4.12 alkanes 4.13 alkenes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
How do induces dipole-dipoles interactions form?
there are 2 xenon atoms, their electrons are moving constantly
at any one instant the electron cloud may be distributed unequally, this causes partially charges of delta+ and delta- to develop, instantaneous dipole forms
the instantaneous dipole on one atom induces a dipole on a neighbouring atom
there is electrostatic force of attraction between the delta- on one atom and delta+ on the other atom, these are induced dipole dipole attractions, they are present but are weak
why does butane have higher bp than methyl propane even though they have identical relative formula mass?
methylpropane molecules cannot fit together as closely as butane molecules
they have fewer points of surface contact
so they have weaker london forces
what is the equation for complete combustion using propane?
C3H8 + 5O2 = 3CO2 +H2O
what are the produces of complete combustion of alkanes?
carbon dioxide
water
What is the equation for incomplete combustion using ethane?
2C2H6 + 5O2 = 4CO + 6H2O
what is the products of incomplete combustion of alkanes?
carbon monoxide
water
why is production of carbon monoxide a problem?
binds to haemoglobin in your blood better than oxygen
so less oxygen reaches cells
causes fatigue, headaches and nausea
at high concentrations could become fatal
why do radicals have a dot?
represent unpaired electron
what is homiletic fission usually started by?
ultraviolet light
what are the 3 radical reaction types?
initiation
propagation
termination
what is the definition of initiation?
the first stage of radical reaction in which radicals form when a covalent bond is broken by homolytic fission
what is the formula for initiation?
molecule =uv radical + radical
how many initiation steps takes place?
1
what is the definition of propagation?
the steps that continue a free radical reaction. The radical reacts with another reactant molecule to form a new radical and a new molecule
forms a chain reaction
what is the formula for propagation?
radical + molecule = molecule + radical
how many propagation steps take place?
2
what is the definition of termination?
the steps at the end of a radical reaction where 2 radicals join to form a molecule
what is the formula for termination?
radical + radical = molecule
how many termination steps are there?
3
what are stereoisomers?
compounds with the same structural formula, but different arrangement of atoms in space
when does cis/trans isomerism take place?
when there is a hydrogen and a different group on either side of a double bond
when is it cis isomerism?
hydrogen are on same side
(forms a c shape if you connect)
when is it trans isomerism?
hydrogens are on different sides
what are the cahn-Ingold Prelog rules?
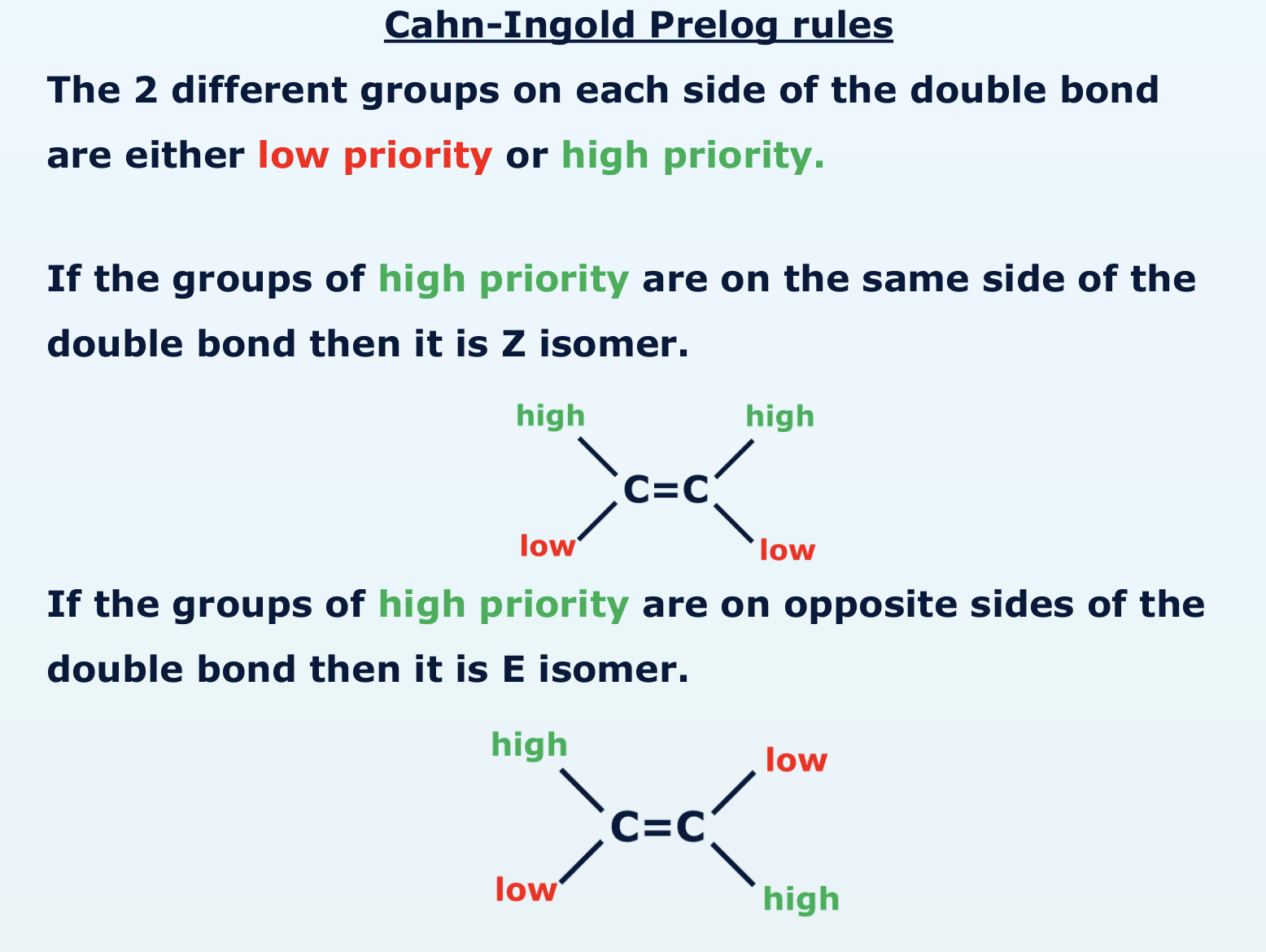
how do you know whether something is high or low priority?
