Animal Biology Lab 11 - Spring 2025
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for Animal Biology Lab.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Subclass Prototheria
A subclass of Mammalia that includes duck-billed platypuses and echidnas; they are oviparous and lack nipples.
Subclass Theria
A subclass of Mammalia that includes all marsupial and placental mammals; they are viviparous.
Infraclass Metatheria
An infraclass of Theria that includes opossums, kangaroos, and koalas; their embryos spend little time developing inside the mother's uterus and mostly develop outside the uterus within a marsupium.
Infraclass Eutheria
An infraclass of Theria that includes rodents, whales, bats, elephants, felids, canids, humans, etc.; developing young are attached to mother by a placenta within the uterus.
Order Lagomorpha
An order of Eutheria that includes rabbits, hares, and pikas; they are herbivorous with long incisors for snipping vegetation, and all permanent teeth grow continuously throughout life.
OrderRodentia
An order of Eutheria that includes mice, rats, squirrels, beavers, porcupines, etc.; their sharp incisors grow continuously throughout life, and it is the largest mammalian order.
Order Carnivora
An order of Eutheria that includes dogs, cats, weasels, bears, raccoons, seals, etc.; most are carnivorous, and heterodont teeth are adapted for killing other animals and consuming flesh.
Order Chiroptera
An order of Eutheria that includes bats; forelimbs are modified into wings, and bats are the only mammals capable of true flight.
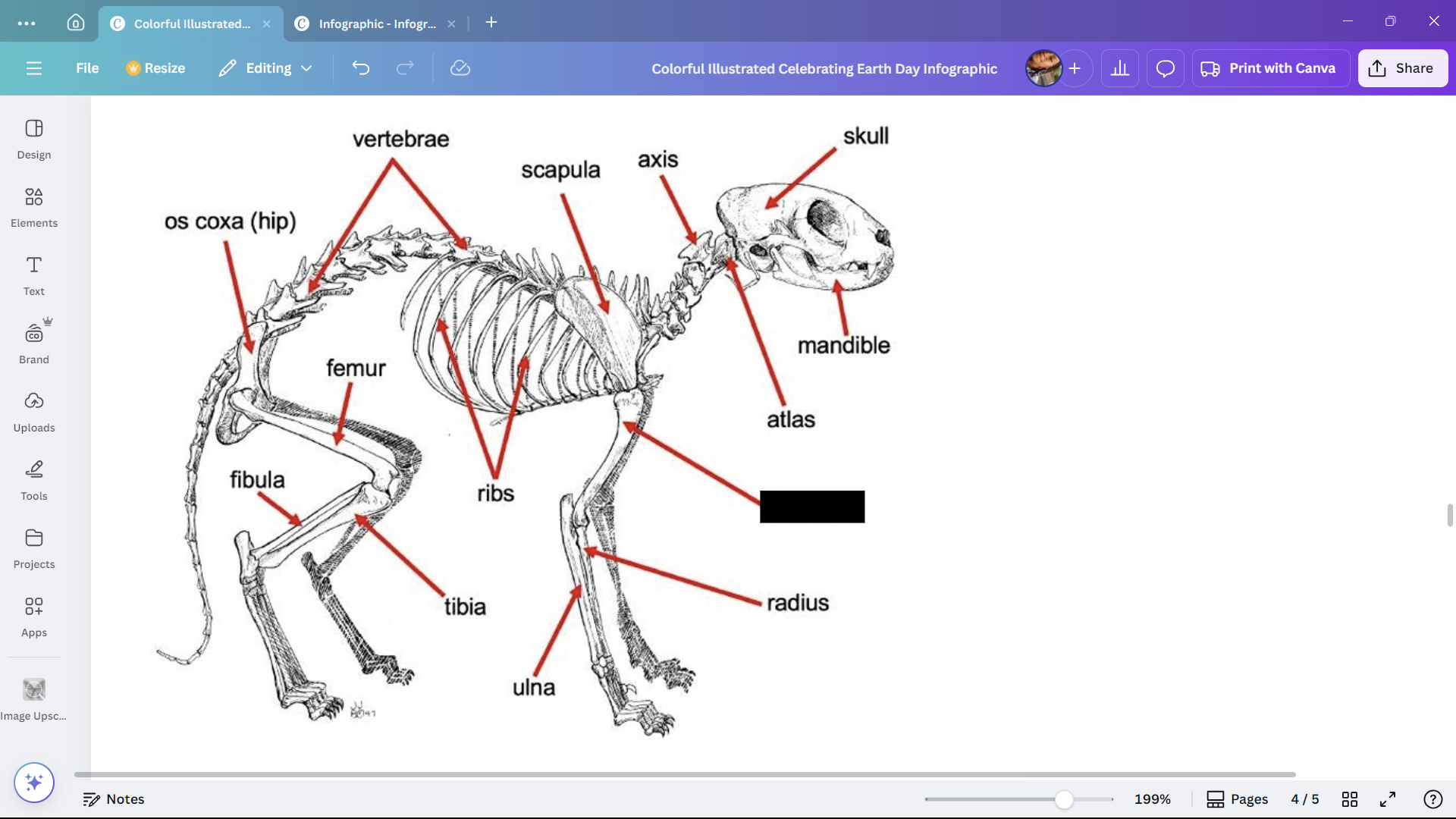
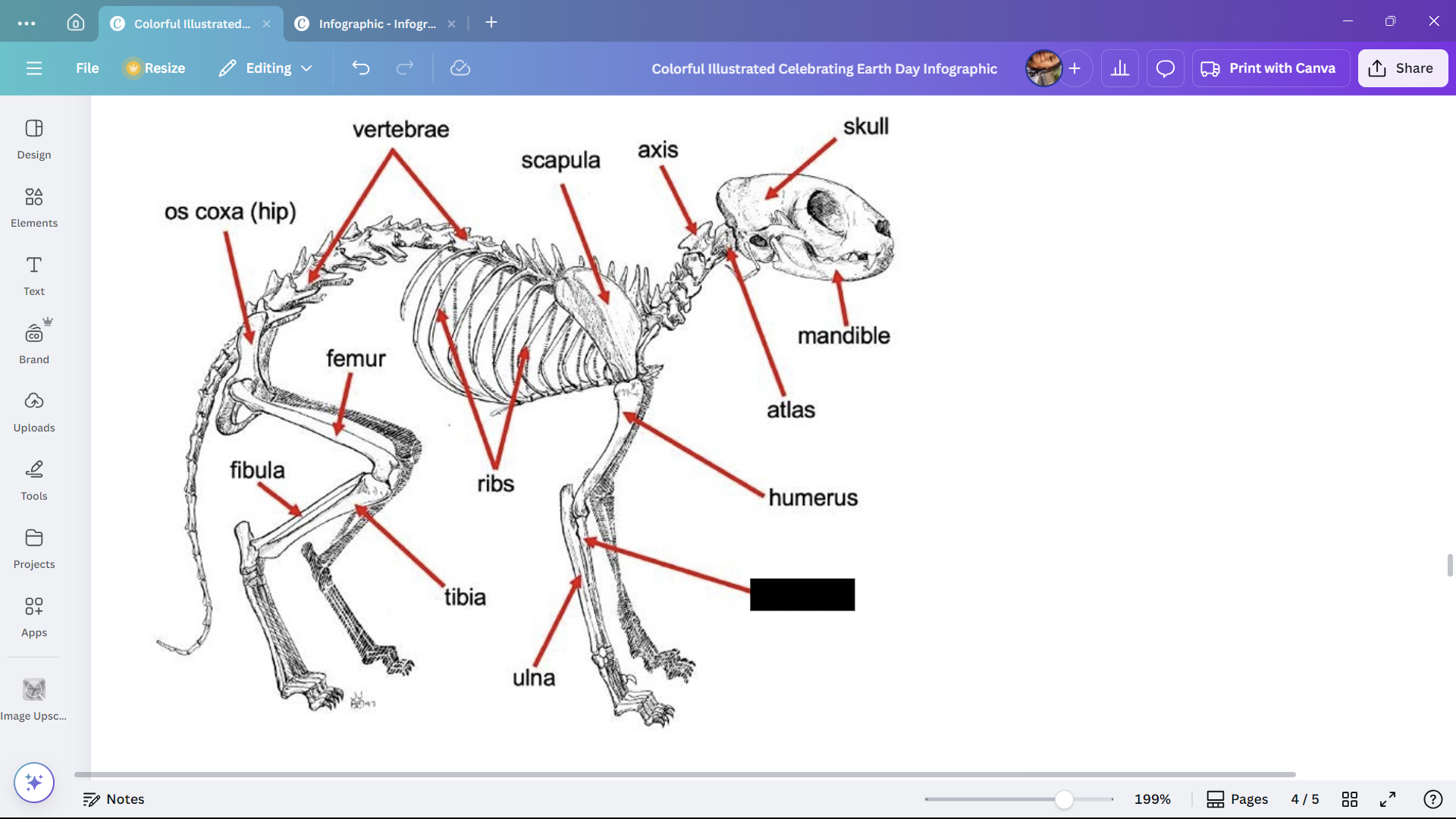
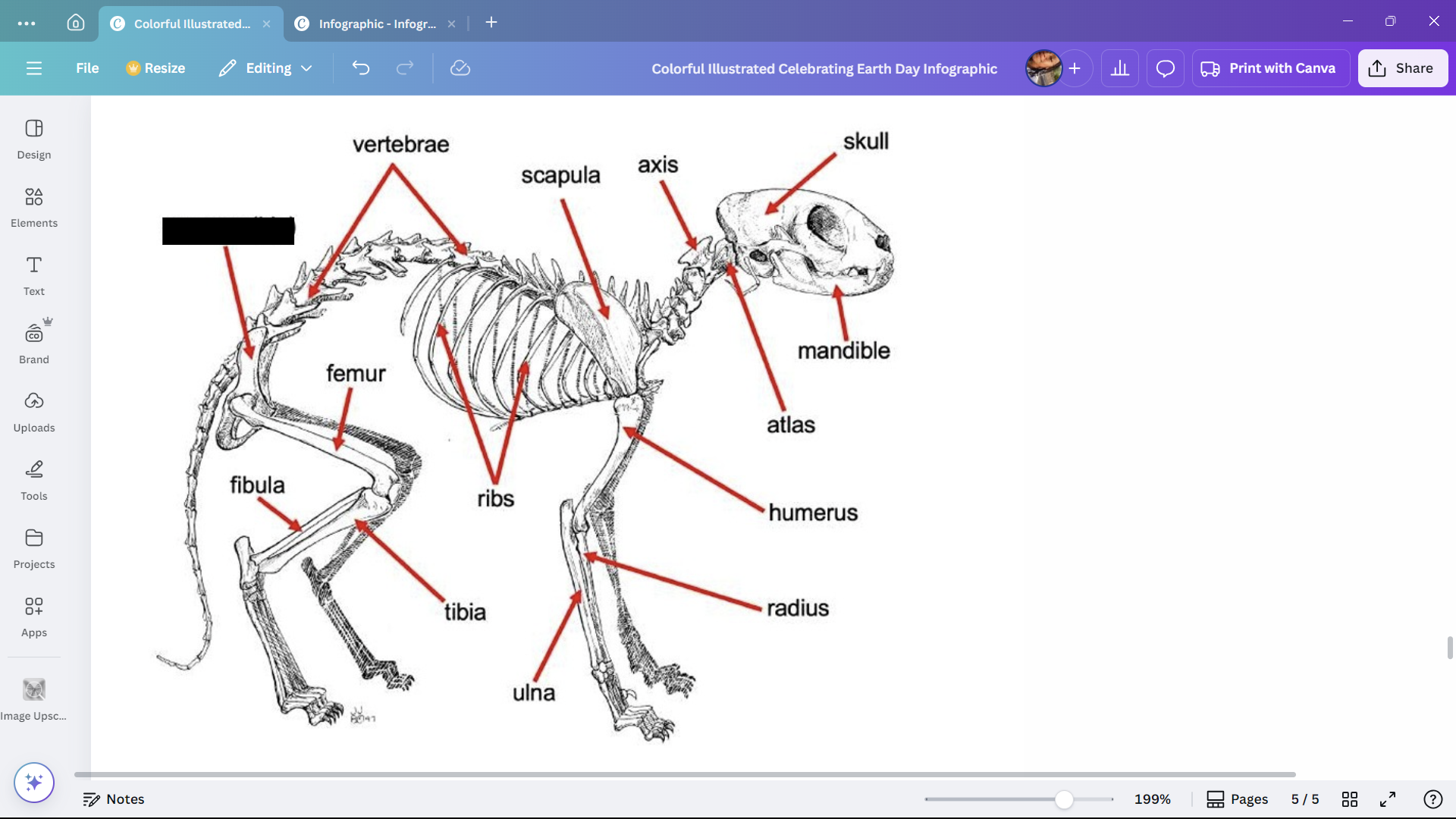
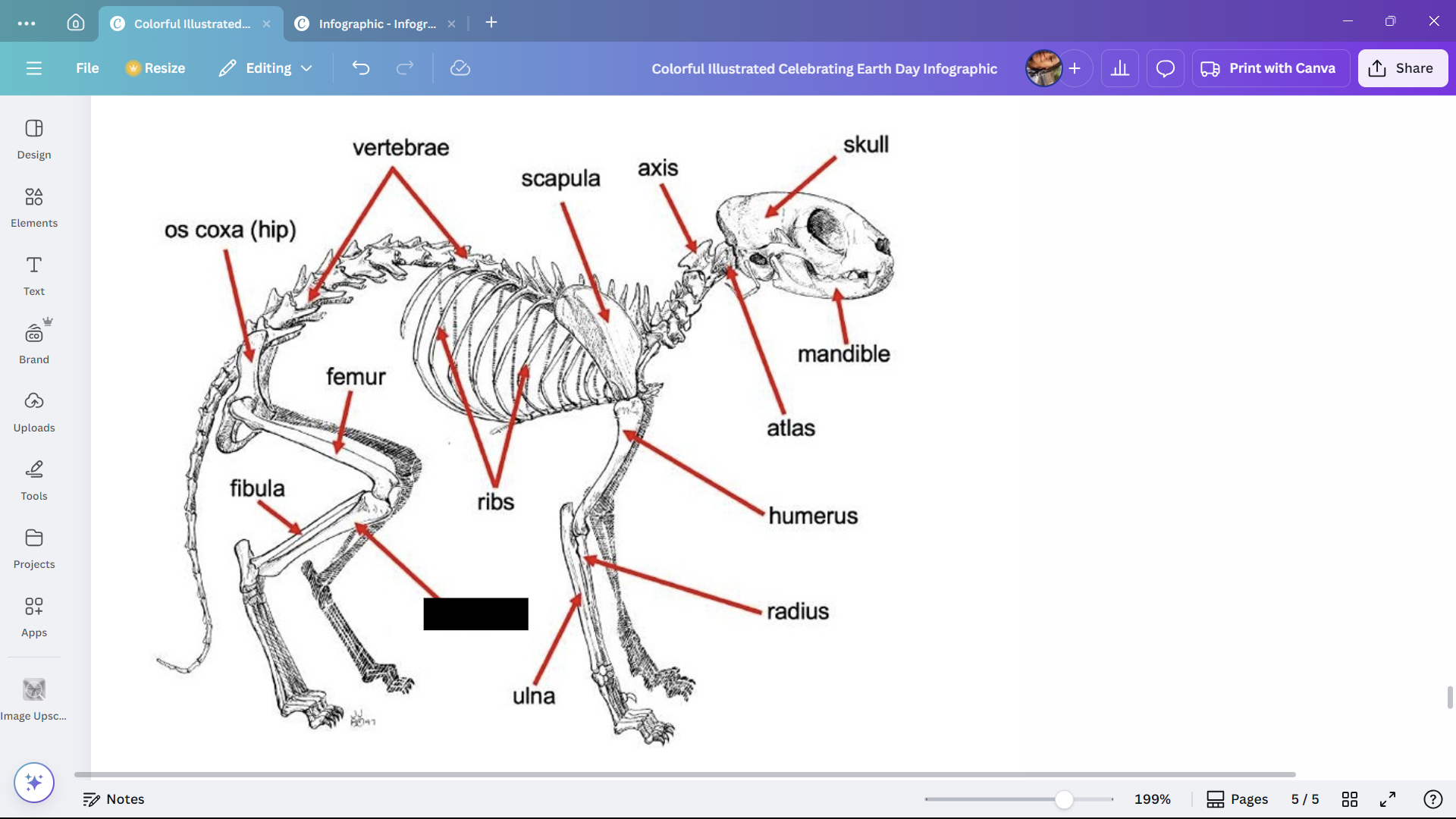
Skull
Skeletal structure found in the head region of a cat.
