Tropical Rainforest
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
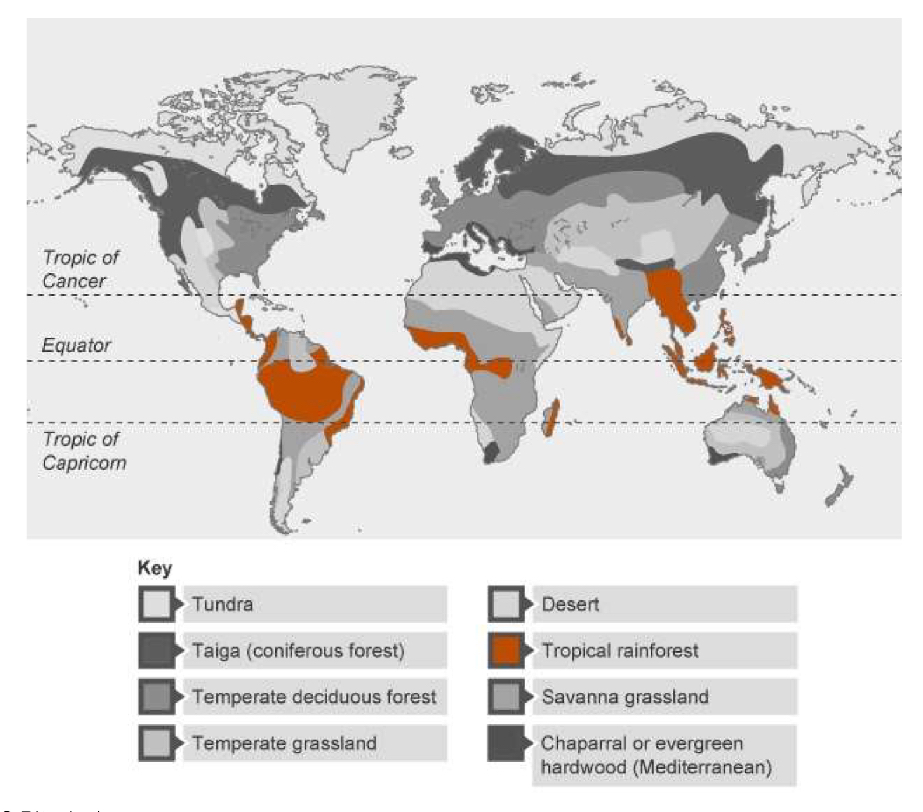
What is the distribution of a tropical rainforest?
Found in a large band surrounding the equator
What is the climate like in tropical rainforest?
The climate is the same all year round there is no definite season
The temperature is between 20 to 28°C and only varies by a few degrees over the year. This is because the suns energy is more intensely the equator as it is overhead all year round.
Rainfall is very high around 2000 mm per year it rains every year
What are the plants like in tropical rainforest?
Most trees are evergreen to help them take advantage of the continual growing season
Many trees are really tall and the vegetation cover is dense very little light reaches the forest floor
There are lots of epiphytes which are plants that grow on other living plants and take nutrients and moisture from the air e.g orchids and ferns
What are people like in tropical rainforest?
Many indigenous people have adapted to life in the rainforest
They make a living by hunting and fishing gathering nuts and berries and growing vegetables in small garden plots
How is soil like in tropical rainforests?
The soil isn’t very fertile as heavy rain washes nutrients away
There are surface nutrients due to decayed leaf fall but the layer is very thin as decay is fast in the warm moist conditions
Define biodiversity
is the variety of organisms living in a particular area
What percentage of plant animal and insect species do rainforest hold
50% as they have high biodiversity
How are rainforest stable and productive?
as the climate is constant it is hot and wet all the time meaning plants and animals don’t have to cope with changing conditions as there is always plenty to eat
How do bacteria and plants interdepend in tropical rainforest
The warm, wet climate encourages rapid decomposition by fungi and bacteria on the forest floor. Dead plants and animals are broken down quickly, releasing nutrients into the soil. This makes the surface soil nutrient-rich, allowing plants to grow easily.
