NHP Noninfectious diseases
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is scurvy?
deficiency in vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
Why are guinea pigs and NHP prone to vitamin C deficiency?
guinea pigs and most primates lack this capacity due to absence of the enzyme l-gulonolactone oxidase.
What is ascorbic acid essential for in the body?
The absence of ascorbic acid reduces the function of prolyl hydroxylase, which is required to form hydroxyproline, an amino acid found in collagen but rarely found in other proteins.
Collagen lacking hydroxyproline is more fragile and contributes to the clinical manifestations of scurvy, including vessel wall fragility.
What does hypovitaminosis A do in Macaques?
Increase risk of abortion
What does hypervitaminosis A do in Callitrichids?
Musculoskeletal lameness, paresis cachexia, debilitation, alopecia
See Spinal hyperostosis and spinal ankylosis on pathology
What causes the following in macaques:
Visual impairment
Spastic paralysis of
hindlimbs
Decreased range of
motion in knees
Painful, swollen joints
Contracted tendons
Hand walking
Megaloblastic anemia
Hypovitaminosis B12
What does scurvy cause in NHPs?
Reluctance to move
Joint pain and
tenderness
Lameness, abnormal
locomotion
Gingival swelling,
hyperemia, petechia
Bruising
Microcytic anemia
What unique anatomic pathology do you see in spider monkeys with scurvy?
Squirrel monkeys Acute cephalohematoma.
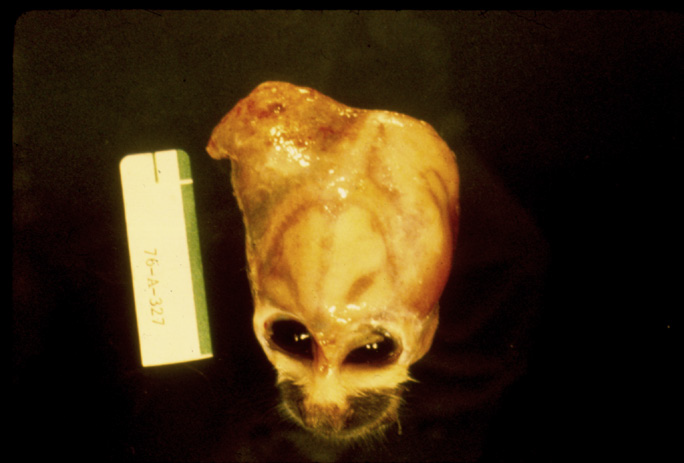
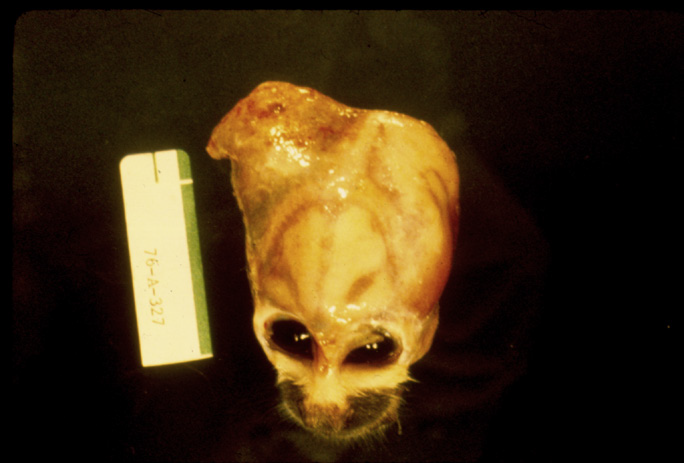
What is likely the cause of this pathology in a spider monkey?
scurvy
Hypovitaminosis D2 clinical signs in old world monkeys?
Failure to grow
Wrists and knee
enlargement
Bowing of long bones
What is rickets?
Hypovitaminosis D
Hypovitaminosis D3 clinical presentation in new world monkeys?
Growth retardation
Impaired ambulation
Fractured long bones
Masticatory weakness,
difficulty chewing
Inanition, death
What is the treatment for hypovitaminosis D?
