VCU DPT - Neuro PT (Management of Patients with Vestibular and Balance Dysfunction - through slide 33)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
what is the pinna
it is the ear, or auricle
name the three little ear bones, in order from outside in
malleus (hammer)
incus (anvil)
stapes (stirrup)
the malleus gets pushed on by what structure
tympanic membrane
within the ear, cranial nerve 8 has two parts
name the two branches, and state what they each go towards
vestibular branch: vestibular canals
cochlear branch: cochlea
what tube connects ears to the throat and mouth
eustacian tube
the semiciruclar canals, otolith organs, and cranial nerve 8 are all a part of the __________ vestibular systm
peripheral
name the 3 semicircular canals
anterior
posterior
horizontal
there are two vestibular apparatus structures, name them
otolith
semicircular canals
_______________ detects sensory motion regarding linear motion and acceleration
__________ detects sensory motion regarding rotation and angular motion
otolith
semicircular canals
what two anatomical componenets make up the otolith
utricle and saccule
what anatomical components make up the semicircular canals
anterior canal
horizontal canal
posteiror canal
match the following into two groups
a. otoliths
b. semicircular canals
c. rotation/angular motion detection
d. linear motion/acceleration detection
e. anterior, posterior, horizontal canals
f. saccule and utricle
a, d, f
b, c, e
semicircular canals detect __________ motion in ____ # of directions
angular motion in 3 directions
describe the whole functional pair thing with semicircular canals
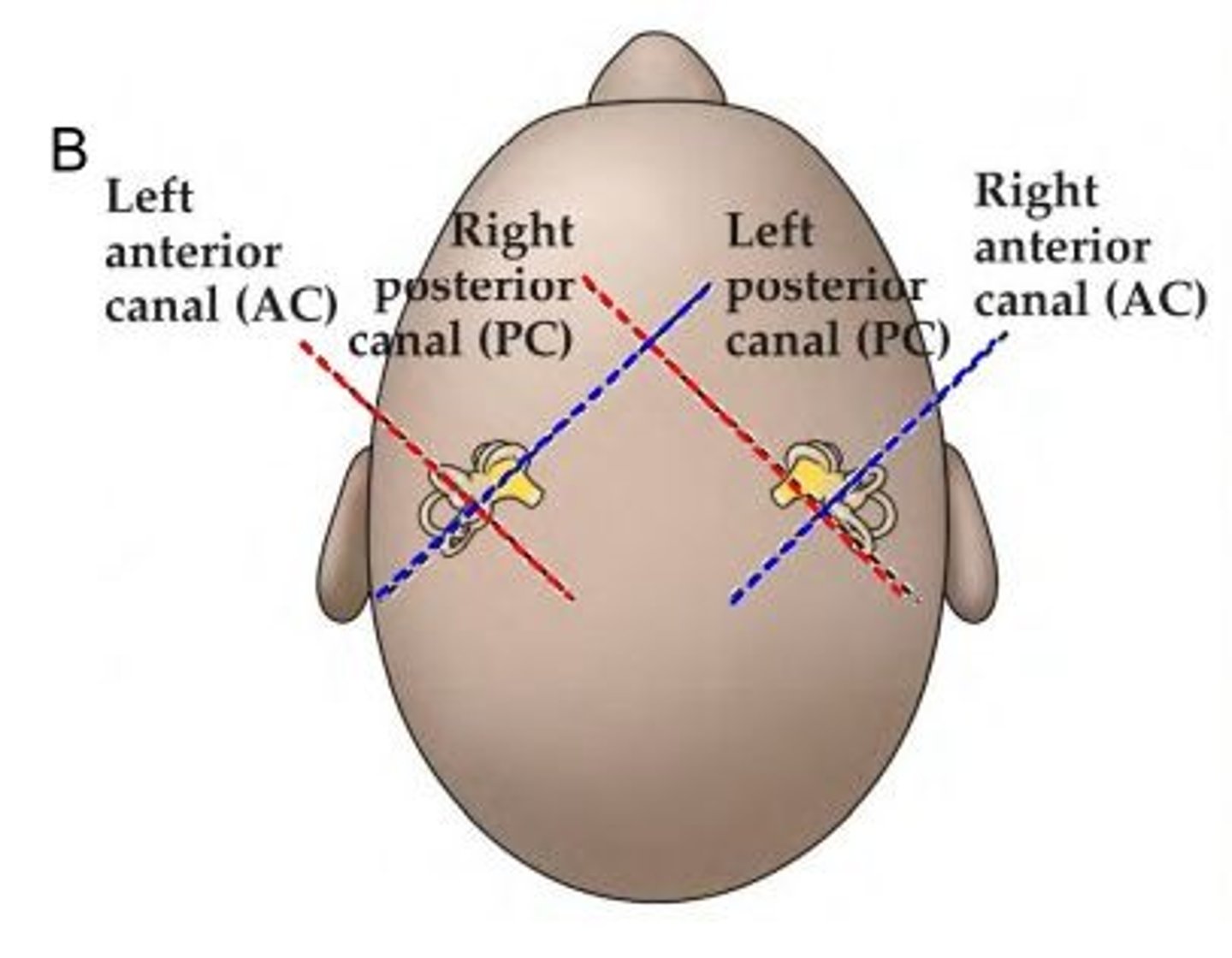
a specific movement will excite one canal while resulting in the inhibition of another canal. this is due to the way they are aligned in the head and to each other. the pairs lie in parallel with each other, so drawing it out might help.