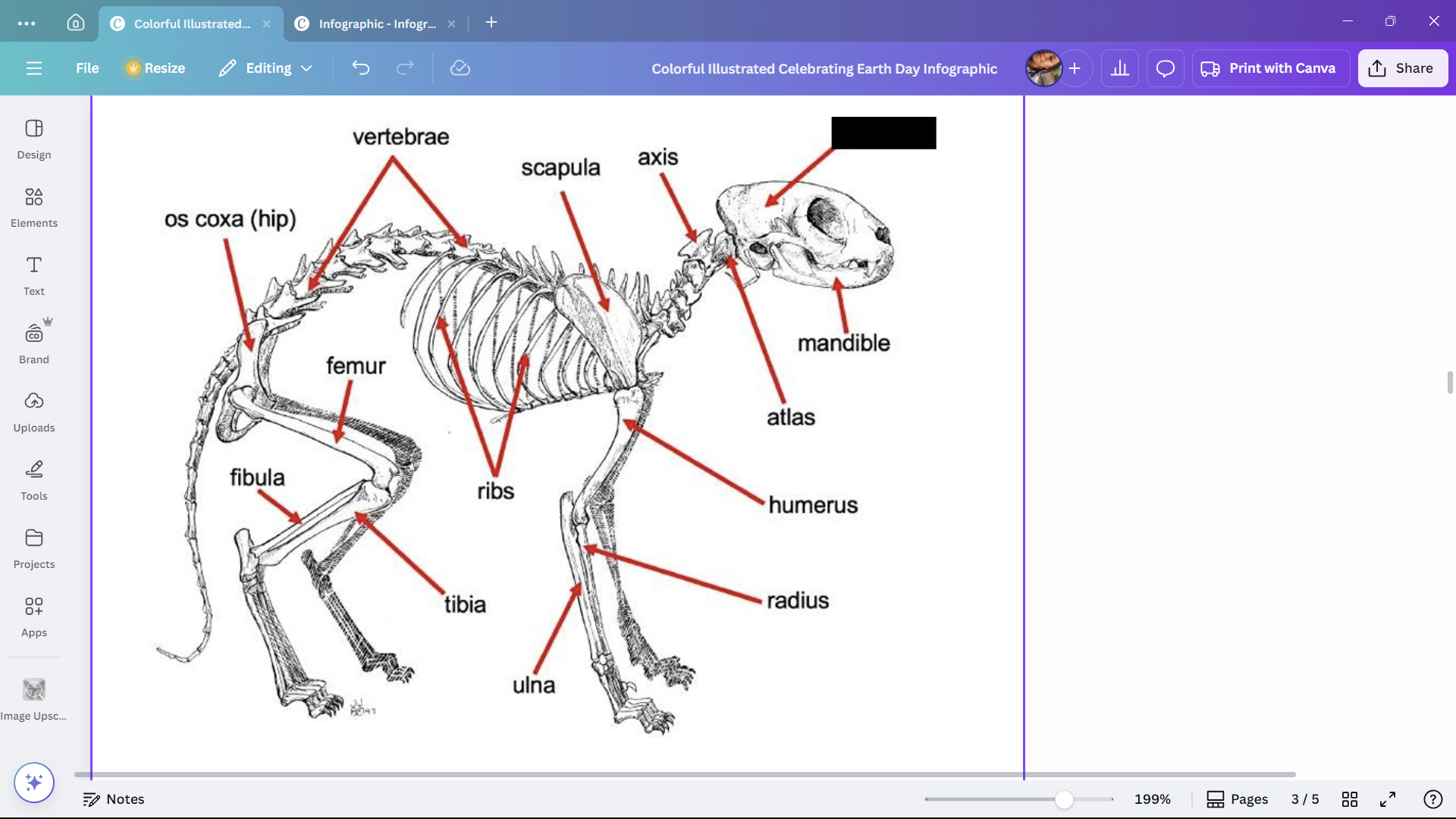
Mandible
The lower jaw of a cat.
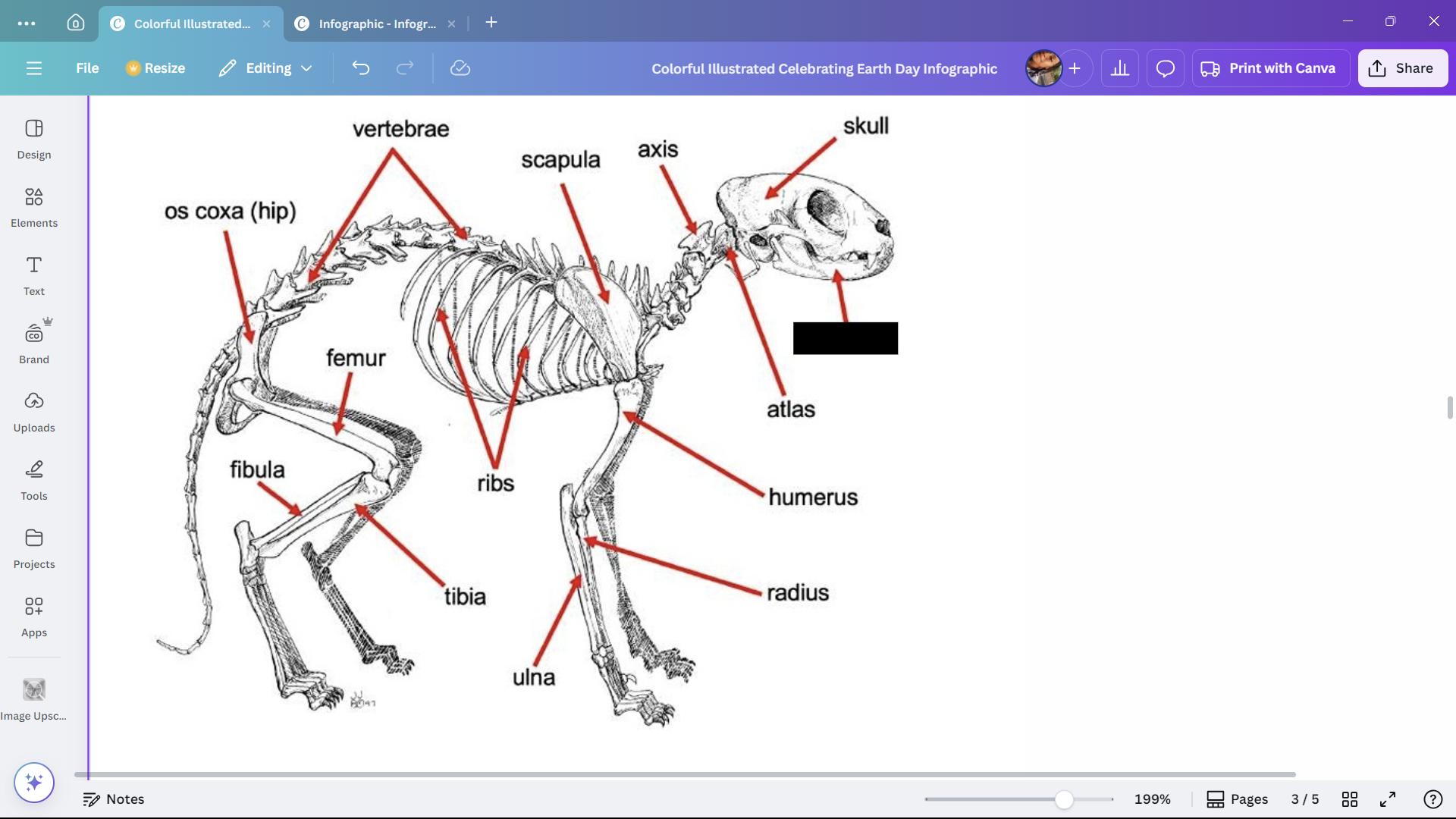
Atlas
A cervical vertebra of a cat that articulates with the skull.