higher the atomic number of the atom attached to the double bond
the higher the priority
(if first atom is carbon on both double bonds, you look at the next atom along)
can cis/trans isomers also be E/Z isomers?
yes
why is E/Z isomerism shown in some alkenes?
double bond doesn’t rotate
each carbon in double bond is attached to two different groups
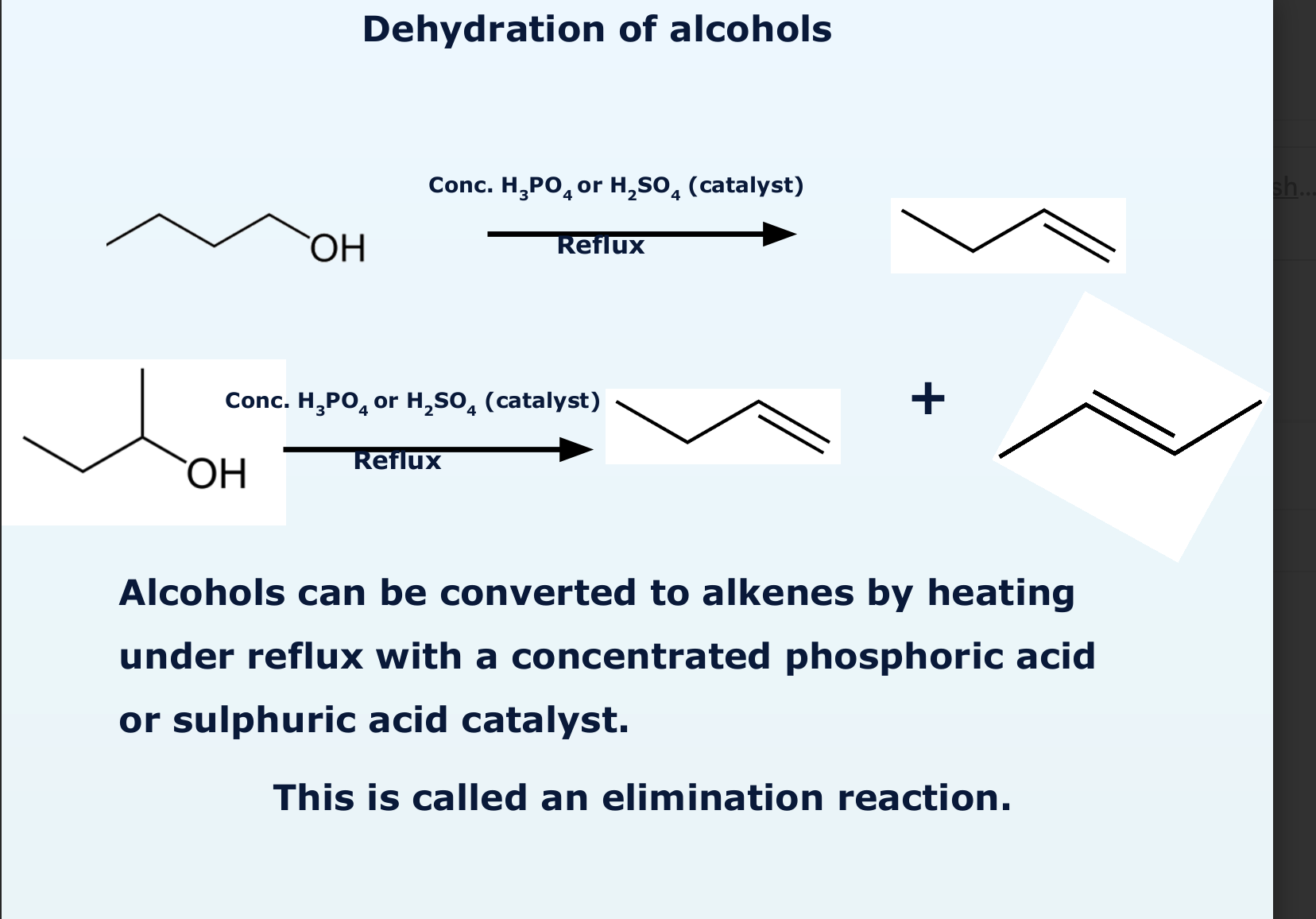
how does dehydration of alcohol take place?