UVB lighting, provide vitamin D in diet
What can cause megaloblastic anemia in NHPs?
Folic acid deficiency
In which species does Hypovitaminosis E cause cardiomyopathy?
Babboons
In which species does Hypovitaminosis E cause anemia?
owl monkeys
What nutritional imbalance contributes to marmoset wasting syndrome?
Calcium deficiency
Can you treat marmosets with wasting disease after clinical signs develop with vitamin E?
No but can be preventative
What are the clinical signs of calcium deficiency in tamarins?
Steatitis and myositis
What can cause Simian bone deficiency and osteomalacia in simians?
Calcium deficiency
What is a potential nutritional cause for Kyphosis
Bowing, fractured long bones in Simians?
calcium deficiency
How is scurvy treated?
Clinical signs resolve within days of
corrective vitamin C therapy.
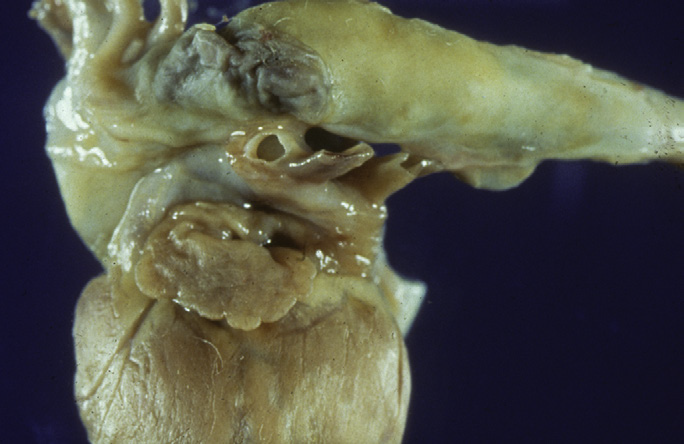
What is a possible cause of aortic aneurysm?
femoral artery bleeding or atherosclerosis or copper deficiency
What are common congenital heart diseases in NHPs?
ventricular septal defects, patent ductus
arteriosis, and atrial septal defects being observed most
frequently
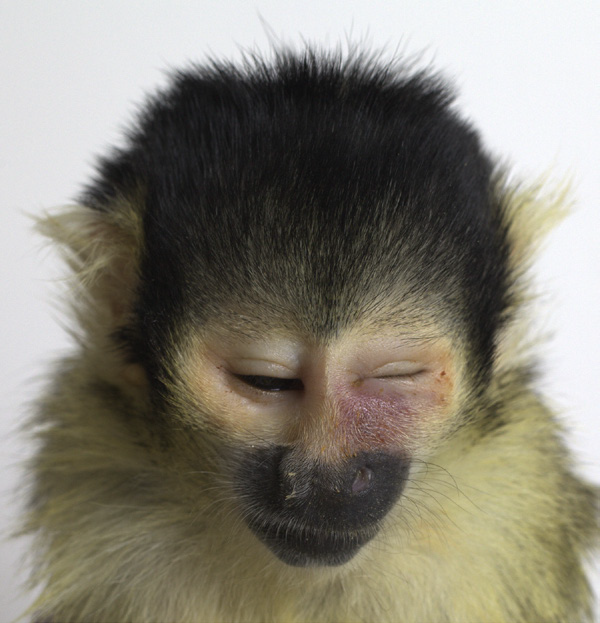

Common noninfectious cause of this photo?
Abscessation of molar teeth
in squirrel monkeys usually extends into the infraorbital
region of the eye and can lead to exophthalmos and blind
ness
What is a common sequela of overeating and over drinking?
Acute gastric dilatation or bloat in nonhuman primates
has occurred following overeating and drinking, following alteration of gastric flora from antimicrobial
therapy, or following anesthesia, transportation, or
other change in routine.
Bloat has been associated with gastric proliferation of
Clostridium perfringens
What noninfectious GI diseases are common in NHPS?
IBD, diverticulosis, rectal prolapse
Which NHPs commonly get amyloidosis?
