04.1C BIO System Transport in Humans (PART C)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Circulatory System (Materials Transported)
Works with other systems of the body to transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, water hormones and wastes throughout the body
Respiratory System (Materials Transported)
Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide
Digestive System (Materials Transported)
Transports nutrients such as glucose and amino acids as well as wastes
Excretory/Urinary System (Materials Transported)
Transports metabolic wastes such as urea and uric acid in the urine
Nervous System (Materials Transported)
Transports ions and neurotransmitters that help with the conduction of electrical impulses along a neuron
Endocrine System (Materials Transported)
Transports hormones that act as chemical messengers throughout the body
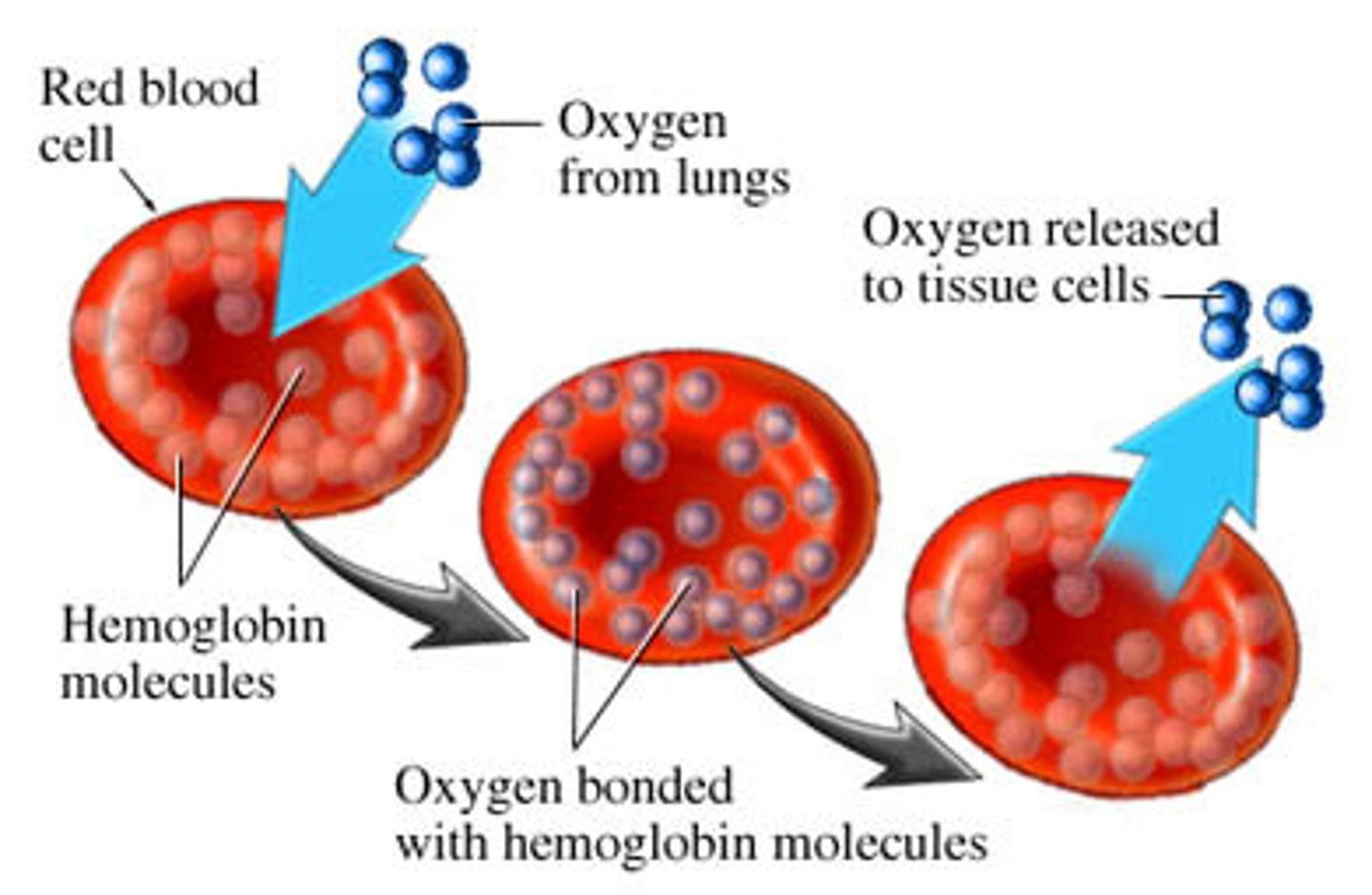
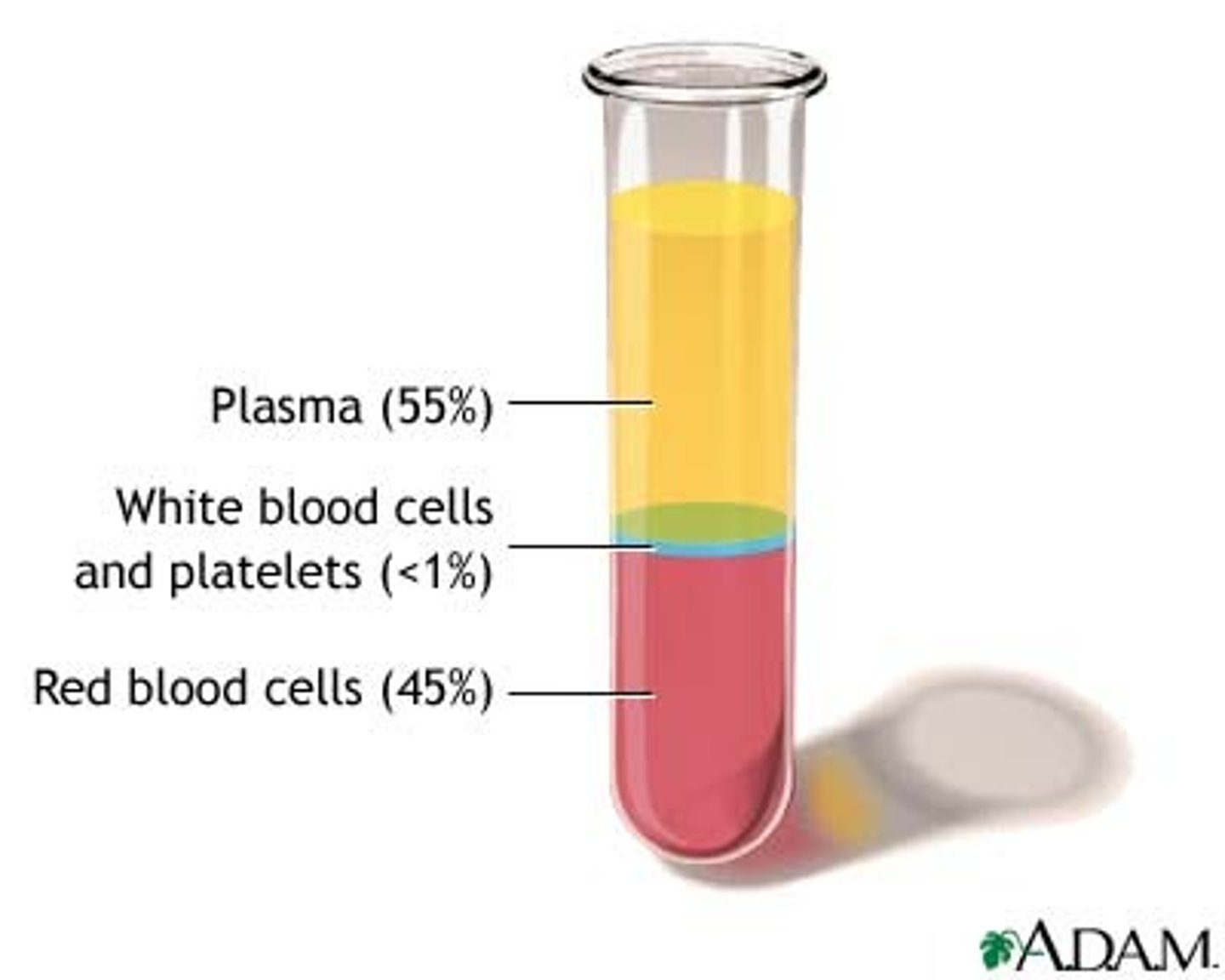
Red Blood Cells
Blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body
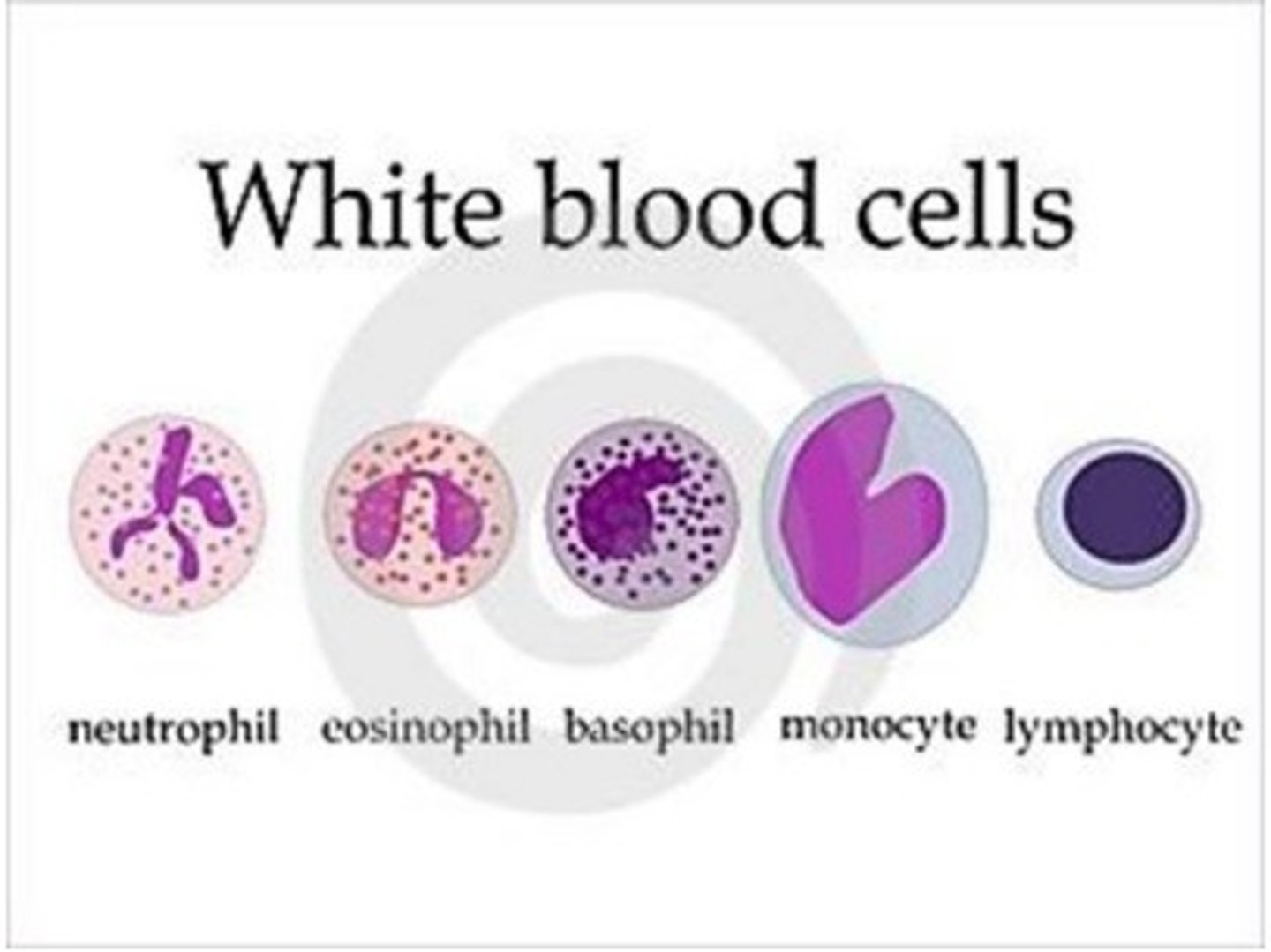
White Blood Cells
Blood cells that destroy disease-causing microorganisms and help fight infection