Left Anterior plane <--> Right Posterior plane
Right Anterior plane <--> Left Posterior plane
Right Horizontal plane <--> Left Horizontal plane
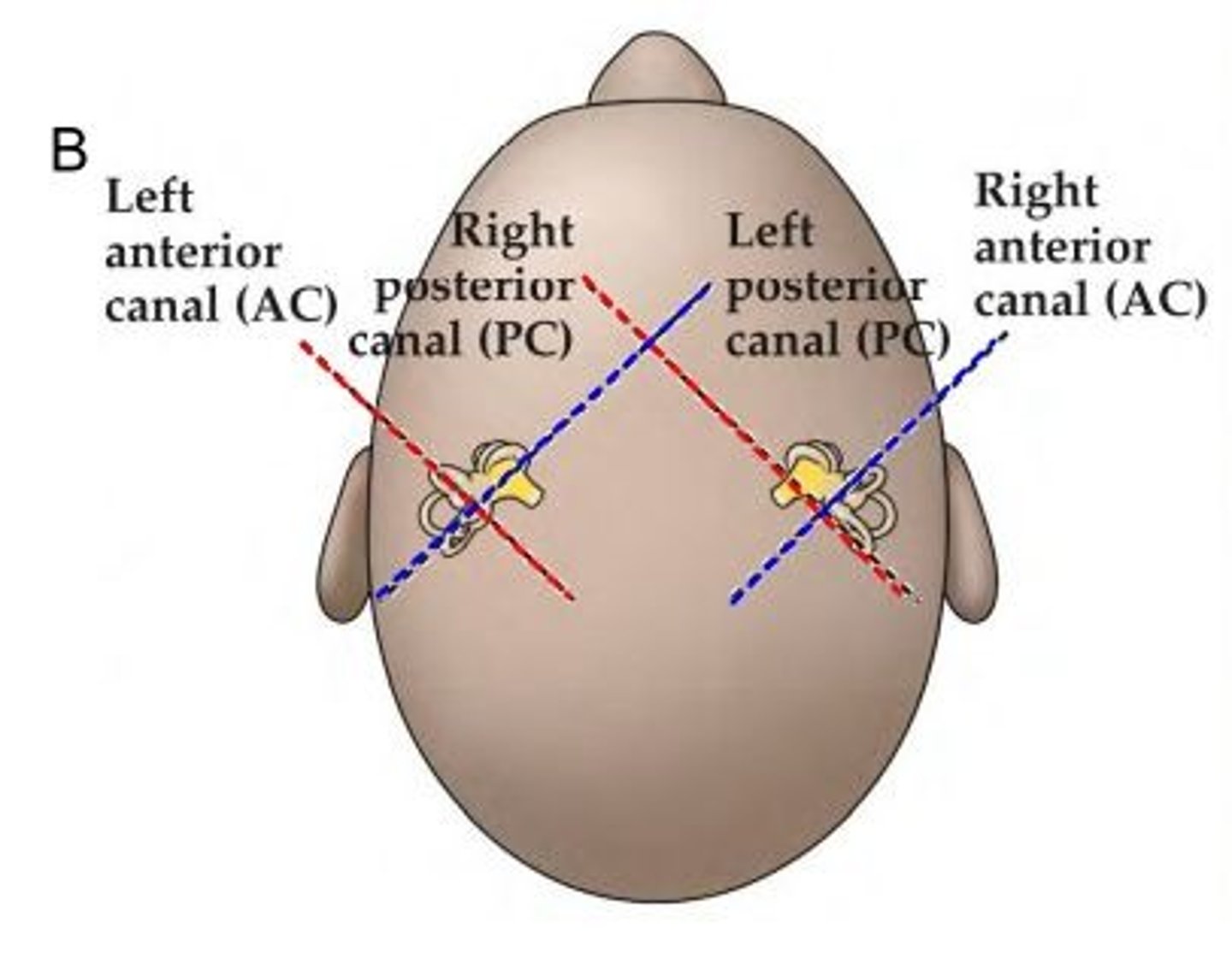
the semicircular canals and their movement systems correspond closely with the ______________
extraocular muscle movement (VOR reflex/system)
in the SCC functional pair, one canal is ________ while the other is ______
excited, inhibited
tell me the functional pairs of SCC
here ypu go
what is the ampulla
the ends of the semicircular canal, which is dilated
this dilated opening holds the crista ampullaris
- and within that, cupula/endolymph/haircells/nn
describe to me how the stereocilia (hair cells) get activated
in the canal, we want to focus on the ampulla
within this ampulla is a crista amupullaris, of which there is a cupula
this cupula is like jelly, and when the surrounding fluid (endolymph) moves to respind to the angular acceleration of our head (more so the fluid stays but head moves), the cupula gets pushed around
at the bottom of the cupula are the stereocilia, with its identifying kinocilium
the endolymph pushes the cupula either towards or away from the kinocilia, thus causing a response
with angular acceleration, the intertia of the endolymph causes it to wash over the ________, deflecting hair cells, and causing them to depolarize/hyperpolarize
what does our brain sense
cupula
angular motion
ex with the posterior canal
we tilt our head down; which way does the endolymph go towards? what about the cupula?