elimination reaction because it makes water as a product
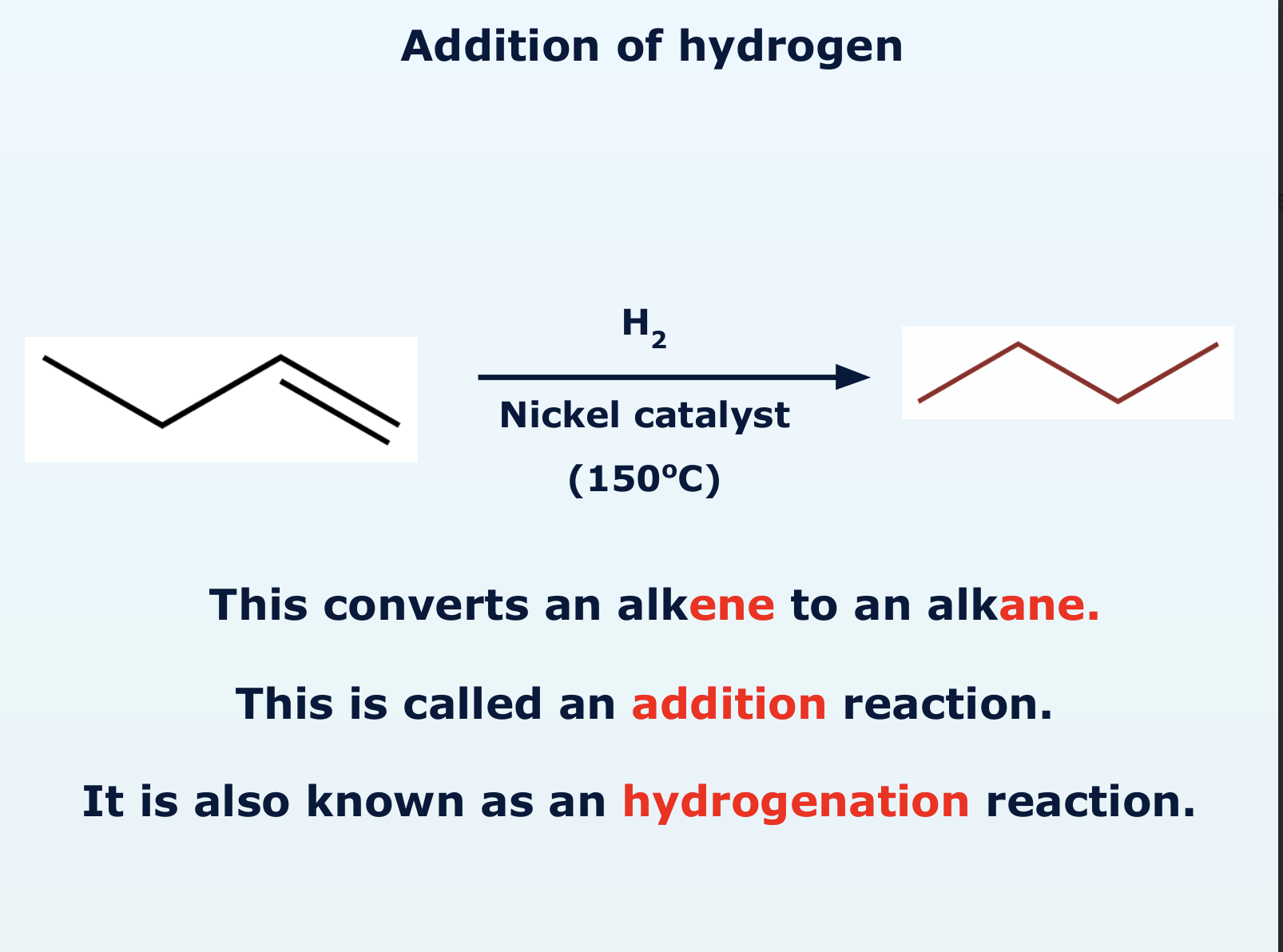
how does addition of hydrogen take place?
