CHEMISTRY MediaLab Question bank
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
TIBC (total iron-binding capacity) is an indirect measurement of which of the following:
Ferritin
Hemoglobin
Ceruloplasmin
Transferrin
Transferrin
Which of the following analytes would be increased due to delay in centrifugation?
Creatinine
Ionized Calcium
Folate
Bicarbonate
Creatinine
Which of the following tests confirms the presence of Bence-Jones proteinuria:
Protein electrophoresis
Sulfosalicylic acid precipitation
Cryoprecipitation
Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis
All of the following are considered cutaneous porphyrias, EXCEPT?
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Acute intermittent porphyria
Congenital erythropoietic porphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Acute intermittent porphyria
Which of the following blood tests is used in the determination of prostate cancer?
Acid phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT or SGPT)
Creatinine
Acid phosphatase
Which of the following blood tests is used to determine acute pancreatitis?
Acid phosphatase
Uric acid
Amylase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Amylase
You are collecting a blood specimen to be used for forensic (legal) alcohol testing. Which of the following must be done before you can start the specimen collection process?
Label the tubes in the presence of the patient.
Must inform the patient that the blood about to be collected is for alcohol testing.
Seal the collection tubes in front of the patient.
Collect the specimen, the patient does not need to be informed what the blood is collected for.
Must inform the patient that the blood about to be collected is for alcohol testing.
To assess drug concentrations during the trough phase:
Blood should be drawn about one hour after the administration of an oral dose of the drug.
Blood should be drawn about half an hour before the next dose is given.
Blood should be drawn about two hours after the administration of an oral dose of the drug.
Blood should be drawn immediately before the next dose is given.
Blood should be drawn immediately before the next dose is given.
An obese adult with premature arteriosclerosis is seen in the clinic. When her serum is tested no chylomicrons are present, LDL levels are normal, and VLDL levels are increased. There is an increase in triglycerides and a slight increase in cholesterol. Lipoprotein electrophoresis reveals a heavy pre-beta band. She has no skin rash and uric acid is increased. This patient most likely has what type of hyperlipoproteinemia?
Type I
Type Ill
Type IV
Type V
Type IV
The measurement of sodium and chloride in the sweat is the most useful test for the diagnosis of what condition/disease?
Steatorrhea
Direct determination of the exocrine secretory capacity of the pancreas.
Cystic fibrosis
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Cystic fibrosis
All of the following laboratory tests are used to determine kidney function, EXCEPT?
Creatinine
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
Amylase
Phosphorus
Amylase
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding troponin as a marker of myocardial infarction (MI)?
It rises much sooner after a myocardial infarction than CK-MB.
It stays elevated much longer than CK-MB.
It is potentially more specific as a cardiac marker than CK-MB.
Troponin T is often elevated in renal failure patients.
It rises much sooner after a myocardial infarction than CK-MB.
An electrophoretic separation of lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme that demonstrates elevation in LD-I greater than LD-2 could be indicative of:
A normal LD isoenzyme pattern
Hemolysis
Pancreatitis
Hepatic injury
Hemolysis
Which of the following action describes the MAJOR property of antidiuretic hormone?
Acts on proximal tubules.
Changes distal tubule water permeability
Acts on Na/K/(H') pump
Cannot be affected by diuretics
Changes distal tubule water permeability
Which compound normally contains the majority of the body's total iron?
Hemoglobin
Enzymes
Myoglobin
Cytochromes
Hemoglobin
What is the cause of iron overload in hereditary hemochromatosis?
Absorption of excessive amounts of iron in the small intestine
Ingestion of excessive amounts of iron from diet or supplements
Inability of the body to excrete normal amounts of dietary iron
Failure of developing red blood cells to incorporate iron into protoporphyrin IX
Absorption of excessive amounts of iron in the small intestine
Toxic levels of lithium can cause lethargy, apathy, muscle weakness up to and including seizures and coma. What is the toxic level of lithium?
0.5-1.2 mmol/L
1.2-1.5 mmol/L
1.5-2 mmol/L
>2 mmol/L
1.5-2 mmol/L
The accuracy of an immunoassay is its ability to discriminate between results that are true positive and results that are true negative. Two parameters of test accuracy are specificity and sensitivity. Which of these statements apply to an immunoassay with high specificity?
Accurately identifies the presence of disease
Accurately identifies the absence of disease
Has many false-positives
Has few false-negatives
Accurately identifies the absence of disease
High levels of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) are associated with:
Decreased cardiovascular risk
Increased cardiovascular risk
Increased renal failure risk
Increased liver failure risk
Increased cardiovascular risk
Which one of the following statements about lead poisoning is false?