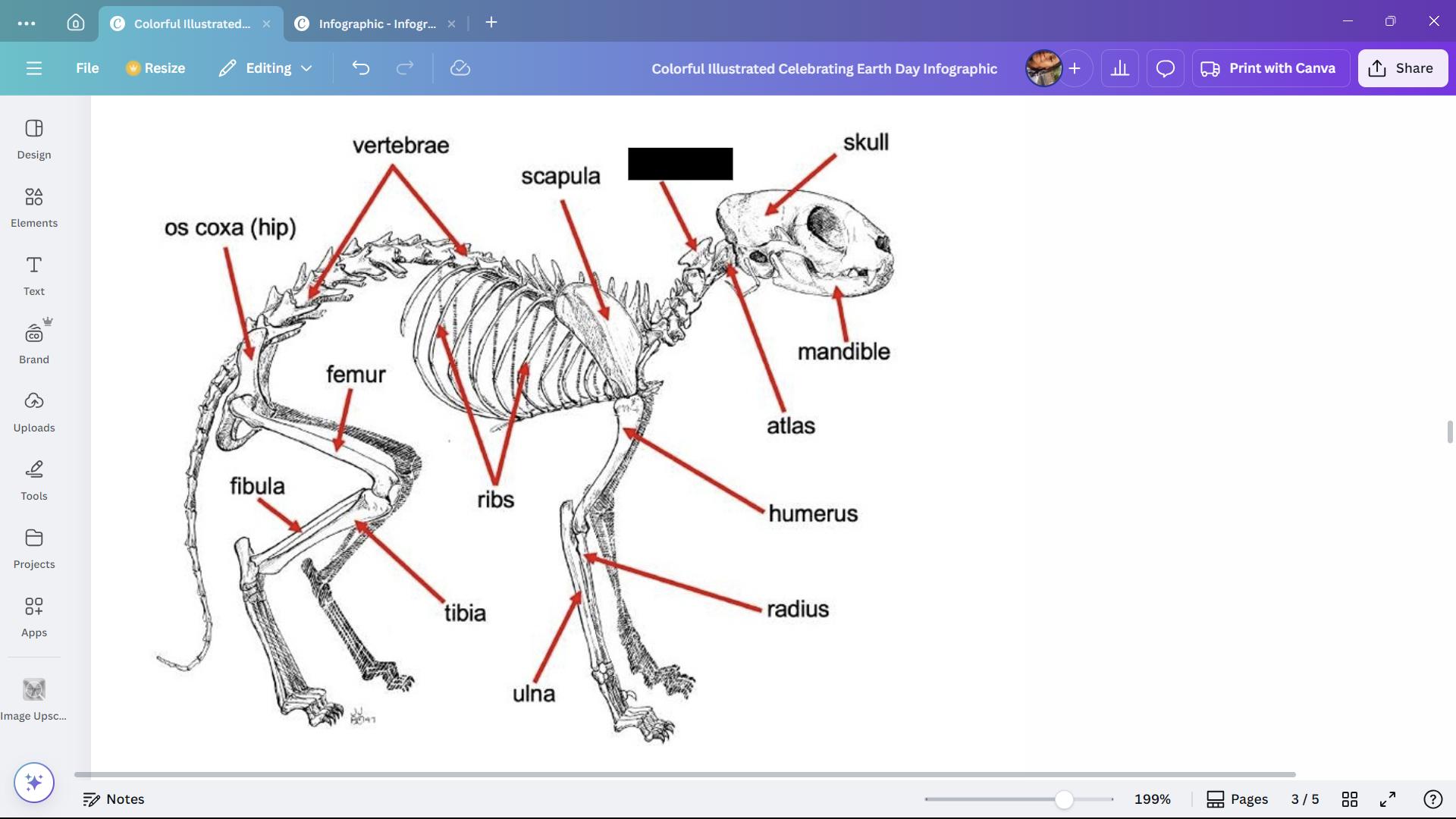
Axis
A cervical vertebra of a cat that articulates with the atlas.
