Exam 3 principles II
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
History of Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy was invented by Thomas C. Edison, with the first commercial fluoroscope available in 1896, producing faint images and requiring dark adaptation.
Image Intensification
A process involving several components: input phosphor, photocathode, electrostatic focusing lenses, and output phosphor, which collectively enhance the brightness and clarity of the imaging.
Electrostatic Focusing Lenses
Charged plates in the image intensifier that repel electrons and focus them toward the output phosphor using electrostatic repulsion.
Output Phosphor
The final component of the image intensifier that absorbs electrons and emits multiple light photons, greatly increasing image brightness compared to the input phosphor.
Camera Tube
A device attached to the image intensifier that converts the light signal from the output phosphor into an electronic signal for processing and display.
Minimum Source-to-Skin Distance
The requirement that the distance between the x-ray tube and the patient’s skin must not be less than 30 cm to ensure patient safety.
Fluoroscopic Mode vs. Radiographic Mode
In fluoroscopic mode, low mA (2-5 mA) is used for real-time imaging, whereas in radiographic mode, high mA (100-1200 mA) is utilized for capturing static images.
Photospot Camera
A device that allows radiologists to view and record images while they are being recorded, improving accuracy and quality of assessment.
When increasing the kVp in Fluoroscpy….
it increases the avg energy of the primary beam
During image intensification, it takes _______ electron(s) to make ____ light photons
one; many
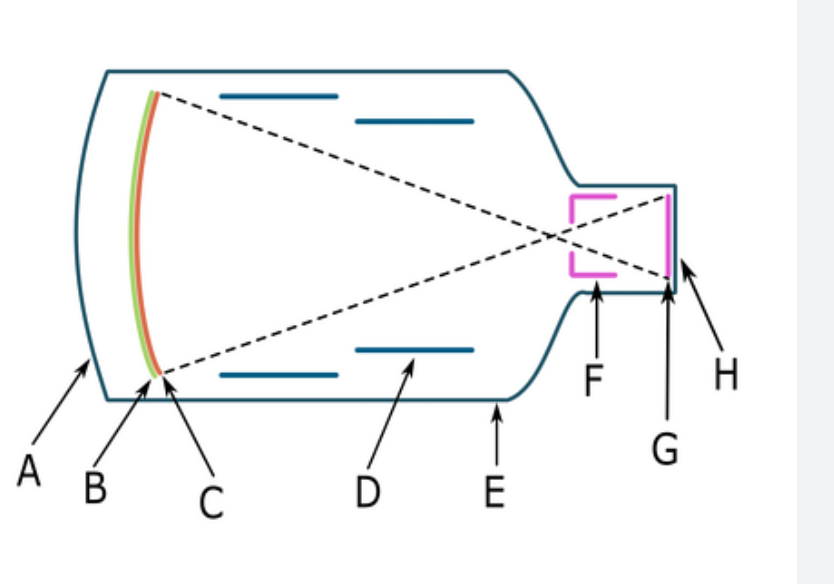
The Electric charge of D
negative
Image intensification process in order, from Exposure to display
x-ray photons, light photons, electrons, light photons, electrons
which substance is used as the photodetector in digital fluoroscopy flat panel detectors
Amorphous Silicon
Which of the component is typically composed pf Cesium and Antimony
Photocathode
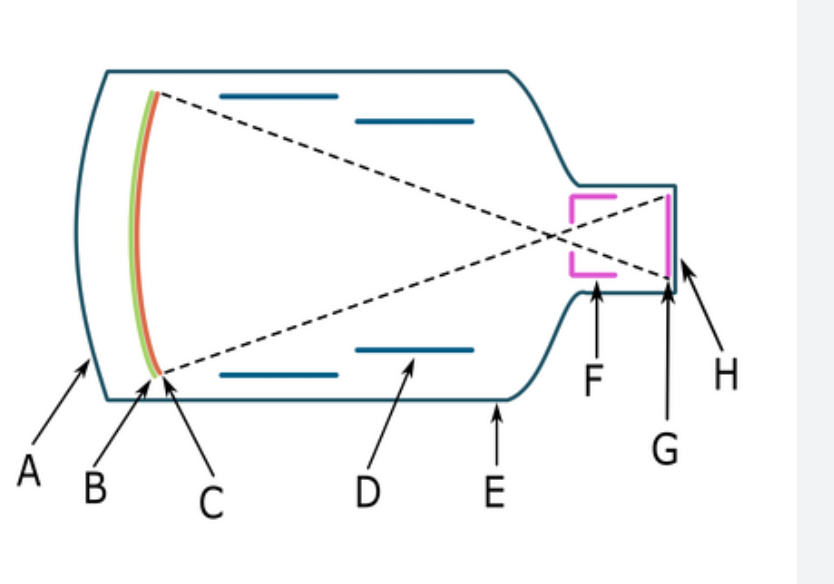
G
output phosphor
What is the minimum SSD for a Mini C-Arm
45 cm
What is the milliamperage range that is commonly used in image intensified fluoro
0.5-5 mA
Equation for Minification Gain
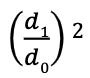
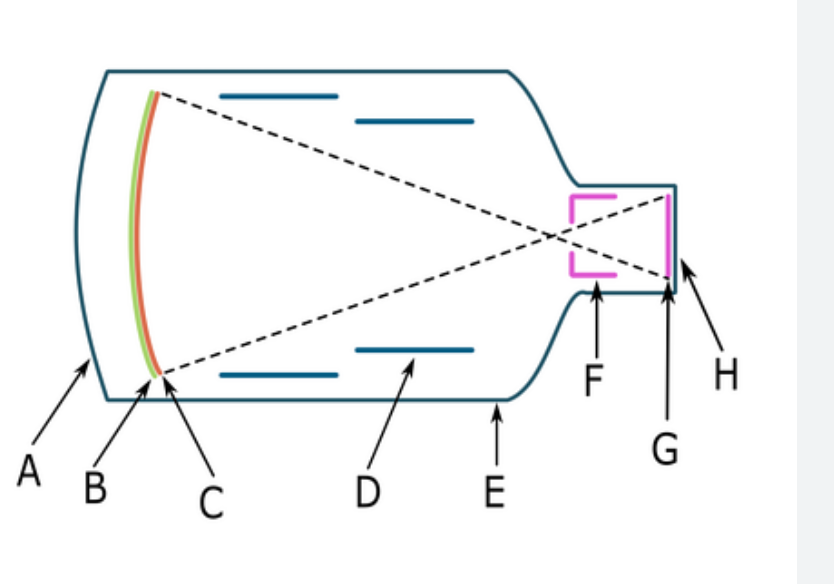
What component is D
Electrostatic Lens
Brightness lag occurs when…
ABC adjusts for varying part thickness