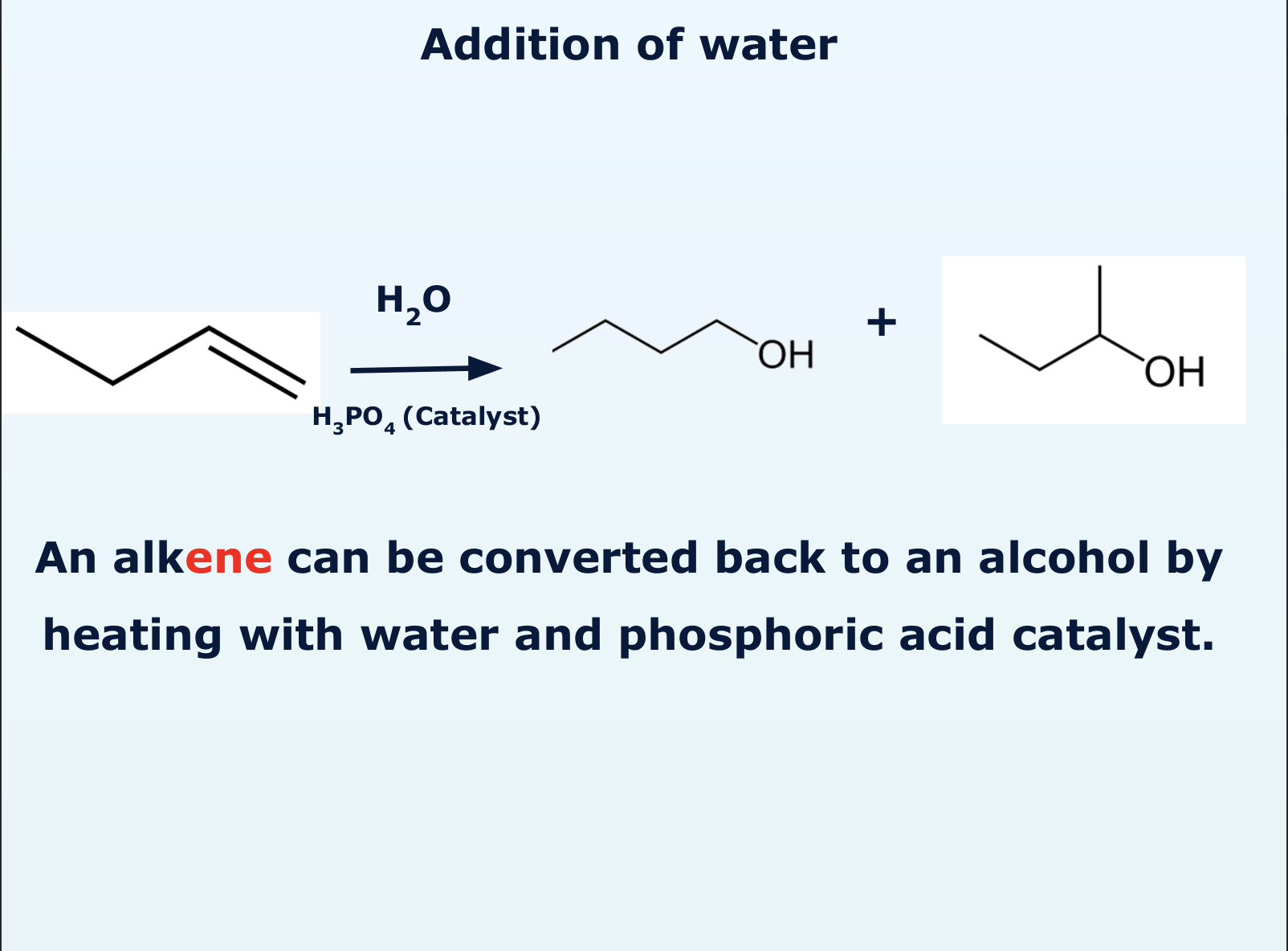
how does addition of water take place?
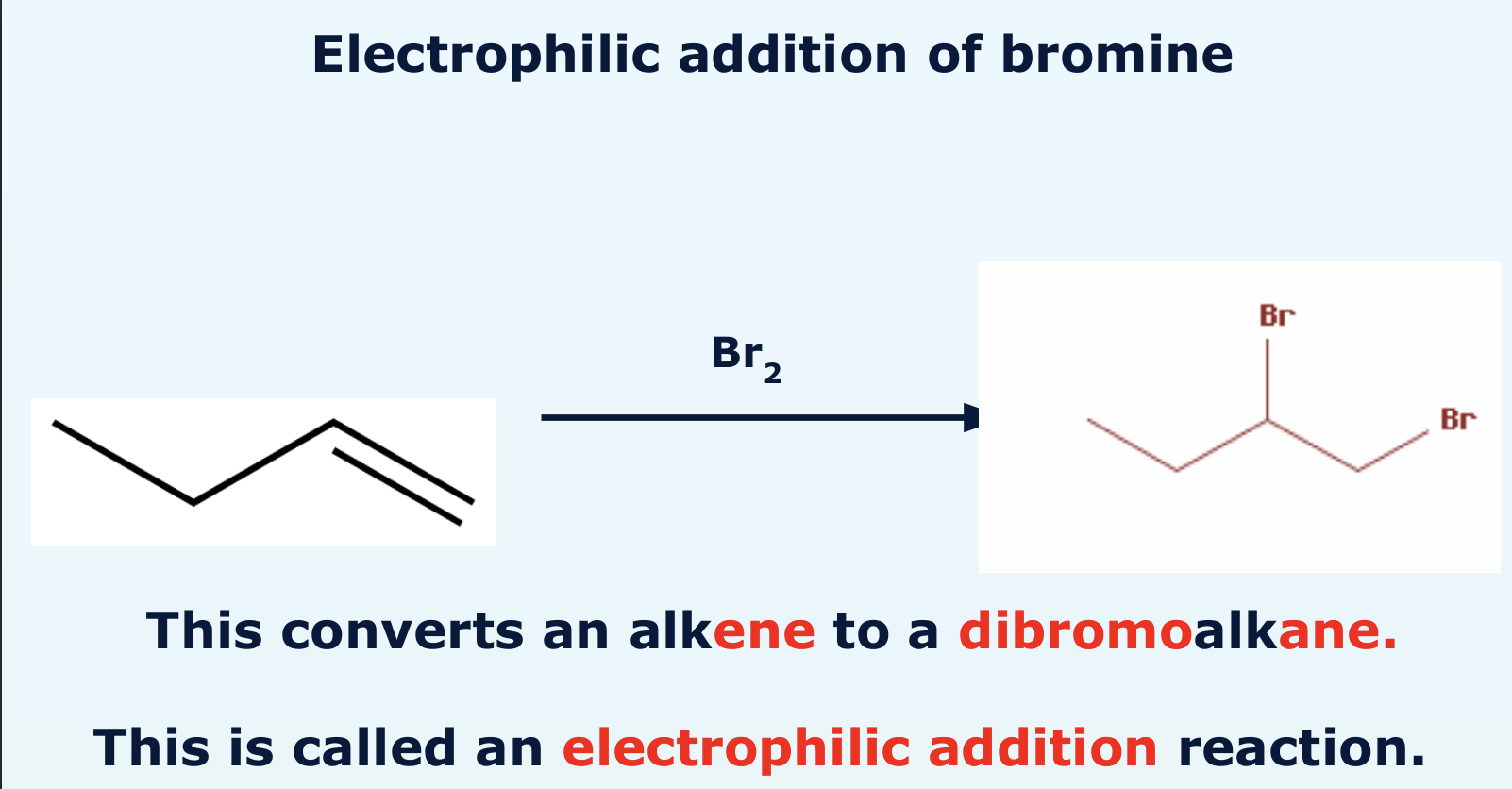
how does electrophile addition of bromine look like in reaction? What does this convert the alkene into?