While lead distributes to all tissues, the central nervous system, kidney, and bone marrow are particularly susceptible to lead toxicity
Whole blood lead measurement is the best test for detecting lead toxicity
Serum lead level is a good inexpensive screening test for lead toxicity
Lead levels below 5 pg/dL in children do not prompt ongoing monitoring
Serum lead level is a good inexpensive screening test for lead toxicity
An electrophoretic separation of lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme that demonstrates elevation in LD-I greater than LD-2 could be indicative of:
A normal LD isoenzyme pattern
Hemolysis
Pancreatitis
Hepatic injury
Hemolysis
Approximately how many doses are required to obtain a steady-state oscillation allowing for peak and trough levels to be evaluated?
1 to 2
3 to 4
5 to 7
>10
5 to 7
All of the following carbohydrates are considered reducing sugars EXCEPT:
Lactose
Sucrose
Glucose
Ribose
Sucrose
Which marker is most useful for the detection of gestational trophoblastic disease?
CEA (Carcinoembryonic antigen)
AFP (a-fetoprotein)
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
CA-125 (cancer antigen 125)
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
Which of the following tests require a 72-hour stool (fecal) collection?
Occult blood
Quantitative fecal fat
Ova and Parasite (O&P)
Stool culture
Quantitative fecal fat
A hepatic function panel A consists of which of the following tests?
AST, ALT, Alkaline Phosphatase, Total Protein, Albumin, Total Bilirubin, Direct Bilirubin
Glucose, BUN, Creatinine, Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, C02, Calcium
Cholesterol, Lipoprotein, HDL, Triglycerides
Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, C02
AST, ALT, Alkaline Phosphatase, Total Protein, Albumin, Total Bilirubin, Direct Bilirubin
Which of the following analytes would be decreased due to delay in centrifugation?
Ionized Calcium
Potassium
ALT
AST
Ionized Calcium
Which of the following tests confirms the presence of Bence-Jones proteinuria:
Protein electrophoresis
Sulfosalicylic acid precipitation
Cryoprecipitation
Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis
In a normal CSF the protein concentration as compared to that in the plasma is generally:
Less than 50%
Less than 30%
Less than 10%
Less than 1%
Less than 1%
To assess drug concentrations during the trough phase:
Blood should be drawn about one hour after the administration of an oral dose of the drug.
Blood should be drawn about half an hour before the next dose is given.
Blood should be drawn about two hours after the administration of an oral dose of the drug.
Blood should be drawn immediately before the next dose is given.
Blood should be drawn immediately before the next dose is given.
Which of the following blood tests is used in the determination of prostate cancer?
Acid phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT or SGPT)
Creatinine
Acid phosphatase
The measurement of sodium and chloride in the sweat is the most useful test for the diagnosis of what condition/disease?
Steatorrhea
Direct determination of the exocrine secretory capacity of the pancreas.
Cystic fibrosis
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Cystic fibrosis
All of the following are causes of hypernatremia EXCEPT:
Excess water loss
Low aldosterone production
Decreased water intake
Increased sodium intake or retention
Low aldosterone production
What is a typical finding for determining the endpoint for the initial or iron-depletion phase of treatment for hereditary hemochromatosis (HH)?
The serum ferritin decreases to between 20 and 50 ng/mL
The hepatic iron index returns to normal
The transferrin saturation drops below 20%
The serum iron falls to below 35 ug/dL.
The serum ferritin decreases to between 20 and 50 ng/mL
Which of the following conditions would be suggested by a jaundiced patient experiencing a marked rise in alkaline phosphatase (ALP), conjugated bilirubin, and a slight rise in alanine aminotransferase (ALT)?
Cardiovascular disease
Hepatitis
Post-hepatic cholestasis
Renal failure
Post-hepatic cholestasis
All of the following hormones stimulate gluconeogenesis, the formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources such as amino acids, glycerol, and fatty acids, EXCEPT?
Insulin
Thyroxine (T 4)
Cortisol
Glucagon
Insulin
Which cardiac biomarker is a regulator of myocyte contraction?
Myoglobin
cTnT
CK-MB
CK-MB isoforms
cTnT
All of the following conditions would be associated with an increased level of alpha-fetoprotein, EXCEPT?
Prostate Cancer
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Viral Hepatitis
Testicular Tumors
Prostate Cancer
Which one of the following cardiac biomarkers could detect a recent reinfarction?
Troponin I (Tnl)
Troponin T (TnT)
Lactate dehydrogenase (LD)
Creatine kinase MB (CK-MB)
Creatine kinase MB (CK-MB)
After complaining to her physician about persistent pelvic pain and abdominal pressure, Mrs. Smith, had laboratory testing ordered. Since her physician would like to rule-out ovarian cancer, which of the following assays would be most helpful?