It is most frequently recognized in aged
macaques and common marmosets
What type of amyloidosis is most common in mammals?
AA or reactive ‘secondary’ amyloidosis is the most common systemic amyloid-associated disease found in mammals
What is the etiology of amyloidosis?
Unknown but In macaques systemic forms may be associated with inflammatory bowel disease, chronic catheterization, or chronic infections such as SRV. Systemic amyloidosis often involves the gastrointestinal tract (colon and small intestine), liver and spleen
How do you treat amyloidosis?
DMSO
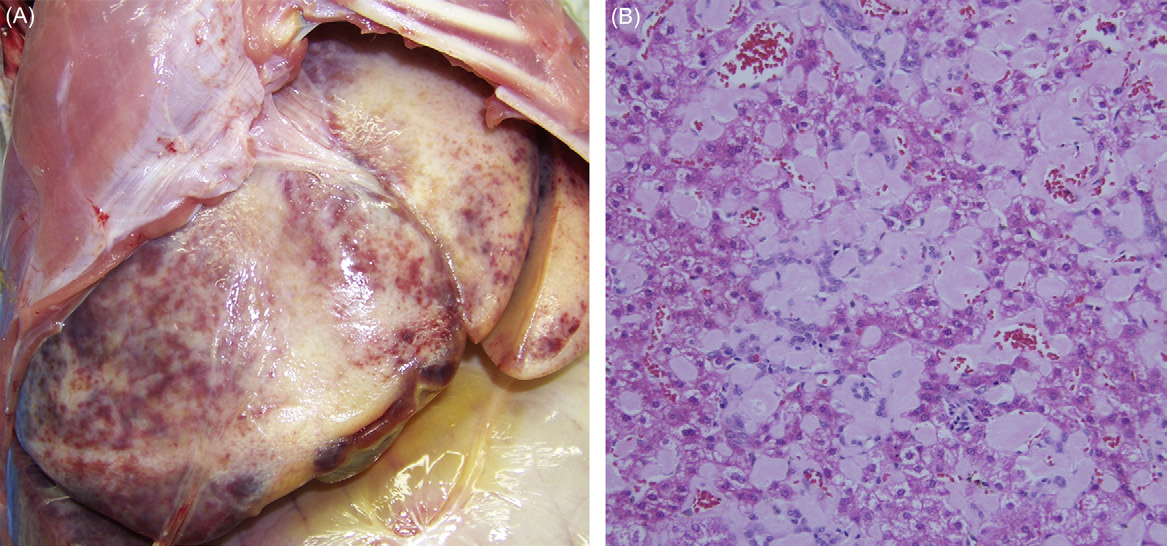
Older macaque with chronic diarrhea, not infectious cause found, what is likely the cause?
Amyloidosis
Which NHPs is hypoglycemia a primary disorder? Why?
Squirrel monkeys, marmosets, and owl monkeys
may develop hypoglycemia as a primary disorder.
Predisposing factors include higher basal metabolic rates, lower percentage of body adipose tissue, limited glycogen reserves, limited gluconeogenic enzymes, and limited ability to utilize ketones or fatty acids
What NHPs are predisposed to Fatal fasting syndrome?
Fatal fasting syndrome, also known as ‘fat macaque
syndrome’ or ‘fatal fatty liver syndrome’, is an acute
metabolic syndrome which may be precipitated by a
variety of causes and which is seen most frequently in
obese middle-aged female macaques. Decreased food
intake is thought to result in a shift to utilization of
fatty acids as a primary energy source overwhelming
the liver’s ability to process these stores and resulting
in severe hepatic lipidosis.
NHP with this liver could be predisposed to what condition?
Fatty liver disease
What is the most frequent neoplasm of Older macaques?
Intestinal adenocarcinoma is the most frequent neoplasm
in older rhesus macaques
What is the principle DDX for intestinal adenocarcinoma in older female macaques?
The principal differential diagnosis in older
female monkeys would be endometriosis.
Clinical signs of intestinal adenocarcinoma?
The cause is unknown but may be associated with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. The cause
is unknown but may be associated with chronic inflammatory bowel disease.