if the endolymph is moving towards the kinocilum, do we get excittion or inhibition
endolymph goes backwards/up/opposite of head
cupula goes with the head
excitation
ex with the posterior canal
we tilt our head up; which way does the endolymph go towards? what about the cupula?
if the endolymph is moving away from the kinocilum, do we get excittion or inhibition
endolymph forward/opposite of head
cupula goes backwards
inhibition
as we move our head.....
a) the endolymph moves _______ of this direction
b) the cupula moves _______ of this direction
a) opposite
b) in the same direction
aas the endolymph pushes towards the kinocilum, what hapens
there is depolarization and excitation
transmitters are released, and afferent fibers fire
as the endolymph pushes away from the kinocilum, what happens
there is hyperpolarization and inhibition
transmittier release is decreased, and there is less afferent fiber firing
as the endolymph pushes _______ the kinocilium, there is inhbition
as the endolymph pushes _______ the kinocilum, there is excitation
away from
towards
match the following
a. away from kinocilum
b. towards kinocilium
c. hyperpolarization
d. depolarization
e. inhibition
f. excitation
a, c, e
b, d, f
_______ is the tonic firing rate
90 firings/sec
horizational canals are repsonsible for what movement of the head
side to side (yaw plane)
if we look the to right, which horizontal canal is excited and which is inhibited
the R is excited
the L is inhibited
anterior-posterior SCC functional pairs are responsible for what movement of the head
up and down (pitch)
(can bias a side with some turning of head to that side)
if we look up, we are exciting which two canals and inhibiting which two?
exciting the posterior, inhibiting the anterior
if we look up and to the R, we are exciting which canal and inhibiting which canal
R posteiror
L anterior
to increase the rate of the ___________ canal firing, we would turn our head to the right before tilting the head up
R posterior
- due to the canals being set not totally centered
what is "LARP" and "RALP"
LARP: Left Ant, Right Post.
RALP: Right Ant, Left Post
SCC functional pairs!!!!!
the _________ is vertically orientated, while the ______ is horizontally orientated in the otolith
saccule
utricle
the saccule senses direction in the ______ plane
name some movements done that use this organ
sagital
jumping jack, squat, etc
the utricle senses direction in the __________ plane
name some movements it would pick up on
horizontal
any forward-backward, left-right movements
- side shuffling, sprinting, etc
describe how the hair cells get activated in the otolih organ
the hair cells are encased within otolithic membrane (macula)
there are some crystals (otoconia) that lay overtop of the macula
as we move, the weight of the crystals will have gravity exert a pull on them, moving them down to a side and bringing the macula along with it
this in turn will produce a shearing force on the hair cells via macula as the head moves
hair cells are embedded in the ____________, and this has ___________ overlaying it that have gravity pull them down
macula/otolithic membrane
otoconia
name some age related changes in the otoconia
fragementation, increased porousness, breakdown of the crystals can occur
- the filaments holding them together deteroirate
as the filaments holding together otoconia deteroritate with age, the crystals can do WHAT
what does this lead to
break away from macula
leads to an imbalance of resportion, and BPPV
are age related changes in the otoconia more seen in women or men?
women
osteoporosis, osteopenia are common histories before this
semicircular canals track ________ in space
rotations
____(semiricular canals/utricle and saccule)_____ provides reflexive control of the eyes (VOR)
SCC
a dysfunction of the SCC would likely result in whaty
spinning
- becuase it gives angular motion!!