what is an electrophile?
atom or group of atoms that is attracted to an electron rich centre and accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond
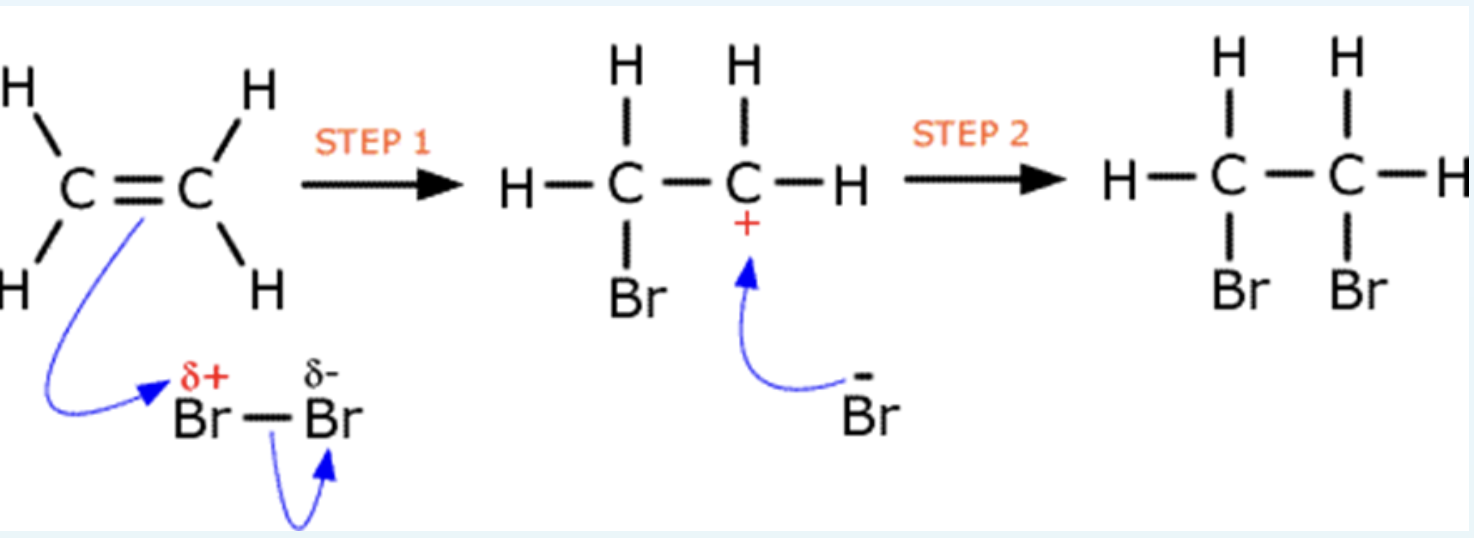
explain how the electrophile addition of bromine to an alkene takes place? with diagram
a bromine molecule approaches a double bond and becomes polarised
one of the bonds break and the electrons move tot he delta positive bromine
the Br-Br bond breaks to form a Br- ion
this forms a type of intermediate called carbocation, these are very reactive and exist for fractions of a second
the Br- acts as a nucleophile and donates its electron pair to the carbocation
how does electrophile addition of hydrogen bromide take place?