Most common neoplasm of the skin in NHPs?
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the most common
skin neoplasm in nonhuman primates
Causes of Squamous Cell carcinoma?
Etiologies include (1) exposure to sunlight, (2)
papillomaviruses, (3) carcinogens such as n-methyl-
N-nitrosourea that may experimentally induce SCCs in
the digestive tract (esophagus), and (4) chronic inflammation at mucosal surfaces such as that induced by
parasites or infection.
Which NHPs are most prone to arthritis?
macaques, gorillas, and chimpanzees.
Reactive arthritis is associated with which pathogen in macaques?
Reactive arthritis, secondary to previous Shigella flexneri
infection, is the best characterized of these entities
and is a well-recognized syndrome in macaques.
Which nhps, old or new are most prone to rickets of D3 origin?
New World
What does cholecalciferol do? Why are new world NHPs prone to vitamin D3 deficiency?
Cholecaciferol or vitamin D3 is derived from animals and is hydroxylated in the liver to form 25(OH)D3 and is further hydroxylated in the kidney to form 1,25(OH)2D3 which is the active hormone.
While Old World primates are able to synthesize
adequate D3 from D2, New World primates must
have a dietary source of D3 to prevent metabolic bone
disease.
Most common clinical signs of metabolic bone disease caused by vitamin D deficiency?
deformation at epiphyseal plates, Microfractures
may occur at these sites with formation of transverse
radiolucent (‘Looser’s’) lines that may be recognized
radiographically.
What is the most common gynaecologic disease of old world primates?
Endometriosis
What is endometriosis?
It is a progressive disease characterized
by the deposition and proliferation of endometrial
tissue outside of the uterine cavity.
Predisposing factors for endometriosis formation?
Contributing risk factors
include radiation, treatment with estradiol implants,
previous hysterotomy, and stress
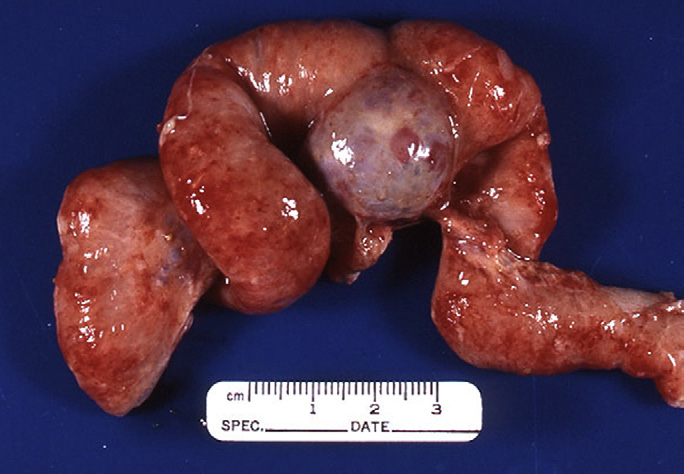
What could this be?
endometriosis
Diagnosis of endometrisosis?
Ultrasonic guided
aspiration of brownish fluid is highly suggestive of the
presence of endometriosis
Most common areas affected by endometriosis?
most commonly associated with the serosa
of the uterus, bladder, omentum, colon, and uterine ligaments. Can be very aggressive.
What on pathology is pathopneumonic for endometriosis?
multichambered mass containing reddish-brown to brown
raised cystic regions or ‘chocolate cysts’.
Treatment of endometriosis?
Treatment options include ovariohysterectomy,
resection of cysts, progesterone therapy, and
leuprolide acetate.
What are some treatment options for self-injurious behaviour?
A number of different therapeutics have been used including benzodiazepine (Tiefenbacher et al., 2005), l-tryptophan (Weld et al., 1998), fluoxetine (Fontenot et al., 2009), guanfacine (Macy et al., 2000), and cyproterone acetate.
Tieffenbacher et al. (2005) reported a bimodal response to diazepam in which the drug decreased self wounding episodes in half of the rhesus macaques but had no effect or exacerbated wounding behavior in the
remaining animals.