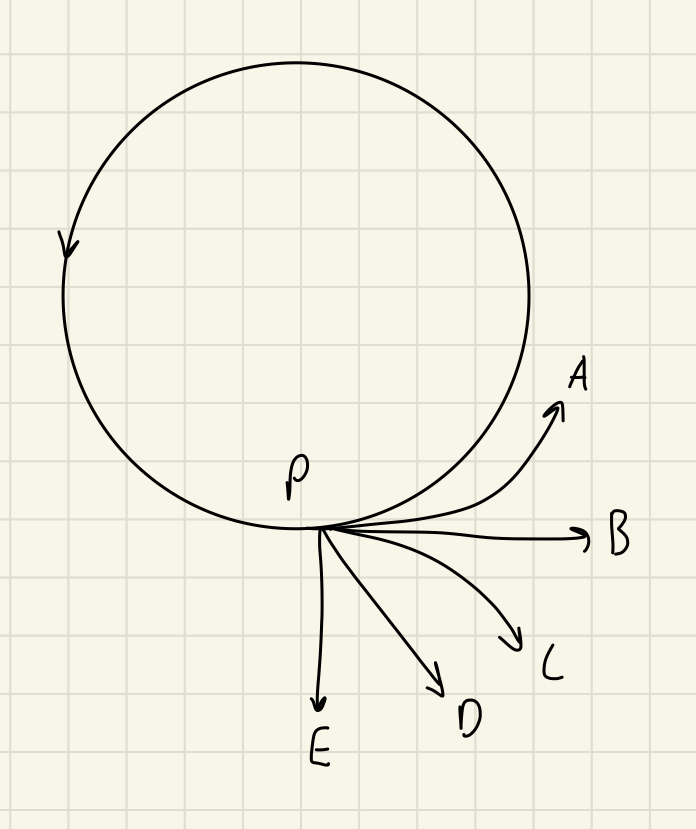
A girl attaches a rock to a string, which she then swings counter-clockwise in a horizontal circle. The string breaks when the rock is at point P in the figure, which shows a bird’s eye view (as seen from above). Which path (A-E) will the rock follow?
B
One of your classmates drew a force diagram for a pendulum bob at the bottom of its swing. He put a horizontal force arrow in the direction of the velocity. Evaluate his diagram by choosing from the statements below
He is incorrect since there are no forces in the direction of the object’s velocity
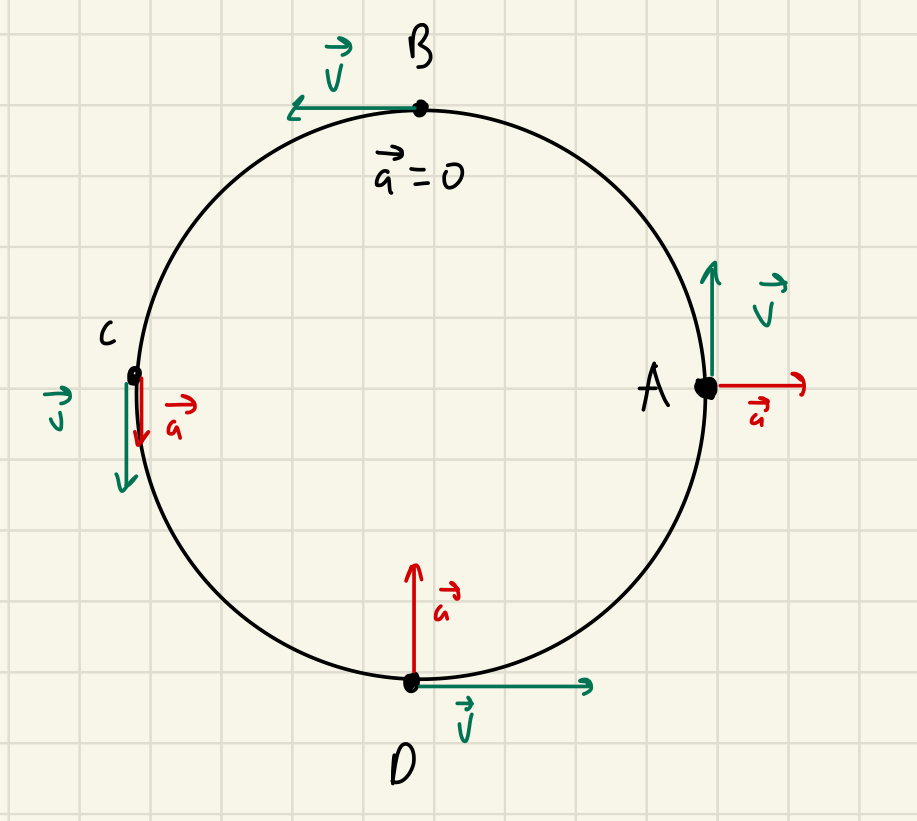
The circle in the figure below represents the path followed by an object moving at a constant speed. At four different points on the circle, the object’s motion is described using velocity and acceleration arrows. Choose the location where the descriptions are correct
Point D
Which of these objects is accelerating? There might be multiple answers
Object slowing down while moving in a straight line
Object moving at constant speed in a circle
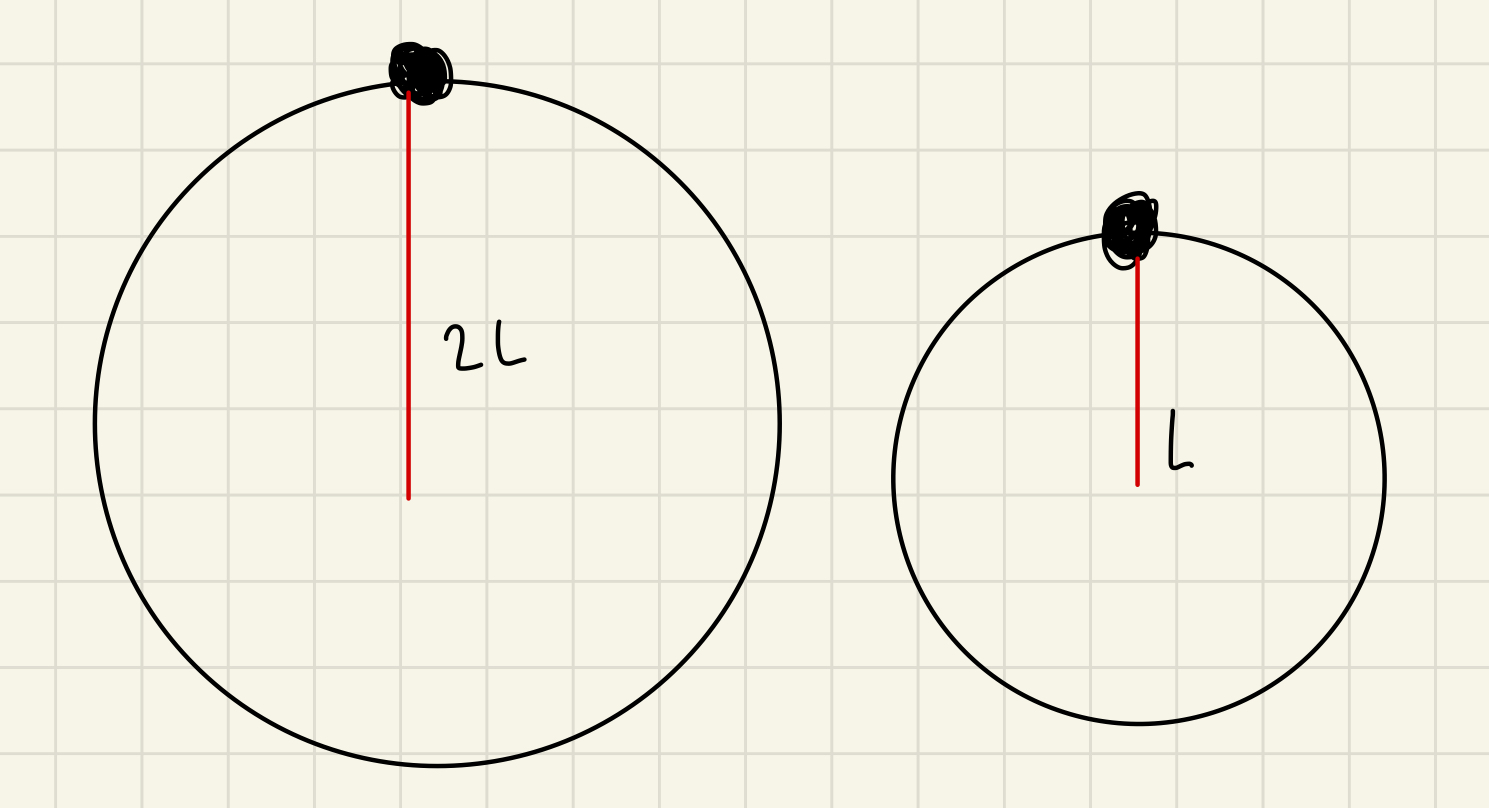