Plants absorb these nutrients and pass them on when eaten by animals. The dense vegetation provides plenty of food, so animal populations are large. When animals and plants die, decomposers return the nutrients to the soil, completing the nutrient cycle and maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
explain how the agouti brazil nut tree and cecropia tree and Azteca ants show interdependence in a tropical rainforest
Many species also form symbiotic relationships, showing further interdependence:
Agouti and Brazil nut tree: The agouti is one of the only animals able to open the hard seed pods of the Brazil nut tree. It eats some of the nuts but buries others, helping new trees to grow. This allows both species to benefit.
Cecropia tree and Azteca ants: The Cecropia tree provides food and shelter for the Azteca ants. In return, the ants protect the tree from insects and vines (lianas) that could harm it. Both species depend on each other for survival.
How are humans interfering with these ecosystems?
Changes to one part of a rainforest ecosystem can have knock on effect on the whole ecosystem for example cutting down trees deforestation can contribute to climate change
Trees intercept and take up a lot of water and release it back into the atmosphere producing moisture further rainfall reducing trees cover may increase the risk of drought affecting the plants and animals that live in the rainforest ecosystem
Trees stabilise soil with their roots and provide nutrients when they drop their leaves with fewer trees. The soil would have less protection from heavy rainfall the few nutrients present would wash away more easily and plant wood struggle to grow.
What are plant tropical rainforest adapted to?
Plants in the rainforest are adapted to high rate for high temperatures and competition for light
Describe how plants have adapted
Trees compete for sunlight by growing tall
Plants have thick, waxy leaves with pointed drip tips that channel rainwater to the tip, encouraging run-off. This prevents the weight of water from damaging the leaves and stops fungi and bacteria from growing in standing water. The waxy coating also helps to repel rain, protecting the leaf surface.
Climbing plants such as Leanna’s used tree trunks to reach sunlight
Many trees have smooth thin buck and then no need to protect the trunk from cold temperatures. The smooth surface also helps water to run off easily.
Large stable buttress root support the tall tree trunks
Plants drop their leaves graduated through throughout the year meaning they can go on growing all year round
What are animals in tropical rainforest adapted to?
Finding food and escaping predators
How are animals adapted
Many animals spend their lives high in the canopy. They have strong limbs to move easily between trees, e.g. howler monkeys. Some birds, like the harpy eagle, have short, pointed wings to help them manoeuvre through dense trees.
Other animals have special features for climbing — tree frogs have suction cups, while flying squirrels have flaps of skin that help them glide between trees.
Camouflage helps species like the leaf-tailed gecko blend in with leaves to avoid predators. Some animals, such as anteaters, are adapted to low light levels on the forest floor and have a strong sense of smell to find food.
Many are nocturnal, such as sloths, which feed at night when it’s cooler to save energy. Others, like jaguars, can swim, helping them cross river channels to hunt and survive in their habitat.
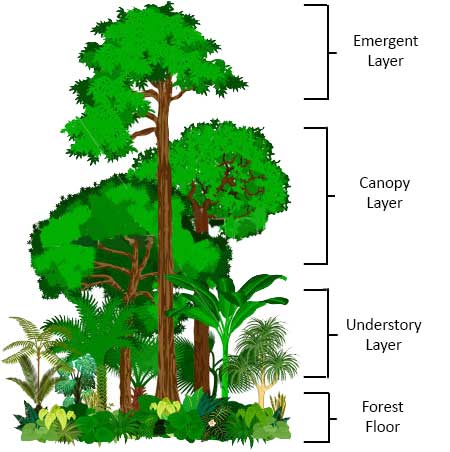
What are the four layers of a rainforest?
Emergent layer: Tallest trees (up to 50 m) get the most sunlight and face strong winds. Example: Kapok tree, harpy eagle nests here.
Canopy layer: Dense layer of trees forming a roof that gets most sunlight and rainfall. Most animals live here — e.g. howler monkeys and sloths.
Under-canopy (understory): Shaded, with smaller trees and shrubs that grow in canopy gaps. Example: jaguarsand tree frogs live here.
Forest floor: Dark, hot, and damp with little light. Covered in decomposing leaves that add nutrients to the soil. Example: anteaters and fungi found here.
Why should tropical rainforests be protected?
Rainforests provide many valuable resources, such as rubber, coffee, chocolate, and medicines. If species become extinct, it becomes harder to discover new medicines and develop new products.
Sustainable development, such as ecotourism, can bring long-term economic benefits to rainforest countries without causing lasting damage.