Disadvantage of using mag mode in conventional fluoroscopy
increased patient dose
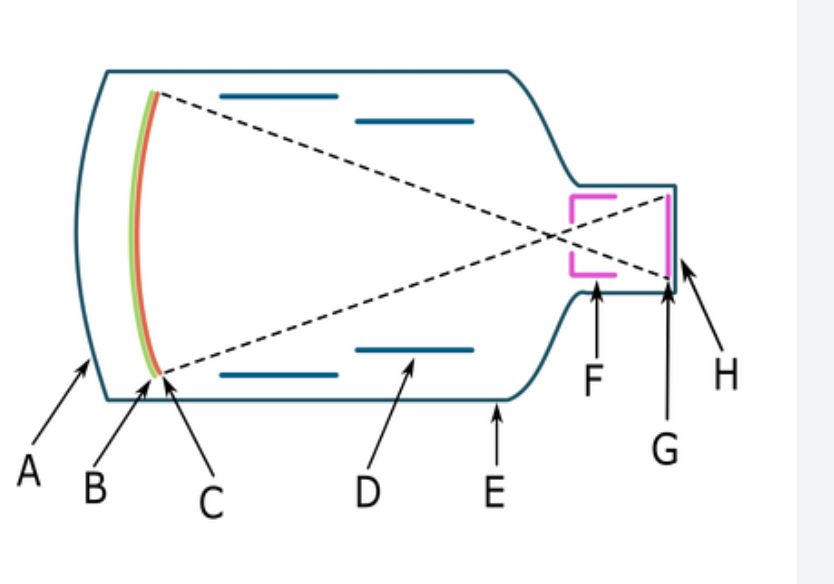
C
photocathode
avg size of input phosphor used in image intensification
25 cm
What formula measures radiation dose received by tech standing in room during an exposure compared to patient dose
inverse square law
in an imaging intensifier which device is located closest to the output phosphor
anode
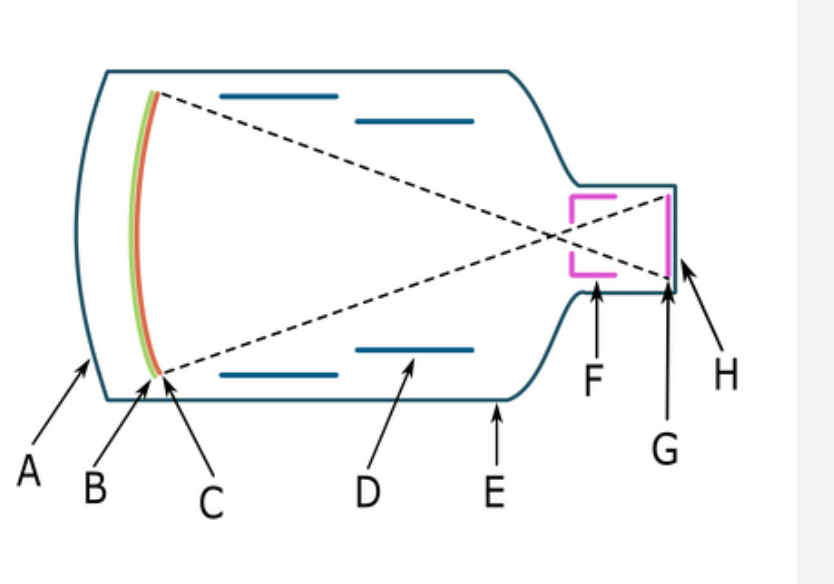
What component is F
accelerating anode
image intensification steps from beginning to end
x-ray photons are converted to light, light photons are converted to electrons, electrons merge to a point, and electrons are converted back to light at output phosphor
During image intensification, it takes ___ light photon(s) at the photocathode to create ____ electron(s)
many; one
purpose of red goggles in early fuoroscopy
adjust viewer’s eyes to better visualize dim images
equation for magnification mode
full size input of phosphor / selected size of input phosphor
What mA is more common in digital fluoroscopy when a FPD is utilized
50 - 1200 mA
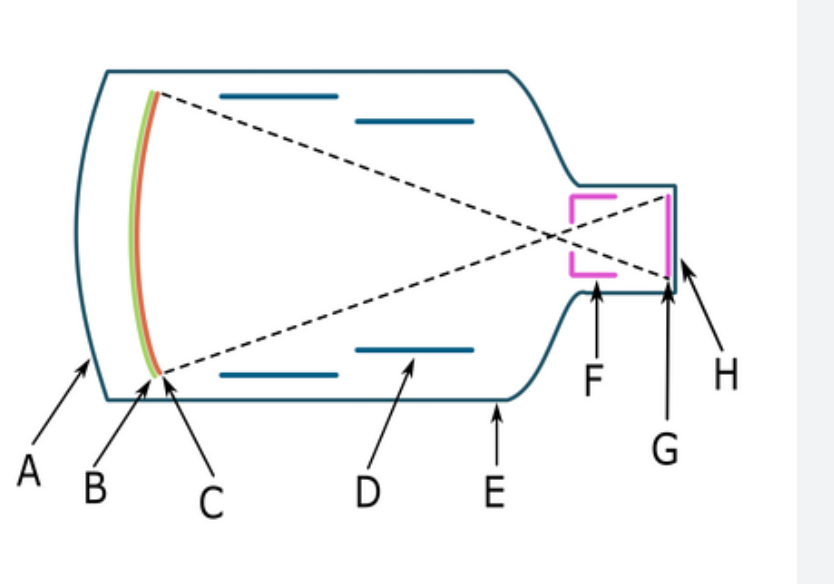
point of intersection
focal point
what component of the image intensification faces the patient
input phosphor