CEA
CA125
CA19-9
PSA
CA125
The immunoassay procedure for serum hCG utilizes antisera against which subunit of hCG?
Alpha
Gamma
Epsilon
Beta
Beta
All of the following hormones increase or decrease plasma glucose concentration by regulating glycogenolysis (converting glycogen to glucose) EXCEPT?
Cortisol
Glucagon
Epinephrine
Insulin
Cortisol
Circulating organic iodine is found primarily in the form of:
Triiodothyronine
Parathyroid hormone
Thyroglobulin
Thyroxine
Thyroxine
A male patient's urea nitrogen value is 15 mg/dL and his creatinine is 5 mg/dL. If this patient is not undergoing dialysis, what conclusion would you draw from these results?
The Patient’s lab results are normal
The patient is in the early stage of renal disease
One of the values is in error
The patient has suffered muscle deterioration
One of the values is in error
Which of the following blood tests is used to evaluate liver function?
Amylase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Creatinine
Uric acid
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Creatinine excretion correlates best with which of the following parameters:
Age
Sex
Muscle mass
Bodyweight
Muscle Mass
Currently the MOST common method for the confirmation of serum barbiturates is:
Immunoassay
Thin-layer chromatography
Gas-liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry
Ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy
Gas-liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry
Which of the following contributes most to serum osmolality:
Magnesium
Albumin
Potassium
Sodium
Sodium
If CSF tubes numbered #1 , #2 and #3 CANNOT be analyzed within one hour, the correct procedure for the microbiology sample tube is to:
Refrigerate it
Freeze it
Leave it at room temperature
Incubate in a 56-degree water bath
Leave it at room temperature
Which one of the following serum constituents is increased following strenuous exercise?
Creatinine
Total lipids
Sodium
Iron
Creatinine
Which of the following statements is TRUE with respect to uncompensated metabolic alkalosis?
pH will be elevated without an elevation of pC02
pH will be elevated with an elevation of pC02
pH will be elevated with a decrease in pC02
pH will be normal with an elevation of pC02
pH will be elevated without an elevation of pC02
Fluorometers are designed so that the path of the excitation light is at a right angle to the path of the emitted light. What is the purpose of this design?
Prevent the loss of emitted light
Prevent the loss of the excitation light
Focus emitted and excitation light upon the detector
Prevent incident light from striking the detector
Prevent incident light from striking the detector
All of the following anticoagulants will produce a significant effect on calcium levels in plasma, EXCEPT?
EDTA
Heparin
Oxalates
Citrates
Heparin
A hospitalized patient has a decreased serum copper level and increased urine copper level. This is MOST consistent with:
Wilson's disease
Addison's disease
Parathyroid disease
Not clinically significant
Wilson's disease
All of the following are therapeutic drugs used to treat cardiac disease, EXCEPT?
Carbamazepine
Digoxin
Procainamide
Quinidine
Carbamazepine
A characteristic of a good cardiac biomarker is that:
=
It can be detected only if it is present in a HIGH concentration in the peripheral blood.
It can be detected even if it is present in a LOW concentration in the peripheral blood.
It can be detected only if it is present in a HIGH concentration in urine.
It can be detected even if it is present in a LOW concentration in urine.
It can be detected even if it is present in a LOW concentration in the peripheral blood.
Elevation in conjugated bilirubin is most likely to be found in which of the following conditions?
Transfusion reactions
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Crigler-Najar syndrome
Biliary obstruction
Biliary obstruction
Ionized calcium is currently most commonly measured using which of the following method?
Flame photometry
Color complex formation between calcium and o-cresolphthalein
Atomic absorption
Calcium ion selective electrodes
Calcium ion selective electrodes
Pernicious anemia refers to cobalamin deficiency that results from a lack of which of the following?
Vitamin B12
Intrinsic Factor
Folate
Vitamin C
Intrinsic Factor
A Renal Function Panel consists of which of the following tests?
AST, ALT, Alkaline Phosphatase, Total Protein, Albumin, Total Bilirubin, Direct Bilirubin
Cholesterol, Lipoprotein, HDL, Triglycerides
Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, C02
Glucose, BUN, Creatinine, Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, C02, Calcium, Albumin, Phosphorus
Glucose, BUN, Creatinine, Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, C02, Calcium, Albumin, Phosphorus
Which of the following is the principle for the biuret method for total protein analysis?
