Biol2200 Exam 3! YAY!
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Identify adaptations that support aquatic life
-DIVERSE body plans
-Acquiring oxygen in water -Mobility in viscous environments
-Diverse ways to feed
Sponge Traits
-before bilateral symmetry
-porifera
-asymmetric body plans
-sessile as adults
-lack true tissues: have differentiated cells, but no tissue
-no multiple germ layers
-metabolic processes by diffusion
Cnardia Traits
-Jellies/ jellyfish/ coral/ anemones
-radially symmetric
-2 true germ layers with an endoderm and ectoderm
-sac with a gastrovascular cavity (not like a mouth and anus)
What are mollusks defined as?
marine protostomes
3 types of mollusks
gastropods, bivalves, cephalopods
Traits of Gastropods
-(snails, nudibranch/shell-less)
-Can be found on land
-Radula: mouth part that can graze, scrape, and chew, looks like a cheese grater
-Stomach in its foot
-Most have a single spiral shell
-Coelomate with hemocoel Both a coelom and a second body cavity called a hemocoel which holds blood: holds digestive and respiratory organs
Traits of Bivalves
-scallops
-no distinct head (suggests that the ancestor had a head at some point and lost it)
-some have sensory organs
-filter feeders, feed through gills, no radula
-coelomate with hemocoel
Traits of Cephalopods
-squids, octopus, nautili
-gained a number of adaptations
-marine hunters (not just predators)
-well-developed sensory organs
-jet propulsion by water expelled from mantle cavity (pulls water in and squirts it out very fast)
-closed circulatory system (no hemocoel)
What is the significance of having a hemocoel as a primary body cavity?
most mollusks have no blood vessels, so blood must be in direct contact with organs that facilitate nutrient acquisition and gas exchange
All chordates are...
coelomates ( we are chordates )
4 key traits of chordates
Notochord, Pharyngeal clefts and slits, Dorsal Hollow Nerve Chord, Muscular post anal tail
What is a notochord?
- exists in all embryos of chordates, but only some adults
- longitudinal, flexible rod that is derived from mesoderm
-provides skeletal support
exists in animals that lack a spine
What are pharyngeal clefts and slits?
arches along the pharynx that develop into slits
-different fates depending on type of organism:
- invertebrates- suspension feeding, pull water over slits and filter out microparticles
-aquatic vertebrates- gills
-tetrapods- no adults have slits
what is a dorsal hollow nerve chord?
-close to outside of body
-germ layer origin: ectoderm
-hollow tube that develops into CNS (aka brain and spinal column)
what is a muscular post anal tail?
in non-chordates, digestive tract runs the body length: post anal tail ends at the post anal (duh)
-reduced in adult chordates (not in dogs, cats, etc)
Lancelets
One of a group of invertebrate chordates:
-notochord protects dorsal hollow nerve chord
-filter-feed using pharyngeal slits
-most basal, attain all traits into adulthood
tunicates
-larvae reflect chordate characters
-adults become sessile (like sponges)
hagfish and lamprey
-rudimentary vertebrae: no backbone or spine
-retain notochord because rudimentary vertebrae run through back of body
-notochord into adulthood
Cambrian explosion and its effects on evolution of chordates
535 MYA
- rise in o2 levels
- receding glaciers
- appearance of diverse body plans
- emergence of predators: prey now have to defend themselves
evolution of jaws
driver of vertebrate diversification:
-Rapid radiation of jawed fish after jaws appear
-Hypothesis: jaws originated from he skeletal rods that support gill slits
plant traits/ associations
-closest relative are charophytes (green algae)
-photosynthetic
-chloroplast have chlorophyll a and b
-protein rings that synthesize cellulose
-unique flagellated sperm structure
-Unique structure during cell division- phragmoplasts: structure associated with the division of cytoplasm during mitosis
why did plants first move from water to land?
more co2, light, nutrients, habitats, and low competition
challenges of plants on land
-loss of water/ desiccation
-too much sun
-natural disasters
-new pests/predators
adaptations of plants for land
-different groups have different strategies for life on land
-prevention of water loss (waxy cuticle, stomata)
-UV protection
-access nutrients efficiently (Developing relationships to access nutrients)
-protect spore from environment (dispersal)
-protect embryos from environment (tissue barriers)
-change life cycle
flavonoids
UV absorbing compounds that prevent DNA damage in plants
more subtle plant adaptations to land
-protection of embryos from environment
-protection of spores from environment (spore coat protects from dry environment)
-alteration of generations (multicellular DIPLOID and HAPLOID life stages)
when was the first evolutions of land plants?