utricle and saccule monitor ____________ in space
absolute head position
t/f: utricle and saccule do no help play a role in posture
false! they DO help posture
what does a dysfunction of the utricle and saccule result in
a sense of being pushed over
t/f: disruption of production or drainage of either fluid (endolymph or perilmpyh) will impair the ENTIRE labrinyth
TRUE
if we disrupt either the production or drainage of the perilymph/endolypmh, what is affected
the entire labrinyth
case scenario: a woman with vertigo/imabalnce has sx with extending and rotating her neck to look up and right. What canal is likely involved
Right posterior
the ___ nerve travels through the internal auditroy meatus w facial nerve, through the cerebellopontine angle, reaches the lateral aspect of the pons, and enters the vestibular nuclear complex
cn 7
what are the 4 components of the vestivular system
vestibular nuclei
pathways
vestibulocerebellum
vestibular cortex
what does the following pathway do:
vestibulothalamocortical
awareness of head position and movement
what does the following pathway do:
vestibuloocular
eye movements
what does the following pathway do:
vestibulocolic
head movement
what does the following pathway do:
vestibulospinal
posture of head and body
what does the following pathway do:
vestibuloreticular
naseua and vomiting
altered consciousness
what does the following pathway do:
vestibulocerebellar
takes info to cerebellum
the vestibular nuclear complex takes up a large part of the _________
name 4 nuclei in the complex
medulla
medial vestibular nucleus
superior vestibular nucleus
inferior vestibular nucleus
lateral vestibular nucleus
the medial and superior vestibular nuclei reveice input from the __________
ampullae of semicircular canals
- and a bit from otoliths
the ampullae of semicircular canals give input to the ______________ vestibular nucleus(i)
- the otoliths also give them some
medial, superior
t/f: the medial and superior vestibular nuclei recieve input from the ampullae of semicircular canals
- and a little from otoliths
true
the __________ vestibular nuclei help promote the vestibulo-oculomotor reflex (VOR) and ocular tilt reflex (OTR)
medial and superior
why does the medial and superior vestibular nuclei have a relationship with VOR and OTR
because the nuclei get input from the ampulla of SCC, and SCC are associated with those reflexes
explain the vestibulo-ocular refelx
as we move our head one way, our eyes stay in the same spot by moving in the opposite direction
helps with gaze stabilization
the medial superior vestibular nuclei sends signals to the nuclei in the extrinsic eye muscles, getting info from the SCC --> MLF --> brainstem --> eye muscles
this is done with gaze stabilization in what reflex
vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)
with VOR, if I turn my head to the R:
a) the ____ horizontal canal is excited
b) the ______ vestibular nuclei are alerted
c) muscles contract, causing _____ of the R eye and _____ of the L
d) the R lateral rectus and L medial rectus are ___________
a) R
b) medial
c) adduction, abduction
d) inhibited
with the ocular tilt reflex, the eyes move _____ of the head
opposite tilt
if our head tilts to the right, with OTR what do my eyes do
right: elevates, twists in
left: depresses, twists out
the descending tract of the medial vestibular nucleus is involved with which tract
medial vestibulospinal tract
- goes down in the MLF
the medial vestibular nucleus descends in the medial vestibulospinal tract via MLF
what does it do
what reflex is it involved with
activates cervical axial mm
helps ongoing postural changes from SCC input
(mostly upper body)
vestibulocollic reflex (VCR)
the lateral nucleus is involved with the _______ reflex
vestibulo-spinal reflex
lateral nucleus recieves input from the ________
medial/superior nucleus receives input from the ________
utricle, cerebellum
SCC
what does the lateral vestibular nuclei help do
control posture of trunk and legs
- via extensors
vestibulo-spinal reflex
when our head tilts to one side, the canals and otoliths activate
impulse is sent to the vestibular nuclei
impulses are sent via the lateral/medial vestibulospinal tracts to spinal cord
extensor activty occurs
DESCRIBES WHAT REFLEX
vestibulo-spinal reflex
a) vestibulo-spinal reflex
b) vestibulocollic reflex
c) ocular tilt reflex
d) vestibular ocular reflex
describe them
a) medial/superior vestibular nuclei go to eye muscles to have eyes move opposite of head, and get gaze stabilization
- MLF
b) using the medial/superior vestib nuclei, goes the cervical axial mm and helps with posture
c) this is when you tilt your head, eyes stay on horizon by moving in oppsoite direction
d) head tilts to one side, and the lateral/medial vestib nuclei help give info to turn on trunk/leg extensor mm
inferior vestibular nucleus recieves info from where
SCCs
utricle and saccule
cerebellum
- input from labrinyth and cerebellum
the _______ is used to modulate vestibular reflexes, with its projections having an inhibitory influnece on vestiblar nuclear complex
cerebellum
thalamus connects vestibular cortex and reticular formation for ________ and __________
also helps with what
arousal
body awareness
spatial awareness vs vertical, discrimination between self moving and enviro