what term describes the number of images per second in a pulsed fluoroscopy
pulse rate
what type of phosphor is commonly used in the indirect-capture of digital fluoroscopy
Cesium Iodide
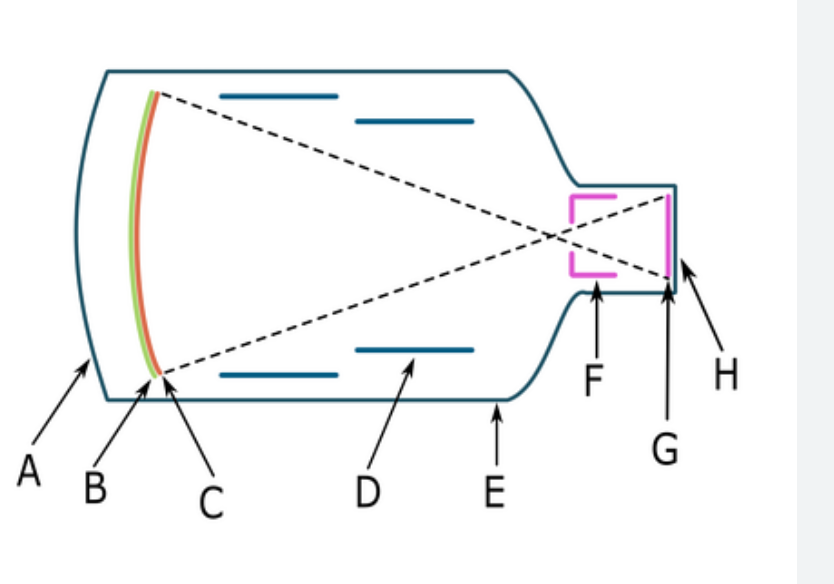
What is the electric charge of F
positive
what technique absorbs x-rays with a photoconductor in fluoroscopic imaging
direct capture FPD
this describes the ratio of light photons at the output phosphor compared to the number of x-ray photons at the input phosphor
flux gain
during magnification mode in fluoro the electrostatic lens receive ___ _____ cahrge
increased negative
this term describes the length of each pulse in pulsed fluoroscopy
pulse width
input phosphor_____ and emits _____.
remnant beam; light energy
flux gain equation
#light photons at output phosphor/#x-ray photons at input phosphor
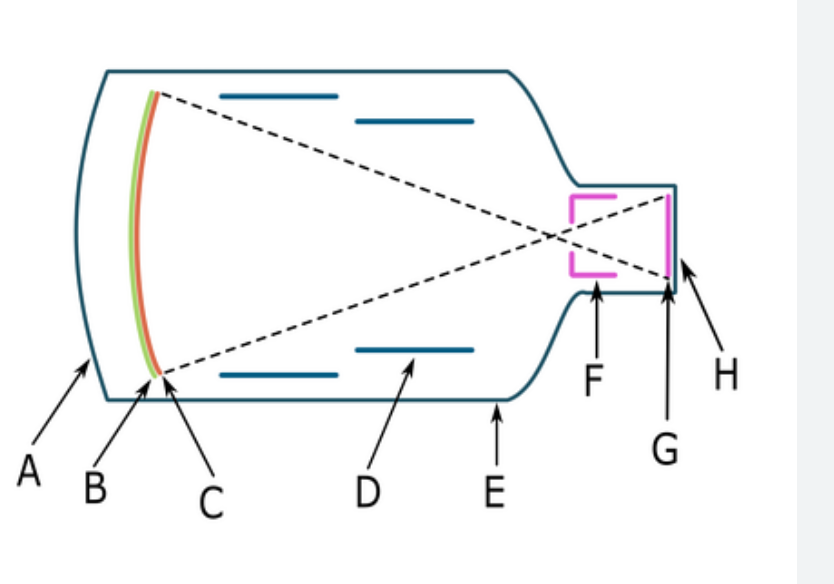
what component is B
input phosphor
Brightness gain of the image intensifier is the:
combination of minification gain and flux gain
What component is responsible for the process of photoemission
photocathode
What device prevents ghosting in flat panel detectors?
backlighting
What percentage of DEL is composed of scintillating material
80%
what type of phosphor is commonly used in conventional fluoroscopy?