470 MYA
Bryophytes
liverworts and mosses
-lack vascular tissue (aka limits height)
-no specialized cells to transport water and nutrients
-lacks roots-> less nutrients acquired
characteristics of early non-vascular land plants
-bryophytes
-sperm traveled through water (need a damp environment )
-dispersal by spores
-dominant lifestage is haploid, not diploid (less genetic variation)
when did vascular plants evolve
425 MYA
vascular plants
Xylem
Water-conducting cells
Lignin provide structural support
Phloem
Distributes sugars, amino acids, products synthesized by plan
Roots absorb water, nutrients
Leaves increase photosynthesis
Leaves increase the surface area that plants need to acquire something
seedless vascular plants:
-resources are transported through the vascular system
-increased height due to vascularization
-roots and leaves (leaves increase photosynthesis)
-diploid dominant life stage (more genetic variation)
-mosses and ferns
Xylem
water-conducting cell tissue
-lignin provide structural support
Phloem
-vascular tissue
-distributes sugars, amino acids, and other organic products
-targets specific parts of body
Unlike seedless vascular plants, seed plants have...
-Seeds to protect embryos
-Pollen to protect male gametes
-Spores enclosed in reproductive structures
seeds - dispersal distance
-embryos with food supplies and a protective coat
-disperse long distances and survive in harsh conditions
pollen - genetic diversity
-male gametophyte (structure that makes gametes) is surrounded by pollen wall
-does not require water to travel and fertilize egg
describe the relationship between sperm, seeds, spores, and pollen
all plants have sperm and spores, but not all have seeds
all plants have sperm, but not all have pollen
How do plants disperse before the evolution of seeds and pollen?
plants dispersed via spores, which were carried by wind or water
How does the evolution of seeds and pollen change dispersal?
enabling reproduction without water, increasing survival rates, and facilitating wider distribution through wind and animals
why do seed plants have higher diversity
Speed dispersal more effective than spore dispersal
Pollen increases genetic recombination- genetic diversity
-seed plants are the only pollen plants
angiosperms
flowering plants
-fruits that surround and aid in seed dispersal
-mutualisms with animals (increase fitness)
gymnosperm
a woody, vascular seed plant whose seeds are not enclosed by an ovary or fruit
what is the fleshy part of the fruit
maternal ovary tissue
importance of plants
Provide foundations for ecosystems
Production of biomass, oxygen, nutrient cycling etc.
Important to trophic levels above them (source of food)
Provide structural support
When they die, they decompose and feed new plant material
plant timeline:
-red algae
-chlorophytes
-charophytes
-bryophytes (first land plants - liverwort, moss, hornwort)
-seedless vascular plants
-gymnosperms
-angiosperms
plants as medicine
treat pain (morphine), cancer (taxol), heart disease (digoxin)
plant-plant interactions
plant species have intense competition, allelopathy, and facilitation
plant-animal interactions
pollinators, dispersers, and herbivores
how do mycorrhizae improve plant productivity
-symbiotic relationship between plants and fungi
-fungi increase nutrient uptake
-plants provide fungi with carbs
specifically, mycorrhizae helps plants grow huge
pollination benefits
-movement of pollen by animals increases likelihood of mating: very specific unlike wind dispersal
seed/fruit dispersal benefits
movement of embryos by animals increases range and habitat diversity: improves ability to move to new habitats and provides fertilizer for the plants
herbivory benefits
-plant/animal antagonism
-herbivores have a significant impact on plant fitness
-plants start to produce physical or chemical defenses against herbivory
-some plants develop mutualisms with body guards to stop attacks
As animals moved from aquatic to terrestrial environments, what challenges did they face? (6)
Water loss, gravity, uv light, gas exchange, reproduction, different weather conditions
main animal adaptations to life on land
exoskeletons, gas exchange structures, reproductive strategies
exoskeletons
prevent water loss
-protect from UV rays
-provides structural support
Gas exchange structures
diffusion: simple invertebrates (sponges, jellies) mostly in moist
gills: invertebrates, in water only
reproductive strategy variation with adaptation
shift to internal fertilization: Fertilization used to be just letting sperm go out in the water: this doesn't work on land
general characteristics of arthropods
paired jointed appendages, exoskeleton made of chitin, well-developed sensory organs, coelomates with reduced coelom, open circulatory system, gas exchange in terrestrial arthropods
non-insect arthropods
Spiders and ticks (Chelicerates)
Predators and parasites
6 pairs of appendages (8 legs)
Myriapods (many feet)
Millipedes → 2 pairs legs/segment
Centipedes → 1 pair legs/segment
Crustaceans
Mostly aquatic, except isopods
Isopods are important decomposers
what is the main body cavity of arthropods?
