Biology - Unit 1
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.1 Monomers and polymers 1.2 Carbohydrates 1.3 Lipids 1.4.1 General properties of proteins 1.4.2 Many proteins are enzyme 1 1.5.1 Structure of DNA and RNA 1.5.2 DNA replication 1.6 ATP 1.7 Water 1.8 Inorganic ions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are monomers ?
Monomers are small, single molecules that can join together via chemical bonds to form larger molecules called polymers.
What are polymers ?
Polymers are larger molecules formed when small, single molecules called monomers join together via chemical bonds.
Condensation Reaction
Is a chemical process where two monomers join together to form a polymer with the removal of a water molecule
Hydrolysis Reaction
Is a chemical process where a polymer is broken down into smaller units ( monomers ) by using a water molecule
Monosacchardies
They are monomers from which larger charbohydrates are made like Glucose, Fructose and Galactose
Structure of an Alpha Glucose
for Beta glucose the OH on carbon 1 atom is on the top
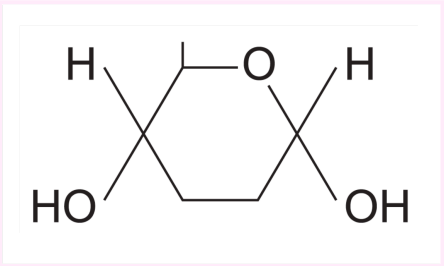
Difference between the structure Alpha glucose and Beta glucose
They are isomers, they have the same molecular fromula but different sturctual fromula
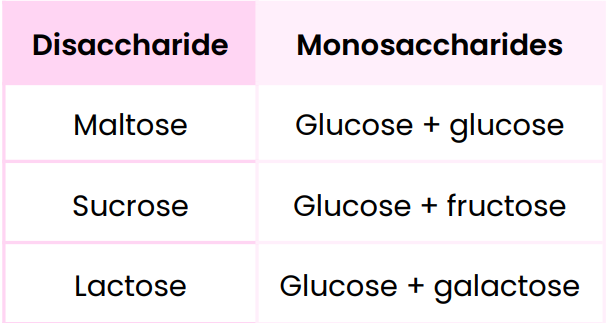
Disaccharides
They are formed when 2 monosacchardies join together by a glycosidic bond via a condensation reaction
Disaccharides & monosaccharides from which they’re made
Polysaccharides
They are formed when many monosaccharides join together by a glycosidic bond via condensation reaction, releasing many water molecules
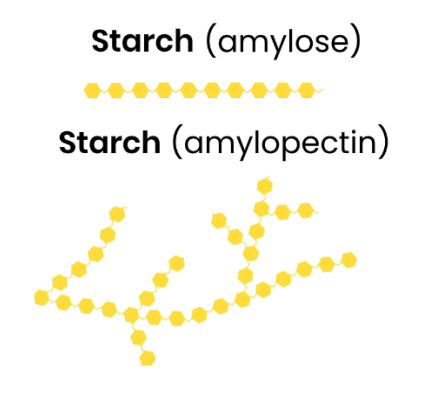
Starch:- Function and Structure
Function
Starch is used as an energy store in plant cells they are Polysaccharide of α-glucose, They have some 1,4-glycosidic bonds so is unbranched (amylose) and Some have 1,4- and 1,6-glycosidic bonds so is branched (amylopectin)
Structure
Helical → compact for storage in cell ● Large, insoluble polysaccharide molecule → can’t leave cell / cross cell membrane ● Insoluble in water → water potential of cell not affected (no osmotic effect)
Glycogen:- Function and Structure
Function
They are used as an energy store in animal cells, They are Polysaccharide made of α-glucose and 1,4- and 1,6-glycosidic bonds → branched
Structure
Branched → compact / fit more molecules in small area ● Branched → more ends for faster hydrolysis → release glucose for respiration to make ATP for energy release ● Large, insoluble polysaccharide molecule → can’t leave cell / cross cell membrane ● Insoluble in water → water potential of cell not affected (no osmotic effect)
Cellulose
Function
● Provides strength and structural support to plant / algal cell walls
Structure
● Polysaccharide of β-glucose
● 1,4-glycosidic bonds so forms straight, unbranched chains and Chains linked in parallel by hydrogen bonds, forming microfibrils
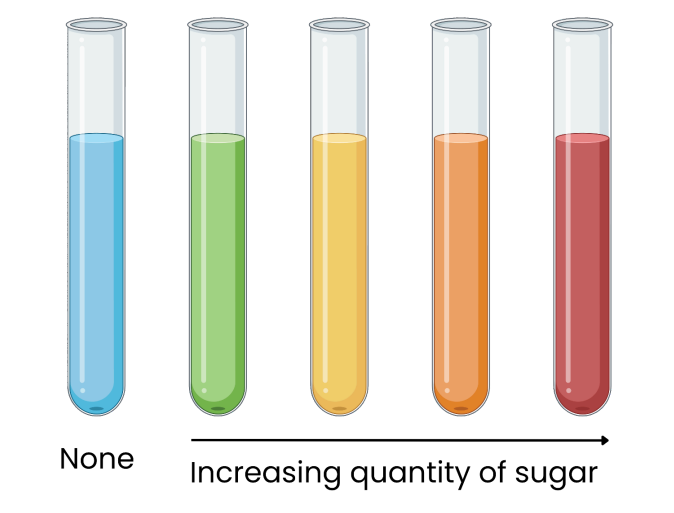
Tests for Reducing Sugars
1. Add Benedict’s solution (blue) to sample
2. Heat in a boiling water bath
3. Positive result = green / yellow / orange / red precipitate
Test for Non- Reducing Sugars
1. Do Benedict’s test (as above) and stays blue / negative
2. Heat in a boiling water bath with acid (to hydrolyse into reducing sugars)
3. Neutralise with alkali (eg. sodium bicarbonate)
4. Heat in a boiling water bath with Benedict’s solution
5. Positive result = green / yellow / orange / red precipitate
Test for Strach
1. Add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide (orange / brown) and shake / stir
2. Positive result = blue-black