Lecture 2 - Pedigrees and Conditional Probabilities (Discussion)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Pedigree
family tree that shows information regarding relevant phenotype
can determine genotype/probable genotypes of individuals
3 types of pedigrees
Recessive, Dominant, Sex-linked
Recessive Trait
trait resulting from a recessive mutant allele
Homozygous dominant = normal phenotype
Heterozygous = mutant carrier
Homozygous recessive = mutant phenotype
Dominant Trait
trait resulting from a dominant mutant allele
Homozygous dominant = Mutant phenotype
Heterozygous = mutant phenotype
Homozygous recessive = normal phenotype
Recessive Pedigree
Produces:
1 unaffected (AA)
2 unaffected carrier (Aa) children
1 affected (aa) child
Dominant Pedigree
Produces:
2 unaffected (aa) children
2 affected (Aa) children
Determining Recessive Traits
Mutant trait shown in homozygous recessive organisms
Heterozygous organisms will not show the mutant trait but will be a carrier
Hallmark of recessive traits: normal parents produce mutant offspring
Loss-of-function mutation
Mutant “a” allele creates mutant phenotypic expression
“A” allele produces normal wild-type phenotypic expression
AA = unaffected (non-carrier), Aa = unaffected (carrier), aa = affected
Determining Dominant Traits
Mutant trait shown in heterozygous and homozygous dominant organisms
Parents who are homozygous recessive and do not show the mutant trait cannot have offspring that possess the mutant trait
Hallmark of dominant traits: mutant parents produce normal offspring
Gain-of-function mutations
Mutant “A” allele creates mutant phenotypic expression
“a” allele produces normal wild-type phenotypic expression
aa = unaffected, Aa = affected, AA = affected
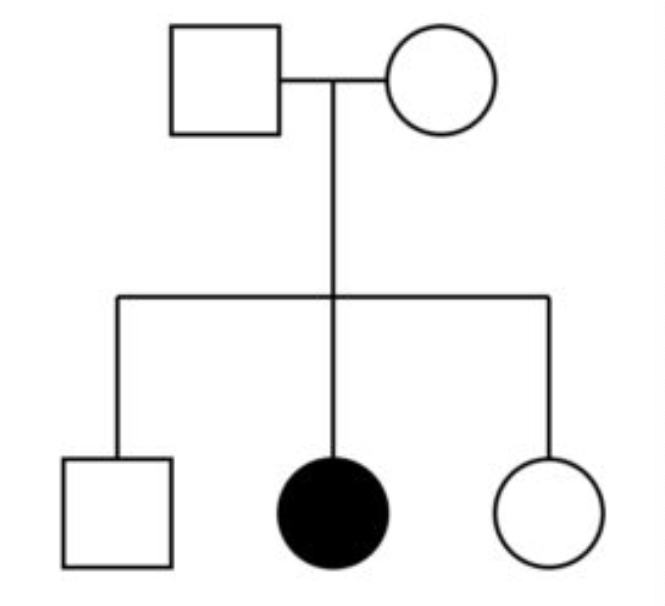
Recessive trait
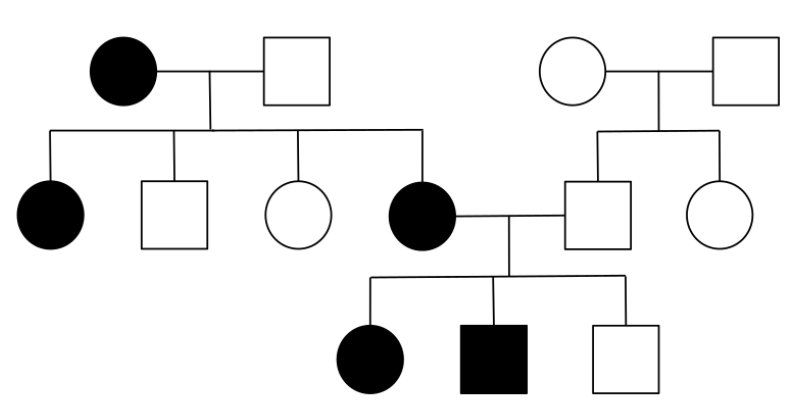
Recessive and dominant trait