hemocoel
gas exchange in chelicerates
book lungs
-strcture of folded tissues that help with bringing oxygen into body
gas exchange in insects
trachea (tubes) deliver O2 directly to organs
non-insect arthropods
-spiders and ticks
-myriapods (many feet)
-crustaceans
key characteristics of all insects
-6 legs
-flight (most)
-metamorphosis
-sexual reproduction with internal fertilization
-terrestrail habitats
-diverse mouthparts
Metamorphosis
incomplete: larvae resemble adults, smaller, wingless (cockroaches)
complete: larvae distinct in phenotype, diet, habitat from adults (butterfly, moth, beetle)
Some insects have different larval habitats such as...
aquatic: mosquitos and dragonflies
underground: beetles
reproductive strategies
Sexual reproduction is common
Internal fertilization supports reproduction on land
Some insects have asexual reproduction
Diversity of mouthparts:
Butterfly- nectar (tubular flowers)
Cicada- xylem
Bee- nectar (open flowers)
Grasshopper- leaves
ecological impacts of insects (3):
insect pollinators are critical for producing fruits and vegetables ($200 billion)
-pest controllers: predatory and parasitic insects can control herbivores in crops
-decomposers: nutrient cycling
Pests and disease insects:
Voracious herbivores: insect pests can decimate crops, increased resistance to pesticides
Vectors of disease:
mosquitos- malaria, zika, yellow fever,
kissing bugs- chugs disease,
tsetse flies- African sleeping sickness
which of the following arthropod traits played a key role in the transition to life on land?
internal fertilization
3 multiple choice options
what happened after jaws first appeared
rapid radiation of jawed fish
hypothesis of jaws
jaws originated from skeletal rods that supported gill slits
-jaws and rods have similar morphology
-jaws and rods derived from the same embryonic cells
adaptations in sharks
skeleton of cartilage, mineralized teeth, adapted for hunting
adaptations of ray finned fish
most diverse group of vertebrates
-first fully mineralized skeleton
-swim bladder maintains buoyancy (derived from lungs)
lobe finned fish
coelacanth, lungfish
-bones in front fins that resemble wrists
-closest living relatives to tetrapods
tiktaalik
-true transitional species between life in water and on land
-more derived bones in wrist
-presence of a neck
-developed rib cage
-large pelvis but not strongly connected to spine (challenge of gravity on land)
when do marine mammals evolve
after land mammals
when are tetrapods in the fossil record and what groups do they involve?
365 MYA
amphibians, mammals, reptiles
what adaptations did vertebrates need to succeed on land?
-new way to move
-increased skeletal support
-new gas exchange methods
-strategies to prevent water loss
derived traits of tetrapods
-limbs with legs
-head separated from body via neck
-bones of pelvic girdle fused to backbone
-adults lack gills: changes to gas exchange organs
amphibian traits
larvae are aquatic
moist skin facilitates gas exchange (some species lack lungs altogether)
external ferilization in water or moist environments
salamanders
-amphibians
-some entirely aquatic, some terrestrial
-some use cutaneous gas exchange (exchange at skin)
frogs
-aquatic larvae distinct from adults
-toads are not monophyletic
-known for vocalizations, aposematism (defense strategies using signals like vocalization or color)
relative to other species that predate tetrapods, what traits make tiktaalik a transitional species?
