Histamine MC
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
The following sequence of events results in the release of histamine (immune stimuli):

H1 receptors are found in various tissues including
bronchi, gut, heart, the uterus, blood vessels and
in some parts of the CNS
The H1 receptors mediate:
smooth muscle contraction (bronchoconstriction)
The H1 receptors are
GPCRs that utilize Gq G-protein, activate phospholipase C (effector) and give rise to second messengers IP3 and DAG
Termination of Histamine Action
Occurs by cellular uptake (major mechanism), receptor desensitization (secondary), and metabolism (minor)
understand
Primary Pharmacological Effects of Histamine
Blood vessels/airways import
Dilation of finer blood vessels causing flushing and decreased total peripheral resistance and decreased BP. Increased capillary permeability resulting in edema. All are H1 mediated.
Bronchoconstriction (H1 mediated)
Effects on the heart:
Increases force of contraction by promoting calcium influx, increased HR
(H1 mediated).
GI
Stimulates gastric secretion (H2 mediated)
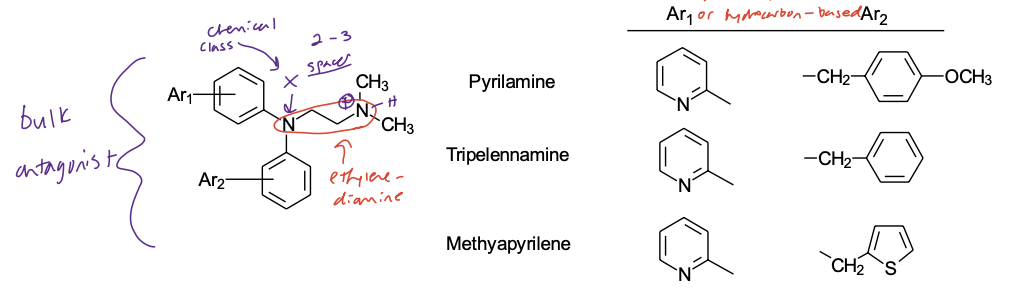
Ethylenediamine Class
(X = N, spacer = (CH2)2
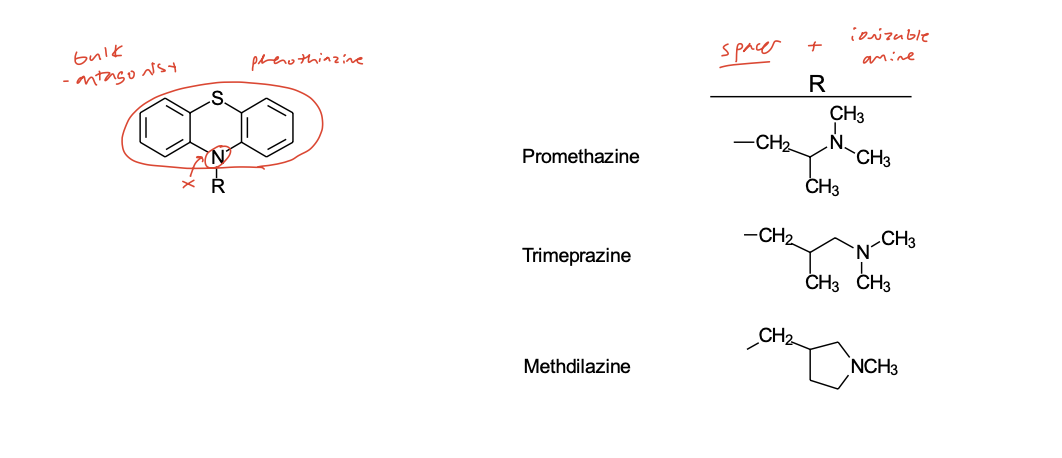
