Electrostatics 1
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Charge, Coulomb's Law
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Strong Nuclear Force is _______ than Electrostatic Force
much stronger, responsible for holding protons and neutrons together in an atomic nucleus.
What is Charge? (two definitions)
It is the property of a material due to which it produces and experiences electric and magnetic effects.
It is the excess and deficiency of electrons in a body.
Negatively charging is a mass-______ process.
Positively charging is a mass-______ process.
increasing
decreasing
1 Coulomb = ______ esu (electrostatic unit)
3 × 109
Is charge a scalar or vector quantity?
Charge is a scalar quantity.
How do you figure out the charge if you have the number of electrons?
Q = ne
How do you figure out the number of electrons if you have the charge?
Q = ne
What is the smallest stable unit of charge?
electron!
Where is charge inside a conductor?
On the surface !
Why can’t insulators be converted to conductors?
They could have been converted to conductors at high temperature or potential difference but usually their burning point is lower than their breakdown point.
Formula for mass with change in velocity?
where m0 is rest mass, v is the velocity and c is the speed of light.
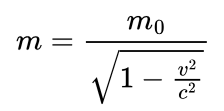
How many fields does a charge produce in its various states of motion?
At rest, a charge produces an electric field only.
At constant non-zero velocity, a charge produces an electric field and magnetic field both?
With acceleration, a charge produces an electric field, a magnetic field, and electromagnetic waves.
How is repulsion the true test of charge?
There will be attraction between a charged body and a neutral body due to induction, but if two bodies are repelling each other, BOTH of them HAVE to be charged.
If two bodies are attracted, at least one of them have to be charged. If two bodies are repelled, both of them have to be charged.
What are the 6 ways a body can be charged?
Friction
Conduction
Induction
Field emission
Thermal emission
Photo-electric emission
Talk about charging by friction.
Both conductor and insulator can be charged
Physical contact is a must
Out of the two bodies, the one which has less binding energy will get positively charged, and the other one will get negatively charged.
Talk about charging by conduction.
Only conductors can be charged
Physical contact is a must
Charge is distributed across both bodies
Talk about charging by induction.
Only conductors can be charged
No physical contact is required
The mechanism
Talk about charging by field emission.
If we put a conducting body in an electric field then there will be some polarisation in the conducting body.
If the intensity of the field is high enough, electrons get emitted from the conducting body and the body becomes positively charged
Only positively charging is possible
Only conductors can be charged
Talk about charging by thermal emission.
If we provide heat to the surface of a metal body, then the electrions on the outer shell of atoms collect that energy and get emitted from the metal body, if the heat energy is greater than binding energy.
Bodies get positively charged.
What is Coulomb’s Law?
If there are two point charges placed at some separation, both charges will experience equal and opposite forces.
Formula for Coulomb’s Law?
Where ‘k’ is Coulomb’s Constant and ‘r’ is the distance between the two point charges.
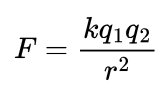
Vector form of Coulomb’s Law?
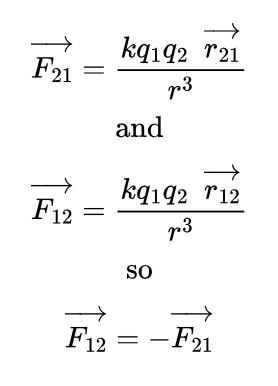
Why is Coulomb’s Law only applicable to point charges?
Continuous bodies don’t have a fixed distance between the centres of charge (due to induced polarisation).
Do you remember that Electrostatic Force is a central force which means that angular momentum is conserved?
Yes.
What does electrostatic force depend on besides charge and distance?
density of medium
polarisation ability
The denser the medium is, the smaller the force is.
The higher the polarisation ability is, the small the force is. (I think)
value of k0?
9 × 109
Formula for Volumetric Charge Density?
Where ‘q’ is the total charge and ‘V’ is the total volume.
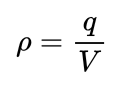
Formula for Arial Charge Density?
Where ‘q’ is the total charge and ‘A’ is the total surface area.
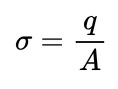
Formula for Linear Charge Density?
Where ‘q’ is the total charge and ‘L’ is the total length.
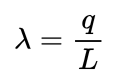
Why isn’t volumetric charge density seen on conductors?
Because in conductors the charge resides on the surface so only arial charge density and linear charge density can apply.
Formula for electrostatic force on a continuous body due to a point charge in colinear position?
where ‘r’ is the distance between the point charge to the line charge and ‘l’ is the length of the line charge.
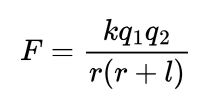
If two charges are hinged from a single point through an insulating wire then the angle of deflection depends on?
The angles depend only on the mass of the charges. Greater the mass, lesser will be the angle of deflection.
If there are two like charges ‘Q1’ and ‘Q2’ and there is a third unlike charge ‘q’, and the distance between ‘Q1’ and ‘Q2’ is ‘r’ and the distance between ‘Q1’ and ‘q’ is ‘x’, then what is the value of ‘x’ for which ‘q’ is in equilibrium?
It does not depend on the magnitude of charge of ‘q’.
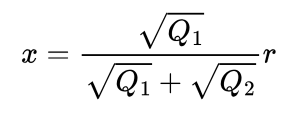
If there are two like charges ‘Q1’ and ‘Q2’ and there is a third unlike charge ‘q’, and the distance between ‘Q1’ and ‘Q2’ is ‘r’ and the distance between ‘Q1’ and ‘q’ is ‘x’, then what is the magnitude of charge of ‘q’ for which ‘q’ is in equilibrium?
It does not depend on ‘x’ or ‘r’.
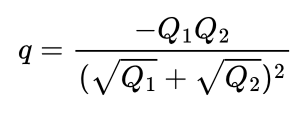
If there is a charge ‘q’ at each vertex of an equilateral triangle of side length ‘a’, what should be the magnitude of charge of ‘Q’ placed at the centre of the triangle?
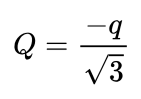
If there is a charge ‘q’ at each vertex of a square of side length ‘a’, what should be the magnitude of charge of ‘Q’ placed at the centre of the square?
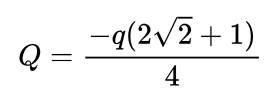
Setup: two charges are hinged at a single point by insulating threads of same length.
If the whole setup is taken into an artificial satellite where g is basically 0, what is the angle between the two threads?
180 degrees.