BONES IN FINS
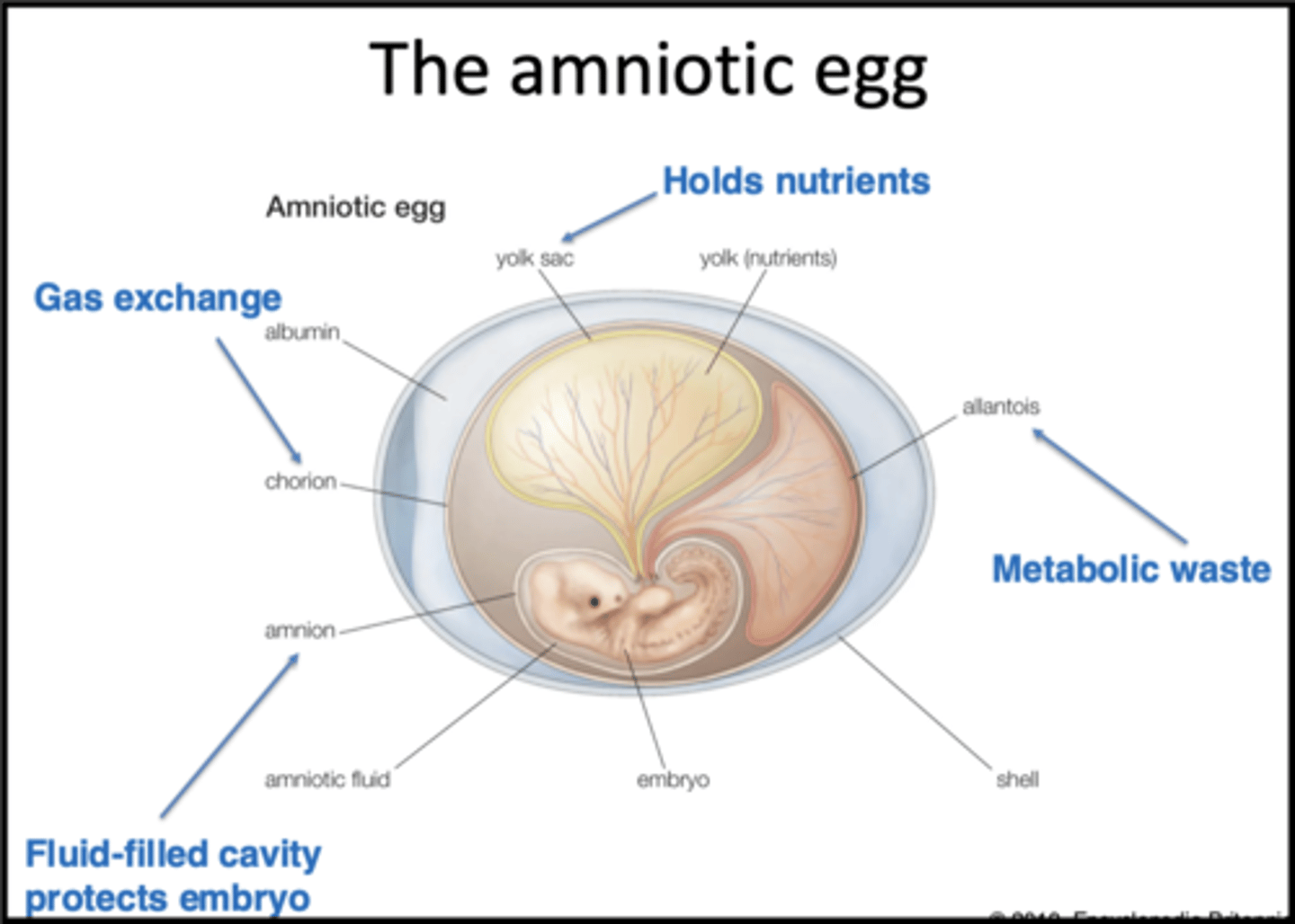
draw the amniotic egg- label the four membranes
Amnion directly protects embryo during development; fluid-filled cavity
Yolk sac holds the yolk (nutrients that have been provided by the parent) so the embryo has what it needs
Allantois: Where we store metabolic waste → where to place toxic compounds away from the body so it doesn’t affect embryo’s development
Chorion is semi-permeable to facilitate gas exchange
3 derived traits of amniotes
-eggs with shells or internal gestation (reduced water loss of developing embryo)
-less permeable skin (reduced water loss of adults)
-rib cage used for ventilation (get more air, efficient gas exchange)
reptile traits
Scales/feathers containing keratin: prevents desiccation
Lay shelled eggs on land- Internal fertilization prior to shell secretion
Vary in temp regulation strategies
Snakes/lizards are ECTOTHERMS
Birds are ENDOTHERMS
lizards
from a few cm to 3+ cm
broad diet reflected in teeth
snakes
lizards -> snakes (loss of legs)
-adapted for hunting (some have venom)
turtles
-shells fused to vertebrae
-terrestrial, freshwater, and marine
mammal derived traits (6 things)
-Mammary glands
-Hair- from keratin
-Fat layer under skin Endotherms
-Larger brains
-Extended parental care
- Diverse teeth
monotremes
platypus, echidna
-lay eggs (external gestation)
-have mammary glands but lack nipples
marsupials
opossums, kangaroos
-simple placenta (not nutrient rich)
-complete embryonic development outside uterus
eutherians
placental mamals
-bears, marine mammals, giraffes
-complete placenta
-development in the uterus
-longer gestation time
derived traits of primates
hands and feet adapted for grasping
-flexible digits
flat nails instead of claws
large brains and short jaws (in comparison with organisms of same size)
eyes look forward- hand eye coordination (predators have forward eyes)
what trait is unique to monkeys and apes
flexible or opposable thumbs Most known trait Grasping more effective with thumbs
hominins
hominids excluding the African apes; all the human species that ever have existed (share a common ancestor with chimps, but did NOT evolve from chimps
hominids
Creatures that walk upright