Embryology
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
capacitation
process of the sperm head becomes more permeable to calcium ions, which diffuse into the sperm and stimulate lashing of the tail
capacitation
what must sperm go through before they can penetrate the egg?
polyspermy
The fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm
Artificial insemination
the oldest and simplest reproductive technology
Artificial insemination
Man’s sperm are used to artificially inseminate another women
In Vitro Fertilization
eggs are harvested, fertilized, and returned
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer
Traveling down the uterine tube seems to improve the chance of implantation when the conceptus reaches the uterus
Surrogate Mother
carries child (and sometimes also provides egg) for a women who does not have a functional uterus
Artificial Insemination
Most women use sperm from anonymous donors but are able to select from a catalog that specifies the donors physical and intellectual traits
Oocyte donation
eggs are obtained from a donor, fertilized, and transplanted to uterus of the client
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer
eggs and sperm are introduced to fallopian tube proximal to the obstruction
Artificial Insemination
especially useful if only male is infertile
In Vitro Fertilization
fertilization occurs in laboratory glassware
embryo adoption
A few days later, the pre-embryo is flushed from the donor’s uterus before it implants, and the embryo is transferred back to the uterus of the mother who wishes to have the child
Oocyte Donation
opposite of sperm donors
In Vitro Fertilization
sometimes this results in multiple births
In Vitro Fertilization
expensive reproductive technology
chorionic villi
Fetal blood flows through growths called ____, which project into the placental sinus?
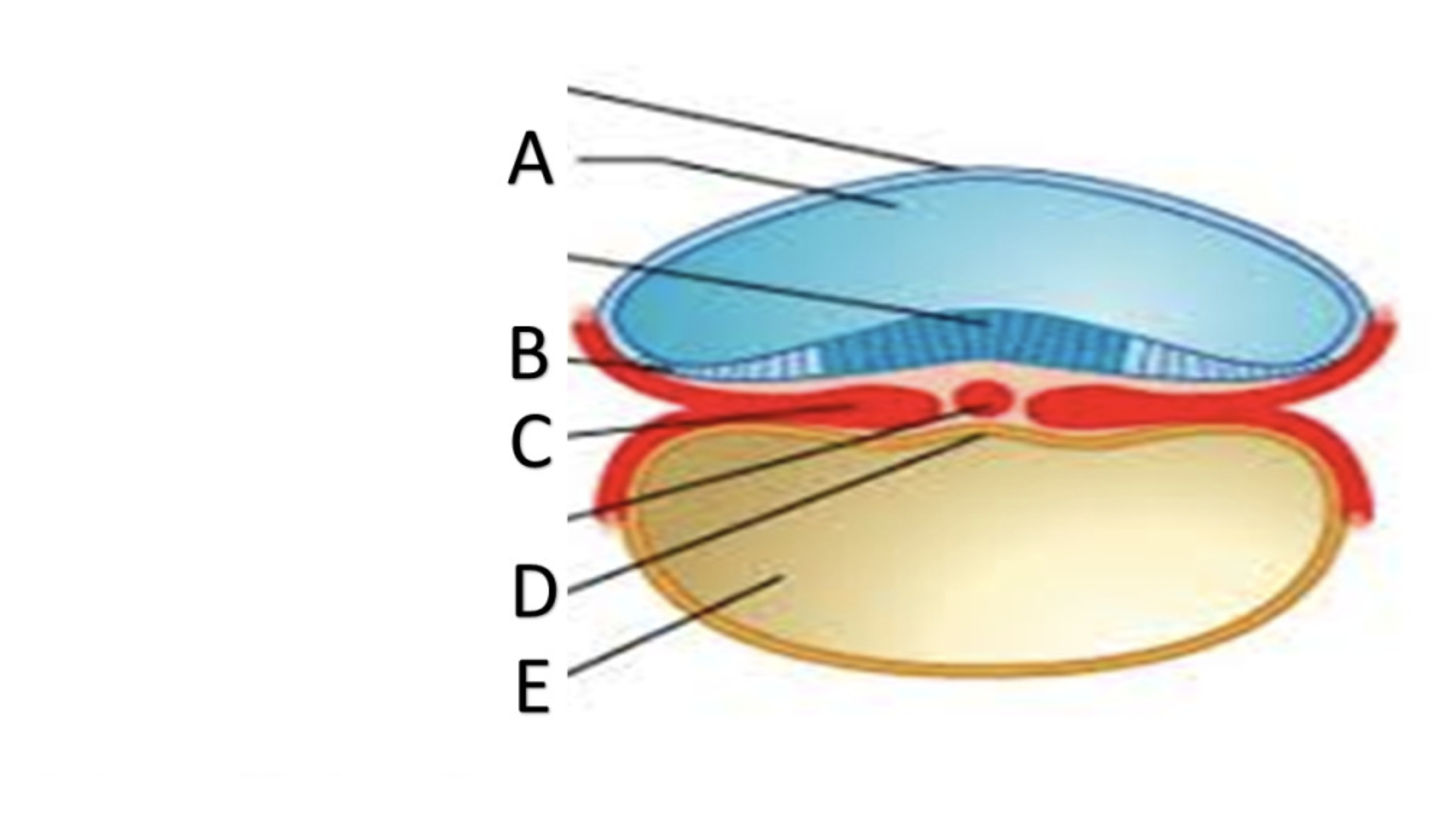
Blastocyst
A
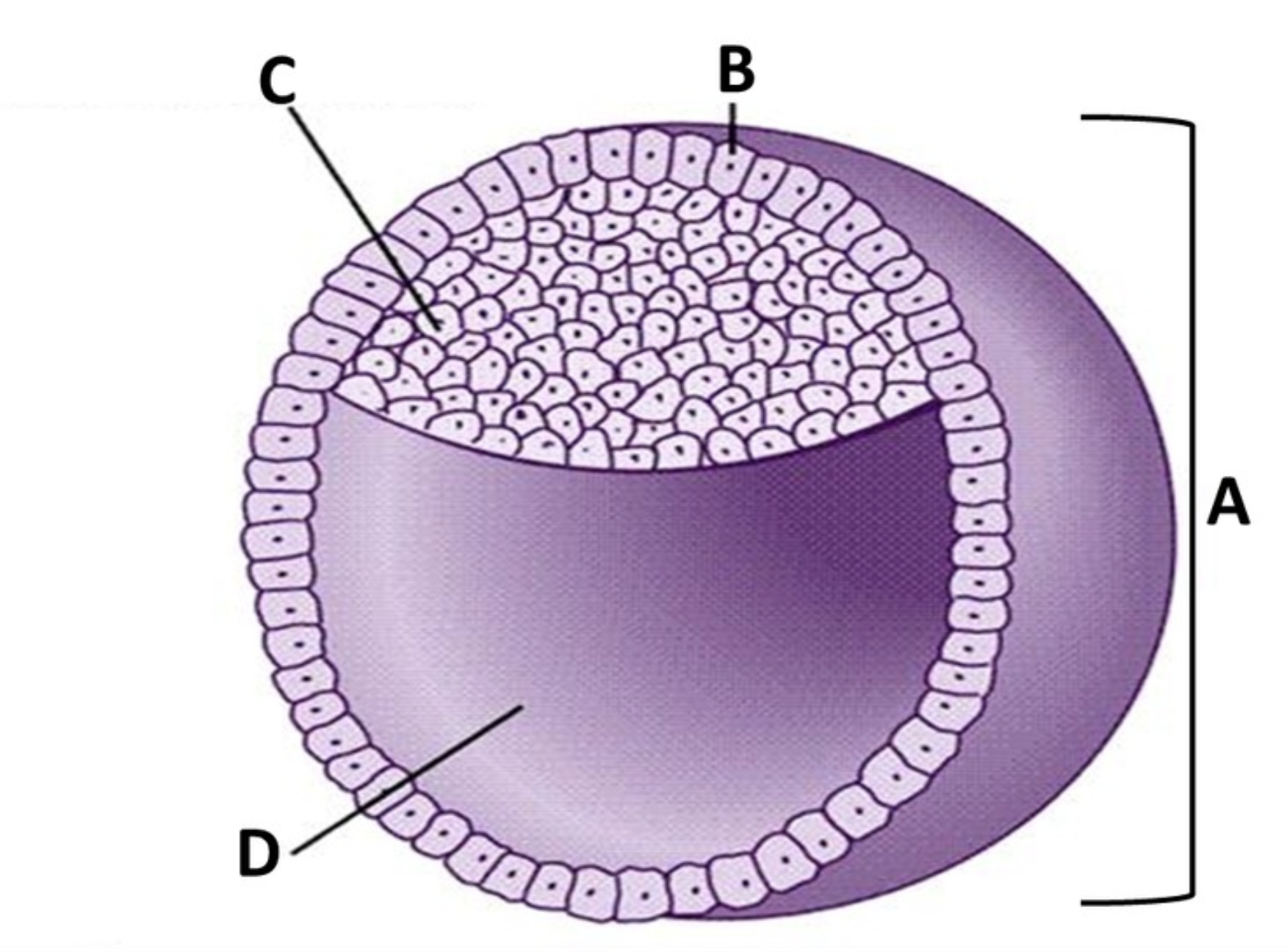
Trophoblast
B
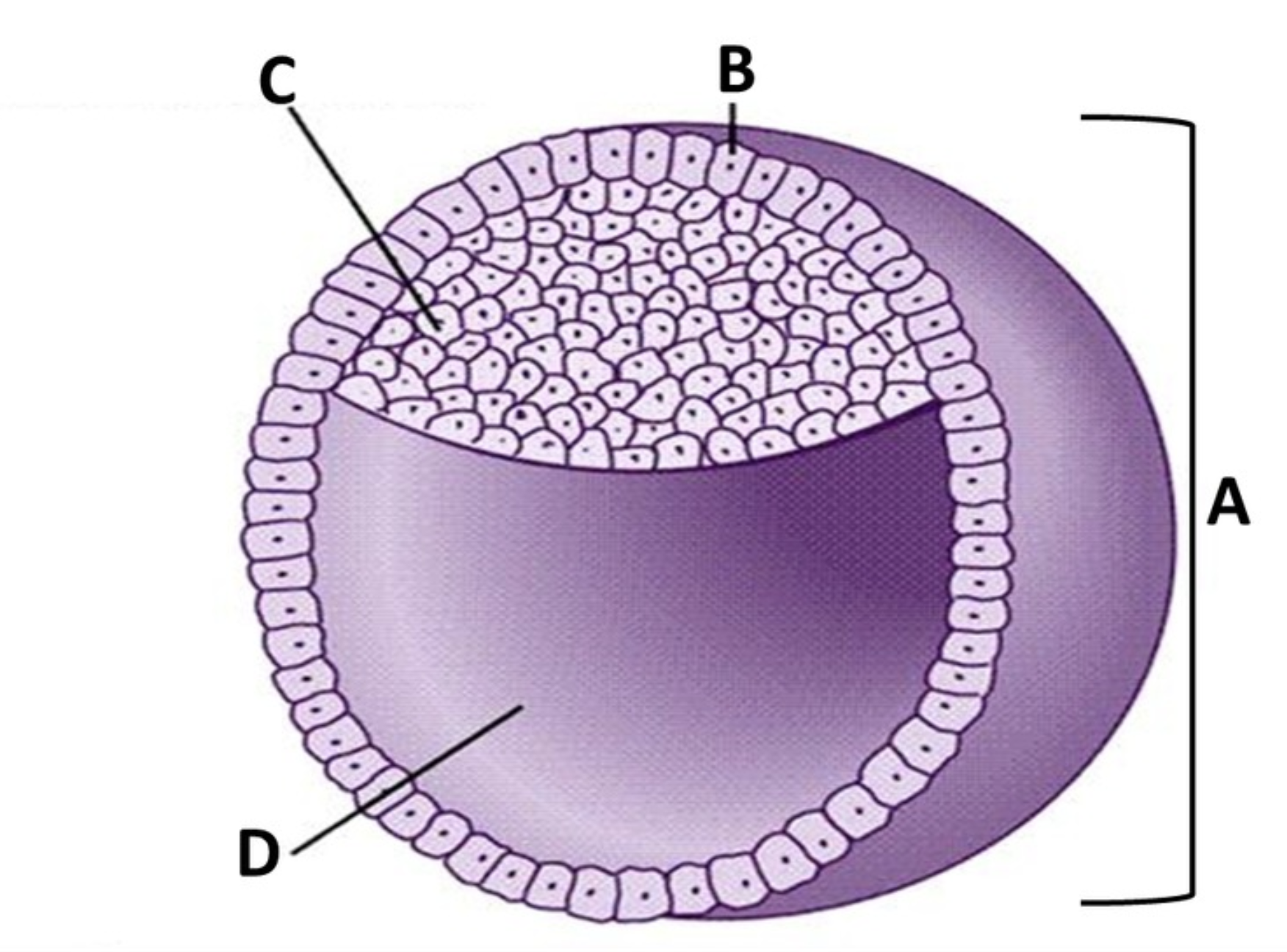
Embryoblast
C
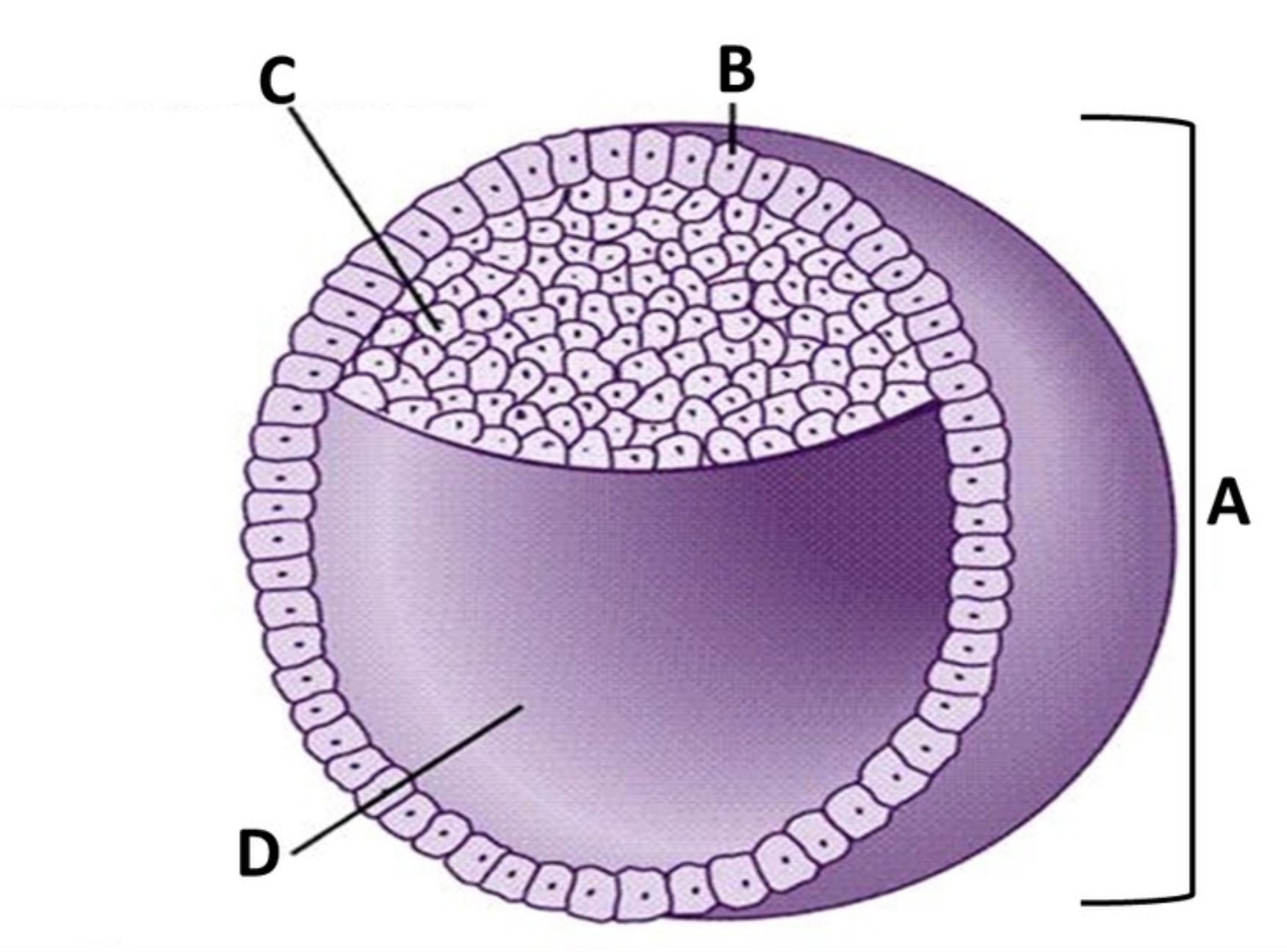
Blastocoel
D
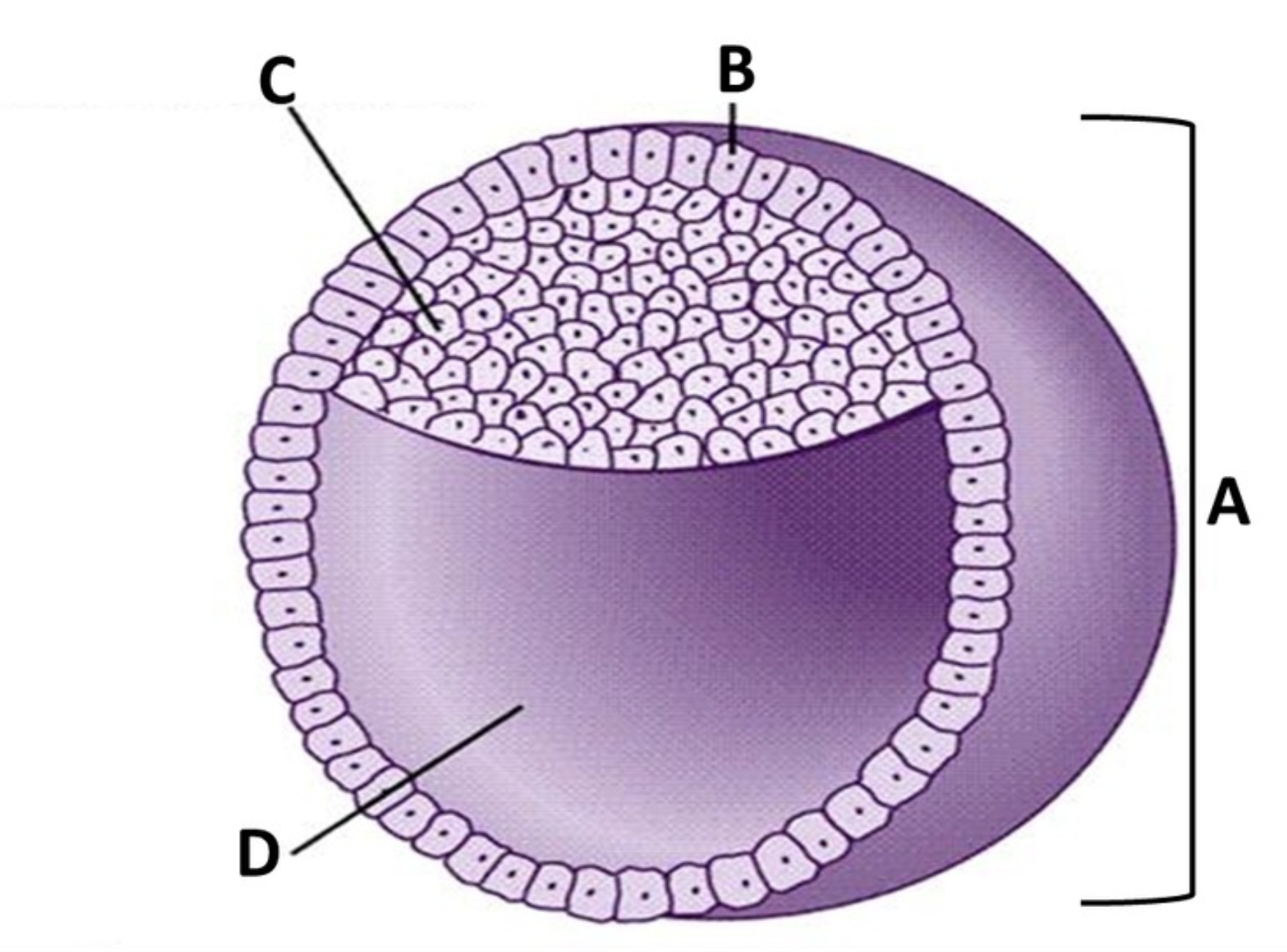
cleavage
refers to mitotic division that occur in the first 3 days, whith the conceptus migrates down the uterine tube
blastomeres
the first two daughter cells
morula
the 16 cell stage
Blastocyst
The morula lies free in the uterine cavity on days 4 and 5 and divides into 100 cells or so, while the zona pellucida disintegrates and releases the conceptus
trophoblast
outer layer of squamous cells
embryoblast
an inner cell mass
blastocoel
a hollow internal cavity
trophoblast
will form part of the placenta
embryoblast
will become the embryo itself
Embryogenesis
When the blastomeres become arranged into the primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
epiblast, hypoblast
The embryoblast flattens into an enbryonic disc composed of initially two layers. the ____ and _____.
Epiblast
What faces the Amniotic Cavity?
Hypoblast
What faces the Yolk Sac?
yolk sac
What does the Hypoblast face?
epiblast
The primitive Streak forms along the?