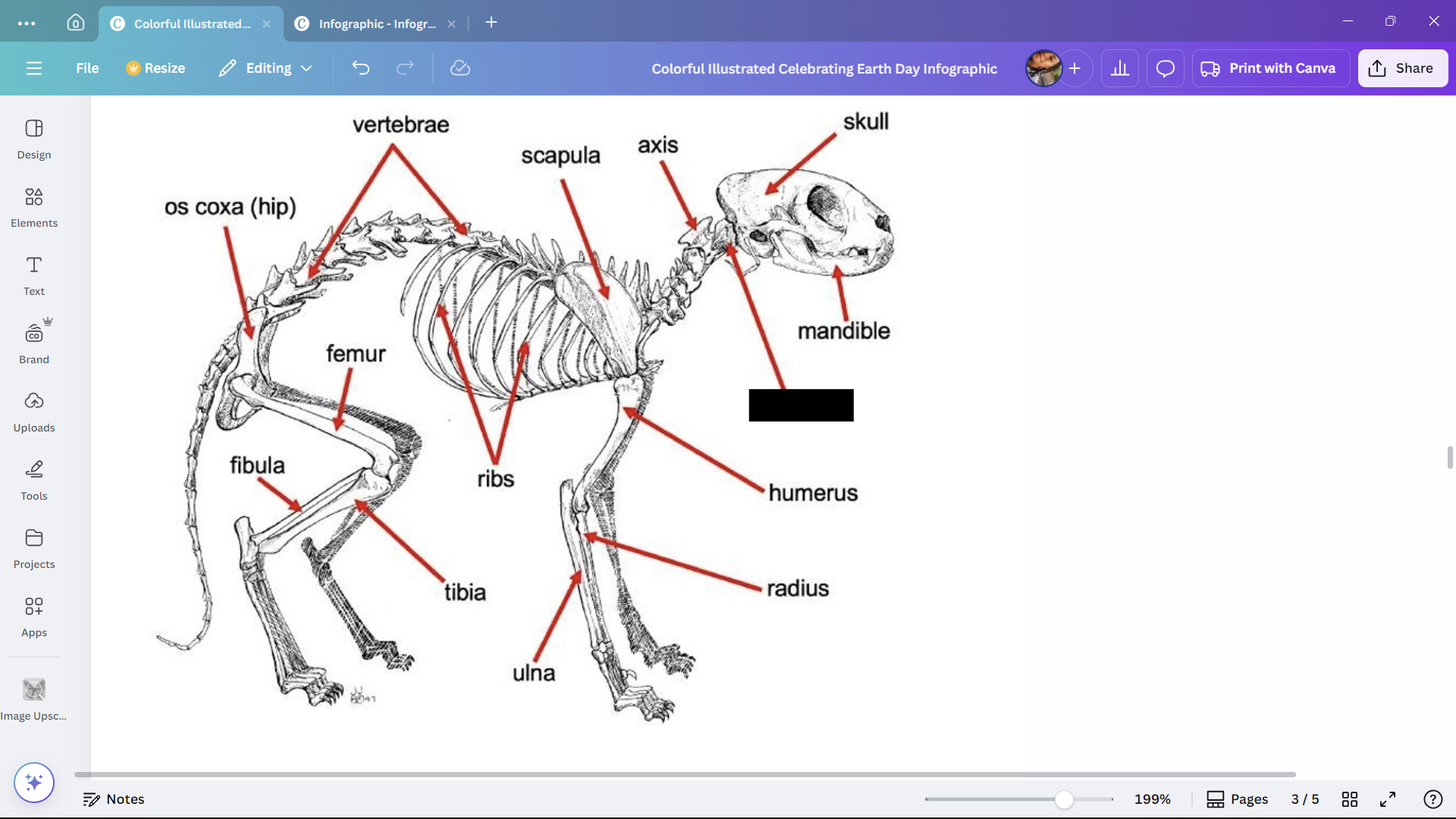
Scapula
The shoulder blade of a cat.
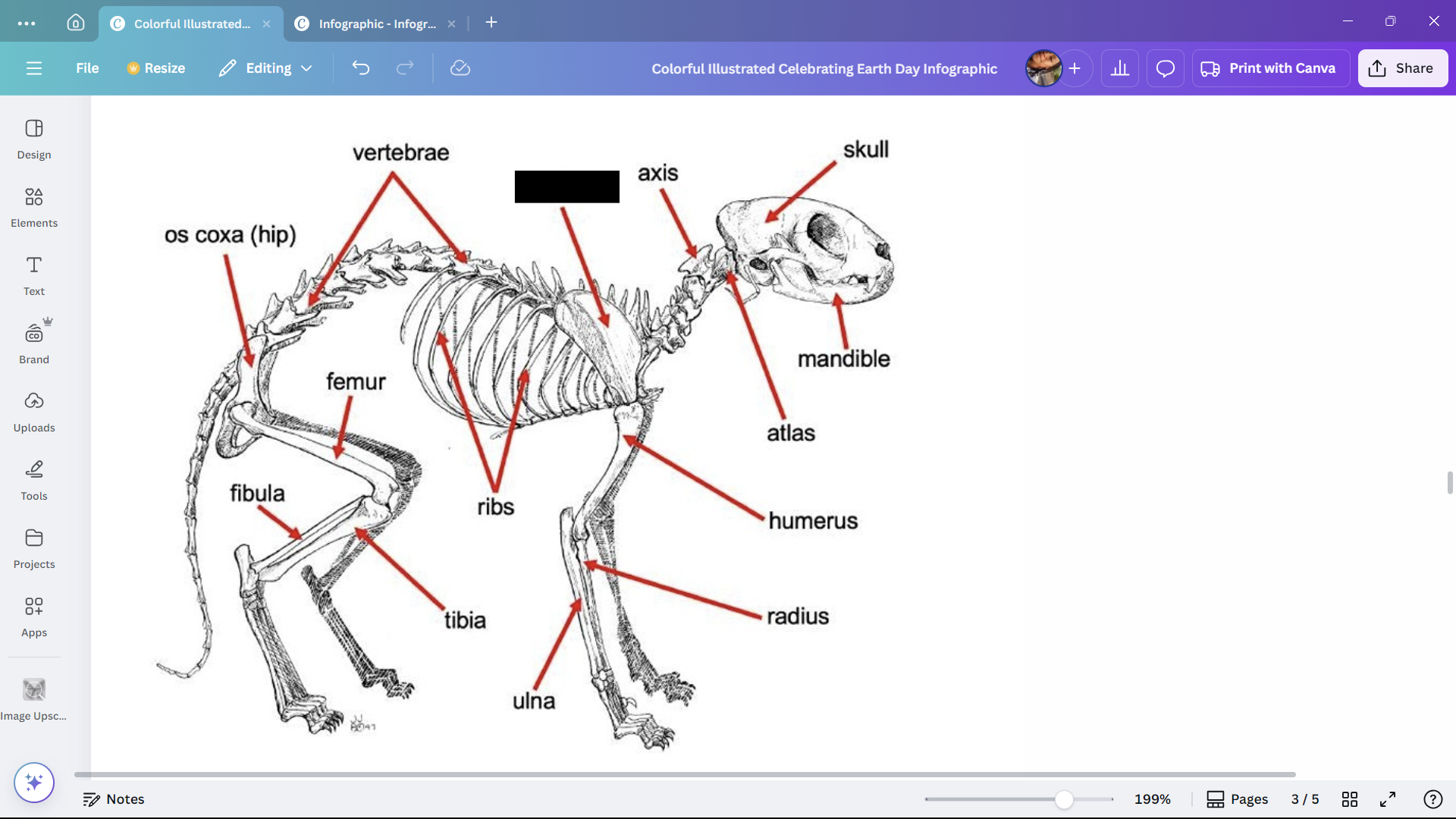
Humerus
The upper arm bone of a cat.
Radius
One of the bones in the forearm of a cat.
Ulna
One of the bones in the forearm of a cat.