Digestion of protein; measurement of nitrogen content
Formation of violet-colored chelate between Cu2+ ions and peptide bonds
Globulins are precipitated in high salt concentrations
Proteins separated based on electric charge
Formation of violet-colored chelate between Cu2+ ions and peptide bonds
Methotrexate is a highly toxic medication that blocks DNA synthesis in all cells. What medication needs to be administered after methotrexate to prevent cytotoxic effects in normal cells of the body?
Theophylline
Leucovorin
Digoxin
Vancomycin
Leucovorin
A 46-year old known alcoholic with liver damage is brought to the ER unconscious. One would expect lipid values to be affected in what way?
Increased
Decreased
Normal
Unaffected by the alcoholism
Increased
Which of the following parameters, according to the American Heart Association (AHA), is not included in the diagnosis of the presence of metabolic syndrome in adults?
An elevated waist circumference.
An elevated triglyceride level.
An elevated fasting glucose
An elevated high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
An elevated high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
Which analyte shows no difference between capillary and venous values?
Glucose
Phosphorus
Bilirubin
Calcium
Phosphorus
Which of the following analytes would be increased due to delay in centrifugation?
Glucose
Ionized Calcium
Potassium
Bicarbonate
Potassium
An osmometer can use any of the following principles EXCEPT:
Freezing point depression
Vapor pressure
Electrostatic charge
Freezing point depression and vapor pressure
Electrostatic charge
Aspirin ingestion prevents the synthesis of this signaling molecule in the platelet?
Thromboxane A2
Calcium
Collagen
ADP
Thromboxane A2
Which of the following analytes would be increased due to delay in centrifugation?
AST
Folate
Glucose
Ionized Calcium
AST
Which type of lipoprotein is the least dense?
Chylomicrons
VLDL
LDL
HDL
Chylomicrons
GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase) is an enzyme found in many body tissues including the kidney, prostate, brain, pancreas, and liver, however, its clinical applications is confined to the evaluation of what system?
Pancreas
Liver
Kidney
Brain
Liver
What is the term used to describe chest pain caused by inadequate supply of oxygen to heart myocardium?
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
Angina
Congestive heart failure (CHF)
Myocardial ischemia
Angina
The measurement of sodium and chloride in the sweat is the most useful test for the diagnosis of what condition/disease?
Steatorrhea
Direct determination of the exocrine secretory capacity of the pancreas.
Cystic fibrosis
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Cystic fibrosis
Which of the following drugs is listed as an anti-convulsants?
Lithium
Gentamicin
Tacrolimus
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital
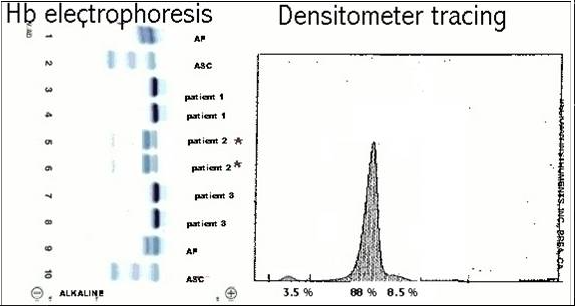
The hemoglobin electrophoresis pattern for patient #2 shows an increase in Hb F and a decrease in both Hb A and Hb A2. These results correlate best with which of these thalassemias?
Beta thalassemia minor
Beta thalassemia major
Delta-beta thalassemia minor
Alpha thalassemia major
Delta-beta thalassemia minor
Which of the following conditions would argue in favor of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) for a given drug?
The drug has a low degree of protein binding.
The drug is given chronically.
The drug has low toxicity and few side effects.
The effective and toxic concentrations are not well defined.
The drug is given chronically.
Which of the following enzymes is associated with conditions affecting skeletal muscles?
Aldolase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Gamma-glutamyltransferase
5'-nucleotidase
Aldolase
An electrophoretic separation of lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme that demonstrates elevation in LD-I greater than LD-2 could be indicative of:
A normal LD isoenzyme pattern
Hemolysis
Pancreatitis
Hepatic injury
Hemolysis
What is the cause of iron overload in hereditary hemochromatosis?
Absorption of excessive amounts of iron in the small intestine
Ingestion of excessive amounts of iron from diet or supplements
Inability of the body to excrete normal amounts of dietary iron
Failure of developing red blood cells to incorporate iron into protoporphyrin IX
Absorption of excessive amounts of iron in the small intestine
Which of the following blood tests is used to determine acute pancreatitis?
Acid phosphatase
Uric acid
Amylase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Amylase
All of the following conditions would be associated with an increased level of alpha-fetoprotein, EXCEPT?
Prostate Cancer
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Viral Hepatitis
Testicular Tumors
Prostate Cancer