Gastrulation
_______ is the process of multiplying epiblast cells migrate medially toward the primitive groove and down into it?
endoderm
Multiplying epiblast cells migrate to replace the hypoblast and form the ____ first?
mesoderm
A day later multiplying epiblast cells migrate to replace the hypoblast and form the ____ second?
Ectoderm
Once the other 2 layers form, the remaining epiblast cells form the ____ ?
mesoderm
An overflow of cells from this layer ____ forms the placenta?
endoderm
This layer forms the gut lines, intestines, liver, and pancreas
mesoderm
This layer forms bones, muscle, heart, and blood
ectoderm
This layer forms epidermis (skin) and nervous system
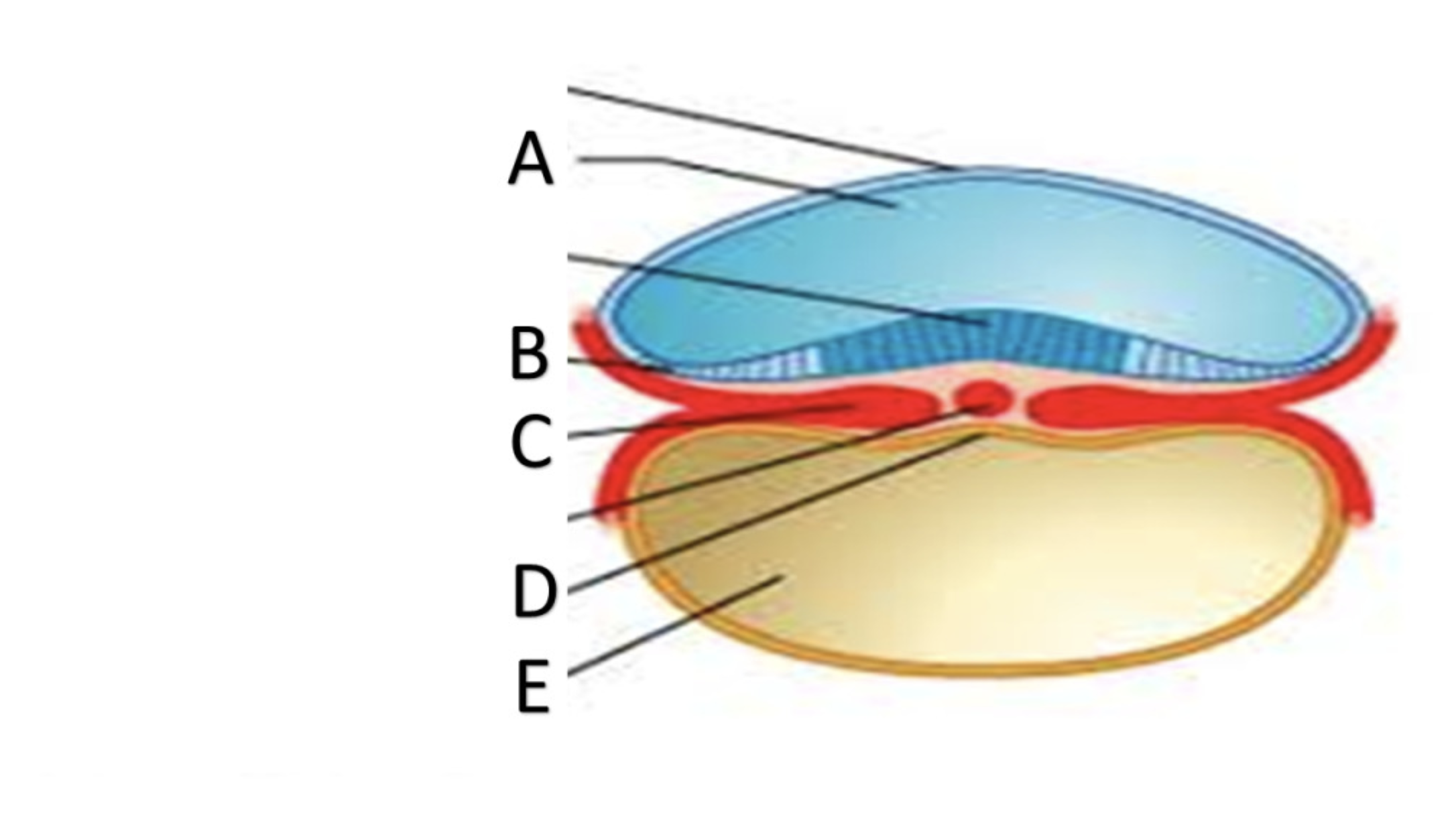
Syncytiotrophoblast
A
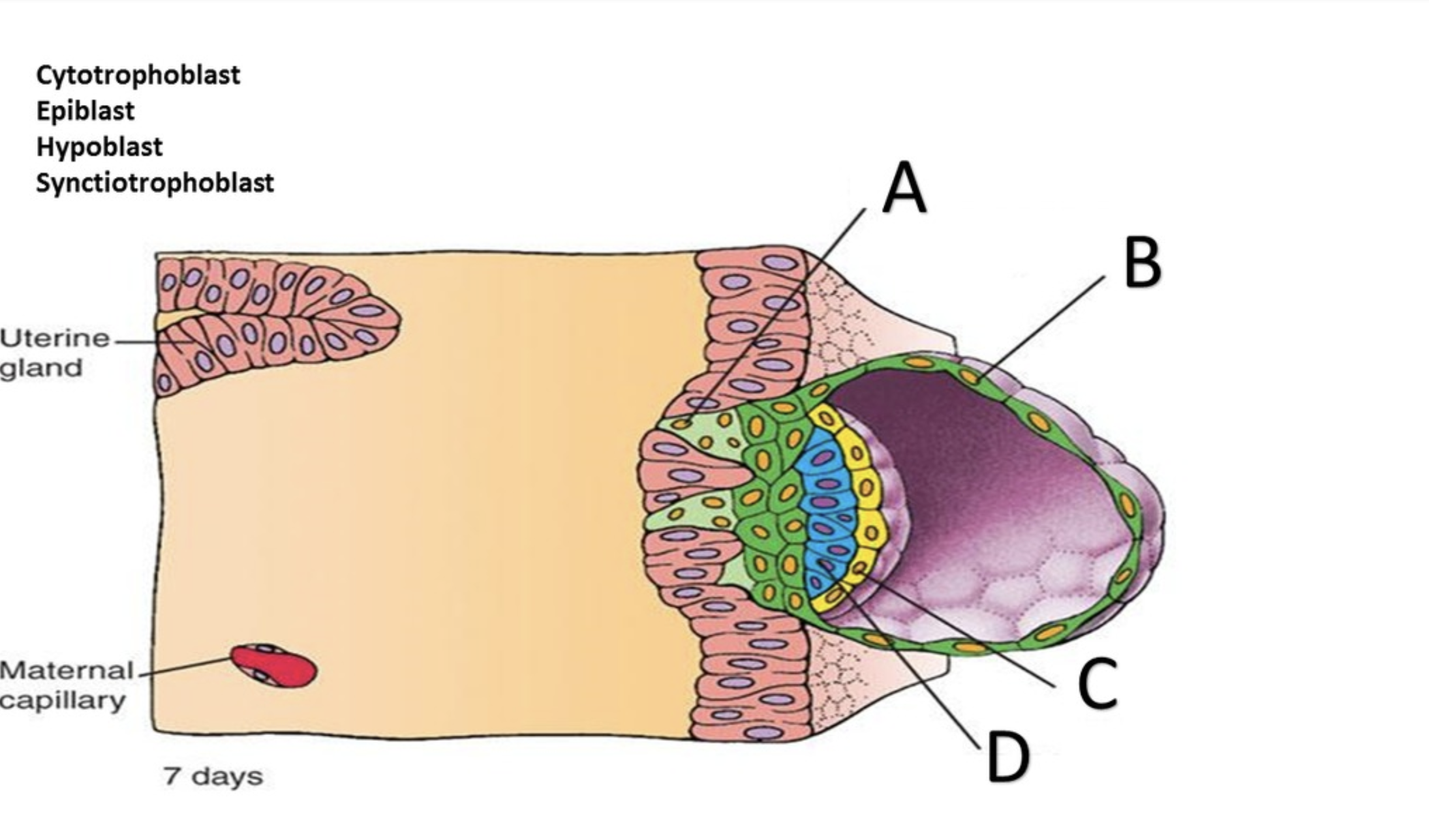
Cytotrophoblast
B
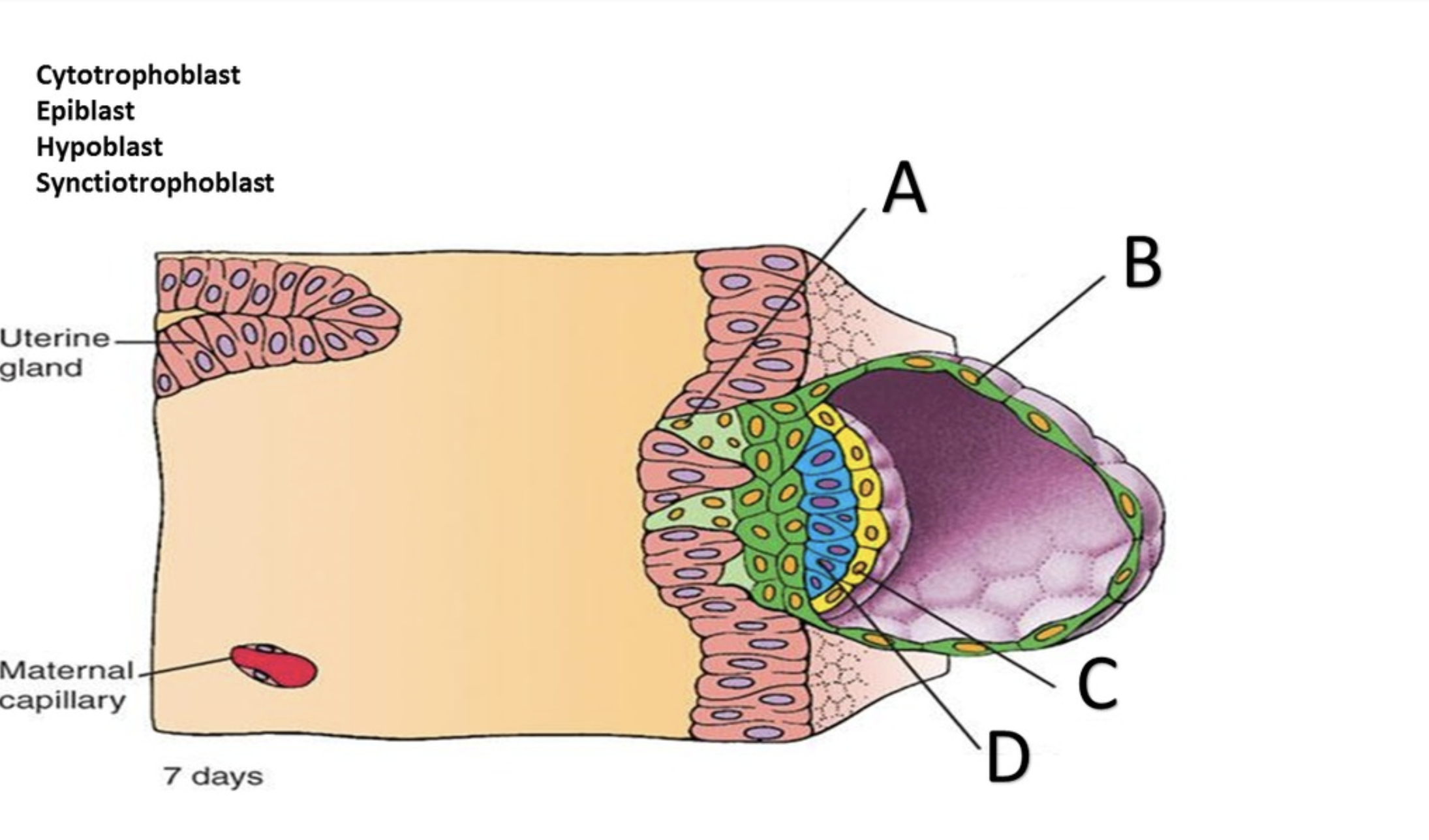
Hypoblast
C
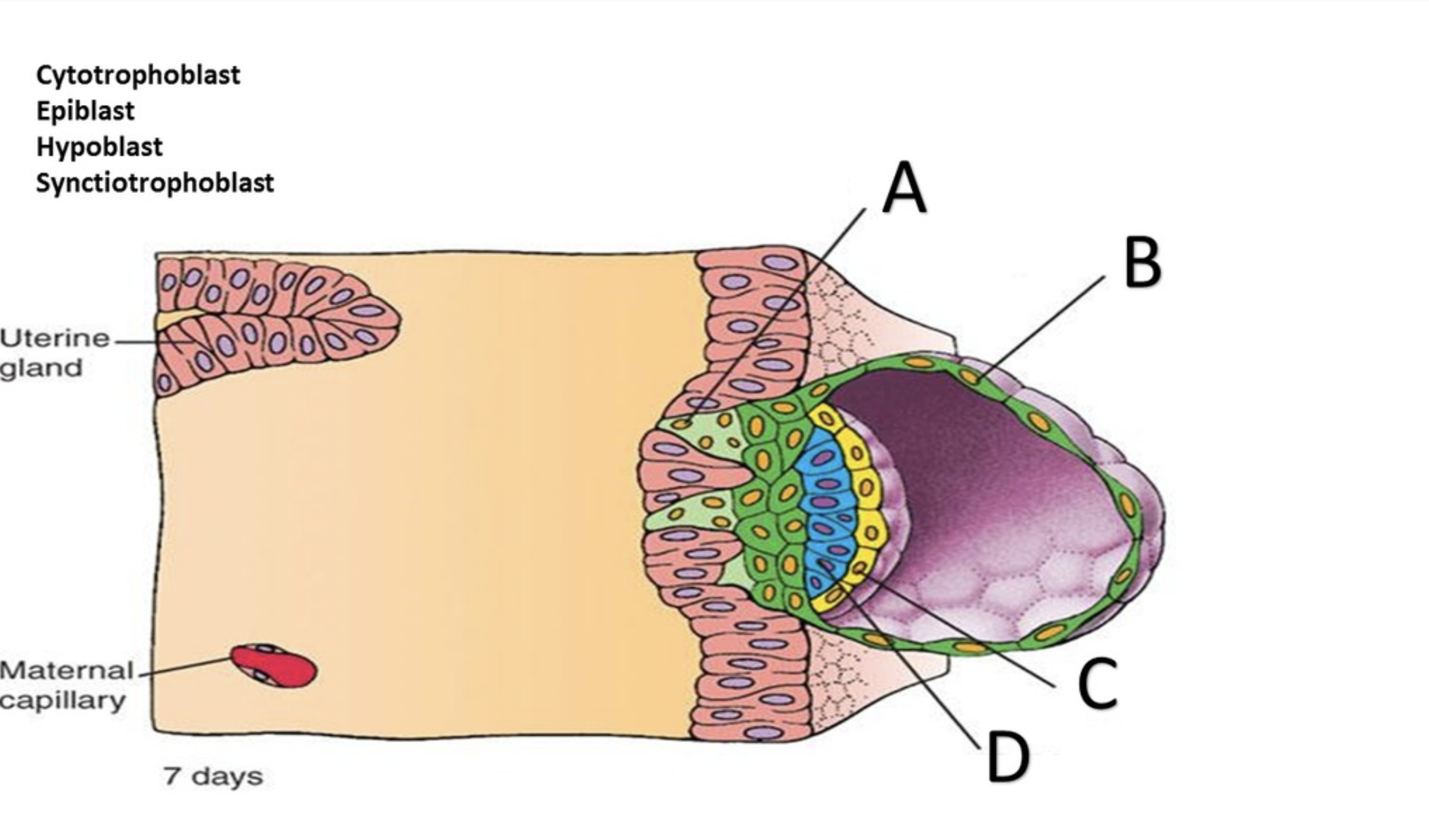