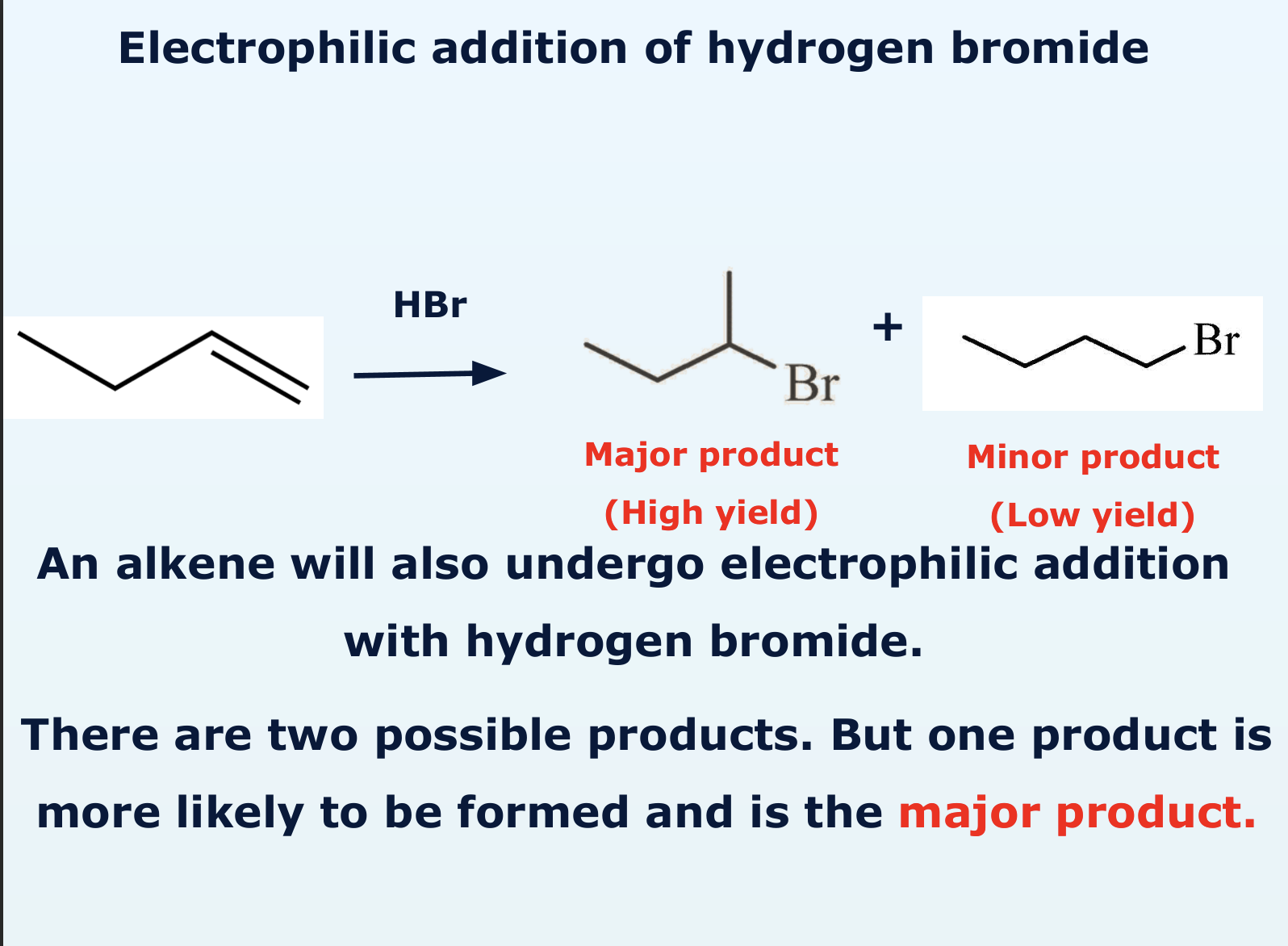
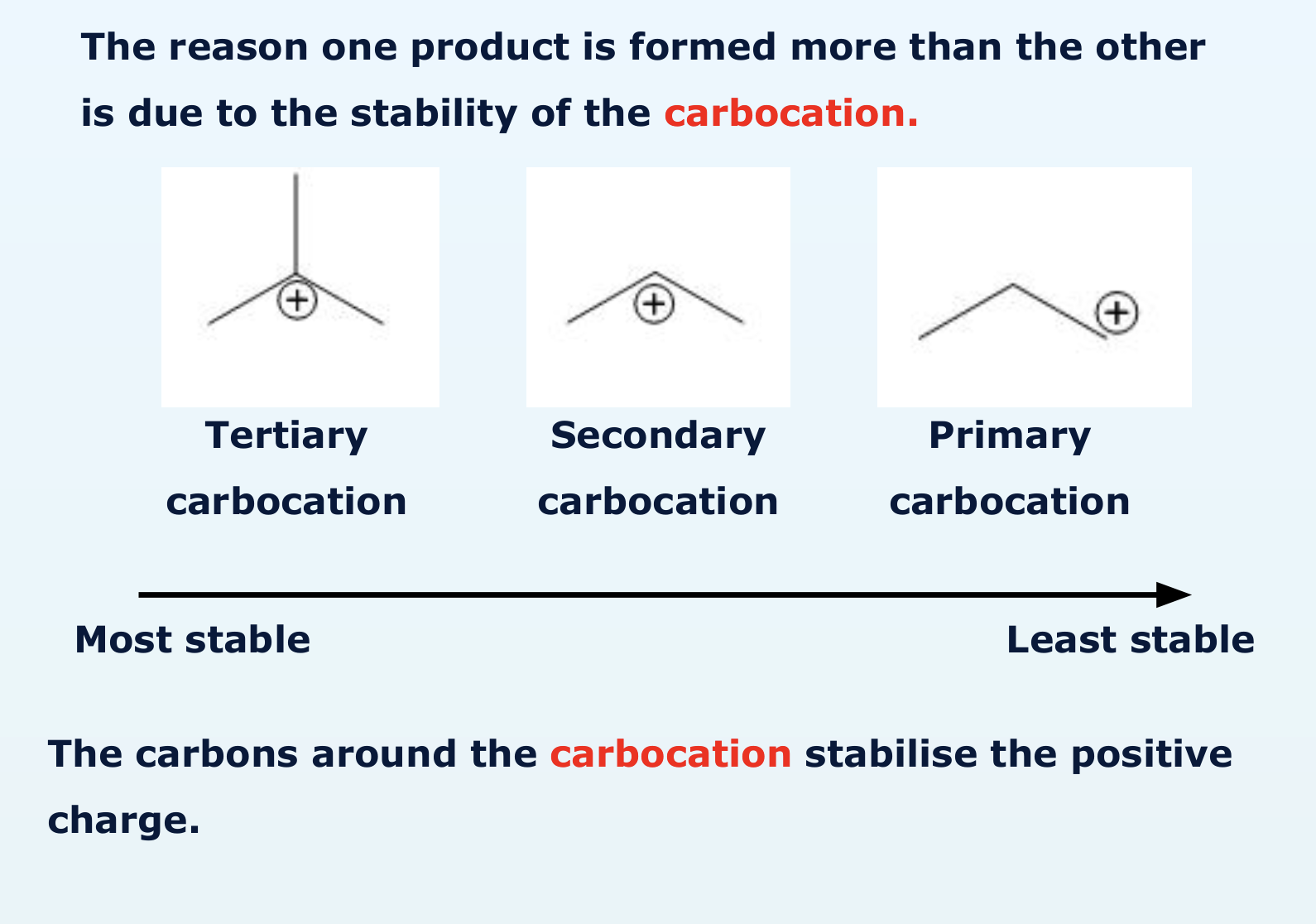
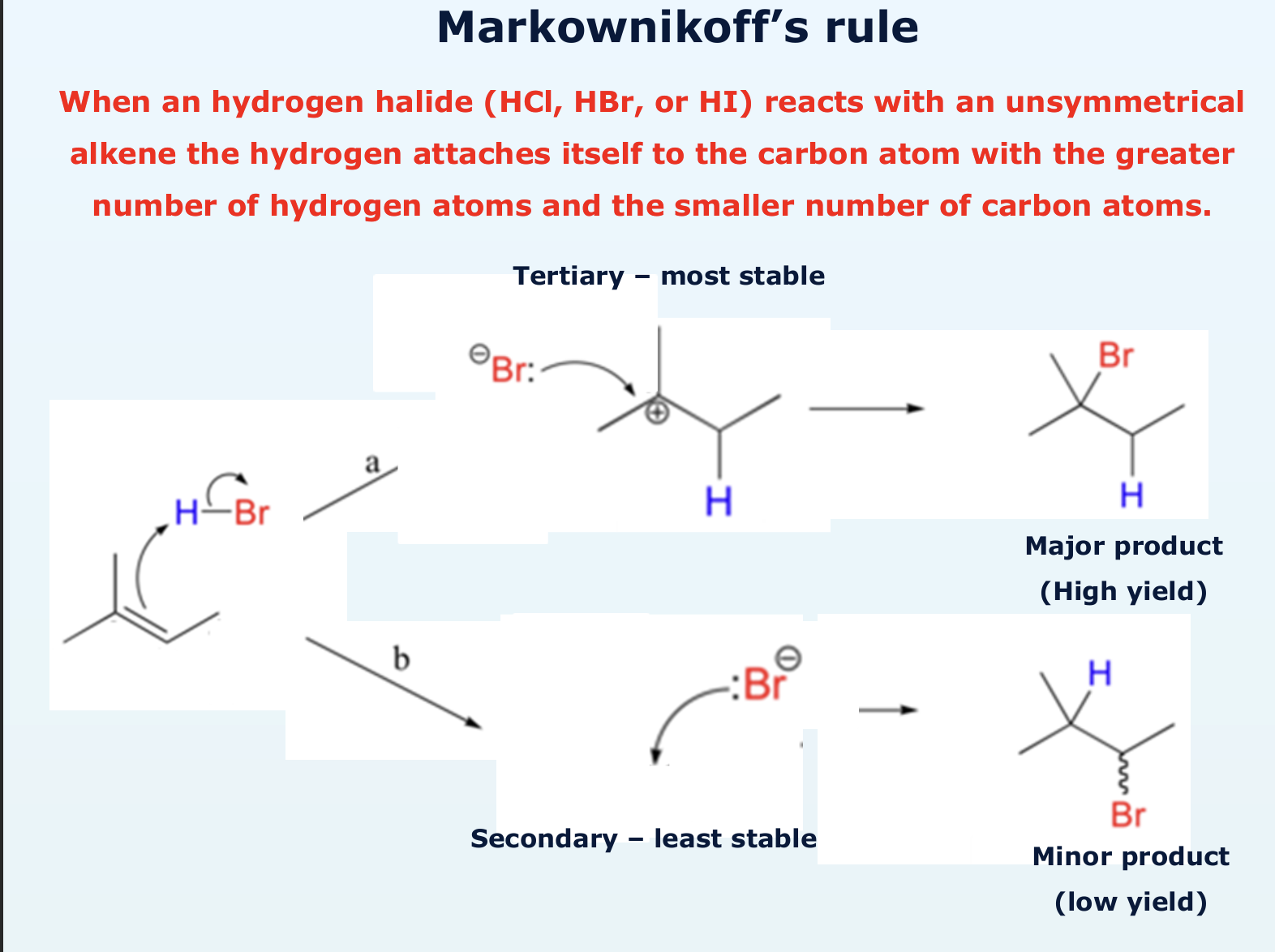
why are there two possible products of the electrophile addition of hydrogen bromide?