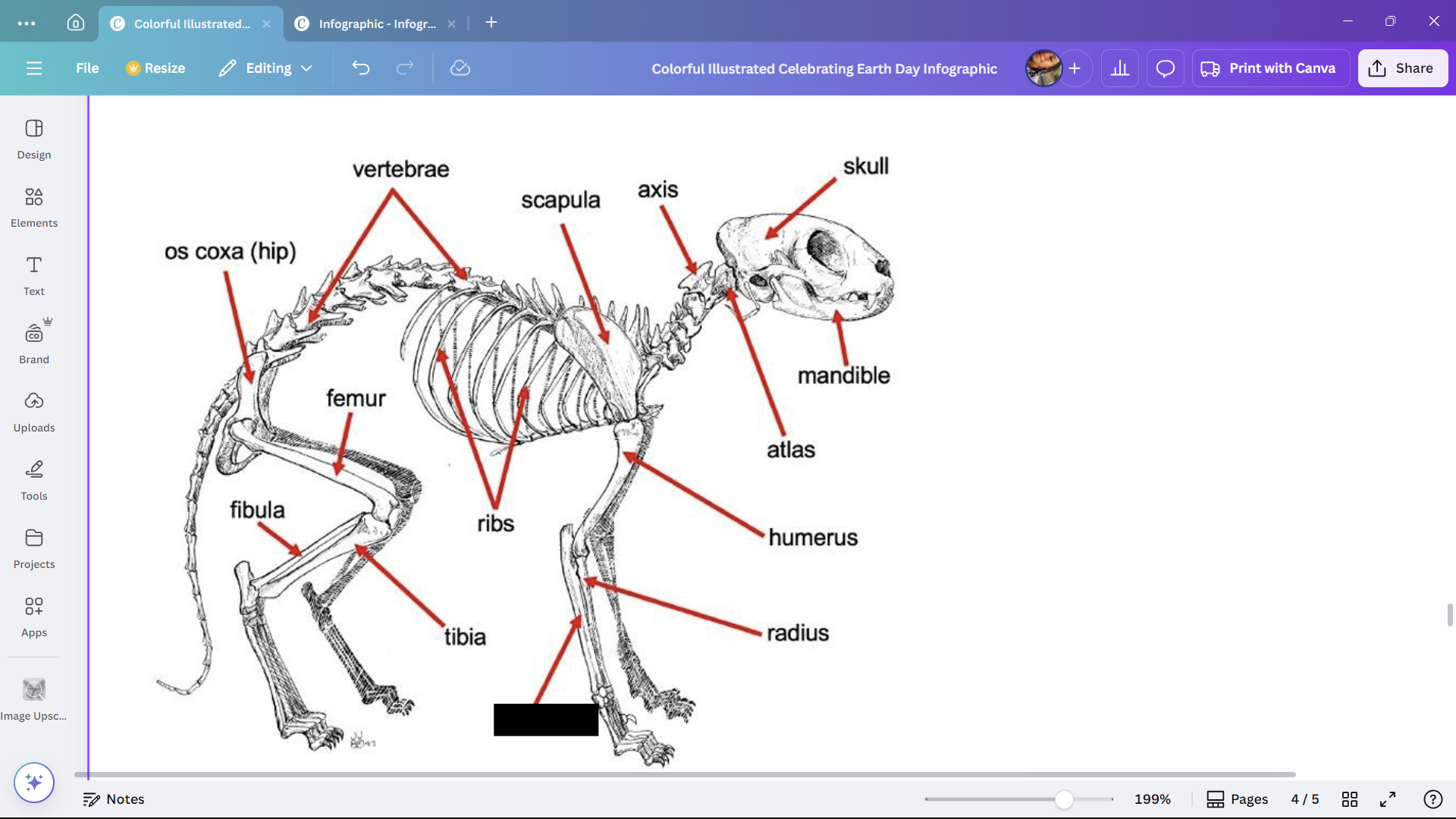
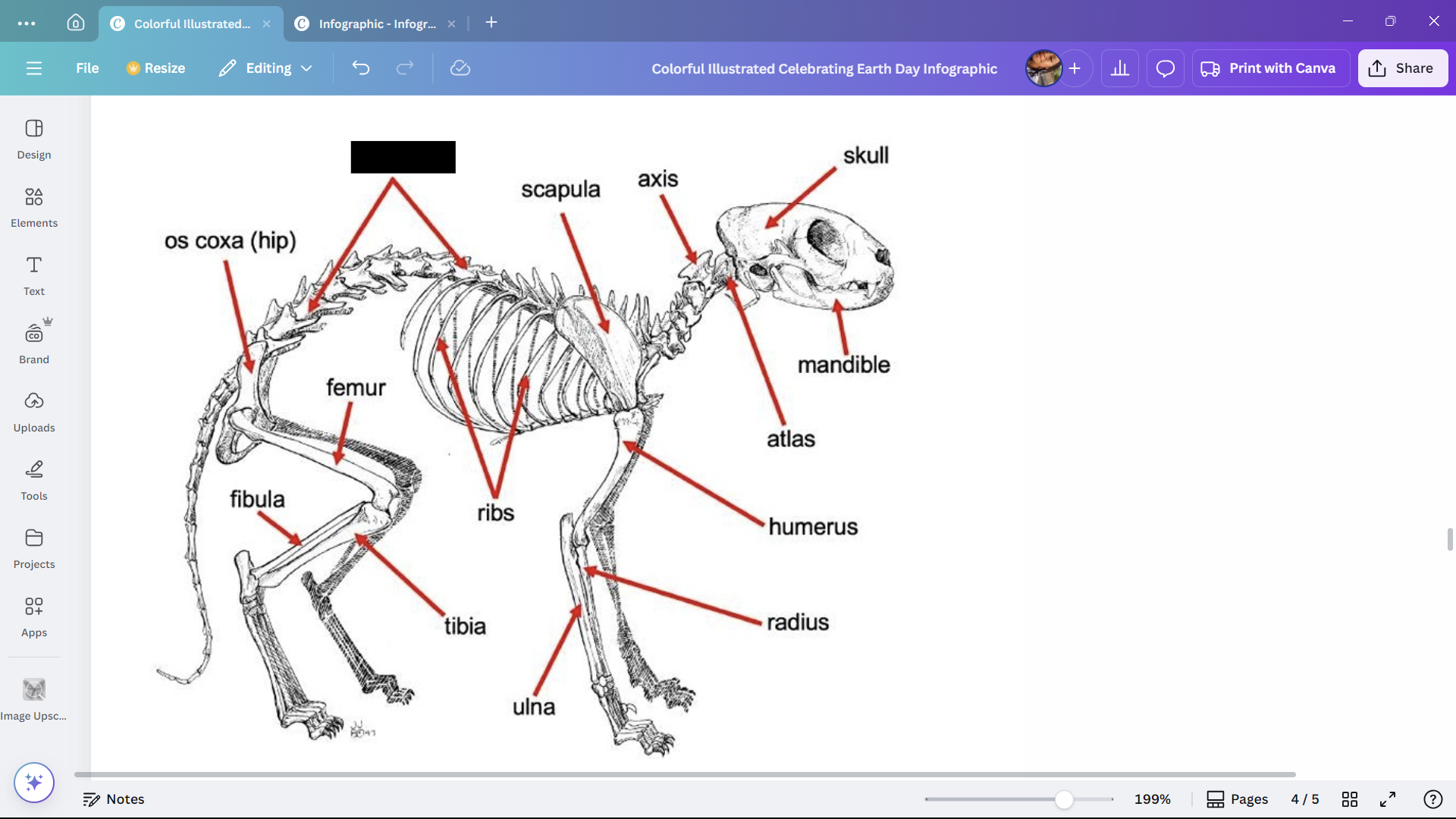
Ribs
Bones enclosing the thoracic cavity of a cat.