Two identical balls are attached to the end of strings and swung in a horizontal circle. One string has a length of L and the other has a length of 2L. Both balls are swung so they have the same period
The ball on the long string has twice the acceleration of the ball on the short string

A car drives at a constant speed first over a hill and then through a dip. The picture below shows the view from the side. At which point will the force the seat exerts on the driver of the car be lowest
Point B

A car travels counterclockwise around the curved section of road shown below. Which of the following arrows shows the direction of the car's velocity at the moment shown?
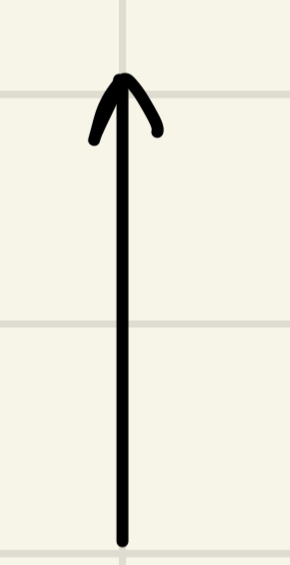
In which of the following situations would you expect the magnitude of the force the seat of your car exerts upward on you to be less than the magnitude of the force Earth exerts downward on you?
When you are driving at constant speed over the top of a circular hill
How does a person standing on the ground explain why you, sitting on the left side of a slippery back car seat, slide to the right when the car makes a high-speed left turn?
You tend to move in a straight line and thus slide with respect to the seat that is moving to the left under you.