Protecting rainforests also helps reduce the greenhouse effect, as trees absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) and release oxygen. Deforestation increases CO₂ levels, contributing to climate change, which affects all countries, not just those where deforestation occurs.
Rainforests also help regulate the Earth’s climate and water cycle. Without them, the risk of droughts and flooding in some regions increases.
What are the 6 ways tropical rainforest can be sustainably managed
replanting
selective logging
ecotourism
education
conservation
reducing debt
international hardwood agreement
how can replanting sustainably manage rainforest?
Replanting (also called afforestation) is when new trees are planted to replace those that have been cut down. This helps to maintain the forest cover and ensure that the rainforest ecosystem can recover.
It means future generations will still be able to use the rainforest’s resources, such as timber, without permanently damaging the environment.
Replanting also helps absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂), reducing the greenhouse effect, and keeps the nutrient and water cycles balanced.
Some countries make sure that for every tree cut down, several new ones are planted, keeping deforestation sustainable.
how can selective logging sustainably manage rainforest?
Selective logging means only certain trees are cut down, usually the oldest or most valuable, while the majority of trees remain standing. This makes it much less damaging than clear-felling, because the forest structure and canopy stay intact, protecting the soil from erosion and allowing young trees to grow beneath.
By keeping most of the forest in place, biodiversity is maintained, and the forest can regenerate naturally. It also means the rainforest can continue to provide resources like timber in the long term, making it a sustainable way to use the forest.
Some countries also use horse or helicopter logging which(where horses or helicopters drag felled trees out the forest) avoids building large roads and causes minimal damage to surrounding trees and soil.
how can ecotourism sustainably manage rainforest?
Ecotourism minimises damage to the environment and benefits local people. Only small groups of visitors are allowed into areas at a time, and strict rules are used to reduce environmental impacts — for example, ensuring waste and litter are disposed of properly to avoid polluting land and water.
Ecotourism provides a sustainable source of income for local people, who can work as guides, provide accommodation, or transport. This means they don’t need to cut down trees or farm to make money.
It also raises awareness of conservation and brings in money to help protect the rainforest. For example, ecotourism in Costa Rica has been very successful — it is the country’s largest source of income and has led to over 20% of the country being protected from development.
how can education sustainably manage rainforest?
Educating both the international community and local people can help reduce rainforest destruction. International education raises awareness about the impacts of deforestation, encouraging consumers to choose products from sustainable sources, which reduces demand for unsustainable goods.
Local communities may damage the forest, for example through illegal logging, because of poverty and a lack of awareness of long-term consequences.
Teaching them about the impacts of deforestation and providing alternative livelihoods can reduce this pressure. For example, the Rainforest Alliance in Guatemala educates communities about sustainable ways to earn a living, helping them avoid activities that harm the rainforest while still supporting their families.
how can conservation sustainably manage rainforest?
Many countries have set up national parks and nature reserves within rainforests to protect them.
Damaging activities, such as logging, are restricted in these areas. However, a lack of funds can make it difficult to enforce these restrictions effectively.
To help, some countries have set up conservation funds that overseas governments and businesses can invest in. In return for this money, the rainforest is protected, and the funds can be used to enforce restrictions and promote the sustainable use of rainforest resources. For example, in 2018, Norway paid $70 million into a Brazil-Amazon fund, which was used for conservation projects.
how can managing debt sustainably manage rainforest?
Many tropical rainforests are located in lower-income countries that often borrow money from wealthier countries or organizations, such as the World Bank. These loans must be repaid with interest, which can force countries to exploit their rainforests through logging, farming, or mining in order to generate income.
Reducing debt can help prevent this, allowing forests to be conserved. One effective method is a conservation swap, where part of a country’s debt is cancelled in exchange for a guarantee that the money will be spent on rainforest protection. For example, in 2011, the USA reduced Indonesia’s debt by $20 million in exchange for conserving its rainforests.
how can international hardwood agreements sustainably manage rainforest?
International hardwood agreements aim to reduce the impact of global demand for tropical hardwoods, such as mahogany or teak, which are used to make furniture.
High demand from wealthier countries has caused some tropical hardwood trees to become increasingly rare as more are cut down.
International agreements, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), help prevent illegal logging and promote the sustainable use of timber. The FSC labels timber that has been sustainably sourced, allowing consumers to choose products that do not contribute to unsustainable deforestation.