Epiblast
D
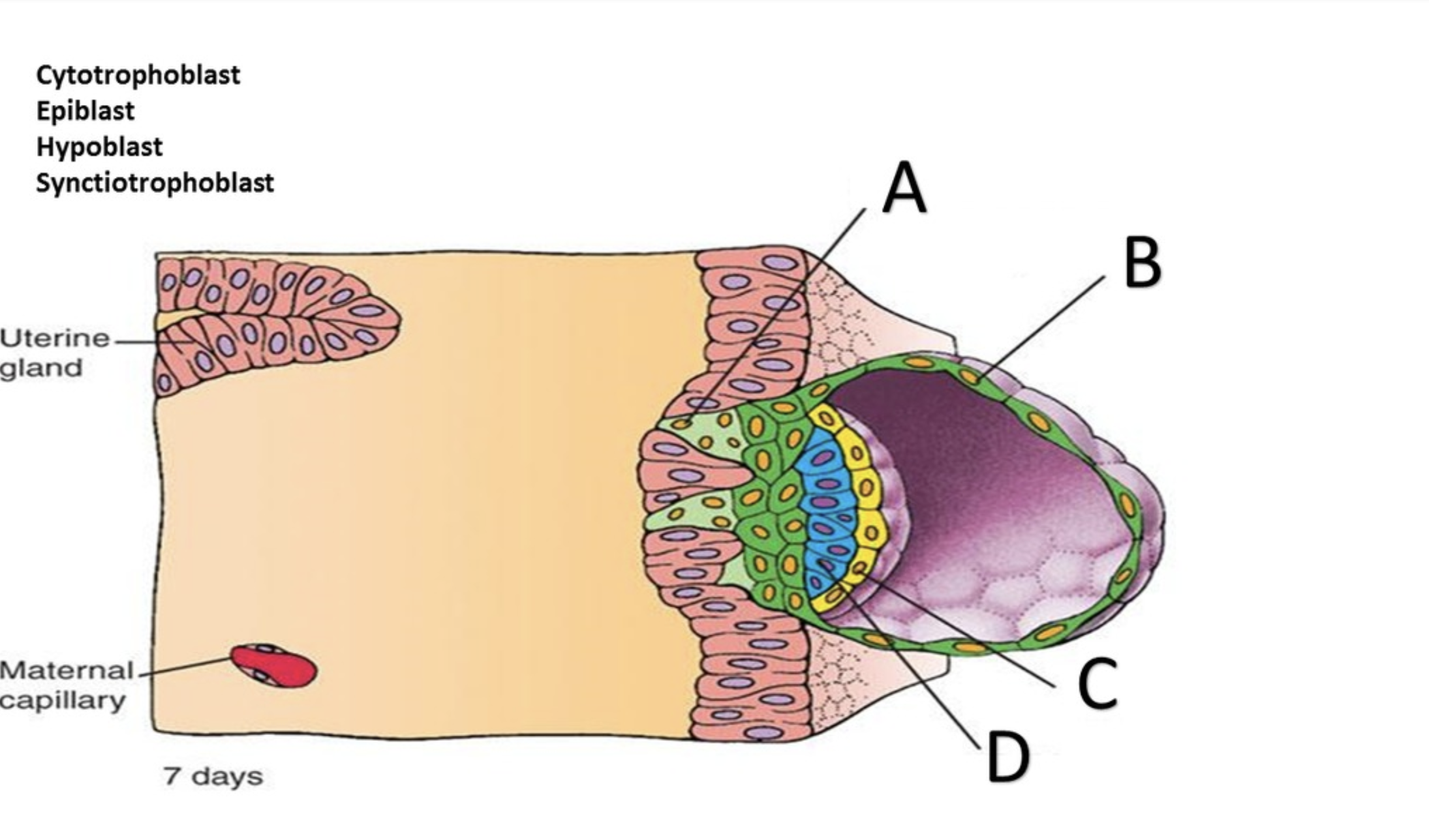
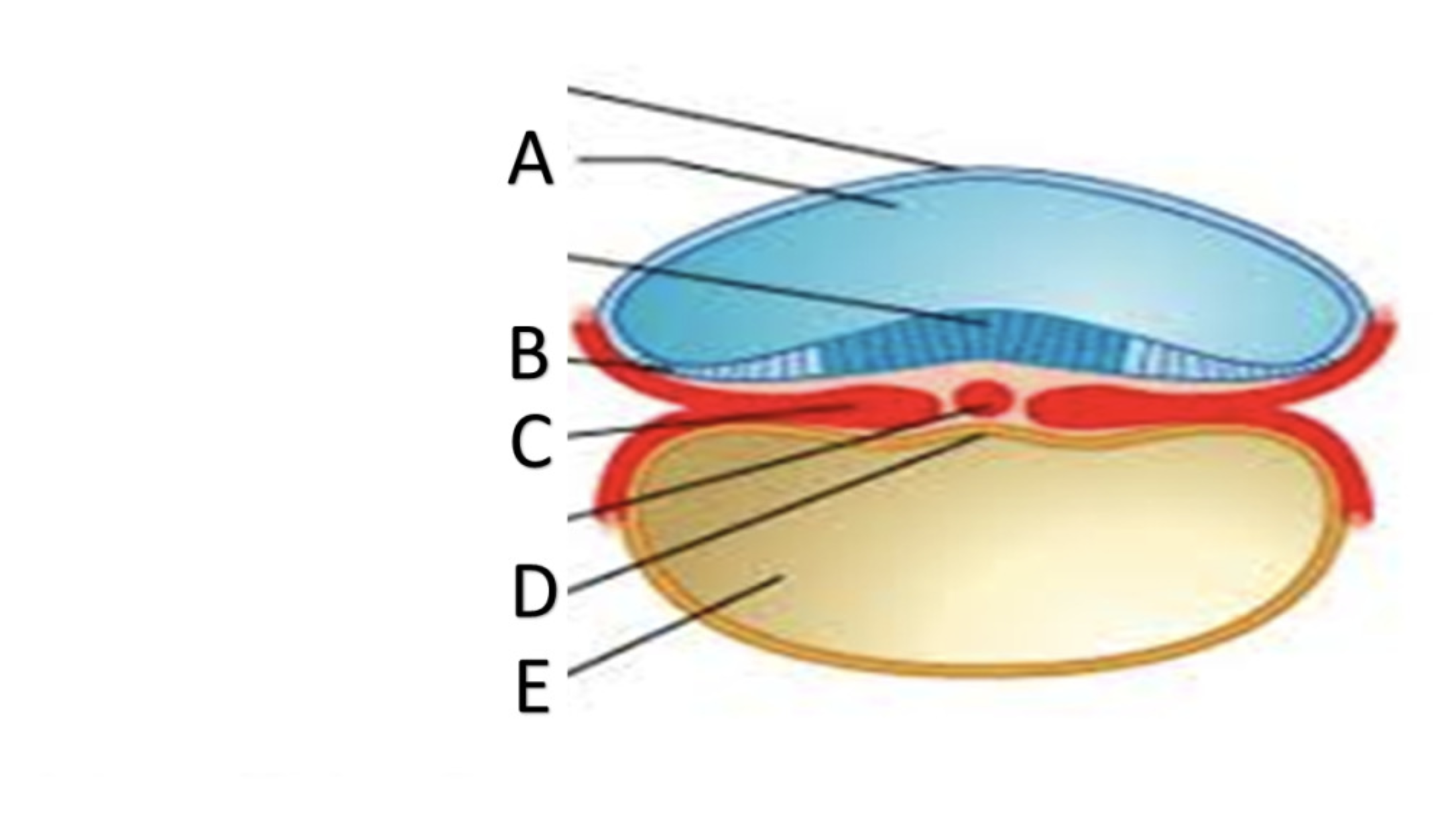
Amniotic cavity
A
ectoderm
B
Mesoderm
C
Endoderm
D
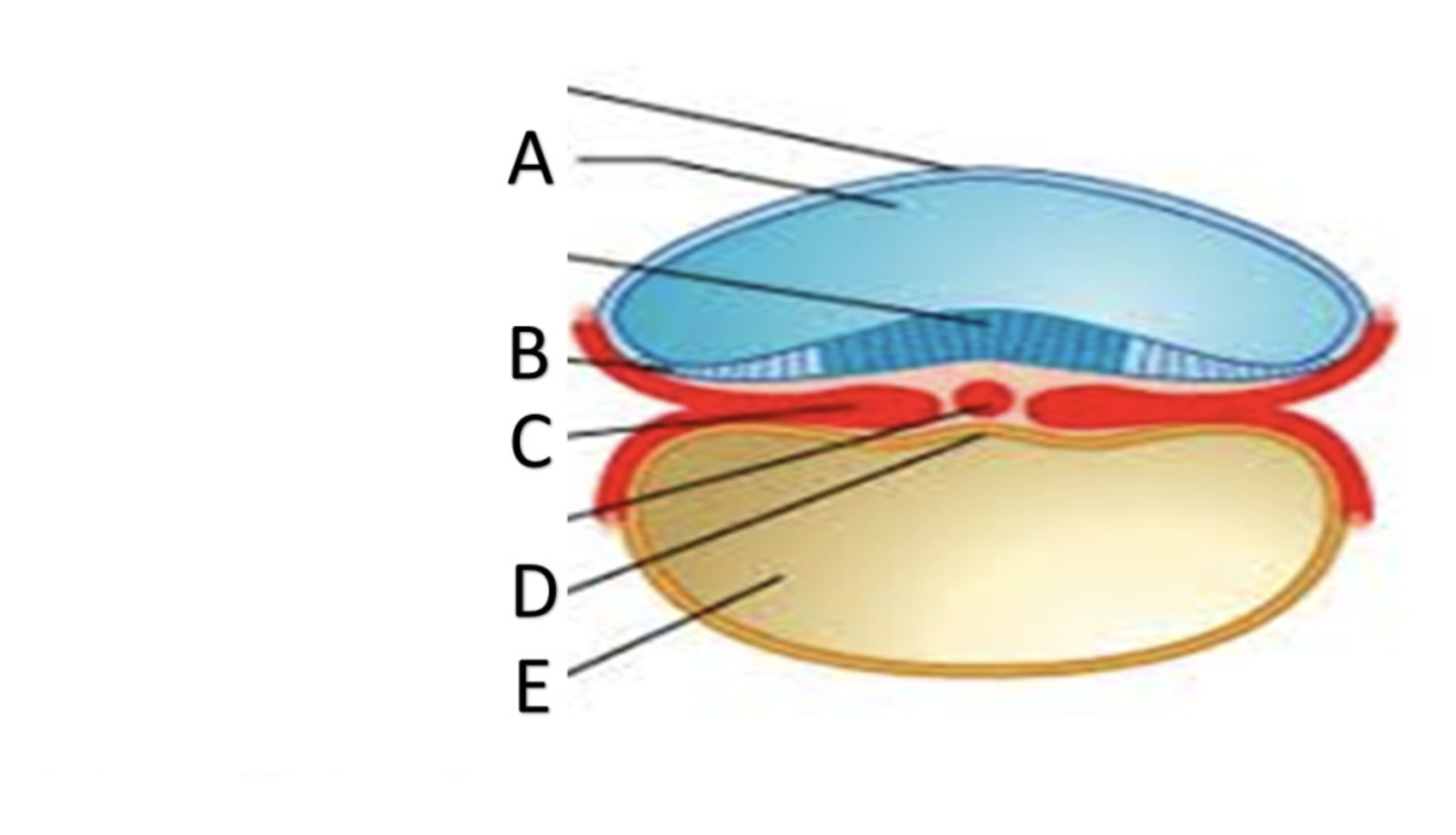
Yolk Sac
E
Fetus
By the end of the 8 weeks, all of the organ systems are present, the individual is about 3 cm long, and is now considered a ____
Organogenesis
The germ layers differentiate into organs and organ systems
Uterine Milk
The conceptus absorbs this fluid as it travels down the tube and lies free in the uterine cavity?
Trophoblastic Nutrition
The conceptus it consumes so-called decidual cells of the endometrium?
Placental Nutrition
Nutrients diffuse from the mother’s blood through the ______ into the fetal blood?
Uterine Milk
The accumulating fluid forms the blastocoel?
Trophoblastic Nutrition
Progesterone from the corpus luteum stimulates these cells to proliferate and accumulate a store of glycogen, proteins, and lipids?