is a major product high or low yield?
high yield
is a minor product high or low yield?
low yield
explain what Markownikoff’s rule is
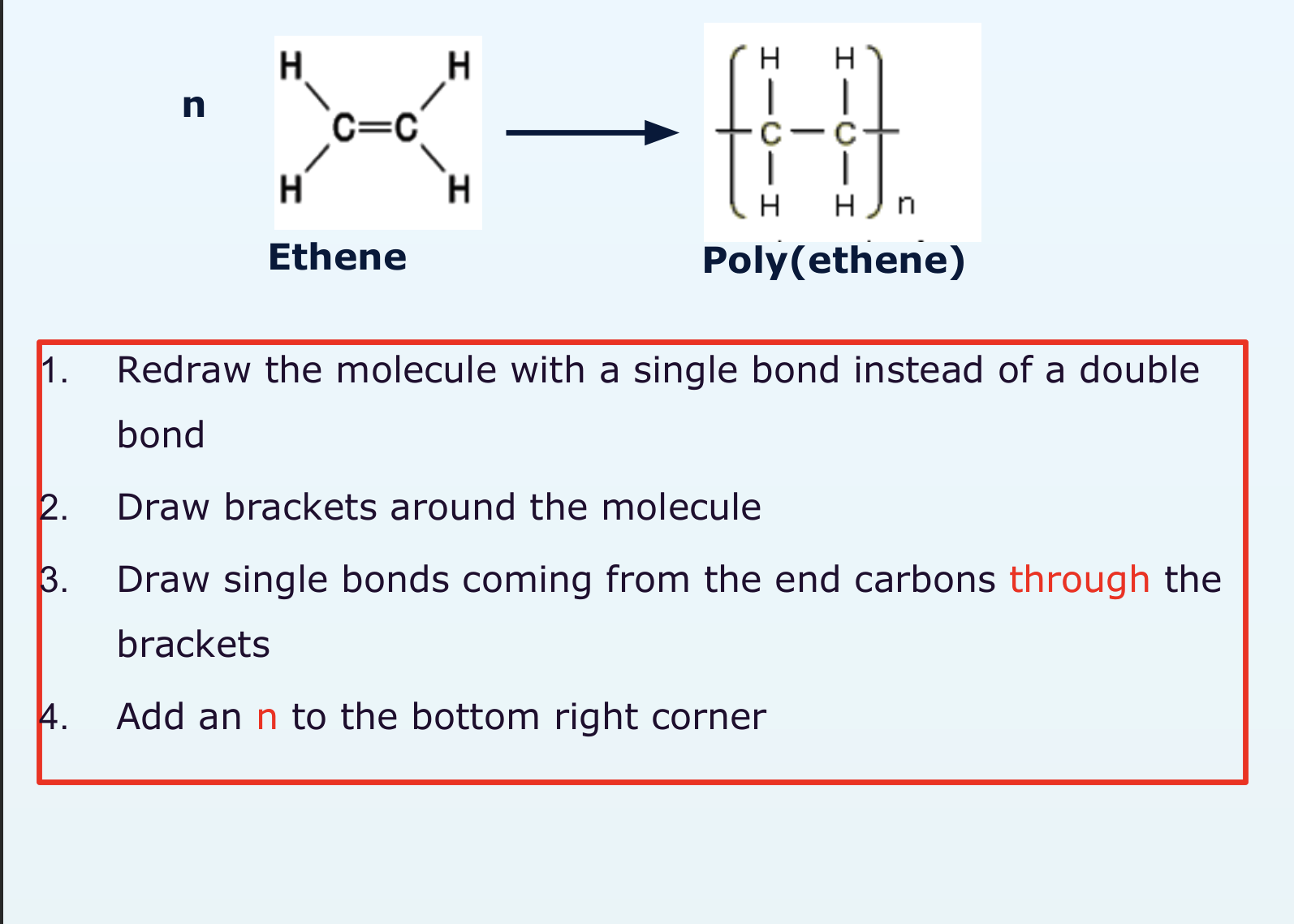
how do you change a monomer to a polymer in an equation?
how does recycling work?
polymers are sorted, then chopped into flakes, washed, dried and then melted into pellets for manufactures to make new products
why does PVC need to be recycled separately?
PVC can’t be recycled normally because high content of chlorine forms hydrogen chloride which is corrosive
how is PVC recycled?
it is dissolved in solvent
then it’s recovered by precipitation
the solvent can be reused
how can you use waste polymers as fuel?
some polymers are derived from petroleum or natural gas so have high stored energy value
so can be incinerated to produce heat, generating steam which turns a turbine to produce electricity
what is feedstock recycling?
chemical or thermal process that reclaims monomers, gases or oil from waste polymers
the products resemble those in crude oil and can be reused without needing to be sorted or washed
what are biodegradable polymers?
these are broke down by microorganisms into water, carbon dioxide and biological compounds
usually made from starch or cellulose or contains additives which change traditional structures of polymers
what are photodegradable polymers?
polymers that contain bonds that are weakened by absorbing light to start the degradation
alternatively, light-absorbing additives are added