Cesium Iodide
function of electrostatic lens in image intensifier
repel electrons
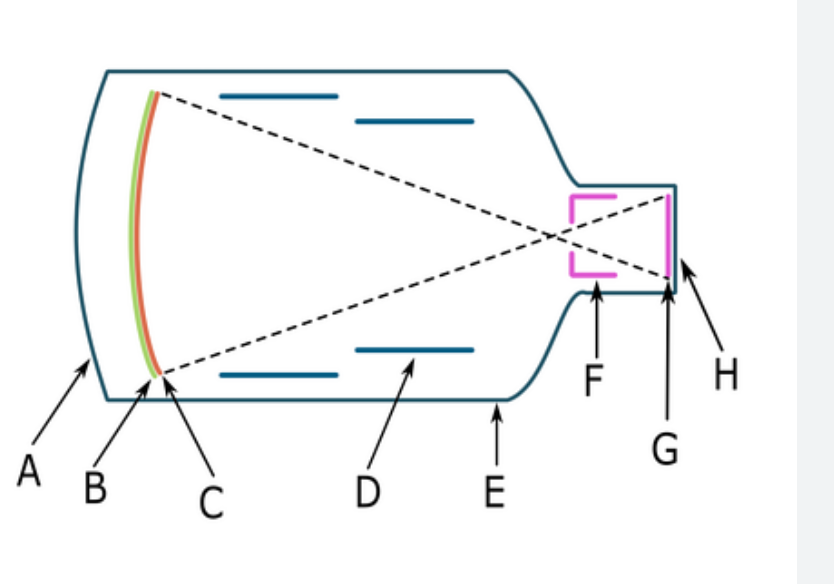
B
input phosphor
what is the constant charge of the accelerating anode
25 kV
What is the minimum SSD for a C-Arm
30 cm
order of image intensification in fluoroscopy
input phosphor, photocathode, electrostatic lens, anode, output phosphor, camera tube, ACD
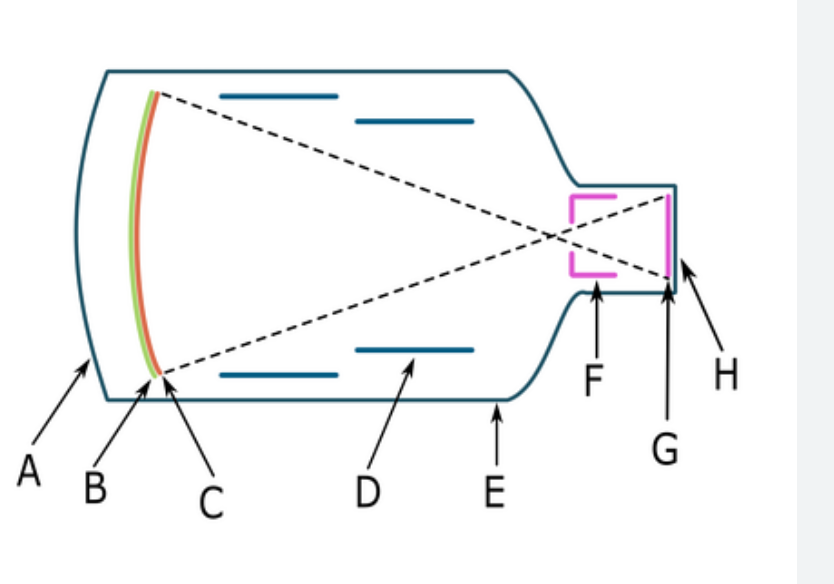
G
output phosphor
function of anode in the image intensifier
attract electrons
What absorbs x-ray photons with scintillator in digital fluoroscopy
indirect-captured -FPD
this term represents the ability of an image intensifier to convert x-ray energy into light energy and increase brightness of the image in the process
brightness gain
What are associated with magnification in image-intensified fluoroscopy
Higher patient dose and smaller input phosphor use
what is the type of phosphor used in the direct flat panel detectors?
N/A none are used
what is the minimum amount of lead required for protective aprons used in fluoroscopic imaging
0.5 mm Pb
in the image intensifier, the output ohosphor:
absorbs electrons and produces a brighter image
The focal point of an image intensifier is….
where electrons convergewh
what. occurs when electronic magnification is used?
FOV enlarged to fill display screen
input phosphor
absorbs x-ray photons and emits light
what is the input phosphor made up of?
Cesium Iodideor Sodium Iodide crystals.
accelerating anode
attracts electrons toward output phosphor
in image intensification the input phosphor….
absorbs remnant beam and emits light in response
brightness gain
ability of the image intensifier to convert x-ray to light
a higher brightness gain will create…
greater efficiency of image intensifier
why is more radiation needed as the image intensifier ages
it loses its efficiency and needs more radiation to produce same brightness level
minification gain
diameter of input phosphor vs diameter of output phosphor causing a brighter image output