Placental Nutrition
Consisting of chorionic villi embedded in the mother’s endometrium?
Trophoblastic Nutrition
The syncytiotrophoblast digests these cells and supplies the nutrients to the embryoblast?
Placental Nutrition
Begins to develop about 11 days after conception, becomes the dominant mode of nutrition around week 9, and is the sole mode of nutrition from the end of week 12 until birth?
Trophoblastic Nutrition
Is the only mode of nutrition for the first week after implantation and remains the dominant source through the end of week 8?
Uterine Milk
Is the only mode of nutrition from fertilization through implantation?
Ductus Venosus
____ turns into the ligamentum teres?
Ductus Arteriosus
____ turns into the ligamentum arteriosum?
Foramen ovale
_____ turns into the fossa ovalis?
fertilization
Blue
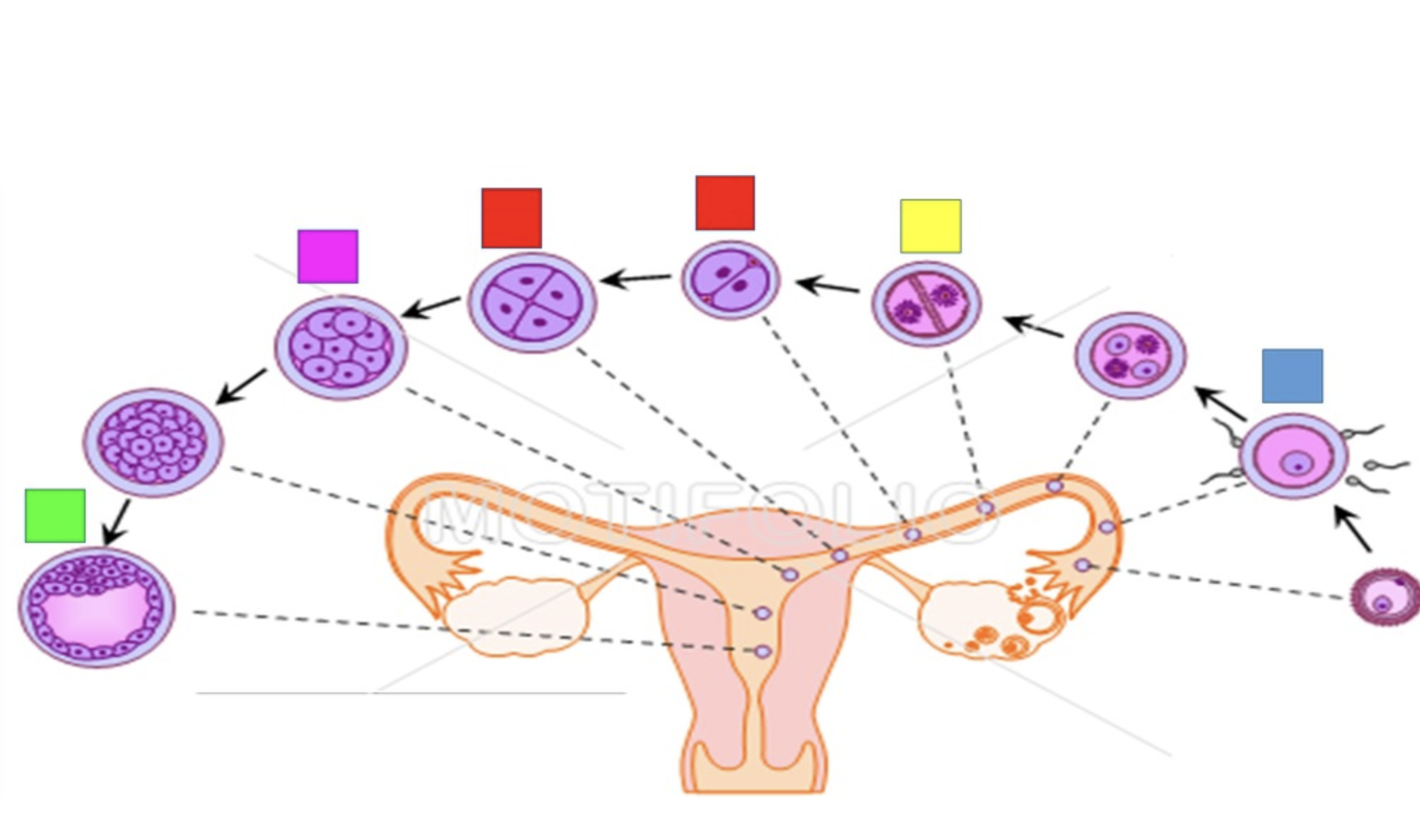
cleavage
yellow
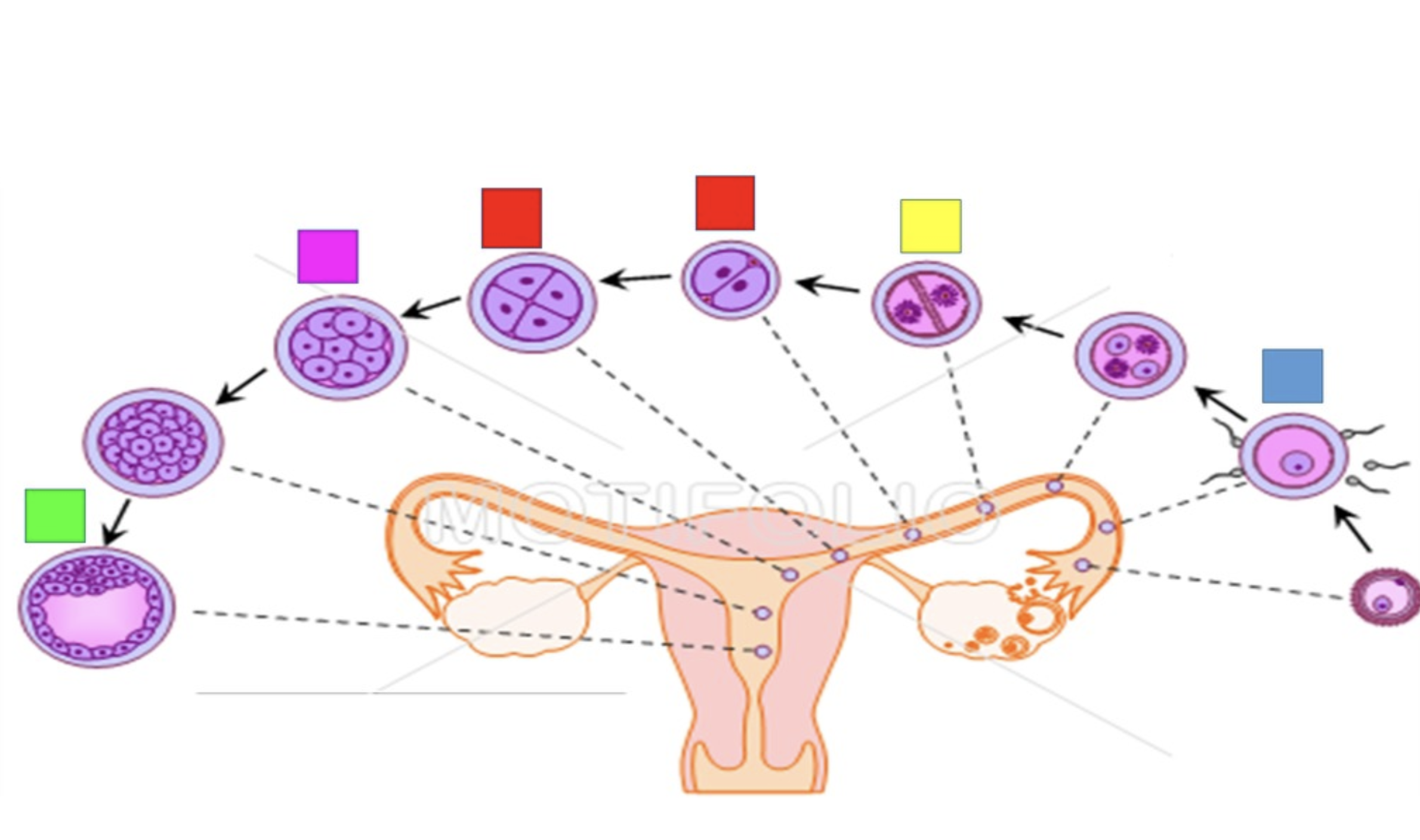
blastomere
red
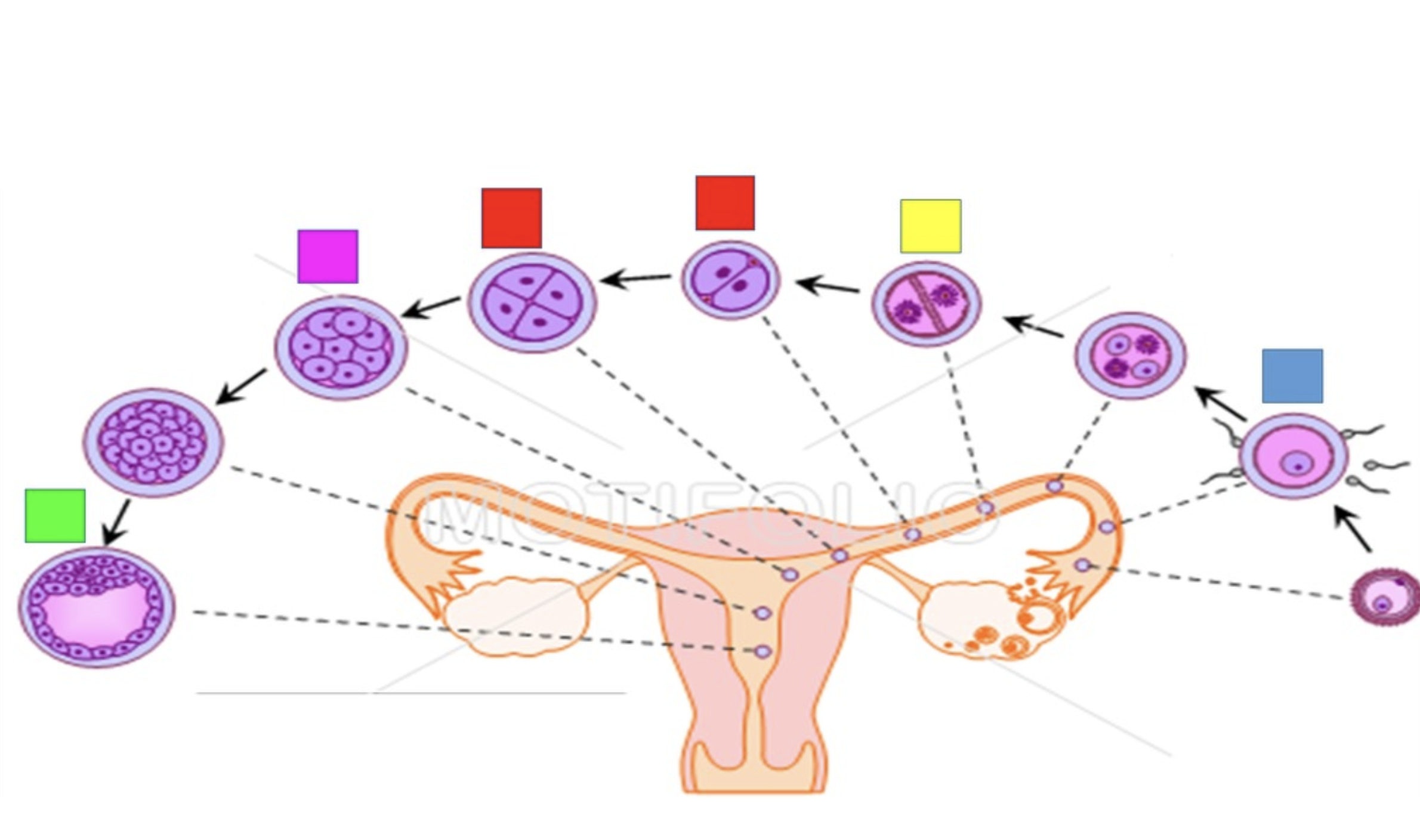
morula
pink
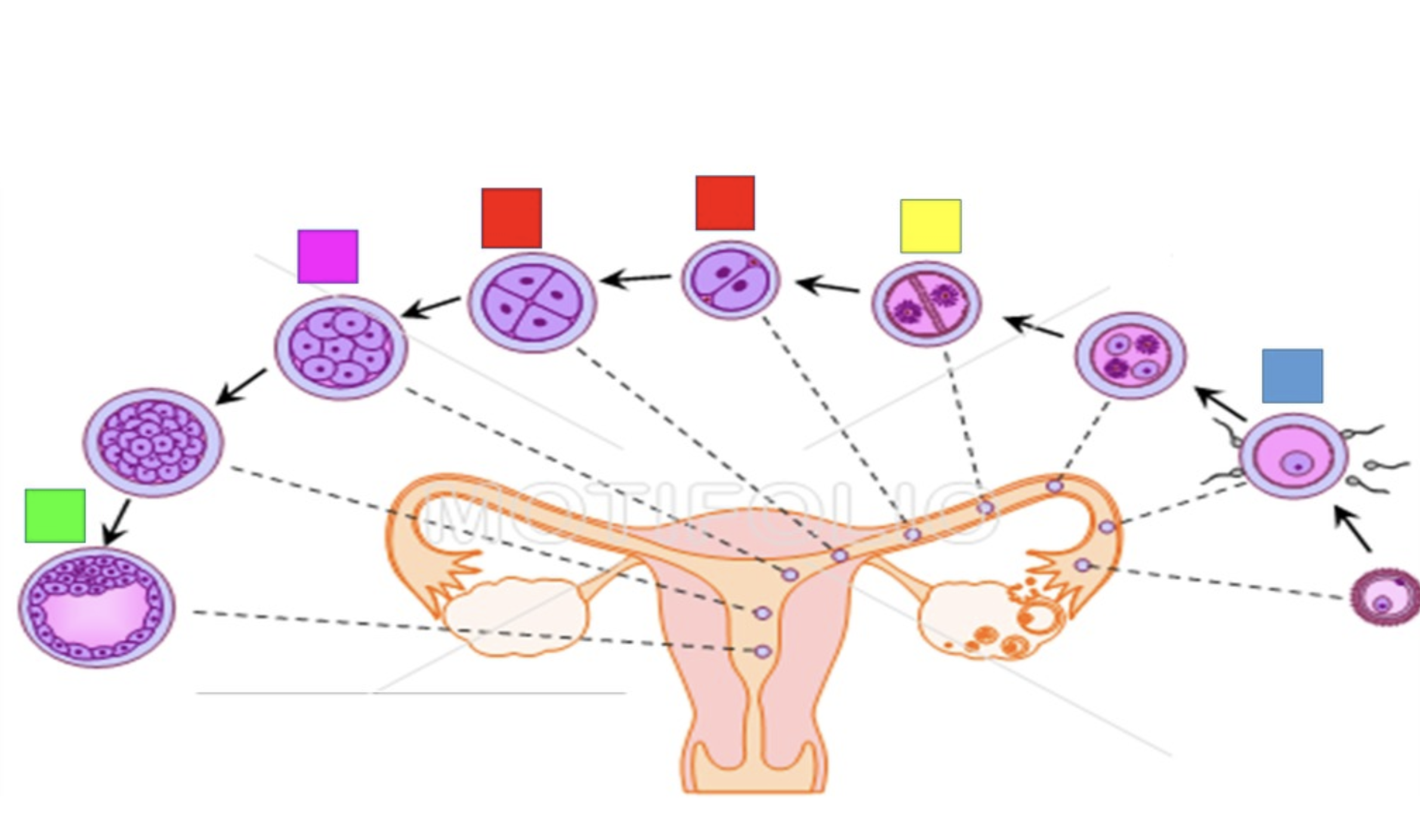
Blastocyst
green
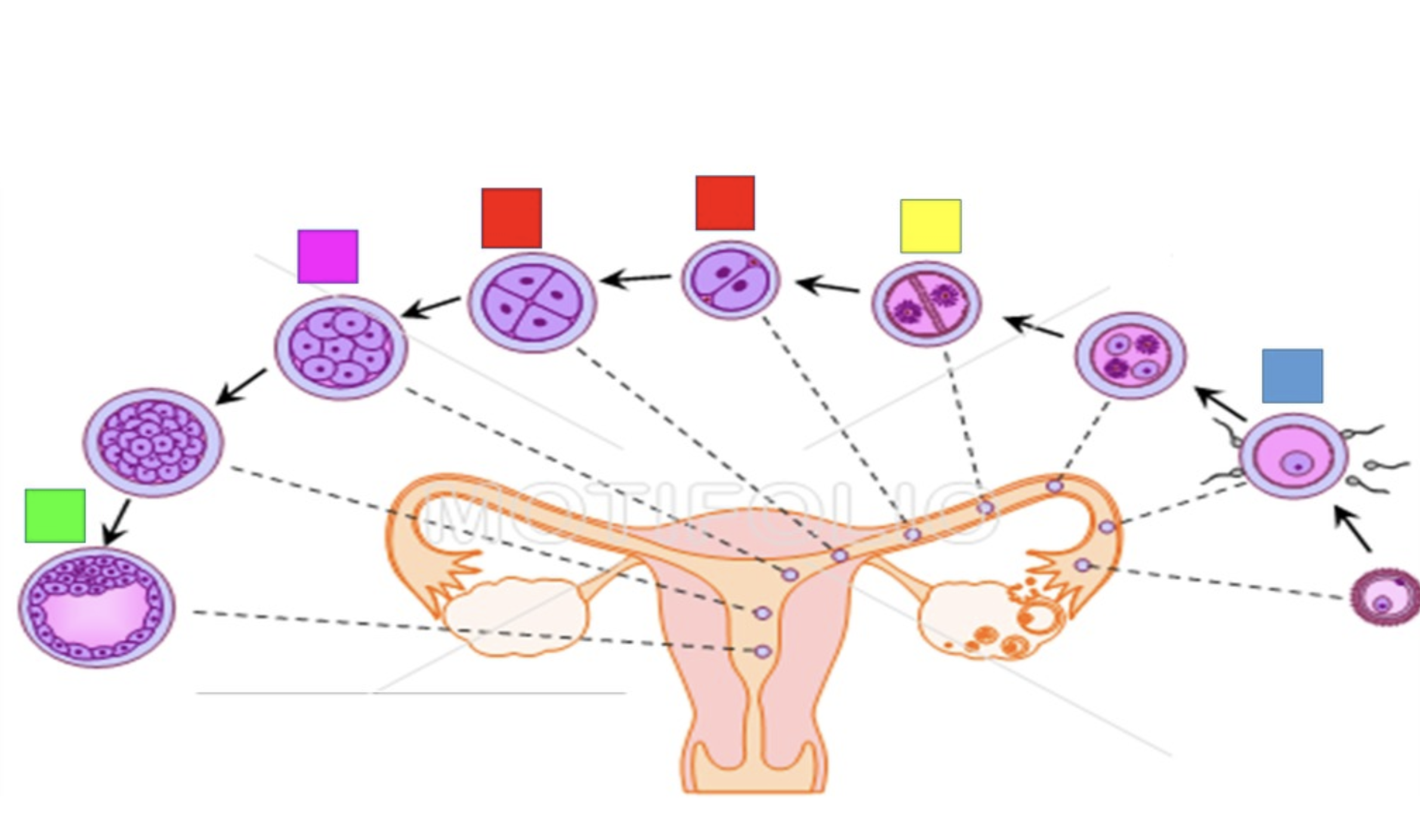
embryo
A developing individual is first classified as a _____ when the three primary germ layers have formed.
Syncytiotrophoblast
the outer cell mass of a blastocyst, concerned with anchoring and nourishing the embryo, is called the _____?
Uterine Milk
Prior to implantation, a conceptus is nourished by_____?
amniotic fluid
The fetus floats in _____, composed in large part of its own urine
ductus arteriosus
Prior to birth, a shunt called the _____ is between the pulmonary trunk and the aortic arch, allowing blood to bypass the lungs.
chorion
The placenta is composed partly of maternal tissue and partly of. the ______, one of the four embryonic membranes
