Radioactive decay and stability
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Knowledge and terms for radioactive decay spec 3.8.1.3 AQA A-level physics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What does the inverse-square law demonstrate?
Radiation spreads out uniformly as a sphere. When an EM wave spreads out, the area over which it spreads is (inversely) proportional to the radius squared.
What is λ?
The decay constant, the probability of a nucleus decaying per unit time.
Definition of the half-life?
The time taken for the number of particles/activity in a source to halve.
How to determine half-life from a nuclei-time graph?
Measure time taken for sample size to halve. Do this across several half-lives and find a mean.
How to determine half-life no with nuclei-time graph?
Plot ln (N) against time. This forms a straight line. Modulus of the gradient is the decay constant. Substitute into half-life formula.
When can the decay constant be used to model the decay of nuclei? Why?
When there is a large number of nuclei in the sample, because the decay constant models the number of nuclei statistically; decay is a random process.
Applications of nuclei with short half-life.
Radioactive tracers in medical diagnosis. Needs to be long enough for tests, but short enough to reduce exposure to the healthy tissue of a patient.
Applications of nuclei with long half-life.
Dating of objects; carbon-dating for organic objects. Achieved by measuring the current amount of carbon-14 and comparing it to the initial amount, the percentage of which is approximately equal in all living things.
Prove the modulus of the gradient of a ln(N0) - time graph is the decay constant.
??
What is I in the inverse square law?
Intensity of the gamma radiation, Wm-2
What is k in the inverse square law?
Constant of proportionality.
What is x in the inverse square law?
distance from the source, m
Equation for radiation at two different points.
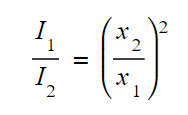
What makes some nuclei unstable?
The larger nuclei are more unstable. Attractive range of strong nuclear force is 0.5fm-3fm so for nuclei large than this, the electrostatic force of repulsion is greater than the strong nuclear force holding nucleons together.
What type of radiation uses inverse square law?
only gamma radiation
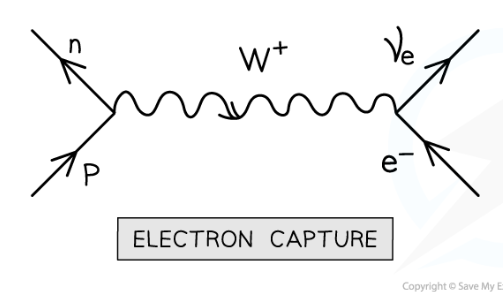
What is electron capture? And equation?
when an atomic electron is absorbed by a proton on the nucleus. A neutron and electron neutrino are released. Mediated by the W+ boson.
p + e- = n + ve
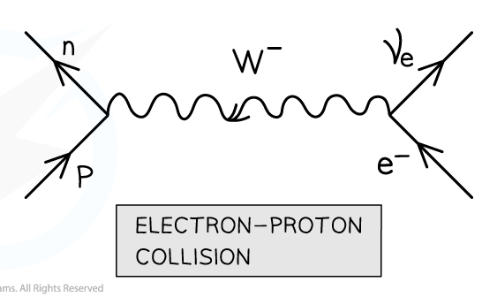
What is electron-proton collision (decay)? And equation?
when an electron collides with a proton, a neutron and an electron neutrino are emitted. Mediated by the W- boson.
p + e- —> n + ve
A (large) nucleus has more neutrons than protons. Explain why there is an imbalance of proton and neutrons numbers.
Strong nuclear force (SNF) affects nucleons or protons and neutrons.
SNF attraction extends up to 3 fm (allow 1–4 fm)
The SNF is repulsive below about 0.8 fm (allow 0.3 to 1 fm and prevents the nucleus totally collapsing)
Electromagnetic/electrostatic repulsive force (only) acts between protons
EM forces are long range/infinite/acts across whole nucleus/acts on all protons(so increases as proton number increases)
More neutrons are needed to hold nucleus together/add to binding force/increase instability/reduce stability
Fewer protons are required so as to reduce the repulsion/reduce instability/increase stability
Which type of radiation is most appropriate for sterilisation of radioactive instruments?
Gamma radiation as it is the only kind of ionising radiation that can penetrate metal/is the most penetrating
Why don’t irradiated surgical instruments become radioactive once sterilised?
Ionising radiation ionises atoms therefore does not affect the nucleus of the atom.
Suggest reasons why results do not follow the inverse square law
source may not be pure emitter (of gamma)
Dead time in a G-M detector
the source is not a point source
The random nature of radiation count
What is dead time in a G-M detector
the minimum time interval interval after an ionising event during which the detector is insensitive to further radiation and unable to register another count.