Platelets
cell fragments that play an important part in forming blood clots
Plasma
Liquid part of blood that contains blood cells and contains water, salts, enzymes, antibodies and other proteins
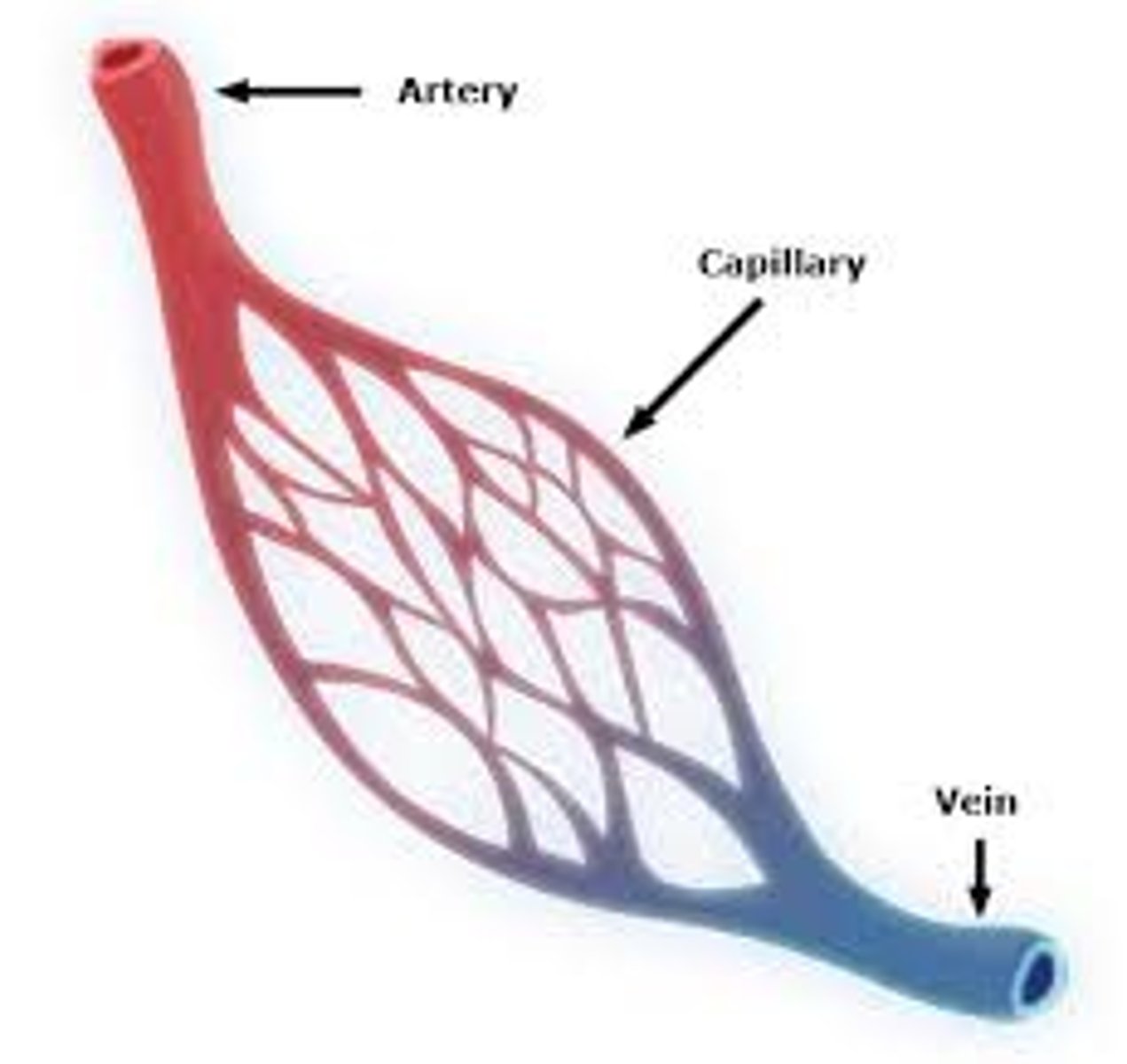
Artery
A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart and with the exception of the pulmonary artery contains oxygenated blood
Vein
A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart and with the exception of the pulmonary vein contains deoxygenated blood
Capillary
