6. Crystal Structures I
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is a crystalline material?
It has atoms arranged in a repeating array, exhibiting long-range order. Examples include metals, many ceramics, and some polymers.
What is a unit cell?
The repeating entity that defines the structure in a crystalline solid. Examples: BCC, FCC, and HCP.
What are the characteristics of a unit cell?
Number of atoms per unit cell.
Coordination number: Number of nearest-neighbor atoms.
Atomic packing factor (APF): Volume of atoms in the unit cell per volume of the unit cell
What is the atomic packing factor (APF)?
APF = (Volume of atoms in the unit cell) / (Volume of the unit cell). It indicates how efficiently atoms are packed in a structure.
How many atoms are in a BCC unit cell?
2 atoms
What is the coordination number and APF of a BCC structure?
Coordination Number: 8
APF: 0.68
How many atoms are in an FCC unit cell?
4 atoms
What is the coordination number and APF of an FCC structure?
Coordination Number: 12
APF: 0.74
How many atoms are in an HCP unit cell?
6 atoms
What is the coordination number and APF of an HCP structure?
Coordination Number: 12
APF: 0.74
What is theoretical density, and how is it calculated?
The mass of atoms in a unit cell divided by its volume.
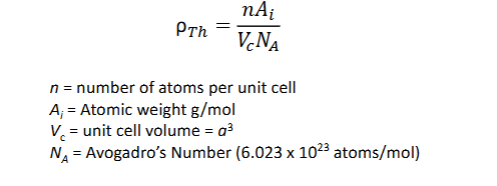
How does crystal structure affect mechanical properties?
Properties like Young’s modulus, resilience, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and toughness depend on bond strength and atomic packing.
What are examples of materials with BCC, FCC, and HCP structures?
BCC: Chromium, iron (α-iron), molybdenum.
FCC: Aluminum, copper, gold.
HCP: Cadmium, cobalt, zinc.
How do the close-packed directions differ in BCC, FCC, and HCP?
BCC: Along cube diagonals.
FCC: Along face diagonals.
HCP: Along diagonals of the hexagonal face.
What is crystal structure
Spatial arrangment of atoms in crystalline solids
What is crystal morphology
shape and size of crystals or grains (e.g. coarse, elongated or columnar, equiaxed, fine)