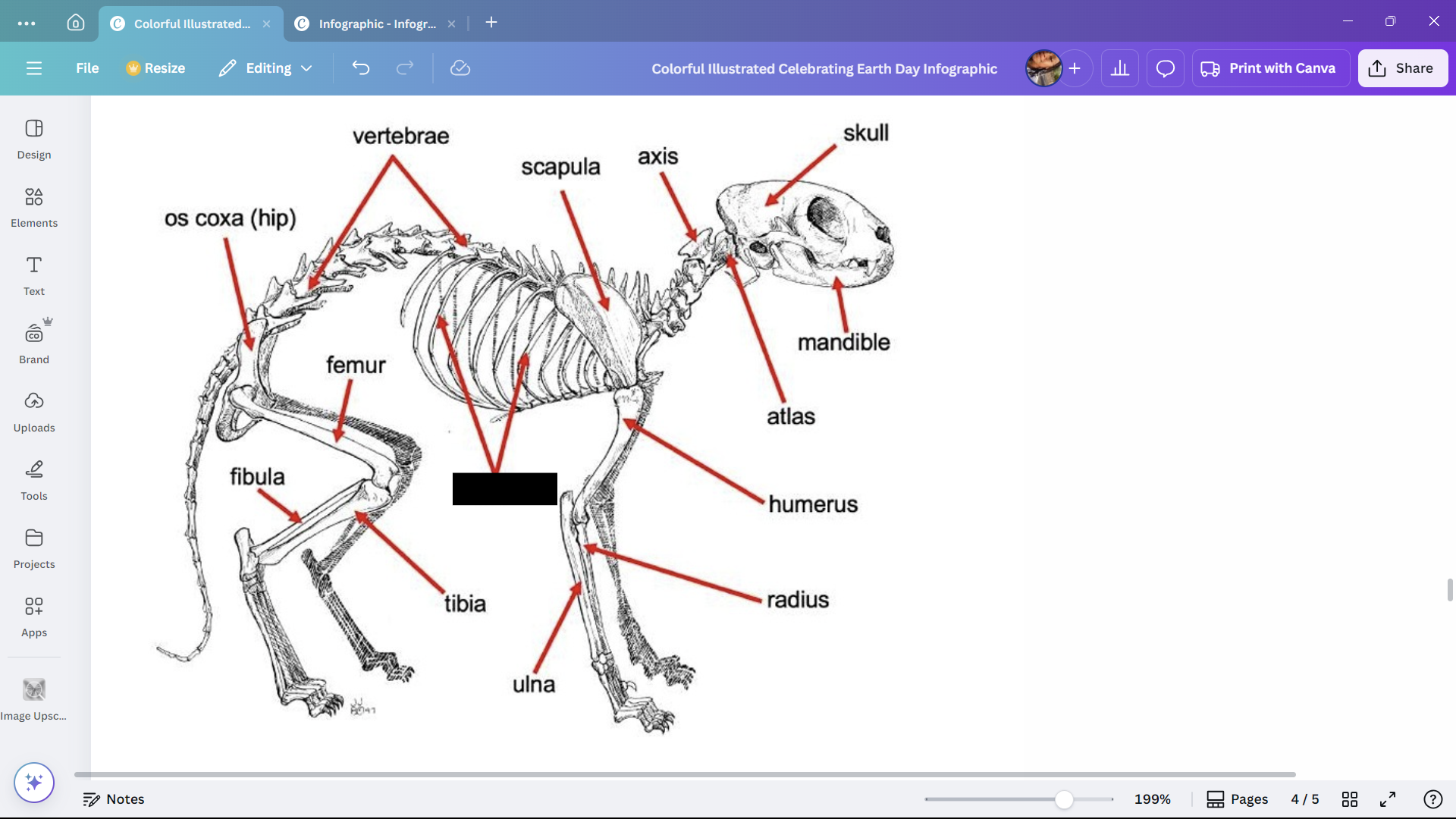
Vertebrae
Bones forming the vertebral column of a cat.
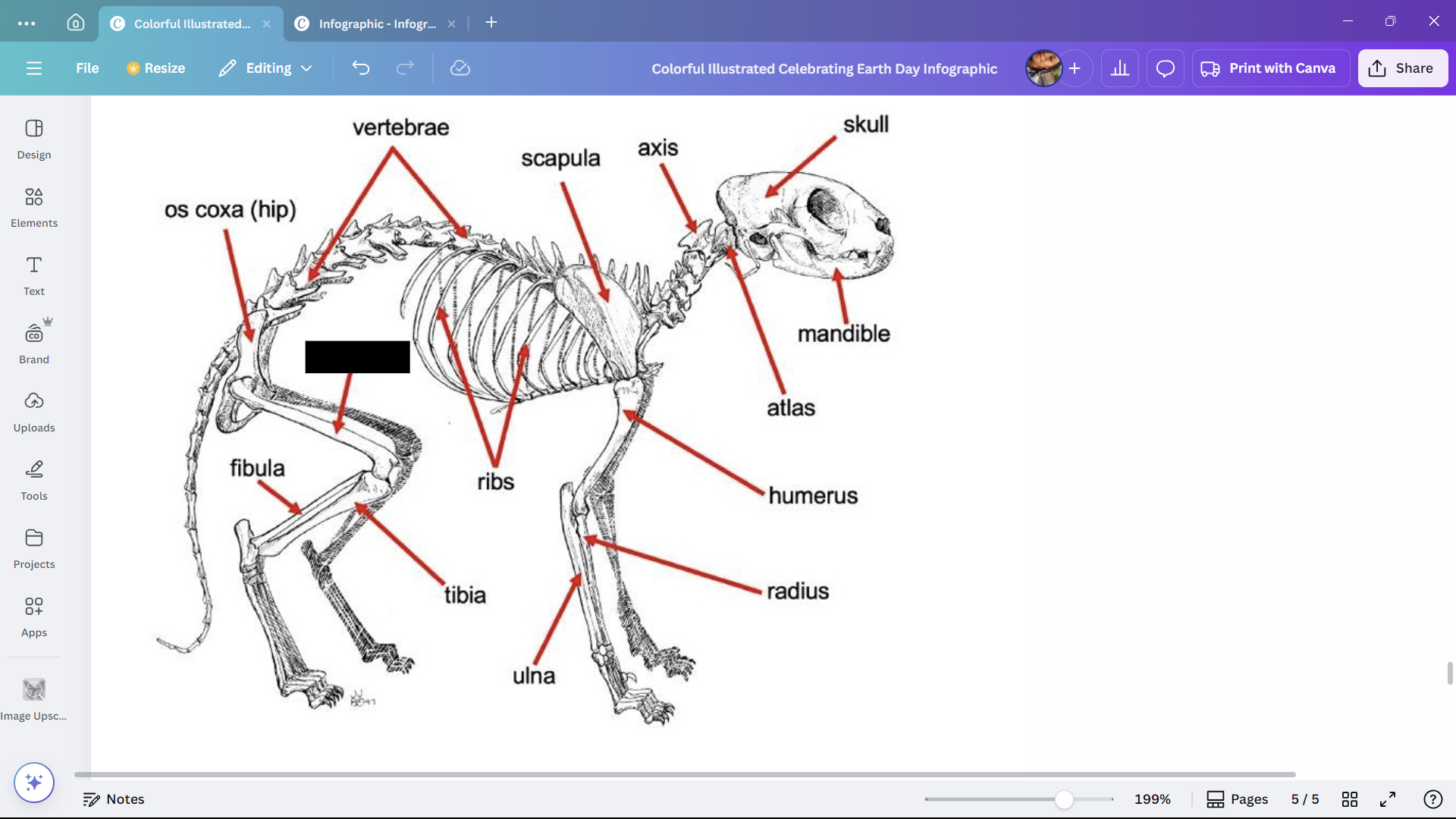
Os coxa (hip)
The hip bone of a cat.
Femur
The thigh bone of a cat.
Tibia
The larger of the two lower leg bones of a cat.