A tiny blood vessel where substances are exchanged between the blood and the body cells
Oxygenated blood (Description)
Blood rich in oxygen
Deoxygenated blood (Description)
Blood that is oxygen-poor
Oxygenated Blood (Location)
Blood returning from the lungs to the left side of the heart that is then pumped throughout the body
Deoxygenated Blood (Location)
Blood returning from the body to the right side of the heart which is then pumped to the lungs
Circulatory System (Role in Transport)
This system aides in transport of all materials throughout the body when the heart pumps blood throughout the arteries, veins, and capillaries
Respiratory System (Role in Transport)
This system aides in the transport of oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the body
Digestive System (Role in Transport)
This system breaks down large macromolecules into small molecules that can be taken up by the cells and eliminates materials that can NOT be broken down or absorbed
Excretory/Urinary System (Role in Transport)
This system eliminates waste products that are produced by the cells which travel through the blood and then are eliminated by the kidneys as urine and through the skin as sweat
Nervous System (Role in Transport)
This system transports of ions and the neurotransmitters to generate fast-acting electrical impulses along neurons
Endocrine System (Role in Transport)
This system transports slow-acting chemical messengers called hormones throughout the body to trigger cells, tissues, glands and organs to do something
Heart
A hollow, muscular organ that contains 4 chambers and pumps blood throughout the body
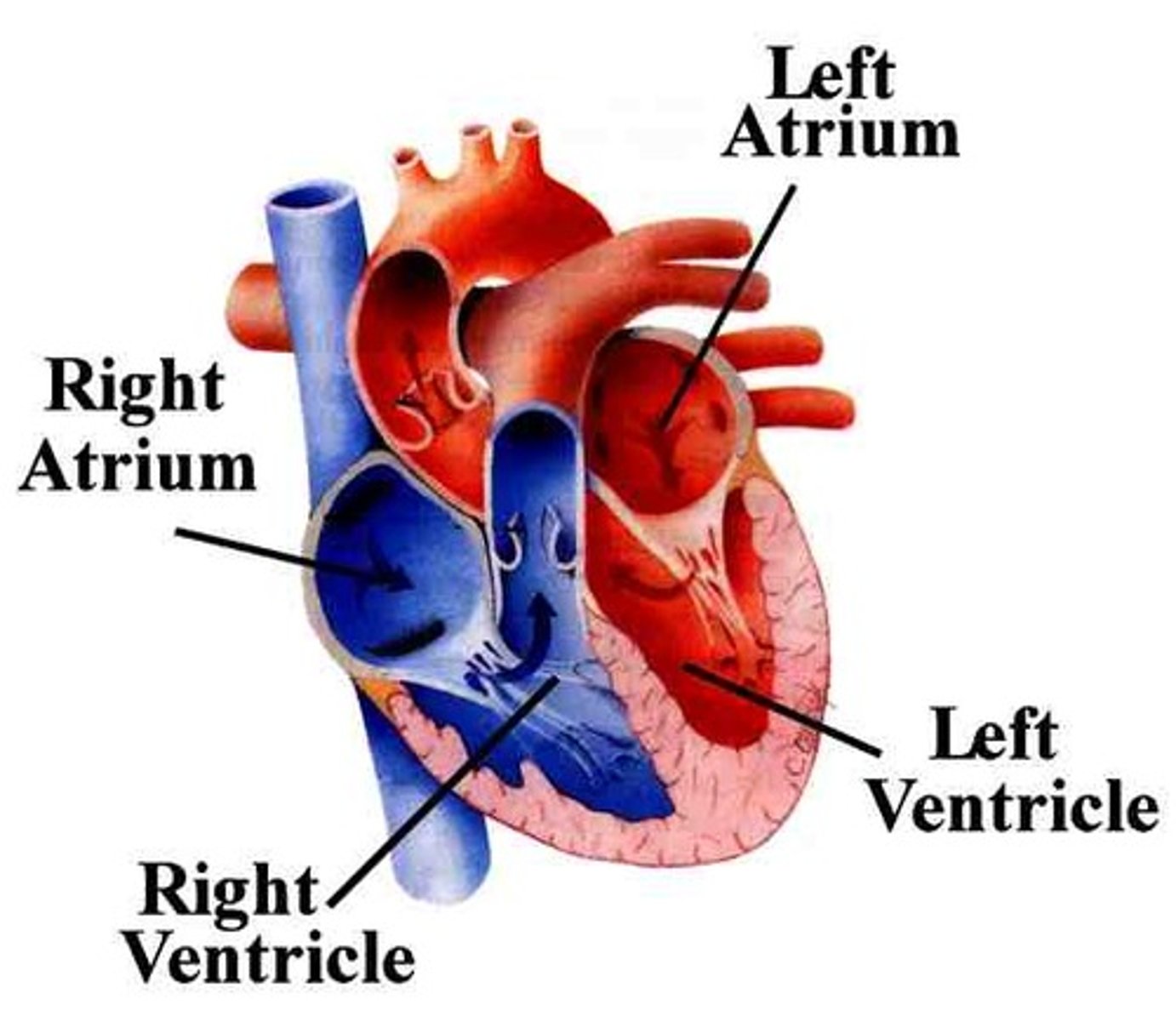
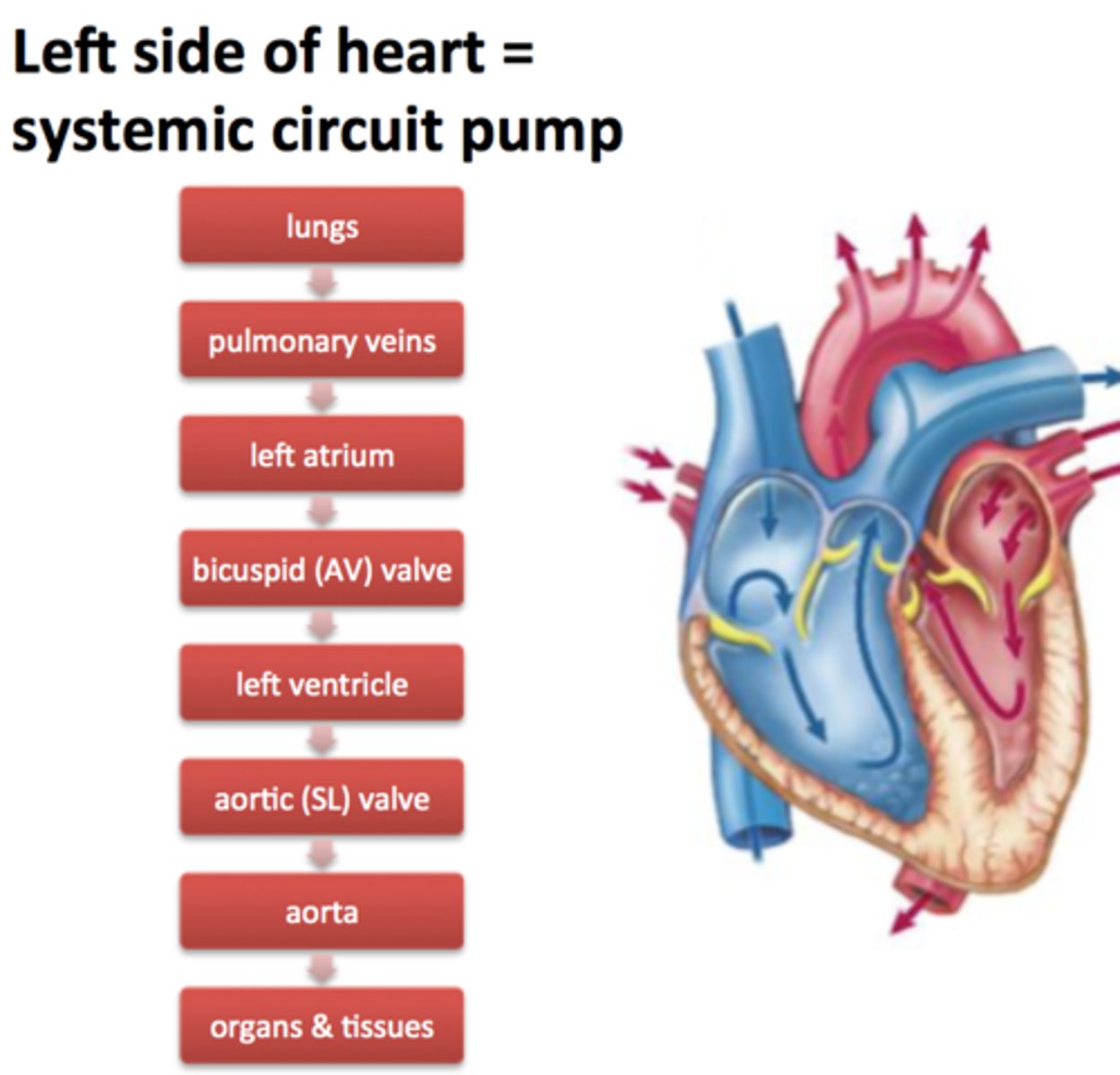