Phenothiazine Class
(Join the aromatic rings of ethylenediamines with a S atom)
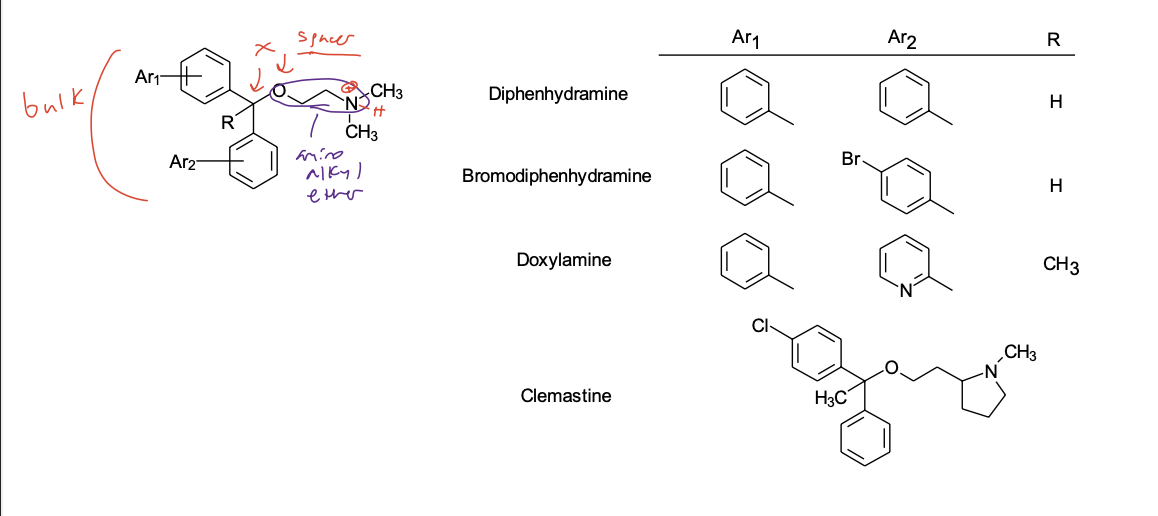
Aminoalkyl Ether Class
(or Ethanolamine Class) (X = C-O)
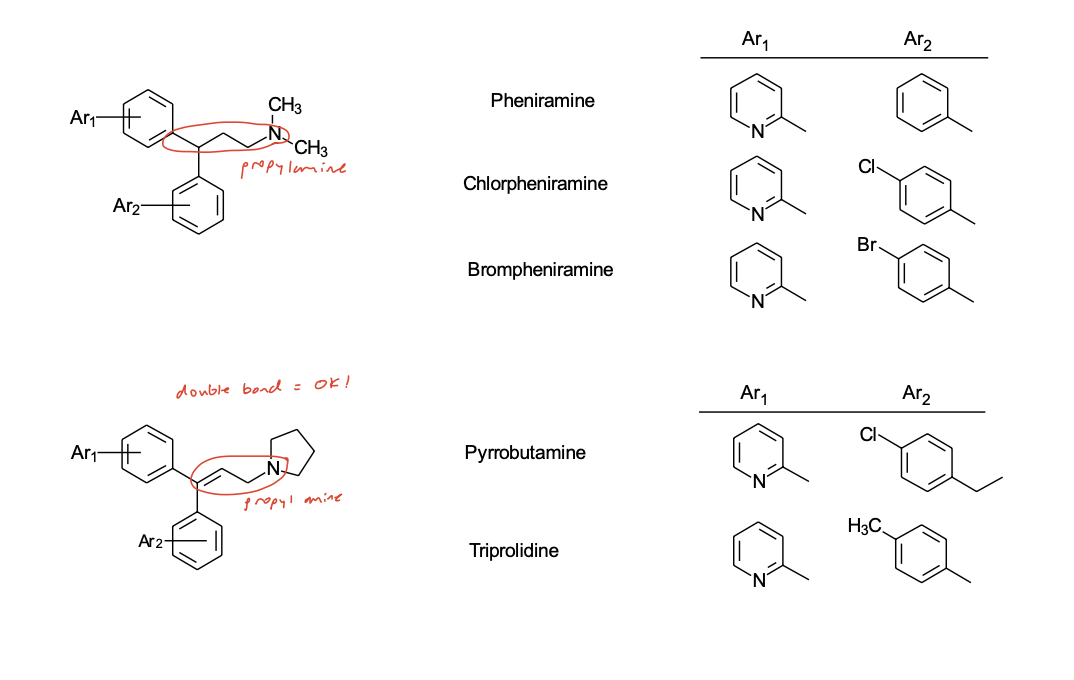
Propylamine Class
(X = sp3 carbon-pheniramines or sp2 carbon propenylpyrrolidines)
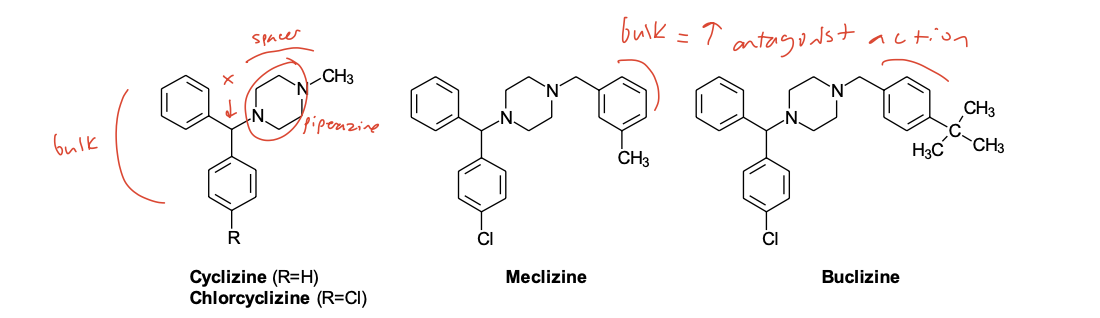
Piperazine Class
(the Cyclizines)
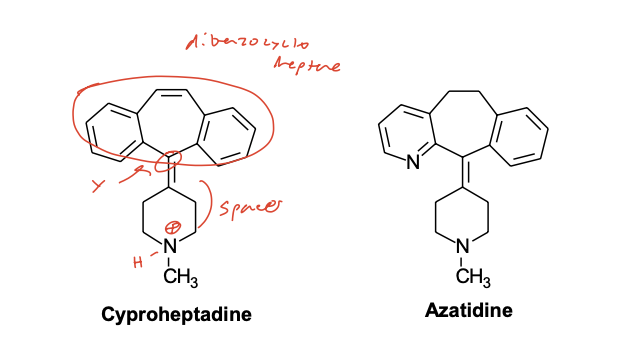
Dibenzocycloheptanes/heptenes:
Dibenzocycloheptanes/heptenes: Joined aromatic rings from the propylamine class
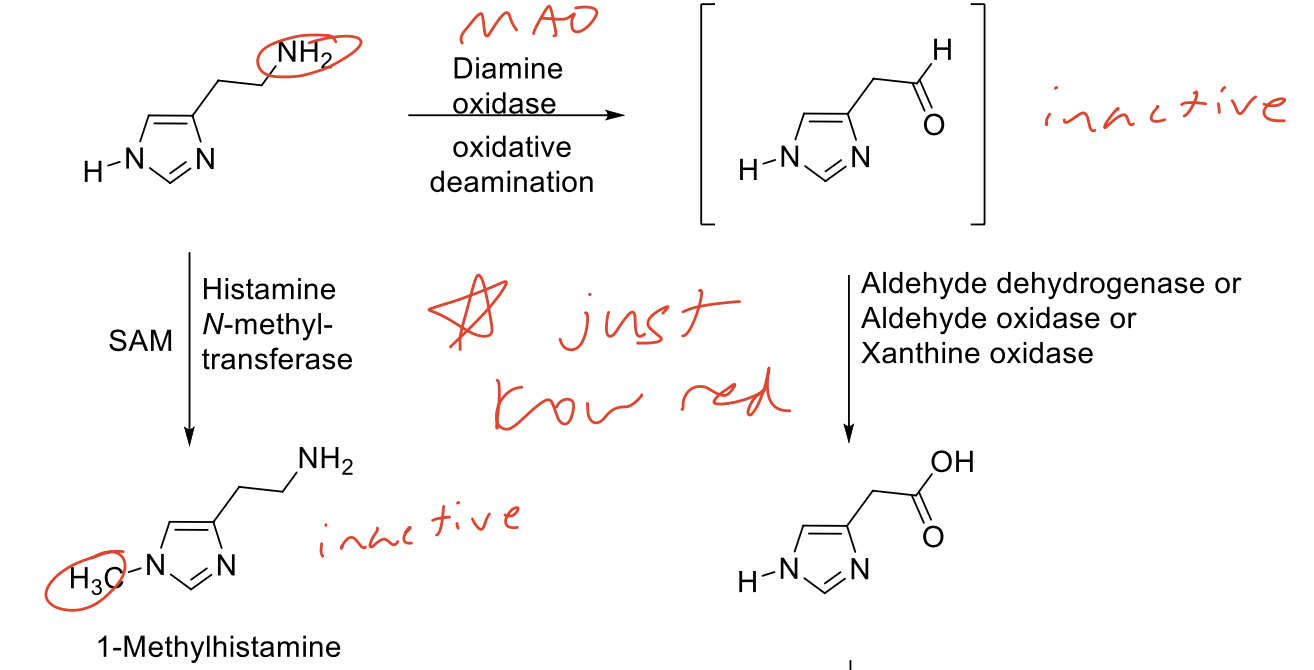