implantation
attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall
morula
when a conceptus arrives in the uterus, it is at what stage of development?
blastocyst
the stage of the conceptus that implants in the uterine wall
amnion
Fetal urine accumulates in the _____ and contributes to the fluid there
trophoblastic nutrition
For the first 8 weeks of gestation, a conceptus is nourished mainly by?
teratogen
viruses, drugs, and radiation the cause congenital anatomical deformities are called?
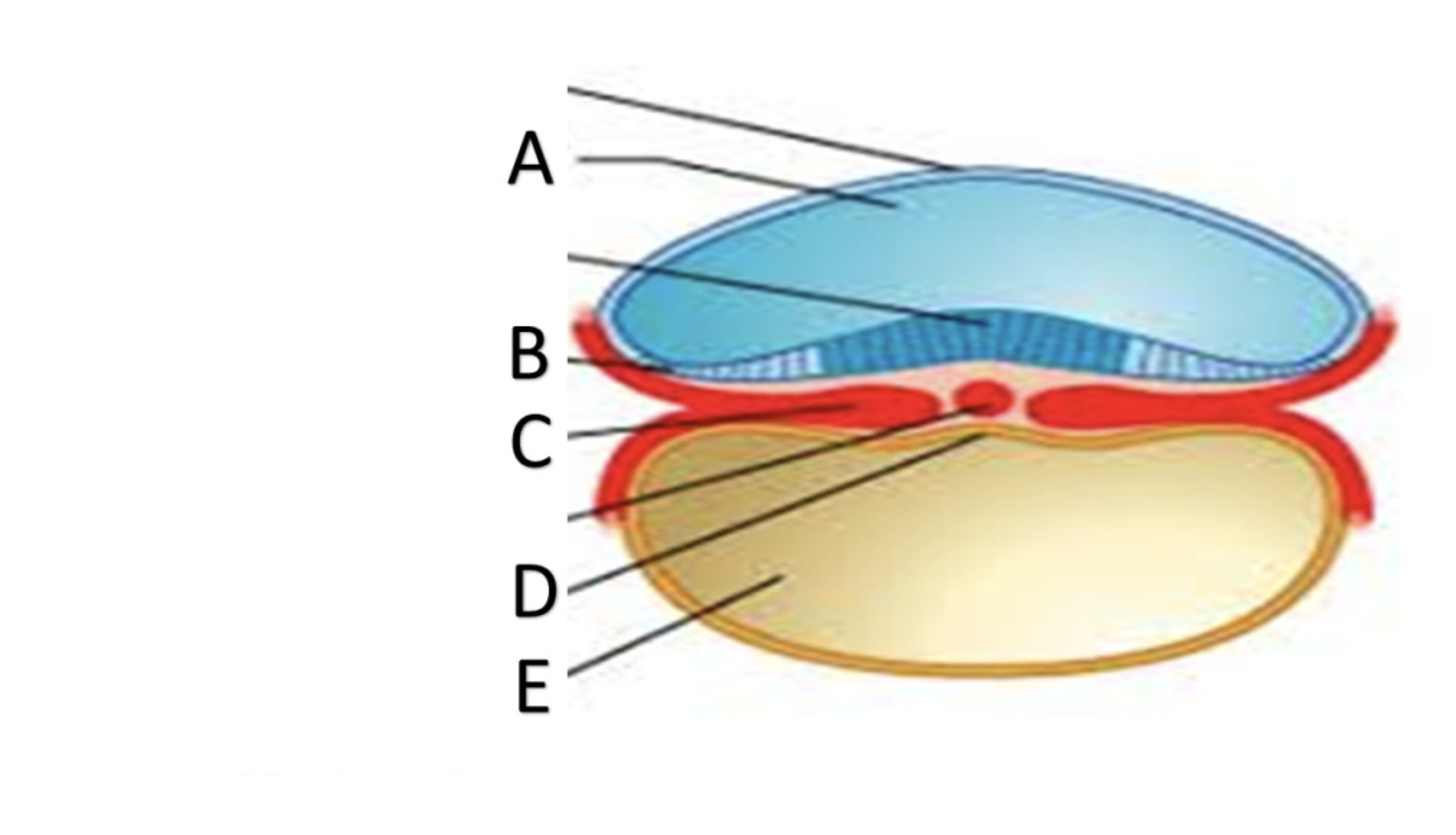
blastocoel
A
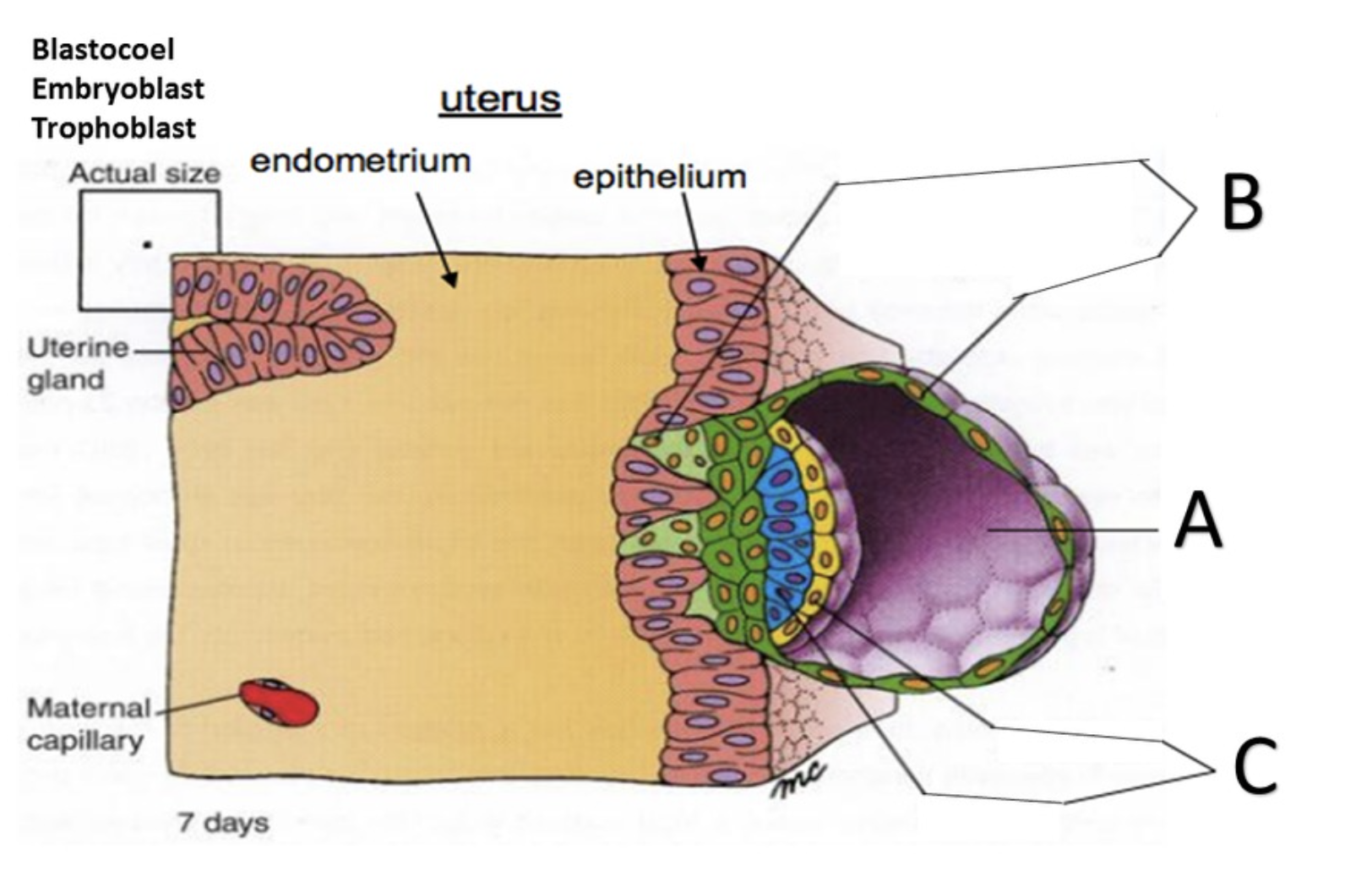
Trophoblast
B
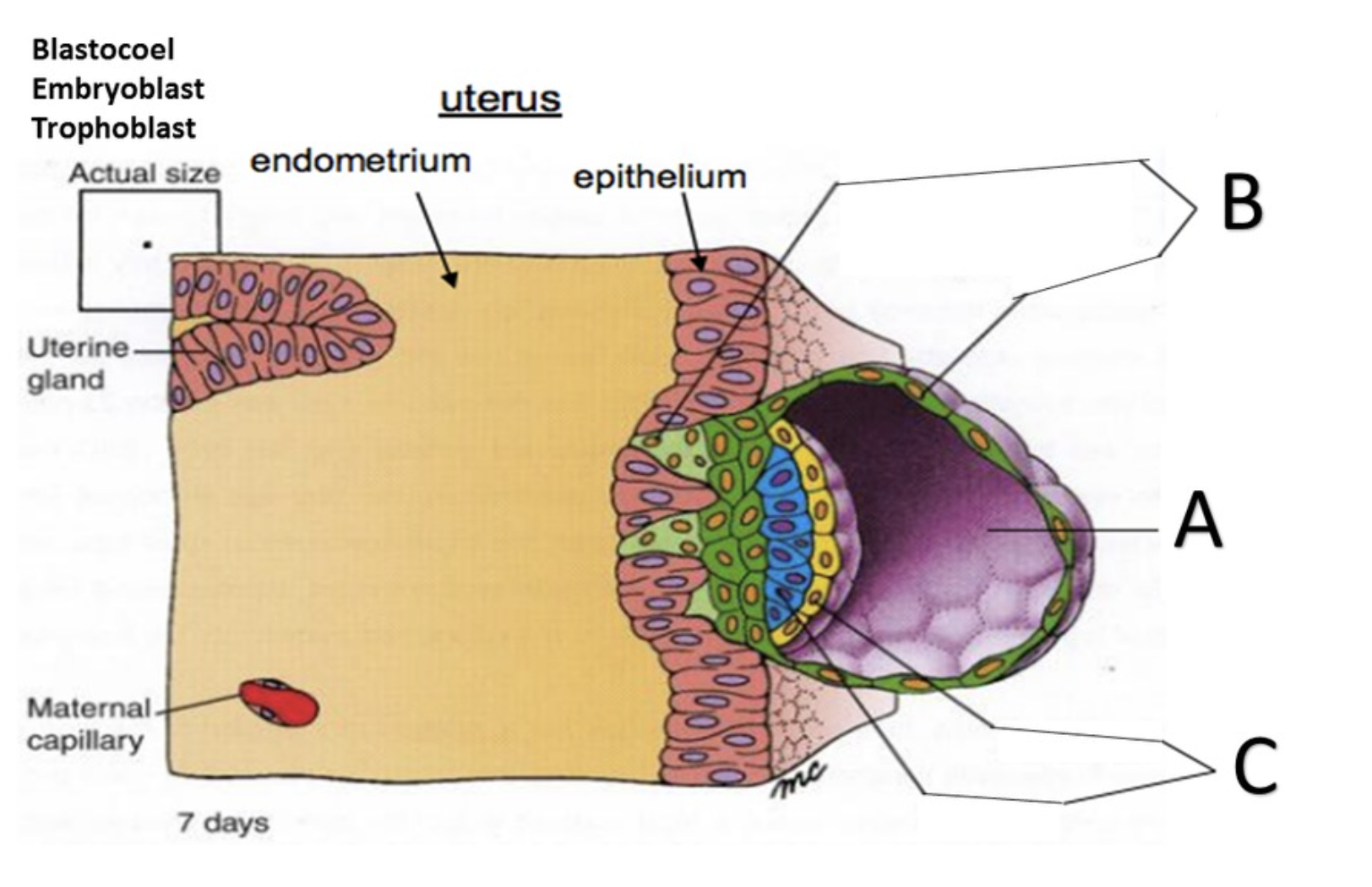
Embryoblast
C
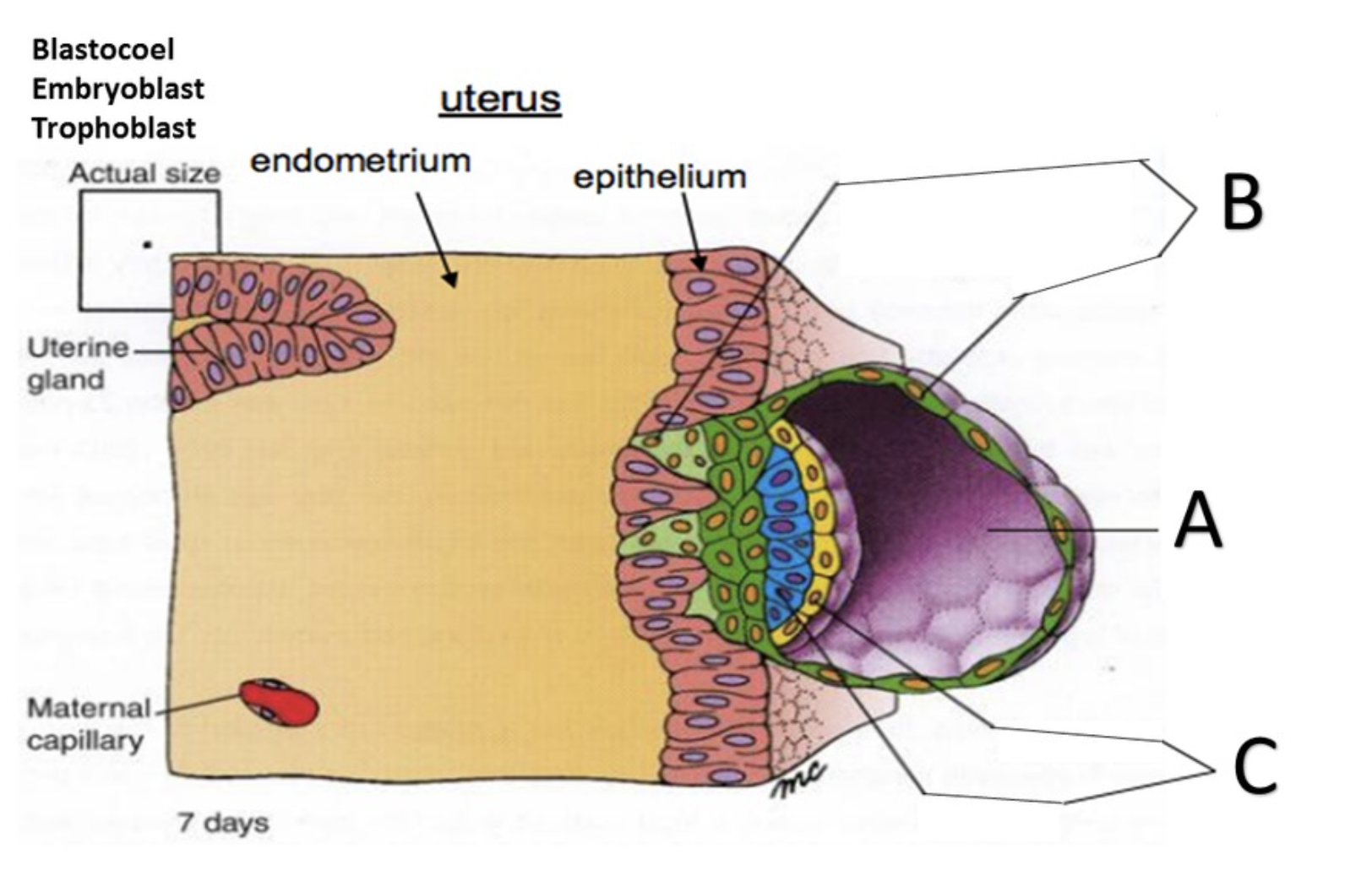
Syncytiotrophoblast
In the superficial layer, in contact with the endometrium, the plasma membranes break down, and the trophoblast cells fuse into a multinucleate mass called the ______?
Cytotrophoblast
the deep layer, close to the embryoblast, is called the ______ because it retains individual cells divided by membranes.
hCG
Stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete estrogen and progesterone, which suppresses menstruation
chorion
outermost membrane, enclosing all the rest of the membranes and the embryo
yolk sac
sac arises from hypoblast
allantois
begins as an outpocketing of the yolk sac
amnion
sac that develops from cells of the epiblast
chorion
the villous _____ forms the fetal portion of the placenta
amnion
contains fluid which protects the embryo
yolk sac i
contributes to the formation of the digestive tract and produces the first blood cells and future egg or sperm cells
Allantois
it forms the foundation for the umbilical cord and becomes part of the urinary bladder