Chronic Inflammation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
When does chronic inflammation occur
Acute inflammation fails to eliminate the stimulus
After multiple episodes of acute inflammation
Secondary to unique biochemical characteristics including virulence factors of the stimulus
Mechanisms of chronic inflammation
persistence/resistence or unresponsiveness
Isolation in tissue
Autoimmunity
Idiopathic
Characteristics of chronic inflammation
Walled off exudate-abscess
Walled off stimulus within granuloma/pyogranuloma
Fibrosis
Prescence of certain leukocytes
Lymphocytes in chronic inflammation causes what
A swelling or mass effect
Th 1 lymphocytes play a role in what?
Foreign body reactions and immune responses to endogenous antigens as well as intracellular pathogens
Part of cell-mediated adaptive immune response
Classic pathway-proinflammatory, anti-tumoral, tissue injury
Th2 lymphocytes are seen with what?
Chronic allergic reactions—> mast cells, eosinophils
Part of humoral adaptive immune response
Play a role in extracellular parasites
Alternative Pathway
What is the star player of chronic inflammation?
What does it do?
Macrophages
Bridges innate and adaptive immune response as an APC and key role in tissue repair
Role of eosinophils in chronic inflammation
accompanied by granulomatous inflammation that infiltrate in dense sheets, grossly forming plaques, and wrap around collagen causing degeneration
When do abscesses form?
When acute inflammation fails to eliminate stimulus
What is an abscess
a collection of neutrophils mixed with cell debris and a fibrous capsule that eventually walls off infection and requires lancing
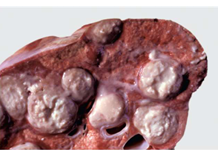
What type of cell predominates with granulomatous
Macrophages
Factors determining granulomatous inflammation ensues
Inciting agent
Host immune response
Interplay of inflammatory mediators
uncommon idiopathic forms
nodular/tuberculoid granulomatous are arranged how
in discrete nodules/masses ± necrotic center
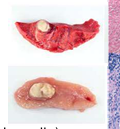
Diffuse/lepromatous granulomatous have macrophages arranged how
in discrete sheets, poorly demarcated and widespread distribution
Ex: Paratuberculosis
Johne’s disease
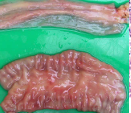
Pyogranulonatous are a collection of what
neutrophils and macrophages
Lymphoplasmacytic includes
thick Sheets or nodules of lymphocytes and plasma cells that are seen in inflammatory bowel disease in cats/dogs
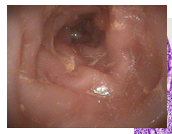
What is classic example of neoplastic transformation
injection site sarcomas in cats
What is sclerosis
a specific type of fibrosis in which tissue is replaced by firm fibrous connective tissue after injury or inflammation
What is rodent ulcer
oral plaque on upper lip around philtrum causing swelling of region with variable ulceration