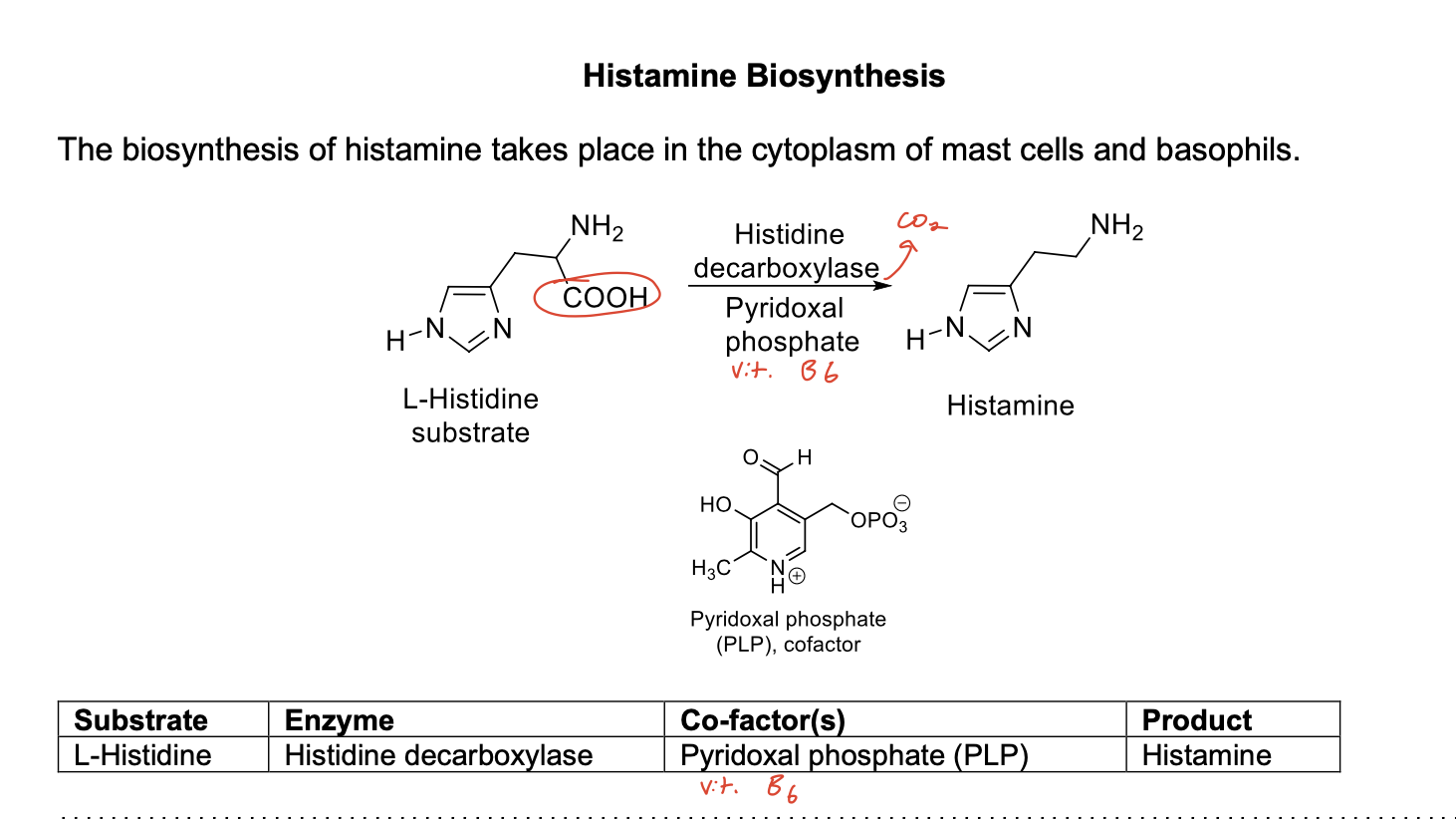
Histamine Biosynthesis
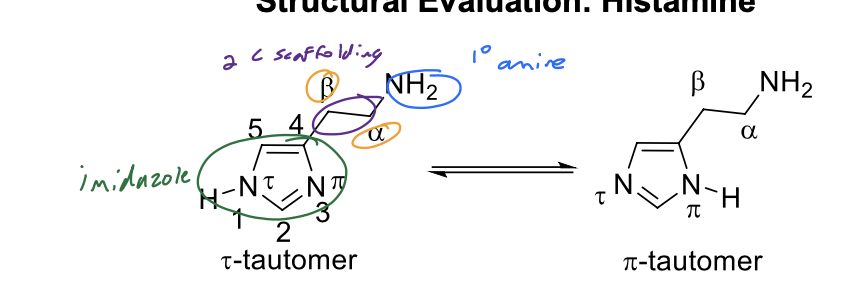
Structural Evaluation: Histamine
1. Histamine consists of an imidazole heterocycle and an ethylamino side chain.
2. The methylene groups are designated as a and B.
3. Histamine is a basic molecule with pKa’s of 5.80 (imidazole), 9.40 (aliphatic primary amine).
5. At physiologic pH (7.4), histamine exists primarily in its protonated/ionized form (aliphatic primary amine is protonated/ionized). Protonation/ionization of this nitrogen atom is important for binding to various histamine receptors.
ion-dipolole/ionic