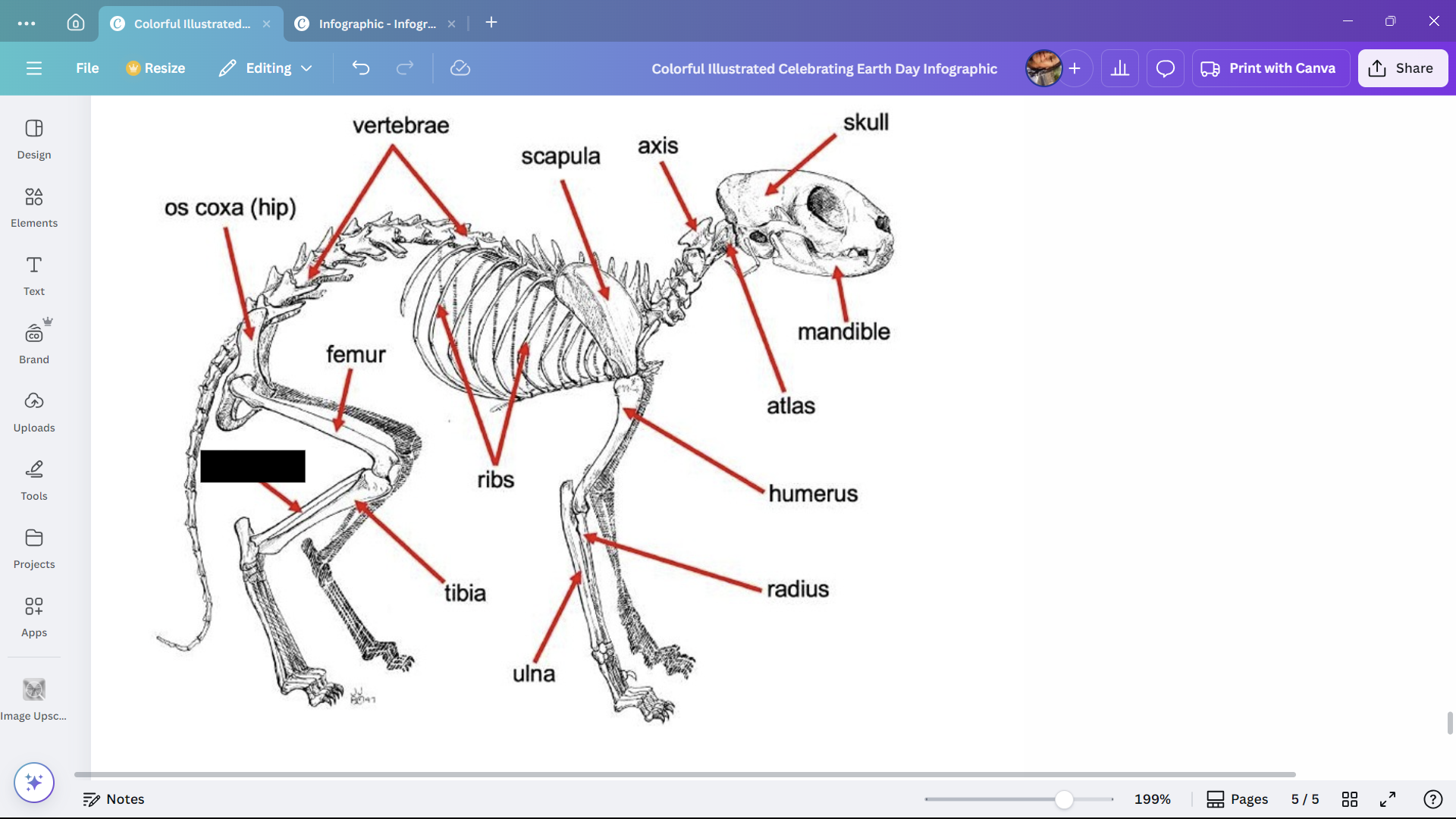
Fibula
The smaller of the two lower leg bones of a cat.
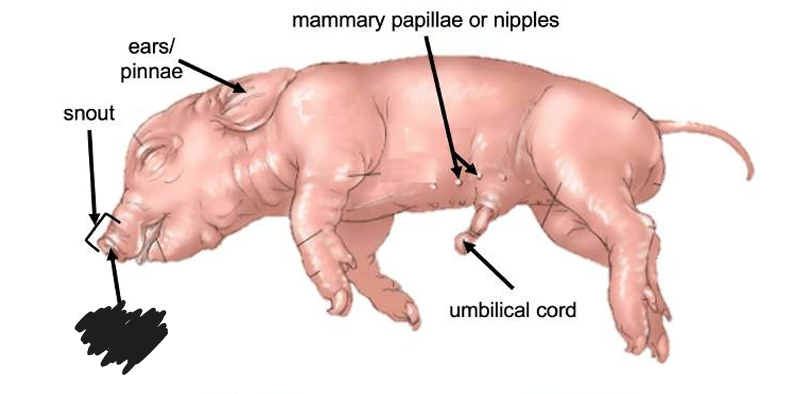
Snout
The external structure located on the head region of a fetal pig.
External nares or nostrils
The external structure located on the head region of a fetal pig that function for air intake.
Vibrissae or whiskers
Tactile (touch) reception providing sensory data for spatial orientation on the head region of a fetal pig.
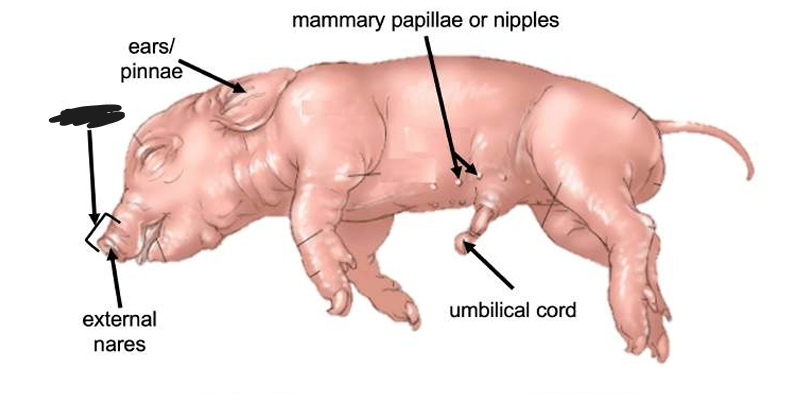
Ears or pinnae
The external structure located on the head region of a fetal pig used for hearing.
Mammary papillae or nipples
Structure located on the trunk region of a fetal pig.
Umbilical cord
Structure located on the trunk region of a fetal pig; it connects the fetus to the placenta.
Urogenital opening
Structure located on the trunk region of a fetal pig that is the external opening of the urogenital tract.
Anus
Structure located on the trunk region of a fetal pig that is the external opening of the digestive tract.
Genital papilla (females)
Structure located on the trunk region of a female fetal pig.
Scrotum (males)
Structure located on the trunk region of a male fetal pig.
Trachea
Moves air to and from the lungs for respiration.
Esophagus
Moves swallowed food from the mouth to the stomach.
Thyroid
Production of certain hormones.
Heart
Pumps blood throughout the body via blood vessels.
Lungs
Primary organs of respiration.
Diaphragm
Pulls air into the lungs; improves respiratory efficiency in mammals.
Liver
Detoxifies absorbed digested compounds; produce bile.
Gallbladder
Store bile produced in the liver.
Stomach
Holds ingested food and initiate its chemical digestion.
Small intestine
Completion of food digestion; absorption of nutrients and water.
Pancreas
Produce digestive enzymes & secrete them into the small intestine.
Cecum
House bacteria that break down cellulose in plant material.
Spiral colon
Absorption of water and electrolytes; transport feces to the rectum.
Spleen
Store red blood cells; regulate blood volume; produce lymphocytes.
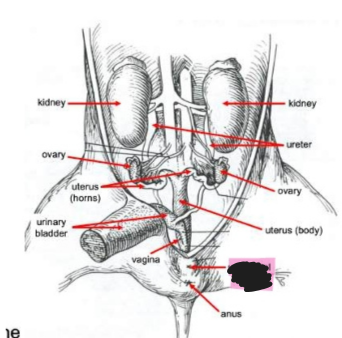
Kidneys
Filter metabolic waste from the blood; conserve water and salts.
Ureters
Move urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
Urinary bladder
Temporary storage of urine before it is eliminated from the body.
Penis (males)
Carry urine out of the body; deposit sperm into the female reproductive tract for reproduction.
Testes (males)
Produce sperm for reproduction; produce testosterone.
Ovary (females)
Produce eggs for reproduction; produce estrogen & progesterone.
Uterus (females)
Embryonic development of fetuses.
Vagina (females)
Entrance to the female reproductive tract; part of the birth canal.