Pulmonary Circuit
A system of blood vessels that carry blood to the lungs for gas exchange and returns it to the heart

Systemic Circuit
A system of blood vessels that carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body
Respiratory System (Organs)
Mouth, nose, pharynx, trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, diaphragm
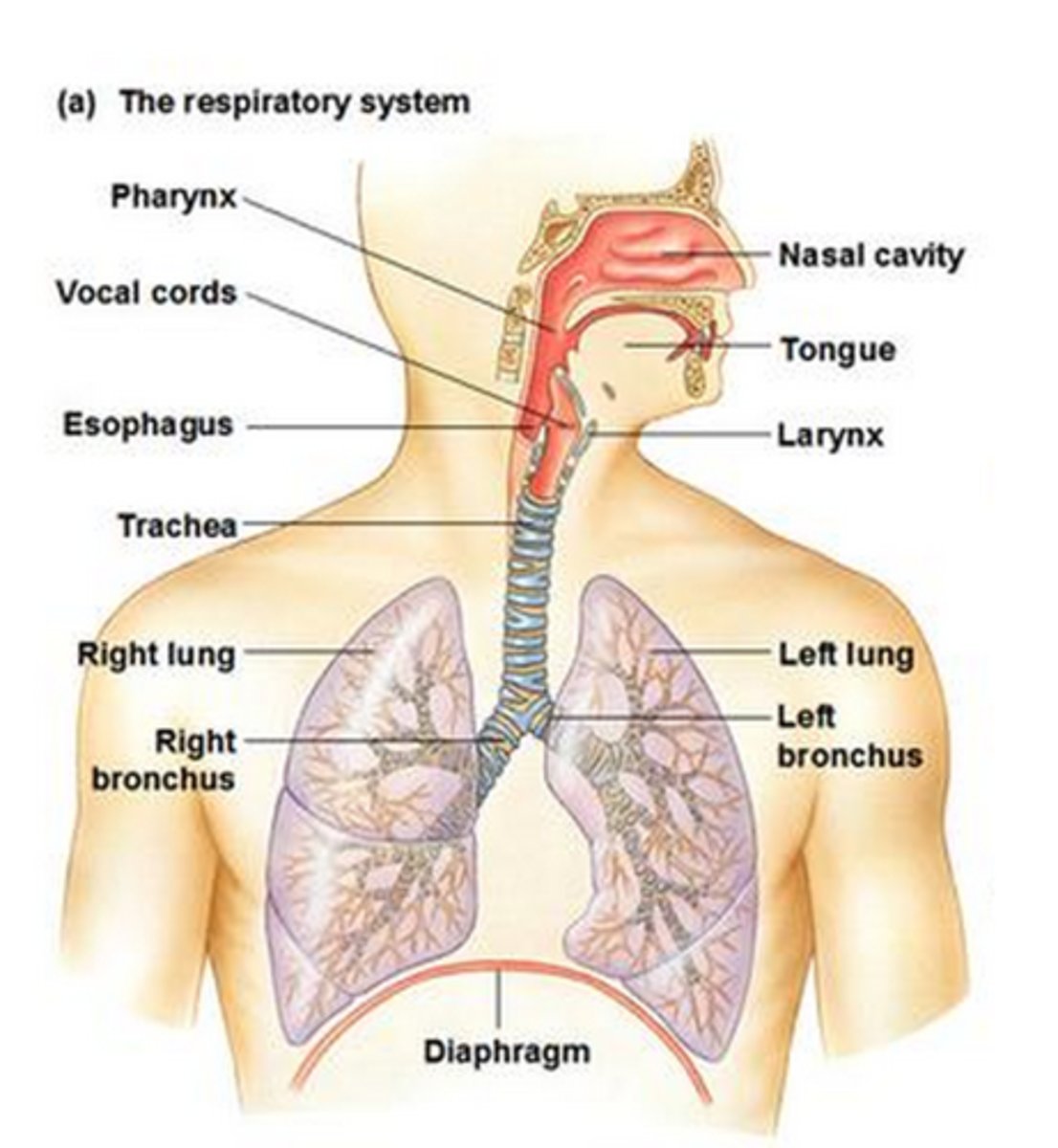
Pharynx
The region at the back of the throat that acts as a passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
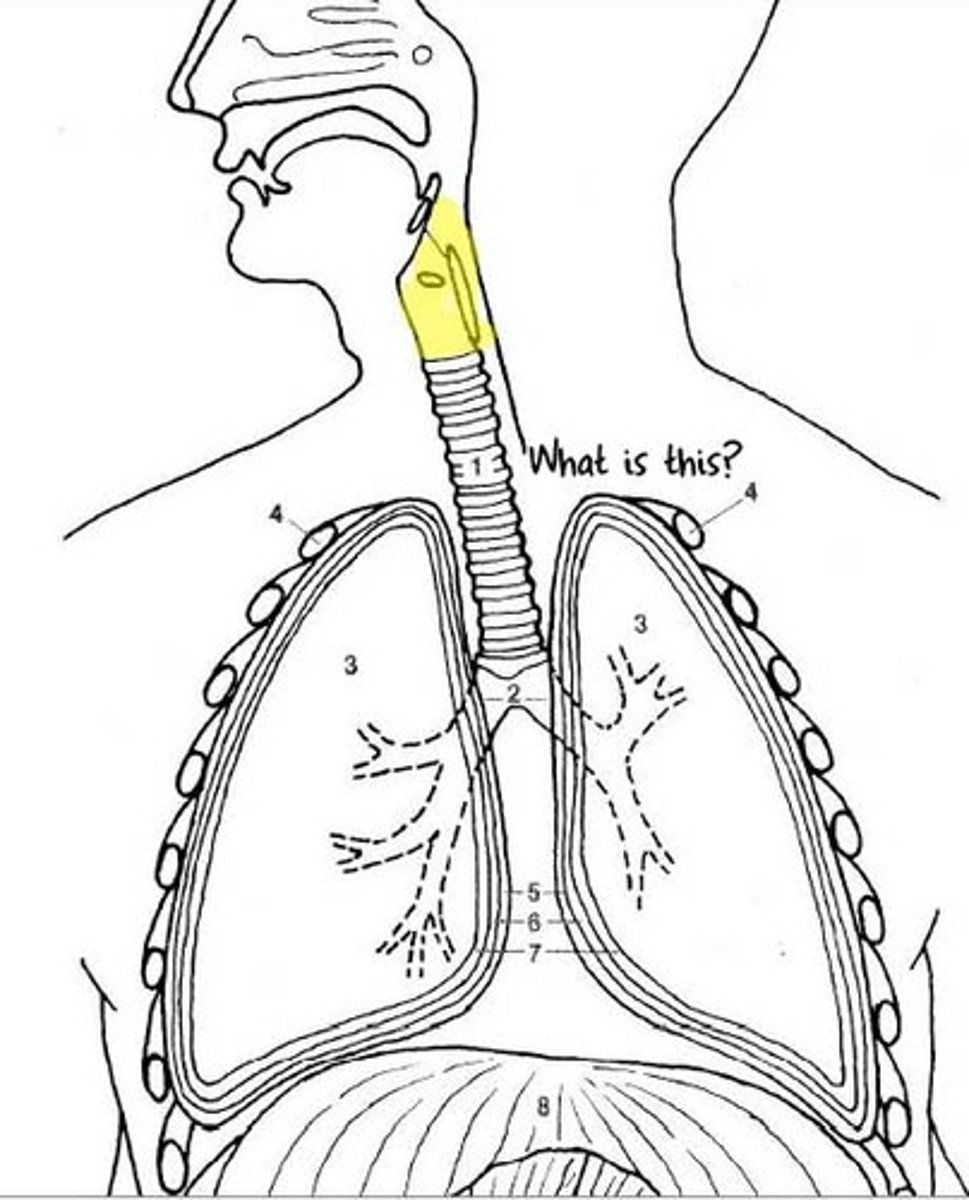
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs; also known as the windpipe
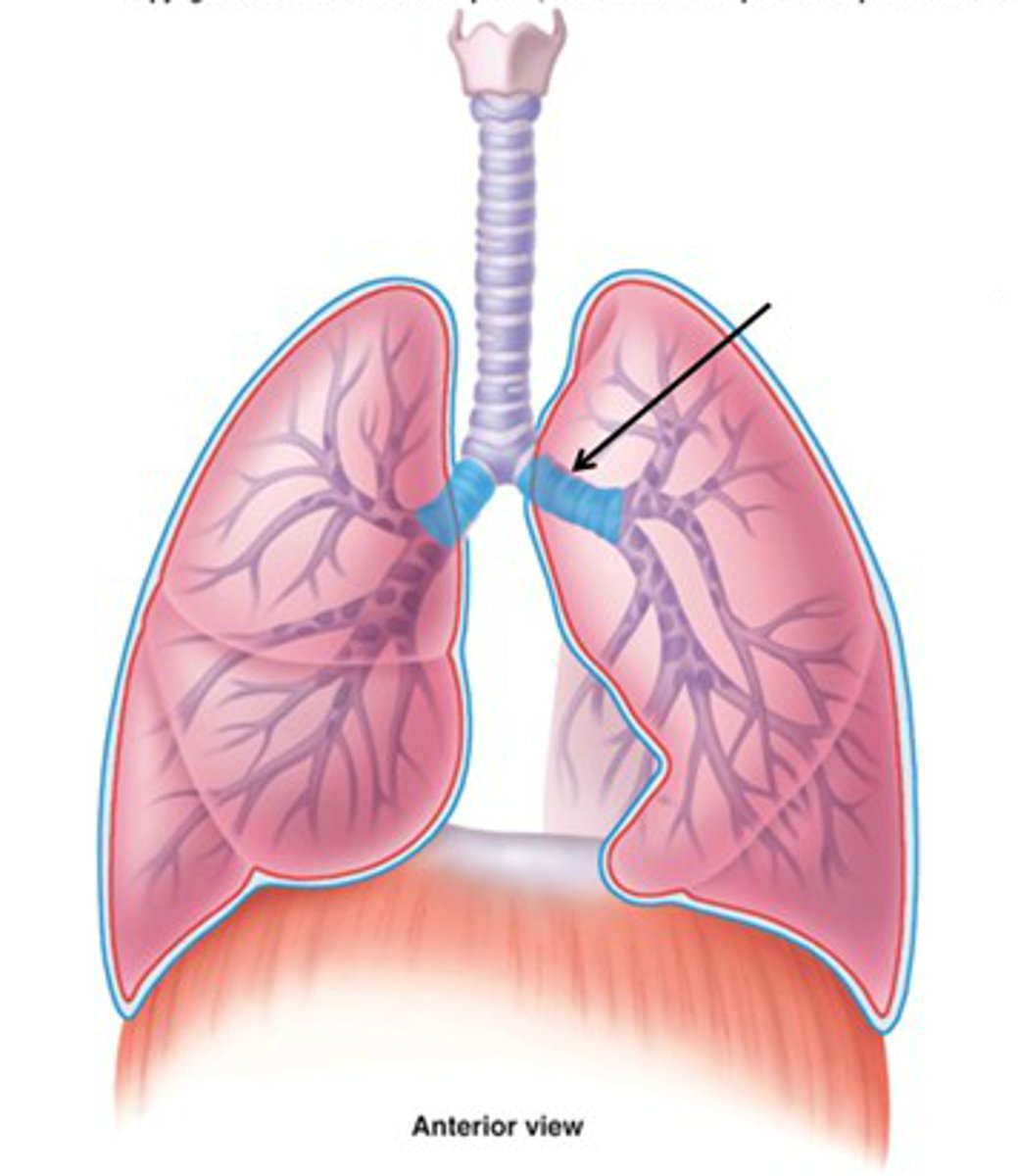
Bronchi
Two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
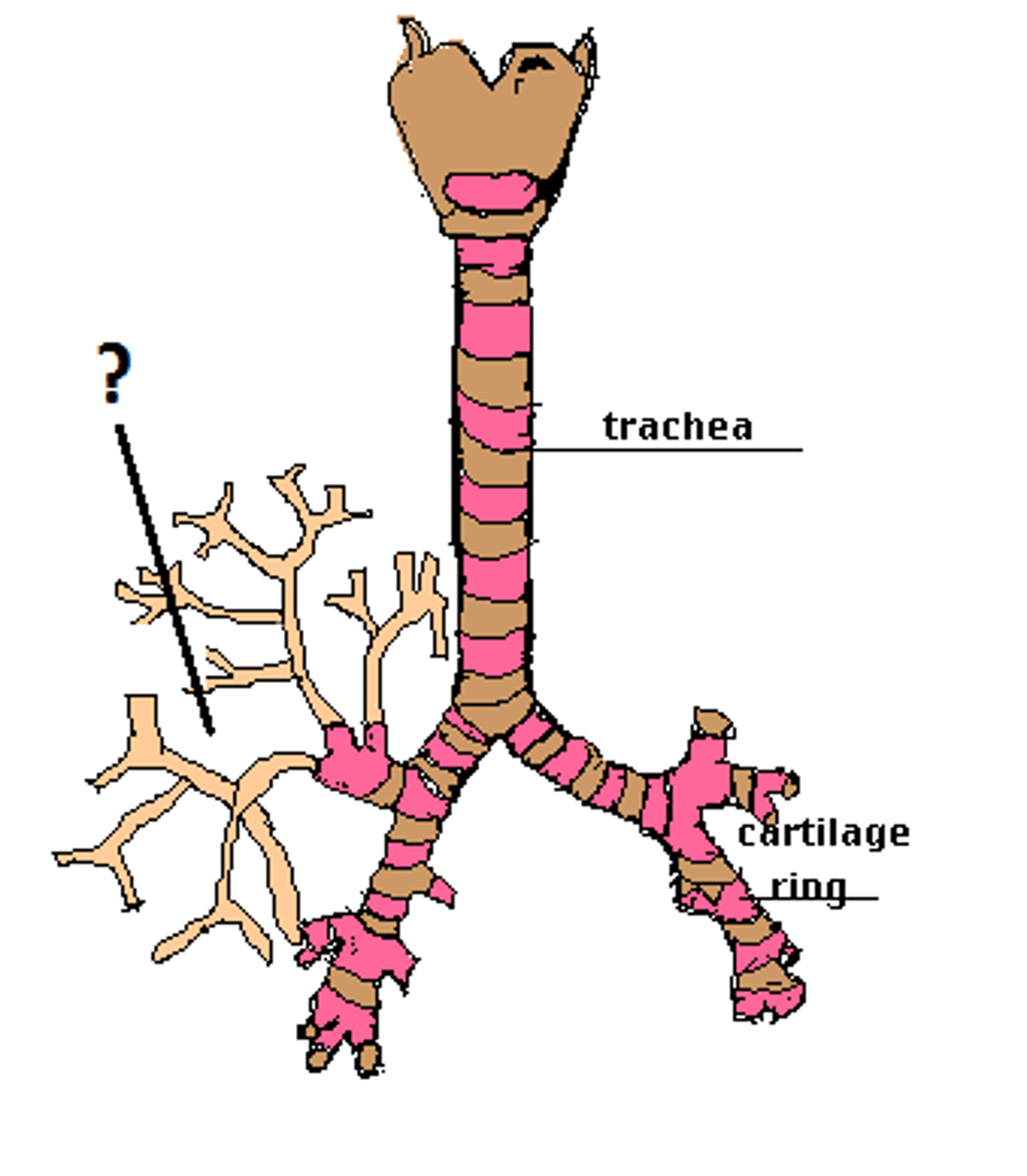
Bronchioles
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
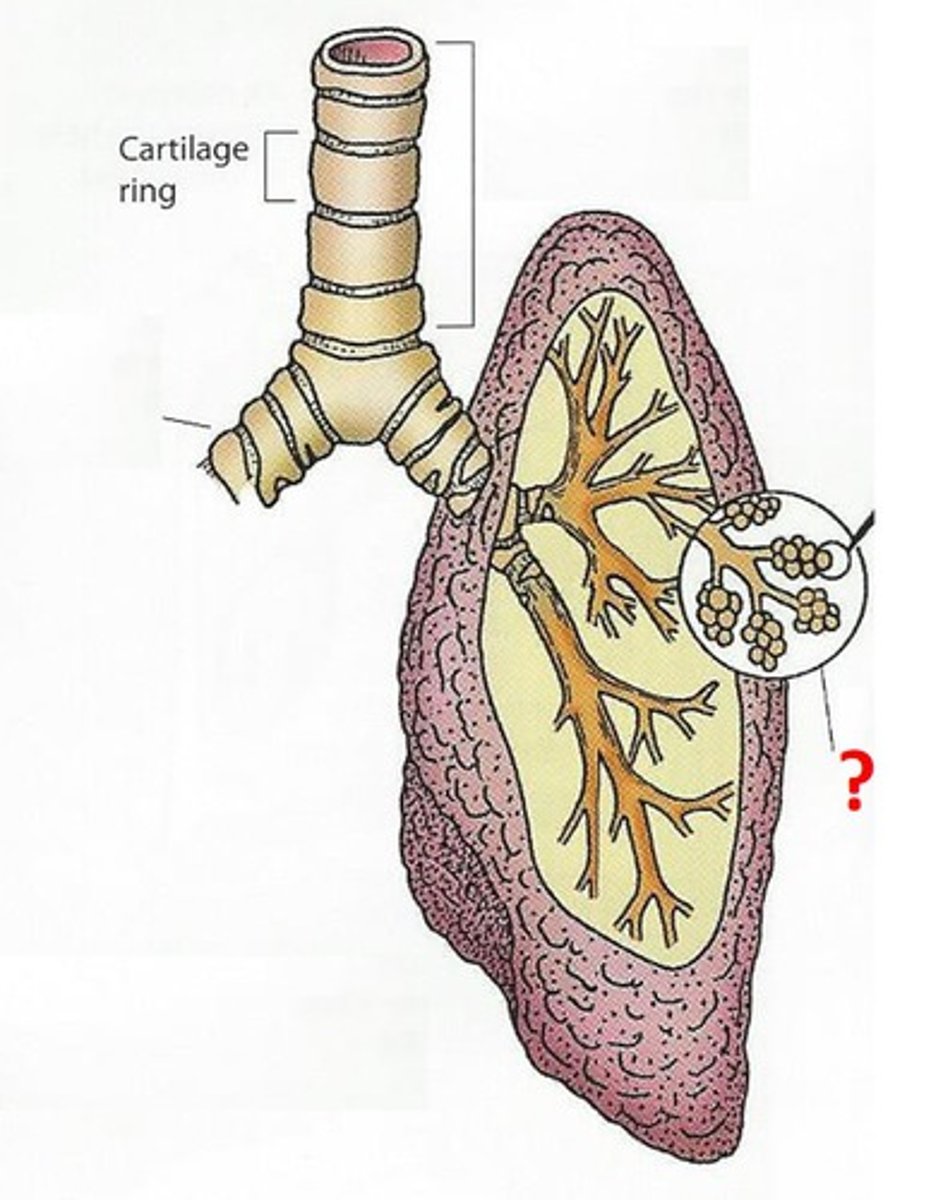
Alveoli
Tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
Lungs
Main organs of the respiratory system
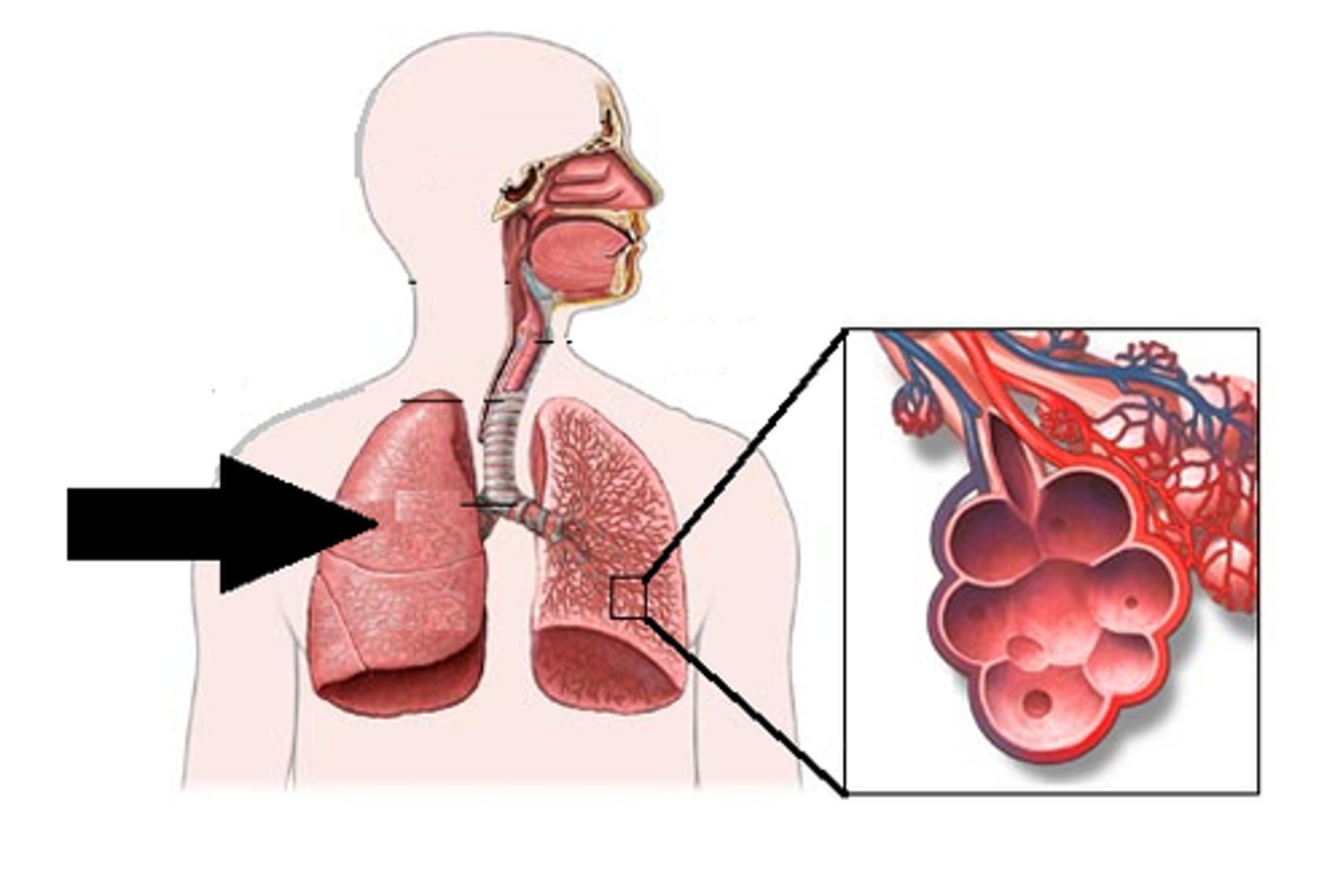
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps move air into and out of the lungs